微服务学习-SpringCloud -Nacos (服务注册源码学习)
文章目录
- 源码版本及下载
- 服务注册核心流程图(看不清请双击打开大图)
- 源码详解
-
- 客户端注册源码
- 服务端注册源码
源码版本及下载
此次源码版本为1.4.1,2.x版本在服务请求时使用了grpc的方式,所以先以1.4.1版本学习,后续再看2.x版本。
源码下载地址:: link
打开页面后,下拉到最下面,下载nacos-1.4.1.zip,解压导入idea即可。
服务注册核心流程图(看不清请双击打开大图)
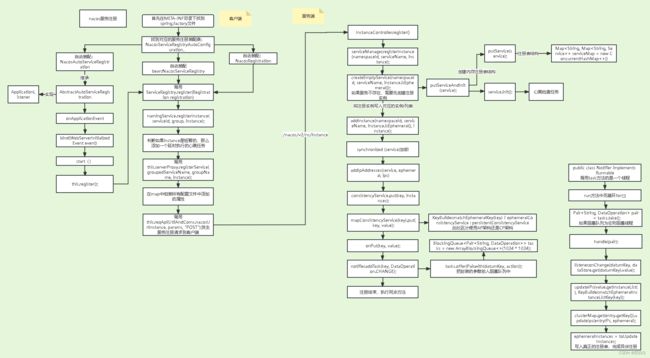
此图主要是对核心注册流程进行了大概梳理,可以在后续详细看源码时配合互补。
源码详解
客户端注册源码
在微服务使用nacos需要在pom文件中引入依赖:
com.alibaba.cloud
spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery
2.2.5.RELEASE
- 开始分析客户端源码
SpringCloud这一套组件都是基于SpringBoot开发的,那么SpringBoot引入其它组件的方式是什么呢?
自动装配
所以第一步,我们先找它的在自动装配类。
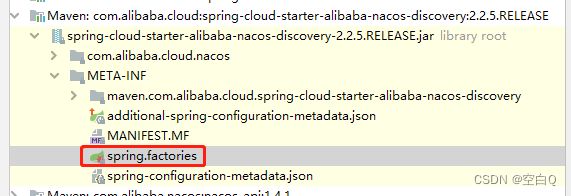
打开文件:
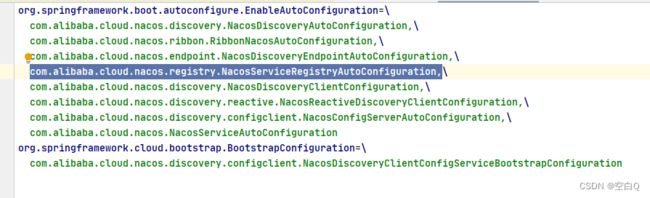
由类名推断服务注册的自动装配类为:
com.alibaba.cloud.nacos.registry.NacosServiceRegistryAutoConfiguration
我们打开此类:
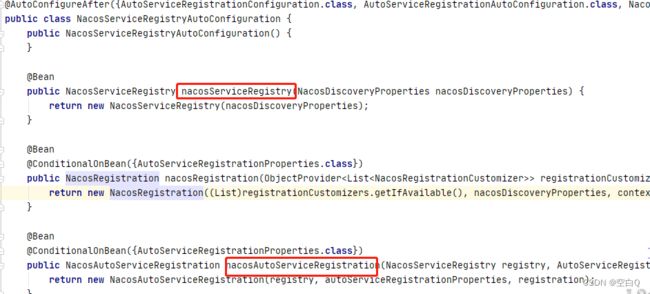
对应我画的流程图,我们重点关注第一个和第三个bean。
先看NacosAutoServiceRegistration。
当Springboot启动时,会发布事件。我们来看NacosAutoServiceRegistration,继承了AbstractAutoServiceRegistration,

在看AbstractAutoServiceRegistration类,我们发现它实现了ApplicationListener。
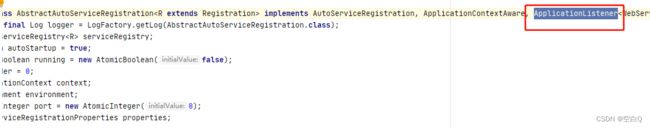
当我们实现了ApplicationListener时,我们就需要实现它的onApplicationEvent方法。
public void onApplicationEvent(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
this.bind(event);
}
/** @deprecated */
@Deprecated
public void bind(WebServerInitializedEvent event) {
ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
if (!(context instanceof ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext) || !"management".equals(((ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext)context).getServerNamespace())) {
this.port.compareAndSet(0, event.getWebServer().getPort());
this.start();
}
}
onApplicationEvent监听了WebServerInitializedEvent事件。调用this.start()方法。
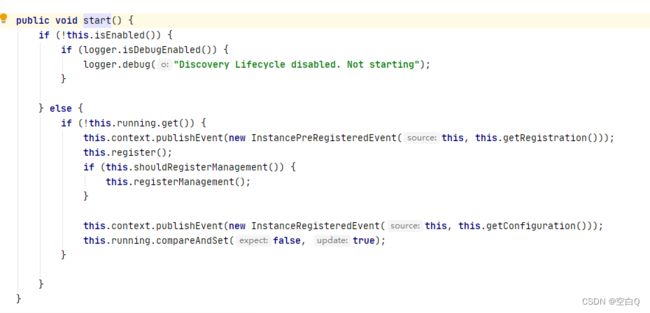
进入start方法,忽略分支内容,直接看主线,也就是this.register().
