Mybatis框架源码笔记(十)之Mybatis中的设计模式
1 Mybatis框架中应用到的设计模式
-
1、单例模式:例如LogFactory、ErrorContext
-
2、工厂模式:例如SqlSessionFactory、ObjectFactory、MapperProxyFactory
-
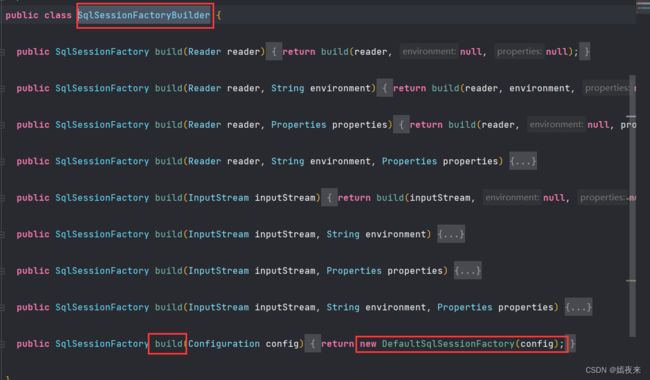
3、建造者模式:例如SqlSessionFactoryBuilder、XMLConfigBuilder、XMLMapperBuilder、XMLStatementBuilder、CacheBuilder
-
4、代理模式:mybatis实现的核心,比如MapperProxy、ConnectionLogger、用的jdk的动态代理等
-
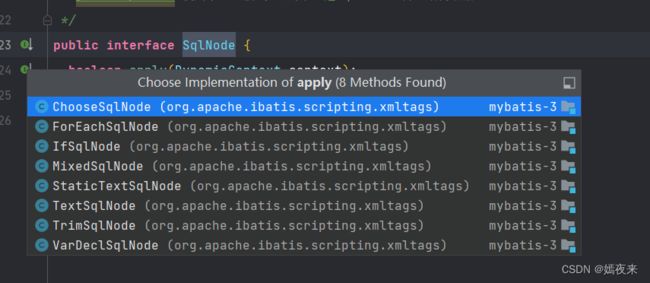
5、组合模式:例如SqlNode和各个子类ChooseSqlNode等【生成树形结构数据】
-
6、模板方法模式:例如BaseExecutor和SimpleExecutor,还有BaseTypeHandler及其子类
-
7、适配器模式:例如Log的Mybatis接口和它对jdbc、log4j等各种日志框架的适配实现
-
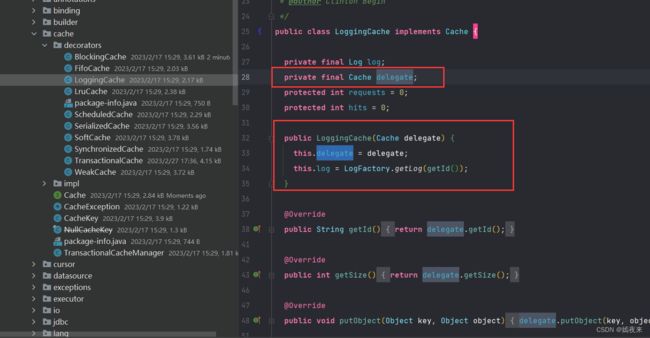
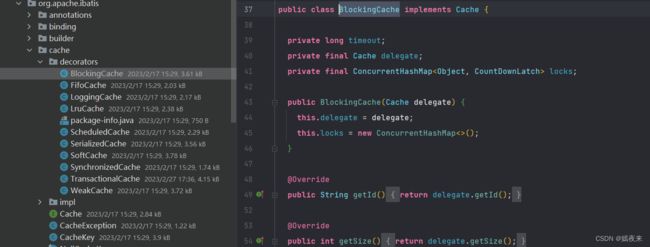
8、装饰者模式:例如Cache包中的cache.decorators子包中的各个装饰者的实现
-
9、迭代器模式:例如迭代器模式PropertyTokenizer
2 Mybatis框架中各设计模式的核心代码说明
2.1 单例模式
Mybatis的异常信息拼接类ErrorContext在设计的时候使用到了单例模式。
2.2 工厂模式
在进行SqlSession创建的过程中,Mapper层接口的动态代理对创建等过程都是用到了工厂模式。
2.3 建造者模式
在SqlSession创建的过程中、全局配置文件解析,mapper映射文件解析等过程处理中使用了大量的建造者模式完成复杂对象的创建。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
MappedStatement
package org.apache.ibatis.mapping;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.keygen.Jdbc3KeyGenerator;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.keygen.KeyGenerator;
import org.apache.ibatis.executor.keygen.NoKeyGenerator;
import org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log;
import org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.scripting.LanguageDriver;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public final class MappedStatement {
private String resource;
private Configuration configuration;
private String id;
private Integer fetchSize;
private Integer timeout;
private StatementType statementType;
private ResultSetType resultSetType;
private SqlSource sqlSource;
private Cache cache;
private ParameterMap parameterMap;
private List<ResultMap> resultMaps;
private boolean flushCacheRequired;
private boolean useCache;
private boolean resultOrdered;
private SqlCommandType sqlCommandType;
private KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
private String[] keyProperties;
private String[] keyColumns;
private boolean hasNestedResultMaps;
private String databaseId;
private Log statementLog;
private LanguageDriver lang;
private String[] resultSets;
MappedStatement() {
// constructor disabled
}
public static class Builder {
private MappedStatement mappedStatement = new MappedStatement();
public Builder(Configuration configuration, String id, SqlSource sqlSource, SqlCommandType sqlCommandType) {
mappedStatement.configuration = configuration;
mappedStatement.id = id;
mappedStatement.sqlSource = sqlSource;
mappedStatement.statementType = StatementType.PREPARED;
mappedStatement.resultSetType = ResultSetType.DEFAULT;
