C#,码海拾贝(07)——埃尔米特(Hermite)曲线插值算法,《C#数值计算算法编程》源代码升级改进版
一、埃尔米特插值算法简介
1.1 Charles Hermite
Charles Hermite was a noted 19th century French mathematician known for his work on number theory, quadratic forms, invariant theory, orthogonal polynomials, elliptic functions, and algebra. From the very beginning, he was more interested in advanced studies than in his curriculum, publishing two important papers while he was still in his secondary school. Later, he entered École Polytechnique to study mathematics but because of a deformity in his right feet, which required him to use a cane, he had to leave the academy the following year. He studied privately for five years and earned his baccalauréat and licence at the age of twenty-four. Meanwhile he started corresponding with eminent mathematicians, writing down his discoveries in the letters. Indeed, in spite of his phenomenal researches, he had few publications to his credit; circulating most his discoveries through letters, short notes and course lectures, which formed the basis of further research by other mathematicians. He was also a grand teacher, being appointed professor of analysis both in École Polytechnique and Sorbonne. In spite of his deformity, he was always in a happy mood, dividing his time between his family, teaching and research.
查尔斯·埃尔米特是19世纪著名的法国数学家,以其在数论、二次型、不变量理论、正交多项式、椭圆函数和代数方面的工作而闻名。从一开始,他就对高等教育比对课程更感兴趣,在中学时发表了两篇重要论文。后来,他进入理工学院学习数学,但由于右脚畸形,需要使用拐杖,他不得不在第二年离开学院。他私下学习了五年,并在二十四岁时获得了学士学位和执照。与此同时,他开始与著名的数学家通信,把自己的发现写在信中。事实上,尽管他进行了非凡的研究,但他几乎没有值得称赞的出版物;通过信件、短文和课程讲座传播他的大部分发现,这为其他数学家的进一步研究奠定了基础。他还是一位特级教师,被任命为理工学院和索邦大学的分析教授。尽管他有残疾,但他总是心情愉快,把时间分配在家庭、教学和研究之间。
1.2 Hermite curves
Hermite curves are very easy to calculate but also very powerful. They are used to smoothly interpolate between key-points (like object movement in keyframe animation or camera control). Understanding the mathematical background of hermite curves will help you to understand the entire family of splines. Maybe you have some experience with 3D programming and have already used them without knowing that (the so called kb-splines, curves with control over tension, continuity and bias are just a special form of the hermite curves).
埃尔米特曲线非常容易计算,但也非常强大。它们用于在关键点之间平滑插值(如关键帧动画或摄影机控制中的对象移动)。了解hermite曲线的数学背景将有助于您了解整个样条曲线族。也许你有一些3D编程的经验,并且在不知道的情况下已经使用过它们(所谓的kb样条,控制张力、连续性和偏差的曲线只是hermite曲线的一种特殊形式)。
To keep it simple we first start with some simple stuff. We also only talk about 2-dimensional curves here. If you need a 3D curve just do with the z-coordinate what you do with y or x. Hermite curves work in in any number of dimensions.
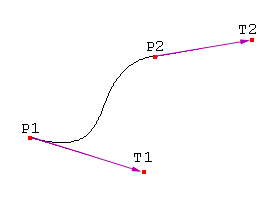
To calculate a hermite curve you need the following vectors:
- P1: the startpoint of the curve
- T1: the tangent (e.g. direction and speed) to how the curve leaves the startpoint
- P2: he endpoint of the curve
- T2: the tangent (e.g. direction and speed) to how the curves meets the endpoint
为了保持简单,我们首先从一些简单的东西开始。我们在这里也只讨论二维曲线。如果你需要一条三维曲线,只需使用z坐标,就像使用y或x一样。埃尔米特曲线可以在任何尺寸中工作。
要计算埃尔米特曲线,您需要以下向量:
P1:曲线的起点
T1:曲线离开起点的切线(例如方向和速度)
P2:曲线的端点
T2:曲线与端点相交的切线(例如方向和速度)
二、改进代码
using System;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Zhou.CSharp.Algorithm
{
///
/// 插值计算类Interpolation.cs
/// 作者:周长发
/// 改编:深度混淆
/// https://blog.csdn.net/beijinghorn
///
public static partial class Interpolation
{
///
/// 埃尔米特不等距插值
///
/// 一维数组,长度为n,存放给定的n个结点的值x(i),要求x(0)
/// 一维数组,长度为n,存放给定的n个结点的函数值y(i),y(i) = f(x(i)), i=0,1,...,n-1
/// 一维数组,长度为n,存放给定的n个结点的函数导数值y'(i),y'(i) = f'(x(i)), i=0,1,...,n-1
/// 存放指定的插值点的x值
/// 指定的查指点t的函数近似值y=f(t)
public static double Hermite(double[] x, double[] y, double[] dy, double t)
{
int n = x.Length;
double z = 0.0;
// 循环插值
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
double s = 1.0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (j != i)
{
s = s * (t - x[j - 1]) / (x[i - 1] - x[j - 1]);
}
}
s = s * s;
double p = 0.0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (j != i)
{
p = p + 1.0 / (x[i - 1] - x[j - 1]);
}
}
double q = y[i - 1] + (t - x[i - 1]) * (dy[i - 1] - 2.0 * y[i - 1] * p);
z = z + q * s;
}
return (z);
}
///
/// 埃尔米特等距插值
/// (使用非等距插值的方法)
///
/// 存放等距n个结点中第一个结点的值
/// 等距结点的步长
/// 一维数组,长度为n,存放给定的n个结点的函数值y(i),y(i) = f(x(i)), i=0,1,...,n-1
/// 一维数组,长度为n,存放给定的n个结点的函数导数值y'(i),y'(i) = f'(x(i)), i=0,1,...,n-1
/// 存放指定的插值点的x值
/// 指定的查指点t的函数近似值y=f(t)
public static double Hermite(double x0, double step, double[] y, double[] dy, double t)
{
double[] x = new double[y.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < y.Length; i++, x0 += step)
{
x[i] = x0;
}
return Hermite(x, y, dy, t);
}
#if __OLD__
///
/// 埃尔米特等距插值
///
/// 等距n个结点中第一个结点的值
/// 等距结点的步长
/// 一维数组,长度为n,存放给定的n个结点的函数值y(i),y(i) = f(x(i)), i=0,1,...,n-1
/// 一维数组,长度为n,存放给定的n个结点的函数导数值y'(i),y'(i) = f'(x(i)), i=0,1,...,n-1
/// 存放指定的插值点的x值
/// 指定的查指点t的函数近似值y=f(t)
public static double Hermite(double x0, double step, double[] y, double[] dy, double t)
{
int n = y.Length;
double z = 0.0;
// 循环插值
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
double s = 1.0;
double q = x0 + (i - 1) * step;
double p;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
p = x0 + (j - 1) * step;
if (j != i)
{
s = s * (t - p) / (q - p);
}
}
s = s * s;
p = 0.0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (j != i)
{
p = p + 1.0 / (q - (x0 + (j - 1) * step));
}
}
q = y[i - 1] + (t - q) * (dy[i - 1] - 2.0 * y[i - 1] * p);
z = z + q * s;
}
return (z);
}
#endif
}
} POWER BY 315SOFT.COM
基于坐标点的计算,从点集计算插值曲线等拓展方法请参阅《拉格朗日插值算法及其拓展》