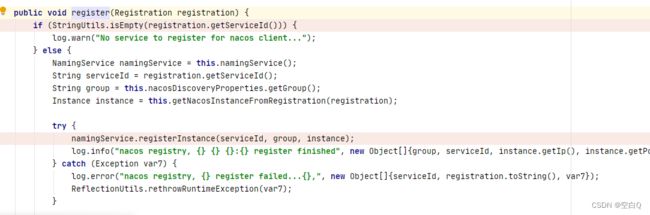
走到这个方法,可以在这边打断点,debug看代码。
往下走,进入namingService.registerInstance(serviceId, group, instance)方法。
public void registerInstance(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
// 心跳检测
NamingUtils.checkInstanceIsLegal(instance);
String groupedServiceName = NamingUtils.getGroupedName(serviceName, groupName);
if (instance.isEphemeral()) {
BeatInfo beatInfo = this.beatReactor.buildBeatInfo(groupedServiceName, instance);
this.beatReactor.addBeatInfo(groupedServiceName, beatInfo);
}
// 进入注册核心方法
this.serverProxy.registerService(groupedServiceName, groupName, instance);
}
public void registerService(String serviceName, String groupName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
LogUtils.NAMING_LOGGER.info("[REGISTER-SERVICE] {} registering service {} with instance: {}", new Object[]{this.namespaceId, serviceName, instance});
// 配置参数写入map中
Map params = new HashMap(16);
params.put("namespaceId", this.namespaceId);
params.put("serviceName", serviceName);
params.put("groupName", groupName);
params.put("clusterName", instance.getClusterName());
params.put("ip", instance.getIp());
params.put("port", String.valueOf(instance.getPort()));
params.put("weight", String.valueOf(instance.getWeight()));
params.put("enable", String.valueOf(instance.isEnabled()));
params.put("healthy", String.valueOf(instance.isHealthy()));
params.put("ephemeral", String.valueOf(instance.isEphemeral()));
params.put("metadata", JacksonUtils.toJson(instance.getMetadata()));
// 通过http请求发生注册信息
this.reqApi(UtilAndComs.nacosUrlInstance, params, "POST");
}
UtilAndComs.nacosUrlInstance=/nacos/v1/ns/instance
这个地址就是服务注册的地址,我们来看官网API:
官网API

具体参数可以看官网。
再往下,简单看看主要代码:
HttpRestResult restResult = this.nacosRestTemplate.exchangeForm(url, header, Query.newInstance().initParams(params), body, method, String.class);
this.execute(url, httpMethod, requestHttpEntity, responseType);
response = this.requestClient().execute(uri, httpMethod, requestEntity);
底层是调用了JdkHttpClientRequest方法发送请求。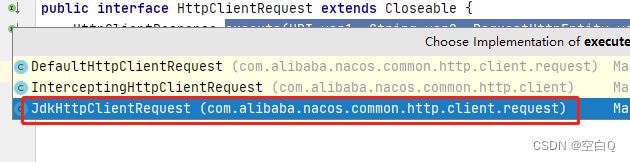
客户端主要注册源码就结束了。
服务端注册源码
服务端就是第一步下载并导入的源码。
找到服务注册方法类:
找到对应的注册的方法
/**
* Register new instance.
*
* @param request http request
* @return 'ok' if success
* @throws Exception any error during register
*/
@CanDistro
@PostMapping
@Secured(parser = NamingResourceParser.class, action = ActionTypes.WRITE)
public String register(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
final String namespaceId = WebUtils
.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
final String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
NamingUtils.checkServiceNameFormat(serviceName);
final Instance instance = parseInstance(request);
// 服务注册核心方法
serviceManager.registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance);
return "ok";
}
看注释注册一个新的实例。
往下走。
// 以AP模式创建注册实例
public void registerInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, Instance instance) throws NacosException {
// 创建空的服务实例
createEmptyService(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral());
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
if (service == null) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.INVALID_PARAM,
"service not found, namespace: " + namespaceId + ", service: " + serviceName);
}
// 添加实例
addInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral(), instance);
}
注意,此处是以AP模式创建的实例,是临时实例。
nacos注册实例分为AP和CP,我们看到服务注册时传入的参数有一个参数控制我们注册的实例是AP还是CP,就是这个参数:
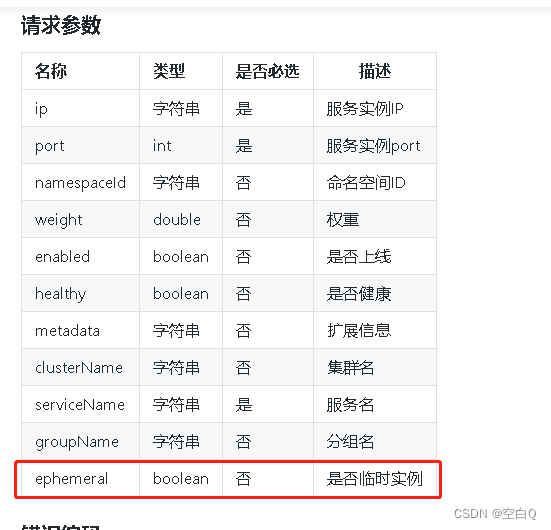
此参数默认为true,也就是默认创建临时实例。后面会重点讲一下AP和CP架构。
我们先加入createEmptyService方法。
public void createEmptyService(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean local) throws NacosException {
createServiceIfAbsent(namespaceId, serviceName, local, null);
}
public void createServiceIfAbsent(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean local, Cluster cluster)
throws NacosException {
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
if (service == null) {
Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("creating empty service {}:{}", namespaceId, serviceName);
service = new Service();
service.setName(serviceName);
service.setNamespaceId(namespaceId);
service.setGroupName(NamingUtils.getGroupName(serviceName));
// now validate the service. if failed, exception will be thrown
service.setLastModifiedMillis(System.currentTimeMillis());
service.recalculateChecksum();
if (cluster != null) {
cluster.setService(service);
service.getClusterMap().put(cluster.getName(), cluster);
}
service.validate();
putServiceAndInit(service);
if (!local) {
addOrReplaceService(service);
}
}
}
- 先看下这个方法
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
主要是用来从注册表中通过namespace获取对应的服务,如果没有获取到,返回null;如果有,返回对应的service。
看一下对应的getService方法:
public Service getService(String namespaceId, String serviceName) {
if (serviceMap.get(namespaceId) == null) {
return null;
}
return chooseServiceMap(namespaceId).get(serviceName);
}
public boolean containService(String namespaceId, String serviceName) {
return getService(namespaceId, serviceName) != null;
}
然后我们来看一下注册表的结构,也就是serviceMap。