mappedStatement.parameterMap = new ParameterMap.Builder(configuration, "defaultParameterMap", null, new ArrayList<>()).build();
mappedStatement.resultMaps = new ArrayList<>();
mappedStatement.sqlCommandType = sqlCommandType;
mappedStatement.keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) ? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
String logId = id;
if (configuration.getLogPrefix() != null) {
logId = configuration.getLogPrefix() + id;
}
mappedStatement.statementLog = LogFactory.getLog(logId);
mappedStatement.lang = configuration.getDefaultScriptingLanguageInstance();
}
public Builder resource(String resource) {
mappedStatement.resource = resource;
return this;
}
public String id() {
return mappedStatement.id;
}
public Builder parameterMap(ParameterMap parameterMap) {
mappedStatement.parameterMap = parameterMap;
return this;
}
public Builder resultMaps(List<ResultMap> resultMaps) {
mappedStatement.resultMaps = resultMaps;
for (ResultMap resultMap : resultMaps) {
mappedStatement.hasNestedResultMaps = mappedStatement.hasNestedResultMaps || resultMap.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
return this;
}
public Builder fetchSize(Integer fetchSize) {
mappedStatement.fetchSize = fetchSize;
return this;
}
public Builder timeout(Integer timeout) {
mappedStatement.timeout = timeout;
return this;
}
public Builder statementType(StatementType statementType) {
mappedStatement.statementType = statementType;
return this;
}
public Builder resultSetType(ResultSetType resultSetType) {
mappedStatement.resultSetType = resultSetType == null ? ResultSetType.DEFAULT : resultSetType;
return this;
}
public Builder cache(Cache cache) {
mappedStatement.cache = cache;
return this;
}
public Builder flushCacheRequired(boolean flushCacheRequired) {
mappedStatement.flushCacheRequired = flushCacheRequired;
return this;
}
public Builder useCache(boolean useCache) {
mappedStatement.useCache = useCache;
return this;
}
public Builder resultOrdered(boolean resultOrdered) {
mappedStatement.resultOrdered = resultOrdered;
return this;
}
public Builder keyGenerator(KeyGenerator keyGenerator) {
mappedStatement.keyGenerator = keyGenerator;
return this;
}
public Builder keyProperty(String keyProperty) {
mappedStatement.keyProperties = delimitedStringToArray(keyProperty);
return this;
}
public Builder keyColumn(String keyColumn) {
mappedStatement.keyColumns = delimitedStringToArray(keyColumn);
return this;
}
public Builder databaseId(String databaseId) {
mappedStatement.databaseId = databaseId;
return this;
}
public Builder lang(LanguageDriver driver) {
mappedStatement.lang = driver;
return this;
}
public Builder resultSets(String resultSet) {
mappedStatement.resultSets = delimitedStringToArray(resultSet);
return this;
}
/**
* Resul sets.
