java spring详解_Spring详解一之IOC容器
1、Spring概述
2、Spring的模块介绍
3、IOC依赖注入
4、创建或获取Bean对象
5、Bean的普通属性赋值
6、Bean的属性文件和集合属性赋值
7、Bean之间的关系
8、Bean的作用域——scope
9、基于xml配置文件的自动注入——autowire
10、IOC之abstract抽象Bean
1、Spring概述
①Spring是一个开源框架
②Spring为简化企业级开发而生,使用Spring开发可以将Bean对象,Dao组件对象,Service组件对象等交给Spring容器来管理(可通过注解@Controller
@Service@Repository@Component@Scope),这样使得很多复杂的代码在Spring中开发却变得非常的优雅和简洁,有效的降低代码的耦合度,极大的方便项目的后期维护、升级和扩展。
③Spring是一个IOC(DI)和AOP容器框架。
④Spring的优良特性
[1]非侵入式:基于Spring开发的应用中的对象可以不依赖于Spring的API
[2]控制反转:IOC——Inversion of Control,指的是将对象的创建权交给Spring去创建。使用Spring之前,对象的创建都是由我们自己在代码中new创建。而使用Spring之后。对象的创建都是由给了Spring框架。
[3]依赖注入:DI(IOC的另一种表达形式)——Dependency Injection,是指依赖的对象不需要手动调用setXX方法去设置,而是通过配置赋值。
[4]面向切面编程:Aspect Oriented Programming——AOP
[5]容器:Spring是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理应用对象的生命周期
[6]组件化:Spring实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用。在Spring中可以使用XML和Java注解组合这些对象。
[7]一站式:在IOC和AOP的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库(实际上Spring自身也提供了表述层的SpringMVC和持久层的Spring JDBC)。
开发使用的工具:STS(spring-tool-suite),是在eclipse中帮开发者安装好了spring的插件,其实就是一个eclipse,目前只有eclipse4.3.2(对应jkd7)这一个版本可以自己在eclipse安装插件了,但可能会出错,建议使用sts,主要是sts提示特别多。
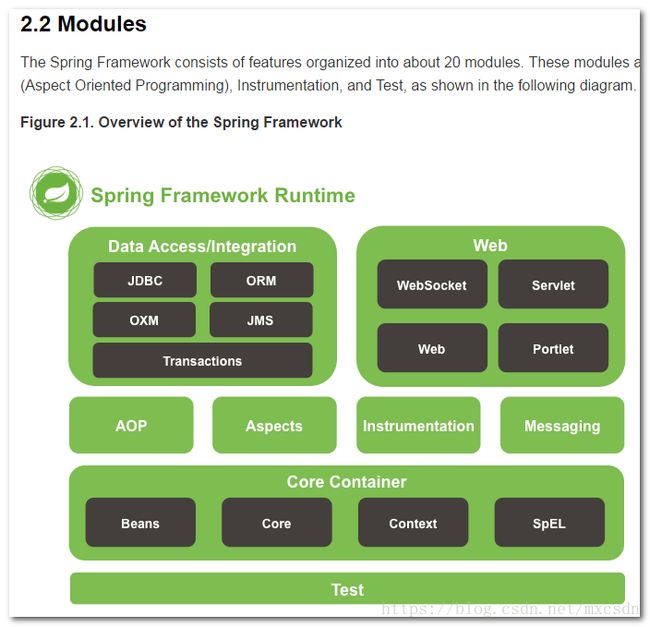
2、Spring的模块介绍
Spring框架分为四大模块:
Core核心模块。负责管理组件的Bean对象
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
面向切面编程
spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
数据库操作
spring-jdbc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-orm-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-oxm-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-tx-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-jms-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
Web模块
spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-webmvc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-websocket-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-webmvc-portlet-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
3、IOC依赖注入
3.1、什么是IOC
IOC全称指的是 Inverse Of Control 控制反转。
使用Spring之前,我们对Bean对象的管制,都是自己手动的去new Xxx()。
而使用了Spring模型之后,我们把new的操作。交给Spring容器。
3.2、什么是DI
DI 指的是DependencyInjection 。是依赖注入的意思。
原来在使用Spring之前。
Class BookService{
private BookDao bookDao;
public void setBookDao( BookDao bookDao ){
this.bookDao = bookDao
}
}
使用了Spring之后。我们只需要使用xml配置,或者注解配置。就可以直接注入。
4、创建或获取Bean对象
一、通过id
二、通过class类名
三、通过创建静态工厂方法
四、通过工厂实例对象(必须先有个工厂实例对象)
五、通过FactoryBean接口方式
4.1、第一个IOC示例程序— 通过id获取对象(重点)
实验1:通过IOC容器创建对象,并为属性赋值★
1、创建一个Java工程:
2、创建log4j.properties日记配置文件
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
3、创建Spring的配置文件
4、创建一个JavaBean对象
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private int age;
5、到Spring配置文件中配置你的Bean对象
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
6、如何从Spring容器中获取Bean对象
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
// 创建一个Spring容器对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"application.xml");
// getBean从Spring容器中获取指定的id值的 bean对象返回
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p1");
System.out.println(person);
}
这里“application.xml”,也可以写成“classpath:application.xml”,因为ClassPathXmlApplicationContext()方法本身就是从类路径(源码src位置)下加载的,所以代码中此处可选。但在配置文件中必须要加上classpath来引入需要的属性配置文件。
问题:
1、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext怎么用?
