并发编程(九)-ScheduledExecutorService源码分析
一、ScheduledExceutorService简介
ScheduledExecutorService 是 Java 并发包中提供的一个接口,继承ExecutorService接口,是Executor框架的一个扩展。它可以用于调度任务在指定的时间或周期性地执行。相比于 Timer 和 TimerTask,ScheduledExecutorService 提供了更加灵活的任务调度机制,可以控制任务的取消、延迟、周期等,同时也支持并发执行多个任务。
ScheduledExecutorService 的实现原理主要是通过它的实现类ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor来完成的,具体流程如下:
-
当调用 ScheduledExecutorService 的 schedule() 方法时,会创建一个 ScheduledFutureTask 对象,该对象封装了需要执行的任务和其执行时间。
-
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 使用了一个 DelayedWorkQueue 来存储待执行的任务。
-
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 是一个基于优先级队列的延迟队列,其中每个任务都有一个延迟时间,当任务的延迟时间到达时,它会被添加到队列中。
-
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 使用一个线程池来执行任务。线程池中的每个线程都会从 DelayedWorkQueue 中获取下一个延迟时间最短的任务并执行。
-
当任务执行完成后,线程会将任务从 DelayedWorkQueue 中移除,并根据需要重新添加到队列中。
-
如果任务是周期行执行的,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor会创建一个新的ScheduledFutureTask对象,并将其放入 DelayQueue 中,以便下一次执行。
-
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 提供了一些方法来控制任务的执行时间和重复执行次数,例如 schedule、scheduleAtFixedRate 和 scheduleWithFixedDelay 等。
总的来说,ScheduledExecutorService 使用了延迟队列和线程池来实现任务的定时执行,它是一种高效、可靠的定时任务执行方式。
二、scheduledExecutorService 如何使用
使用 ScheduledExecutorService 执行定时任务需要经过以下步骤:
-
创建ScheduledExecutorService对象
// 核心线程数 1
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);-
创建要执行的任务
Callable task = () -> {
// 执行任务的代码
return null;
};-
调用 ScheduledExecutorService 提供的定时任务方法
ScheduledExecutorService 提供了多个方法来执行定时任务,例如:
-
schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit):在指定的延迟时间后执行一次任务。
-
scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit):在指定的延迟时间后开始执行任务,并按照指定的时间间隔重复执行任务。
-
scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit):在指定的延迟时间后开始执行任务,执行完成后延迟指定的时间再次执行任务。
例如,使用 scheduleAtFixedRate 方法来执行重复任务:
// 任务的初始延迟时间为 0,时间间隔为 1 秒。
executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(task, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);-
关闭 ScheduledExecutorService
executorService.shutdown();需要注意的是,任务的执行时间不能超过指定的时间间隔,否则会影响下一次任务的启动时间。此外,在任务的实现中,也需要注意线程安全问题,避免对共享资源的竞争和冲突。
三、如何自定义一个scheduledExecutorService
创建 CustomScheduledExecutorService 的类,实现了 ScheduledExecutorService 接口,并将实际的任务执行委托给了一个内部的 ScheduledExecutorService 对象。
将 ScheduledExecutorService 接口中的所有方法都实现一遍,这些方法包括:
-
schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit):在指定的延迟时间后执行一次任务。
-
schedule(Callable
callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit):在指定的延迟时间后执行一次 Callable 对象的任务,并返回一个 ScheduledFuture 对象。 -
scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit):在指定的延迟时间后开始执行任务,并按照指定的时间间隔重复执行任务。
-
scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit):在指定的延迟时间后开始执行任务,执行完成后延迟指定的时间再次执行任务。
-
awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit):阻塞等待任务执行完成,并指定最长的等待时间。
-
execute(Runnable command):在未来的某个时间执行一个任务。
-
submit(Callable
task):提交一个 Callable 对象,并返回一个 Future 对象。
通过自定义 ScheduledExecutorService,我们可以灵活地定制化任务调度的行为,例如可以指定线程池大小、任务队列长度、任务拒绝策略等。
public class CustomScheduledExecutorService implements ScheduledExecutorService {
private ScheduledExecutorService executorService;
public CustomScheduledExecutorService(int corePoolSize) {
DelayedWorkQueue queue = new DelayedWorkQueue();
AbortPolicy handler = new AbortPolicy();
executorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, queue, handler);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