private final Map> serviceMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
其实主要是这样一个结构:
Map
在我们平时使用中,大概是这样一个结构:
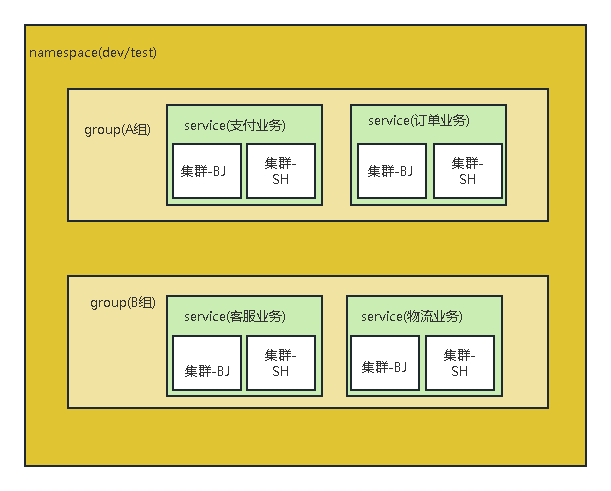
- 再看下下面的这个主要方法,点击进入:
putServiceAndInit(service);
private void putServiceAndInit(Service service) throws NacosException {
// 将服务信息写入serviceMap
putService(service);
// 初始化服务
service.init();
// 监听数据变化
consistencyService
.listen(KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName(), true), service);
consistencyService
.listen(KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(service.getNamespaceId(), service.getName(), false), service);
Loggers.SRV_LOG.info("[NEW-SERVICE] {}", service.toJson());
}
将service数据写入serviceMap后,创建临时实例的方法就结束了,现在我们代码回到创建临时实例createEmptyService处继续向下走,然后再判断一次注册表中是否有service,此次没有的话就会抛出异常。
再往下走,进入核心方法:
addInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance.isEphemeral(), instance);
public void addInstance(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean ephemeral, Instance... ips)
throws NacosException {
String key = KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName, ephemeral);
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName);
synchronized (service) {
// 比较并获取新的实例列表,这个列表中包含了此次新增的实例
List instanceList = addIpAddresses(service, ephemeral, ips);
Instances instances = new Instances();
instances.setInstanceList(instanceList);
consistencyService.put(key, instances);
}
}
先看一下此方法:
String key = KeyBuilder.buildInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName, ephemeral);
public static String buildInstanceListKey(String namespaceId, String serviceName, boolean ephemeral) {
return ephemeral ? buildEphemeralInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName)
: buildPersistentInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName);
}
ephemeral前面我们了解过,是否是临时实例,默认传true,所以一般返回 buildEphemeralInstanceListKey(namespaceId, serviceName)这个结果,所以这里主要是区分nacos是AP还是CP架构的地方。
再往下走:
consistencyService.put(key, instances);
public void put(String key, Record value) throws NacosException {
onPut(key, value);
distroProtocol.sync(new DistroKey(key, KeyBuilder.INSTANCE_LIST_KEY_PREFIX), DataOperation.CHANGE,
globalConfig.getTaskDispatchPeriod() / 2);
}
public void onPut(String key, Record value) {
// 健壮性校验
...
// 核心方法,将任务添加到阻塞队列
notifier.addTask(key, DataOperation.CHANGE);
}
public void addTask(String datumKey, DataOperation action) {
if (services.containsKey(datumKey) && action == DataOperation.CHANGE) {
return;
}
if (action == DataOperation.CHANGE) {
services.put(datumKey, StringUtils.EMPTY);
}
// 放入阻塞队列中,如果队列中无数据时会阻塞
tasks.offer(Pair.with(datumKey, action));
}
放入阻塞队列后,注册基本结束。
nacos会启用一个线程,一直循环将阻塞队列中的客户端的注册信息拿出来实现真正的注册。
下面看下源码:
实现了Runnable接口,所以我们主要看一下run方法:
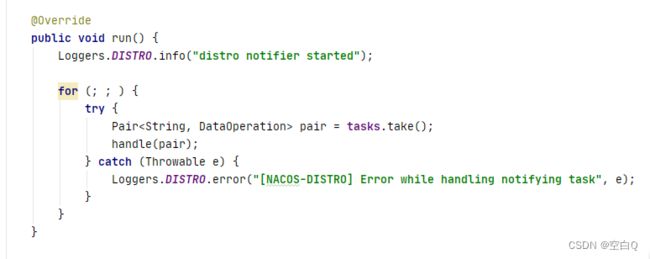
可以看到一个线程一直循环取数据,当队列为空时,阻塞线程。
private BlockingQueue> tasks = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(1024 * 1024);
// 进行实际的注册任务
handle(pair);
服务注册基本流程已经结束。