答:跟使用JavaSE的相对路径一样
2、Bean是在什么时候被创建的?
答:在创建ApplicatiocnContext(类路径)对象一样(默认)
3、如果调用getBean多次,会创建几个?
答:默认创建同一个
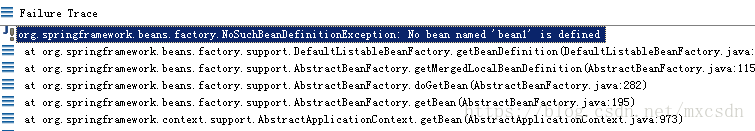
常见的错误:
指定的id不存在。找不到bean对象。
4.2、IOC示例程序—通过类型获取对象(重点)
实验2:根据bean的类型从IOC容器中获取bean的实例★
在application.xml中的配置:
测试推荐:
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
常见错误说明:
当在applicationContext.xml配置文件中。有多个同Person.class类型实现的时候。
按照Class类型查找的时候,如果没有,也会报如下的错误:
4.3、IOC之静态工厂方法创建Bean对象
实验3:配置通过静态工厂方法创建的bean
1、创建一个工厂类
public class PersonFactory {
public static Person createPerson() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("这是通过静态工厂方法创建的Person对象");
return person;
}
}
2、到xml中去配置:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test14() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p14");
System.out.println(person);
}
4.4、IOC之工厂实例方法创建Bean对象
实验4:配置通过实例工厂方法创建的bean
public class PersonFactory {
public static Person createPerson() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("这是通过静态工厂方法创建的Person对象");
return person;
}
public Person createPerson2() {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("这是通过工厂实例对象创建的Person");
return person;
}
}
在xml中的配置:
通过实例的方法,需要先有一个工厂实例对象:
类似情况:级联属性赋值一定要先注入已存在的对象。再注入对象的属性(类似于重新赋值)
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test15() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p15");
System.out.println(person);
}
4.5、IOC之FactoryBean接口创建Bean对象
实验5:配置FactoryBean接口创建Bean对象
1、实现FactoryBean接口
public class PersonFactoryBean implements FactoryBean {
/**
* 返回创建的对象
*/
@Override
public Person getObject() throws Exception {
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("这是FactoryBean接口的方式创建的");
return person;
}
/**
* 返回创建的对象的类型
*/
@Override
public Class> getObjectType() {
return Person.class;
}
/**
* 是否是单例
*/
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
2、在xml配置文件中的配置:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test16() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p16");
System.out.println(person);
}
5、Bean的普通属性赋值
一、通过property标签(name/value)注入
二、通过构造方法或参数名(name/value/index/type)注入
注:通过index标签索引,索引从0开始,要与构造方法的参数顺序一致
三、通过p名称空间
通过构造器为bean的属性赋值
5.1、IOC示例程序—通过构造方法参数名注入值
实验5:通过构造器为bean的属性赋值
配置内容:
测试代码:
@Test
public void test3() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p3");
System.out.println(person);
}
5.1.1、IOC示例程序— index属性指定参数的位置
实验6:通过index属性指定参数的位置
xml中的配置如下:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test4() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p4");
System.out.println(person);
}
5.1.2、IOC示例程序—根据参数类型注入
实验7:根据参数类型注入
xml中的配置:
注:通过参数类型可用区分构造方法的重载
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test5() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p5");
System.out.println(person);
}
5.2Bean的子对象bean赋值
5.2.1、IOC之子对象的赋值(很重点)
实验8:引用其他bean★
创建个新的工程。测试Spring的开发环境。此不重复。请参阅前面,环境搭建。
创建新的Bean对象
public class Car {