ScheduledFutureTask task = new ScheduledFutureTask<>(command, null,
System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(delay));
executorService.getQueue().add(task);
return task;
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Callable callable, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return executorService.schedule(callable, delay, unit);
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit) {
if (command == null || unit == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (period <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
ScheduledFutureTask task = new ScheduledFutureTask<>(command, null,
System.nanoTime() + unit.toNanos(initialDelay));
executorService.getQueue().add(task);
return task;
}
@Override
public ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit) {
return executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(command, initialDelay, delay, unit);
}
@Override
public boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return executorService.awaitTermination(timeout, unit);
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
executorService.execute(command);
}
@Override
public Future submit(Callable task) {
return executorService.submit(task);
}
}
四、源码分析
4.1 ScheduledExecutorService Diagrams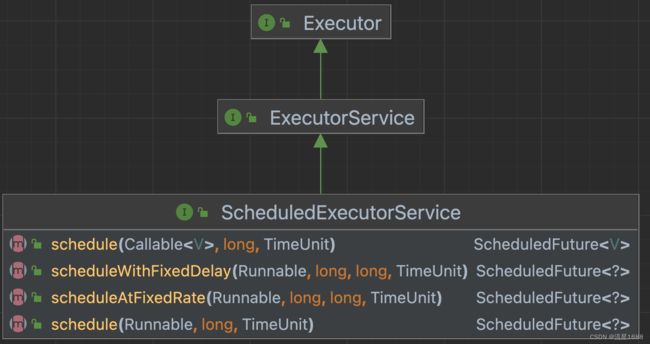
4.2 方法
4.2.1 schedule(Runnable command,long delay, TimeUnit unit) 方法
ScheduledExecutorService 接口中的 schedule() 方法表示在指定的延迟时间后执行一次给定的任务。
方法的参数如下:
-
command:要执行的任务,为一个 Runnable`对象。
-
delay:延迟执行的时间,为一个 long 值。
-
unit:delay 参数的时间单位,为一个 TimeUnit 枚举值。
返回值类型为 ScheduledFuture,表示一个可调度的异步任务,可以用来查询任务是否执行完成,或者取消任务的执行。在该方法中,返回值类型是 ScheduledFuture,表示异步任务没有返回值。
当使用该方法时,指定的任务会在延迟时间之后执行一次,如果任务执行过程中出现了异常,则会抛出异常。如果需要在指定的时间间隔内重复执行任务,可以使用 scheduleAtFixedRate()或 scheduleWithFixedDelay()方法。
// 在指定的延迟时间之后,执行给定的任务。
public ScheduledFuture schedule(Runnable command,long delay, TimeUnit unit); 4.2.2 scheduleAtFixedRate方法
ScheduledExecutorService 接口中的scheduleAtFixedRate方法,表示在预定的时间执行任务,例如延迟执行或者定期执行。其中的 scheduleAtFixedRate方法可以在固定的时间间隔内重复执行指定的任务,具体参数的含义如下:
-
command:要执行的任务,是一个实现了 Runnable 接口的对象。
-
initialDelay:首次执行任务的延迟时间。
-
period:连续执行任务之间的时间间隔。
-
unit:时间单位,例如毫秒、秒、分钟等等。
返回值类型为ScheduledFuture对象,表示任务的计划执行。可以使用 cancel方法取消计划执行。
// 在预定的时间执行任务
public ScheduledFuture scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit);4.2.3 scheduleWithFixedDelay方法
ScheduledExecutorService接口中的scheduleWithFixedDelay方法,表示在指定的时间间隔内反复执行任务。具体参数的含义如下:
-
command:要执行的任务,是一个实现了 Runnable 接口的对象。
-
initialDelay:首次执行任务的延迟时间。
-
delay:上一次执行任务结束到下一次执行任务开始之间的时间间隔。
-
unit:时间单位,例如毫秒、秒、分钟等等。
返回值类型为ScheduledFuture 对象,表示任务的计划执行。可以使用 cancel 方法取消计划执行。
// 在指定的时间间隔内反复执行任务
public ScheduledFuture scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long delay,
TimeUnit unit);五、扩展知识
5.1 scheduleWithFixedDelay与 scheduleAtFixedRate 区别
scheduleAtFixedRate 方法是以任务开始时间为基准来计算下一次执行时间的,也就是说,如果任务的执行时间超过了指定的时间间隔,下一次任务的执行时间会被推迟。如果任务的执行时间比时间间隔还短,下一次任务的执行时间会提前。
scheduleWithFixedDelay 方法是以任务结束时间为基准来计算下一次执行时间的,也就是说,下一次任务的执行时间是从任务结束时间开始计算的。
5.2 ScheduledExecutorService 接口在多线程环境下如何使用?
ScheduledExecutorService接口是线程安全的,可以在多线程环境下使用。通常情况下,创建一个固定大小的线程池,用于执行任务。在执行任务时,需要注意任务的线程安全性,避免多个线程同时修改同一个资源导致的并发问题。
5.3 ScheduledExecutorService 接口和 Timer类的区别是什么?
ScheduledExecutorService 接口相比于 Timer 类更加灵活、可控。它可以通过线程池来控制任务的并发度,避免因为任务执行时间过长而影响后续任务的执行。而 Timer 类则只能创建一个线程来执行所有任务,无法进行灵活的线程控制。另外,ScheduledExecutorService接口提供的方法更加丰富,可以满足不同场景下的需求。