*
* @param resultSet
* the result set
* @return the builder
* @deprecated Use {@link #resultSets}
*/
@Deprecated
public Builder resulSets(String resultSet) {
mappedStatement.resultSets = delimitedStringToArray(resultSet);
return this;
}
public MappedStatement build() {
assert mappedStatement.configuration != null;
assert mappedStatement.id != null;
assert mappedStatement.sqlSource != null;
assert mappedStatement.lang != null;
mappedStatement.resultMaps = Collections.unmodifiableList(mappedStatement.resultMaps);
return mappedStatement;
}
}
public KeyGenerator getKeyGenerator() {
return keyGenerator;
}
public SqlCommandType getSqlCommandType() {
return sqlCommandType;
}
public String getResource() {
return resource;
}
public Configuration getConfiguration() {
return configuration;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public boolean hasNestedResultMaps() {
return hasNestedResultMaps;
}
public Integer getFetchSize() {
return fetchSize;
}
public Integer getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
public StatementType getStatementType() {
return statementType;
}
public ResultSetType getResultSetType() {
return resultSetType;
}
public SqlSource getSqlSource() {
return sqlSource;
}
public ParameterMap getParameterMap() {
return parameterMap;
}
public List<ResultMap> getResultMaps() {
return resultMaps;
}
public Cache getCache() {
return cache;
}
public boolean isFlushCacheRequired() {
return flushCacheRequired;
}
public boolean isUseCache() {
return useCache;
}
public boolean isResultOrdered() {
return resultOrdered;
}
public String getDatabaseId() {
return databaseId;
}
public String[] getKeyProperties() {
return keyProperties;
}
public String[] getKeyColumns() {
return keyColumns;
}
public Log getStatementLog() {
return statementLog;
}
public LanguageDriver getLang() {
return lang;
}
public String[] getResultSets() {
return resultSets;
}
/**
* Gets the resul sets.
*
* @return the resul sets
* @deprecated Use {@link #getResultSets()}
*/
@Deprecated
public String[] getResulSets() {
return resultSets;
}
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
private static String[] delimitedStringToArray(String in) {
if (in == null || in.trim().length() == 0) {
return null;
} else {
return in.split(",");
}
}
}
在org.apache.ibatis.mapping包下还有这些类都使用到了建造者模式,有兴趣可以自行阅读源码

2.4 代理模式
Mybatis 底层封装使用的 JDK 动态代理。
一般来说定义 JDK 动态代理分为三个步骤,如下所示
- 定义代理接口
- 定义代理接口实现类
- 定义动态代理调用处理器
下面我们一起到源码中看看Mybatis框架是如何实现的动态代理。
MapperProxyFactory, 见名知意, 这个累肯定是用来创建动态代理实例对象。
/**
* @author Lasse Voss
*
* @description: 创建Mapper层接口代理类的工厂类
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
/** mapper接口类的全限定路径名 */
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
/** mapper接口类的中的抽象方法名称和对应的动态代理类中的MapperMethodInvoker对象的映射关系集合 */
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
核心代码就这一行:
Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
以上可见, 动态代理的实现是借助JDK 提供的Proxy类来实现的。
这里我们看到在创建动态代理的时候, 搬来应该传入一个InvocationHandler接口的匿名内部类或者InvocationHandler接口的实现类, 治理直接传递一个MapperProxy对象, 由此可见MapperProxy类必然实现了InvocationHandler接口, 去代码里面验证一下:
/*
* Copyright 2009-2023 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandle;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles.Lookup;
import java.lang.invoke.MethodType;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ExceptionUtil;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.util.MapUtil;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4724728412955527868L;
private static final int ALLOWED_MODES = MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED
| MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC;
private static final Constructor<Lookup> lookupConstructor;
// 代理的mapper层接口中的哪个方法,例如: public abstract int com.kkarma.mapper.StudentMapper.insertStudent(com.kkarma.pojo.Student)
private static final Method privateLookupInMethod;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
// 代理的mapper层接口是哪个, 例如: interface com.kkarma.mapper.StudentMapper
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethodInvoker> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
static {
Method privateLookupIn;
try {
privateLookupIn = MethodHandles.class.getMethod("privateLookupIn", Class.class, MethodHandles.Lookup.class);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
privateLookupIn = null;
}
privateLookupInMethod = privateLookupIn;
Constructor<Lookup> lookup = null;
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
// JDK 1.8
try {
lookup = MethodHandles.Lookup.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class);
lookup.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"There is neither 'privateLookupIn(Class, Lookup)' nor 'Lookup(Class, int)' method in java.lang.invoke.MethodHandles.",
e);
} catch (Exception e) {
lookup = null;
}
}
lookupConstructor = lookup;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
/**
* 这里给大家解释一下这个invoke判断里面加这个判断的原因:
* 大家都知道Object对象默认已经实现了很多方法, 我们的Mapper接口在进行定义的时候, 可能定义了静态方法、 默认方法以及抽象方法
* 因此在创建了动态代理对象的时候, 这个动态代理类肯定也包含了很多的方法, 从Object类继承的方法, 从接口继承的默认方法,
* 以及从接口继承抽象方法需要实现取执行SQL语句的方法
*
* 这个if分值判断的只要目的在将无需走SQL执行流程的方法如(toString/equals/hashCode)等先过滤掉
* 然后再抽象方法及默认方法中通过一个接口MapperMethodInvoker再进行一次判断,找到所有需要执行SQL的方法通过PlainMethodInvoker的invoke
* 方法取执行SQL语句获取结果,能够加快获取 mapperMethod 的效率
*/
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {
try {
return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {
if (m.isDefault()) {
try {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));
} else {
return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));
}
} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException
| NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
} else {
return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()));
}
});
} catch (RuntimeException re) {
Throwable cause = re.getCause();
throw cause == null ? re : cause;
}
}
private MethodHandle getMethodHandleJava9(Method method)
throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException {
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return ((Lookup) privateLookupInMethod.invoke(null, declaringClass, MethodHandles.lookup())).findSpecial(
declaringClass, method.getName(), MethodType.methodType(method.getReturnType(), method.getParameterTypes()),
declaringClass);
}
private MethodHandle getMethodHandleJava8(Method method)
throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException, InvocationTargetException {
final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
return lookupConstructor.newInstance(declaringClass, ALLOWED_MODES).unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass);
}
interface MapperMethodInvoker {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable;
}
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
private static class DefaultMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MethodHandle methodHandle;
public DefaultMethodInvoker(MethodHandle methodHandle) {
super();
this.methodHandle = methodHandle;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return methodHandle.bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args);
}
}
}
2.5 迭代器模式
迭代器模式主要包含以下角色:
- 抽象集合(Aggregate)角色:用于存储和管理元素对象, 定义存储、添加、删除集合元素的功能,并且声明了一个createIterator()方法用于创建迭代器对象。
- 具体集合(ConcreteAggregate)角色:实现抽象集合类,返回一个具体迭代器的实例。
- 抽象迭代器(Iterator)角色:定义访问和遍历聚合元素的接口,通常包含 hasNext()、next() 等方法。
- hasNext():该方法用于判断集合中是否还有下一个元素
- next() : 该方法用于将游标后移一位元素
- currentItem() :该方法用来返回当前游标指向的元素
- 具体迭代器(Concretelterator)角色:实现抽象迭代器接口中所定义的方法,完成对集合对象的遍历,同时记录遍历的当前位置。
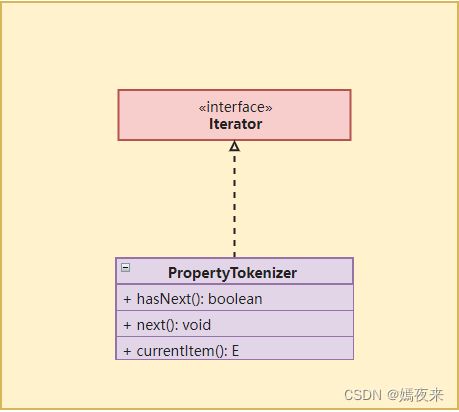
来看看Mybatis中对于迭代器模式的应用。
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
* 属性分词器
*
* @description: 使用了迭代器模式
*/
public class PropertyTokenizer implements Iterator<PropertyTokenizer> {
private String name;
private final String indexedName;
private String index;
private final String children;
public PropertyTokenizer(String fullname) {
int delim = fullname.indexOf('.');
if (delim > -1) {
name = fullname.substring(0, delim);
children = fullname.substring(delim + 1);
} else {
name = fullname;
children = null;
}
indexedName = name;
delim = name.indexOf('[');
if (delim > -1) {
index = name.substring(delim + 1, name.length() - 1);
name = name.substring(0, delim);
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getIndex() {
return index;
}
public String getIndexedName() {
return indexedName;
}
public String getChildren() {
return children;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return children != null;
}
@Override
public PropertyTokenizer next() {
return new PropertyTokenizer(children);
}
@Override
public void remove() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Remove is not supported, as it has no meaning in the context of properties.");
}
}
2.6 适配器模式
将一个系统的接口转换成另外一种形式,从而使原来不能直接调用的接口变得可以调用。
适配器模式涉及3个角色:
1.源(Source):需要被适配的对象或类型,相当于插头。
2.适配器(Adaptor):连接目标和源的中间对象,相当于插头转换器。
3.目标(Target):期待得到的目标,相当于插座。
适配器模式包括3种形式:类适配器模式、对象适配器模式、接口适配器模式(又称缺省适配器模式)
在Mybatis的日志模块中就是使用了适配器模式。Mybatis内部在使用日志模块时,使用了其内部接org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log,但是常用的日志框架的对外接口各不相同。
Mybatis为了复用和集成这些第三方日志组件,在其日志模块中,提供了多种Adapter,将这些第三方日志组件对外接口适配成org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log,这样Myabtis 就可以通过Log接口调用第三方日志了。
关于日志框架的集成实例和原理分析我之前已经写过相关的文章【Mybatis框架源码笔记(六)之Mybatis中集成日志框架原理解析】感兴趣可以自行查看。
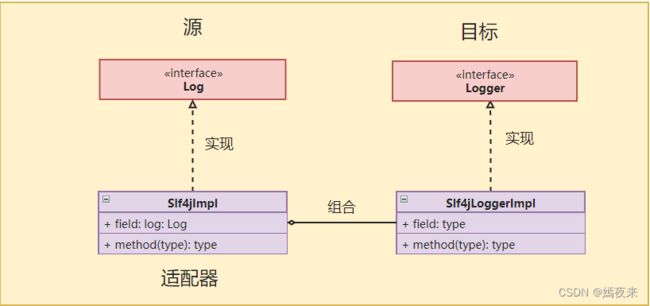
源:Log 接口
package org.apache.ibatis.logging;
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface Log {
boolean isDebugEnabled();
boolean isTraceEnabled();
void error(String s, Throwable e);
void error(String s);
void debug(String s);
void trace(String s);
void warn(String s);
}
适配器:Slf4jImpl
public class Slf4jImpl implements Log {
private Log log;
public Slf4jImpl(String clazz) {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(clazz);
if (logger instanceof LocationAwareLogger) {
try {
// check for slf4j >= 1.6 method signature
logger.getClass().getMethod("log", Marker.class, String.class, int.class, String.class, Object[].class, Throwable.class);
log = new Slf4jLocationAwareLoggerImpl((LocationAwareLogger) logger);
return;
} catch (SecurityException | NoSuchMethodException e) {
// fail-back to Slf4jLoggerImpl
}
}
// Logger is not LocationAwareLogger or slf4j version < 1.6
log = new Slf4jLoggerImpl(logger);
}
@Override
public boolean isDebugEnabled() {
return log.isDebugEnabled();
}
@Override
public boolean isTraceEnabled() {
return log.isTraceEnabled();
}
@Override
public void error(String s, Throwable e) {
log.error(s, e);
}
@Override
public void error(String s) {
log.error(s);
}
@Override
public void debug(String s) {
log.debug(s);
}
@Override
public void trace(String s) {
log.trace(s);
}
@Override
public void warn(String s) {
log.warn(s);
}
}
目标:Logger接口
package org.slf4j;
public interface Logger {
final public String ROOT_LOGGER_NAME = "ROOT";
public String getName();
public boolean isTraceEnabled();
public void trace(String msg);
public void trace(String format, Object arg);
public void trace(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void trace(String format, Object... arguments);
public void trace(String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isTraceEnabled(Marker marker);
public void trace(Marker marker, String msg);
public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void trace(Marker marker, String format, Object... argArray);
public void trace(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isDebugEnabled();
public void debug(String msg);
public void debug(String format, Object arg);
public void debug(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void debug(String format, Object... arguments);
public void debug(String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isDebugEnabled(Marker marker);
public void debug(Marker marker, String msg);
public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void debug(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
public void debug(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isInfoEnabled();
public void info(String msg);
public void info(String format, Object arg);
public void info(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void info(String format, Object... arguments);
public void info(String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isInfoEnabled(Marker marker);
public void info(Marker marker, String msg);
public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void info(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
public void info(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isWarnEnabled();
public void warn(String msg);
public void warn(String format, Object arg);
public void warn(String format, Object... arguments);
public void warn(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void warn(String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isWarnEnabled(Marker marker);
public void warn(Marker marker, String msg);
public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void warn(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
public void warn(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isErrorEnabled();
public void error(String msg);
public void error(String format, Object arg);
public void error(String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void error(String format, Object... arguments);
public void error(String msg, Throwable t);
public boolean isErrorEnabled(Marker marker);
public void error(Marker marker, String msg);
public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object arg);
public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object arg1, Object arg2);
public void error(Marker marker, String format, Object... arguments);
public void error(Marker marker, String msg, Throwable t);
}
目标Logger实现类:Slf4jLoggerImpl
class Slf4jLoggerImpl implements Log {
private final Logger log;
public Slf4jLoggerImpl(Logger logger) {
log = logger;
}
@Override
public boolean isDebugEnabled() {
return log.isDebugEnabled();
}
@Override
public boolean isTraceEnabled() {
return log.isTraceEnabled();
}
@Override
public void error(String s, Throwable e) {
log.error(s, e);
}
@Override
public void error(String s) {
log.error(s);
}
@Override
public void debug(String s) {
log.debug(s);
}
@Override
public void trace(String s) {
log.trace(s);
}
@Override
public void warn(String s) {
log.warn(s);
}
}
2.7 装饰者模式
这个之前在写Mybatis框架源码笔记(五)之Mybatis框架缓存机制原理解析已经详细讲过, 这里不再进行赘述,Mybatis在实现缓存架构的时候使用了装饰者模式, 通过包装和组合的方式实现了强大的缓存功能。
Cache接口
public interface Cache {
String getId();
void putObject(Object key, Object value);
Object getObject(Object key);
Object removeObject(Object key);
void clear();
int getSize();
default ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return null;
}
}
2.8 组合模式
组合模式其实就是将一组对象(文件夹和文件)组织成树形结构,以表示一种’部分-整体’ 的层次结构,(目录与子目录的嵌套结构). 组合模式让客户端可以统一单个对象(文件)和组合对象(文件夹)的处理逻辑(递归遍历).

/**
* SQL Node 接口,每个 XML Node 会解析成对应的 SQL Node 对象
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface SqlNode {
/**
* 应用当前 SQL Node 节点
*
* @param context 上下文
* @return 当前 SQL Node 节点是否应用成功。
*/
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
public class TrimSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final SqlNode contents;
private final String prefix;
private final String suffix;
private final List<String> prefixesToOverride;
private final List<String> suffixesToOverride;
private final Configuration configuration;
public TrimSqlNode(Configuration configuration, SqlNode contents, String prefix, String prefixesToOverride, String suffix, String suffixesToOverride) {
this(configuration, contents, prefix, parseOverrides(prefixesToOverride), suffix, parseOverrides(suffixesToOverride));
}
protected TrimSqlNode(Configuration configuration, SqlNode contents, String prefix, List<String> prefixesToOverride, String suffix, List<String> suffixesToOverride) {
this.contents = contents;
this.prefix = prefix;
this.prefixesToOverride = prefixesToOverride;
this.suffix = suffix;
this.suffixesToOverride = suffixesToOverride;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
FilteredDynamicContext filteredDynamicContext = new FilteredDynamicContext(context);
boolean result = contents.apply(filteredDynamicContext);
filteredDynamicContext.applyAll();
return result;
}
private static List<String> parseOverrides(String overrides) {
if (overrides != null) {
final StringTokenizer parser = new StringTokenizer(overrides, "|", false);
final List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(parser.countTokens());
while (parser.hasMoreTokens()) {
list.add(parser.nextToken().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
}
return list;
}
return Collections.emptyList();
}
private class FilteredDynamicContext extends DynamicContext {
private DynamicContext delegate;
private boolean prefixApplied;
private boolean suffixApplied;
private StringBuilder sqlBuffer;
public FilteredDynamicContext(DynamicContext delegate) {
super(configuration, null);
this.delegate = delegate;
this.prefixApplied = false;
this.suffixApplied = false;
this.sqlBuffer = new StringBuilder();
}
public void applyAll() {
sqlBuffer = new StringBuilder(sqlBuffer.toString().trim());
String trimmedUppercaseSql = sqlBuffer.toString().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.length() > 0) {
applyPrefix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
applySuffix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
}
delegate.appendSql(sqlBuffer.toString());
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> getBindings() {
return delegate.getBindings();
}
@Override
public void bind(String name, Object value) {
delegate.bind(name, value);
}
@Override
public int getUniqueNumber() {
return delegate.getUniqueNumber();
}
@Override
public void appendSql(String sql) {
sqlBuffer.append(sql);
}
@Override
public String getSql() {
return delegate.getSql();
}
private void applyPrefix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!prefixApplied) {
prefixApplied = true;
if (prefixesToOverride != null) {
for (String toRemove : prefixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.startsWith(toRemove)) {
sql.delete(0, toRemove.trim().length());
break;
}
}
}
if (prefix != null) {
sql.insert(0, " ");
sql.insert(0, prefix);
}
}
}
private void applySuffix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!suffixApplied) {
suffixApplied = true;
if (suffixesToOverride != null) {
for (String toRemove : suffixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove) || trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove.trim())) {
int start = sql.length() - toRemove.trim().length();
int end = sql.length();
sql.delete(start, end);
break;
}
}
}
if (suffix != null) {
sql.append(" ");
sql.append(suffix);
}
}
}
}
}
2.9 模板方法模式
模板类定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤。
我们看看Mybatis框架中的末班方法模式的应用
这里用BaseExecutor类中的模板方法来说明一下, BaseExecutor方法中定义了SQL的查询和修改的模板方法, 并且在其他当前类中进行了调用, 但是BaseExecutor中没有进行实现,


这些方法都是通过子类来子类来进行实现的。

子类中对模版方法进行实现
 这些子类跟我们SQL语句类型也是相关的。 有可能只是简单查询, 有可能是批量处理操作, 有可能是可重复使用的操作, 这里我们可以通过模板方法结合策略模式来实现不同的处理逻辑对应处理不同的业务请求类型来实现应用的拓展。设计模式需要不断的coding和实战中记性巩固和加深理解, 不能为了设计而设计,合适的才是最好的, 要多多实战,多多总结才能逐渐掌握。
这些子类跟我们SQL语句类型也是相关的。 有可能只是简单查询, 有可能是批量处理操作, 有可能是可重复使用的操作, 这里我们可以通过模板方法结合策略模式来实现不同的处理逻辑对应处理不同的业务请求类型来实现应用的拓展。设计模式需要不断的coding和实战中记性巩固和加深理解, 不能为了设计而设计,合适的才是最好的, 要多多实战,多多总结才能逐渐掌握。