private int id;
private String name;
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private int age;
private Car car;
在xml中的配置如下:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test7() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p7");
System.out.println(person);
}
5.2.2、IOC之内部Bean的使用
实验8:引用内部bean
xml中配置的内容如下:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test8() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person p8 = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p8");
System.out.println(p8);
System.out.println( applicationContext.getBean("innerCar") );
}
常见错误:内部的Bean不能被外部使用,无法通过spring容器获取
5.3、IOC之P名称空间为bean赋值
实验9:通过p名称空间为bean赋值
xml中的配置:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test6() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p6");
System.out.println(person);
}
5.4、IOC之级联属性赋值
实验10:给bean的级联属性赋值
在xml中的配置:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test13() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p13");
System.out.println(person);
}
常见错误:
级联属性赋值一定要先注入已存在的对象。再注入对象的属性(类似于重新赋值)
6、Bean的属性文件和集合属性赋值
6.1、IOC之List属性的赋值一
实验11:使用list子元素为List类型的属性赋值
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private int age;
private Car car;
private List list;
通过setter方法注入值
要加getter和setter方法
xml中的配置:
list1
list2
list3
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test9() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person p9 = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p9");
System.out.println(p9);
}
6.2、IOC之util名称空间List属性赋值二
util名称空间,可以定义
实验12:通过util名称空间创建集合类型的bean
在xml中的配置:
list1
list2
list3
注:单独的list标签不允许定义在bean外部,但可用通过util名称空间定义
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test12() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p12");
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println( applicationContext.getBean("list1") );
}
6.3、IOC之Map属性的赋值
实验13:使用map子元素为Map类型的属性赋值
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private int age;
private Car car;
private List list;
private Mapmap;
通过setter方法注入值
要加getter和setter方法
在xml中的配置如下:
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test10() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p10");
System.out.println(person);
}
6.4、IOC之Properties属性的赋值
实验14:使用prop子元素为Properties类型的属性赋值
public class Person {
private int id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private int age;
private Car car;
private List list;
private Map map;
private Properties prop;
通过setter方法注入值
要加getter和setter方法
xml中的配置如下:
jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
root
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test11() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p11");
System.out.println(person);
}
7、Bean之间的关系
7.1、IOC之继承Bean配置
实验15:通过继承实现bean配置信息的重用
xml配置文件中的内容:
这是继承的1
这是继承的2
