php redis管道,redis管道pipeline的运用
Redis使用的是客户端-服务器(CS)模型和请求/响应协议的TCP服务器。这意味着通常情况下一个请求会遵循以下步骤:
客户端向服务端发送一个查询请求,并监听Socket返回,通常是以阻塞模式,等待服务端响应。
服务端处理命令,并将结果返回给客户端。
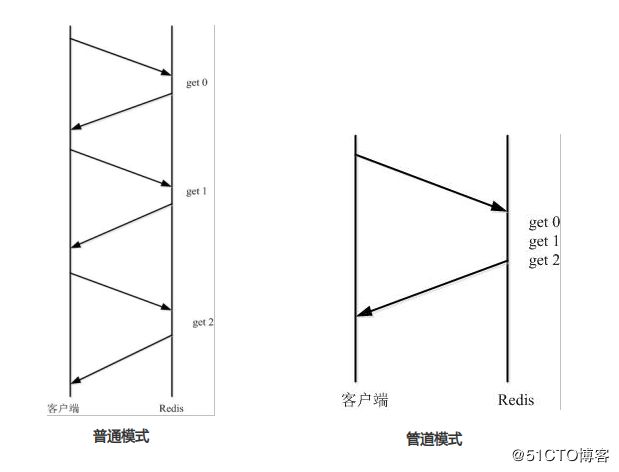
普通模式与管道模式
分析
普通模式:由于通信会有网络延迟,假如client和server之间的包传输时间需要0.125秒。那么上面的三个命令6个报文至少需要0.75秒才能完成。这样即使redis每秒能处理100个命令,而我们的client也只能一秒钟发出四个命令。这显然没有充分利用 redis的处理能力。
管道模式:(pipeline)可以一次性发送多条命令并在执行完后一次性将结果返回,pipeline通过减少客户端与redis的通信次数来实现降低往返延时时间,而且Pipeline 实现的原理是队列,而队列的原理是时先进先出,这样就保证数据的顺序性。 Pipeline 的默认的同步的个数为53个,也就是说arges中累加到53条数据时会把数据提交。其过程如下图所示:client可以将三个命令放到一个tcp报文一起发送,server则可以将三条命令的处理结果放到一个tcp报文返回。
需要注意到是用 pipeline方式打包命令发送,redis必须在处理完所有命令前先缓存起所有命令的处理结果。打包的命令越多,缓存消耗内存也越多。所以并不是打包的命令越多越好。具体多少合适需要根据具体情况测试。
案例一:将100万条数据写入redis
//产生100万条数据到指定文件
declare(strict_types=1);//开启强类型模式
function random($length, $numeric = false)
{
$seed = base_convert(md5(microtime() . $_SERVER['DOCUMENT_ROOT']), 16, $numeric ? 10 : 35);
$seed = $numeric ? (str_replace('0', '', $seed) . '012340567890') : ($seed . 'zZ' . strtoupper($seed));
if ($numeric) {
$hash = '';
} else {
$hash = chr(rand(1, 26) + rand(0, 1) * 32 + 64);
$length--;
}
$max = strlen($seed) - 1;
for ($i = 0; $i < $length; $i++) {
$hash .= $seed{mt_rand(0, $max)};
}
return $hash;
}
$filePath = './data.txt';
for ($i = 0; $i <= 1000000; $i++) {
$str = random(10, true);
file_put_contents($filePath, $str . PHP_EOL, FILE_APPEND);
}
//读取数据通过管道方式写入到redis
$lines = file_get_contents($filePath);//获取文件内容
ini_set('memory_limit', '-1');//不要限制Mem大小,否则会报错
$arr = explode(PHP_EOL, $lines);//转换成数组
//echo $arr['1000000'] ?? 'null';
try {
$redis = new \Redis();
$redis->connect('192.168.1.9', 6379);
$redis->auth('*****');//密码验证
$redis->select(0);//选择库
$redis->pipeline();//开启管道
foreach ($arr as $key => $value) {
$redis->hsetNx('helloworld', (string)$key, $value);
}
$redis->exec();
echo $redis->hGet('helloworld', '1000000') . PHP_EOL;
echo $redis->hGet('helloworld', '1000001') . PHP_EOL;
} catch (\Exception $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
案例二:通过管道批量设置与读取
//批量设置
try {
$redis = new \Redis();
$redis->connect('192.168.1.9', 6379);
$redis->auth('******');
$redis->select(0);
$redis->pipeline();//开启管道
$redis->set('str1', 'h');
$redis->set('str2', 'e');
$redis->set('str3', 'l');
$redis->set('str4', 'l');
$redis->set('str5', 'o');
$redis->set('str6', 'w');
$redis->set('str7', 'o');
$redis->set('str8', 'r');
$redis->set('str9', 'l');
$redis->set('str10', 'd');
$result = $redis->exec();
print_r($result);
} catch (\Exception $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
结果:
Array
(
[0] => 1
[1] => 1
[2] => 1
[3] => 1
[4] => 1
[5] => 1
[6] => 1
[7] => 1
[8] => 1
[9] => 1
)
//批量读取
try {
$redis = new \Redis();
$redis->connect('192.168.1.9', 6379);
$redis->auth('******');
$redis->select(0);
$redis->pipeline();//开启管道
$redis->get('str1');
$redis->get('str2');
$redis->get('str3');
$redis->get('str4');
$redis->get('str5');
$redis->get('str6');
$redis->get('str7');
$redis->get('str8');
$redis->get('str9');
$redis->get('str10');
$result = $redis->exec();
print_r($result);
} catch (\Exception $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
结果:
Array
(
[0] => h
[1] => e
[2] => l
[3] => l
[4] => o
[5] => w
[6] => o
[7] => r
[8] => l
[9] => d
)