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test17() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("p17");
System.out.println(person);
}
7.2、IOC之Bean依赖组件创建顺序
实验16:bean之间的依赖 depends-on属性
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
注:不可以三个互相依赖,否在会包错
测试的代码:
@Test
public void test20() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application2.xml");
}
说明:
默认情况下:在Application.xml中配置的bean对象,默认在创建Spring容器的时候都会创建。而且创建的顺序是在配置文件中从上到下的顺序。
8、Bean的作用域——scope
Scope属性设置范围:
Singleton
Prototype
WEB环境作用域:request/session
8.1、IOC之Bean的单例和多例/作用域(重点)
实验17:测试bean的作用域,分别创建单实例和多实例的bean
scope 属性设置范围:
1、singleton默认情况是singleton,表示Spring容器中只有一个单例。
单例是在Spring容器创建的时候,初始化所有单例Bean对象。
并且每次调用Bean对象的时候,会调用原来Spring容器中的对象
2、prototypeprototype是表示当前配置的Bean对象是多例。
在Spring容器被创建的时候,bean不会被创建出来。
并且每次调用getBean方法的时候都会创建一个对象实例
3、request表示一次请求内,不管调用几次getBean方法,返回的都是同一个bean对象
Object bean = request.getAttribute(xxx);
if (bean == null) {
bean = 创建一个
request.setAttribute(xxx,bean);
}
4、session表示一个Session对象内,不管调用几次getBean方法,返回的都同一个Bean对象
Object bean = session.getAttribute(xxx);
if (bean == null) {
bean = 创建一个
session.setAttribute(xxx,bean);
}
9、基于xml配置文件的自动注入——autowire
先创建Person类和Car类
public class Car {
private int id;
private String name;
public class Person {
private Car car;
public Person(Car car) {
this.car = car;
}
xml中的配置如下:
autowire设置自动装配的方式:
1、Default(默认)和 no一样,都表示不装配,如果对象你不手动设置,就没有值。
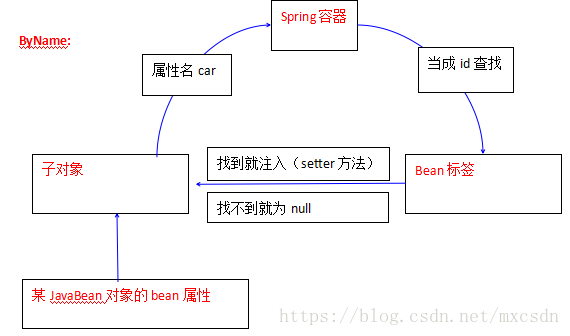
2、byName表示Spring容器会自动按照子对象的属性名,当成是id来查找对象。
找到就注入,找不到就为null
举例:private Car car;
就会以car做为id去spring容器中去查找对象。找到就把值注入给属性car。
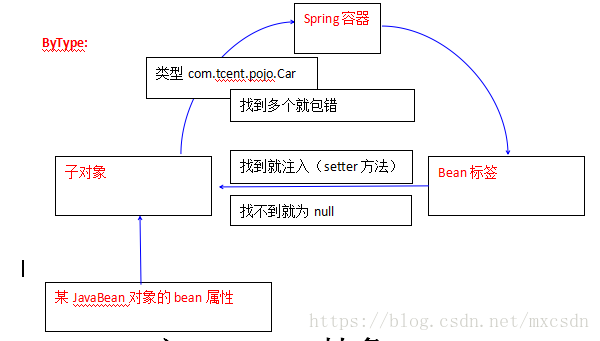
3、byType表示Spring容器会自动的按照子对象的类型去查找bean对象注入。
举例:private Car car;
Spring容器就会自动的按照Car.class类型去Spring容器中查找。
如果说:找到一个,就注入
没有找到,值就为null
找到多个,就报错。
4、constructor表示Spring容器会按照子对象的类型去查找构造方法中,参数需要的类型去注入。
先按照类型查询,如果找到一个就注入,
如果找到多个再按照构造方法中参数的变量名做为id来查找:
如果找到就注入。如果没有找到,就为null
Constructor:先按照byType查找,找到多个再按照byName
10、IOC之abstract抽象Bean
实验18:通过abstract属性创建一个模板bean
xml中的配置:
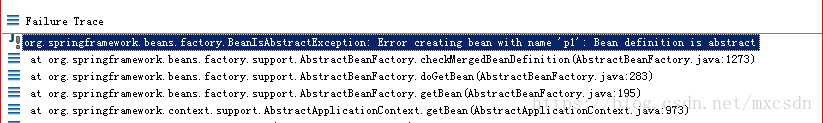
如果配置的bean标签对象,设置了属性abstract=“true”,那么此标签中的对象不能实例化
说明:
在SpringIOC容器中,读取bean配置,创建bean实例之前,必须对它进行初始化,只有在容器实例化后,才可以在IOC容器里获取bean实例并使用。
默认情况下,spring只为每个在IOC容器里声明的bean创建唯一的实例,整个ioc容器范围内都共享该实例
对于单例的bean,生命周期有11个步骤:
1.instantiate bean对象实例化,bean对象实例化,是在加载配置文件的时候实例的。即,我们启动spring容器的时候,加载配置文件,此时就实例化bean了。
2.populate properties 封装属性
3.如果Bean实现BeanNameAware, 执行setBeanName
4.如果Bean实现BeanFactoryAware或者ApplicationContextAware,设置工厂setBeanFactory或者上下文对象setApplicationContext
5.如果存在类实现BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessBeforeInitialization(此点常常用来增强bean)
6.如果Bean实现InitializingBean执行afterPropertiesSet
7.调用指定初始化方法init
8.如果存在类实现BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean) ,执行postProcessAfterInitialization(此点常常用来增强bean)
9.执行业务处理
10.如果Bean实现DisposableBean执行destroy
11.调用指定销毁方法
commons-logging-1.1.3.jar
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar