初识SpringSecurity
SpringSecurity
Spring Security 基于 Spring 框架,提供了一套 Web 应用安全性的完整解决方案。
在用户认证方面,Spring Security 框架支持主流的认证方式,包括 HTTP 基本认证、HTTP 表单验证、HTTP 摘要认证、OpenID 和 LDAP 等。在用户授权方面,Spring Security 提供了基于角色的访问控制和访问控制列表(Access Control List,ACL),可以对应用中的领域对象进行细粒度的控制。
初识SpringSecurity
Spring Security 是针对Spring项目的安全框架,也是Spring Boot底层安全模块默认的技术选型,他可以实现强大的Web安全控制,对于安全控制,我们仅需要引入 spring-boot-starter-security 模块,进行少量的配置,即可实现强大的安全管理!
几个重要的类:
| 类 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter | 自定义Security策略 |
| AuthenticationManagerBuilder | 自定义认证策略 |
| @EnableWebSecurity | 开启WebSecurity模式 |
Spring Security的两个主要目标是 “认证” 和 “授权”(访问控制)。
① “认证”(Authentication)
身份验证是关于验证您的凭据,如用户名/用户ID和密码,以验证您的身份。
身份验证通常通过用户名和密码完成,有时与身份验证因素结合使用。
② “授权” (Authorization)
授权发生在系统成功验证您的身份后,最终会授予您访问资源(如信息,文件,数据库,资金,位置,几乎任何内容)的完全权限。
这个概念是通用的,而不是只在Spring Security 中存在。
环境的搭建
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId>
dependency>
开发文档
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/reference/html5/#jc-httpsecurity
用户的认证与授权
1、.antMatchers(“url”).authenticated()表示有权限才能访问该URL;
2、.antMatchers(“url”).permitAll()表示允许所有人访问,不需要验证;
3、.anyRequest().permitAll()表示除上面外的全部请求允许所有人访问,不需要验证;
4、httpSecurity是链式访问,像过滤器一样从上到下访问,匹配不到前面的才会去匹配后面的URL
/**
* @author acoffee
* @create 2021-09-14 19:26
*/
//AOP(体现了面向切面):我们没有没有去该原来的代码,就加上了拦截
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//授权
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页所有人都可以访问,功能页只有对应有权限的人才能访问
//请求:请求授权的规则
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
}
}
现在我们再进Level页面就会报403的错误
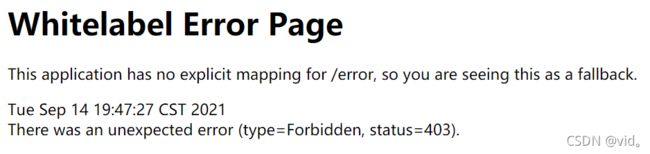
但是一般如果没有权限的话我们会让其跳到登录页面,如下:
//AOP(体现了面向切面):我们没有没有去该原来的代码,就加上了拦截
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//授权
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页所有人都可以访问,功能页只有对应有权限的人才能访问
//请求:请求授权的规则
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//没有权限我们让其跳向登录页面,仅下面这一行代码就能实现
http.formLogin();
}
}
我们接下来模拟一个数据库,使用它的认证功能:
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页所有人都可以访问,功能页只有对应有权限的人才能访问
//请求:请求授权的规则
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//没有权限我们让其跳向登录页面,仅下面这一行代码就能实现
http.formLogin();
}
//认证功能
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//我们这里是模拟数据库:添加了三个用户
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("acoffee").password("123456").roles("vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("root").password("123456").roles("vip1","vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("guest").password("123456").roles("vip1");
}
}
当我们被拦截过后,我们直接登录
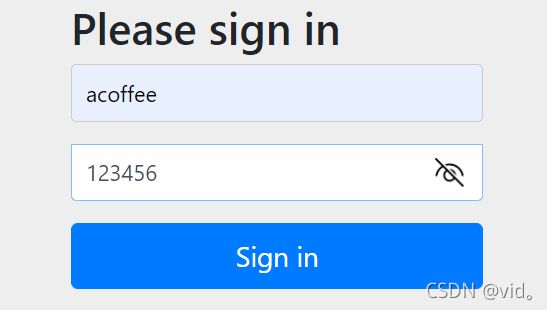
然后他会报500错误,控制台会报以下异常:java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null"
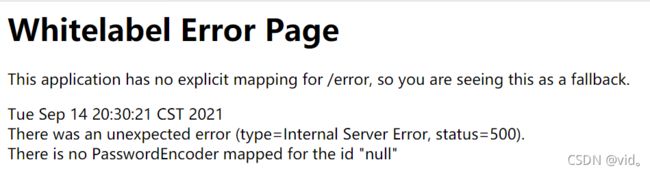
这是什么原因呢?
这种写法在springboot2.1.x 可以直接使用,上面那个异常的意思就是说我们的密码现在是明文,没有加密,所以需要我们对密码进行加密。springSecurtiy 5.0+之后 新增了很多的加密方法。
//AOP(体现了面向切面):我们没有没有去该原来的代码,就实现了权限分级
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//链式编程
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页所有人都可以访问,功能页只有对应有权限的人才能访问
//请求:请求授权的规则
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//没有权限我们让其跳向登录页面,仅下面这一行代码就能实现
http.formLogin();
}
//认证:springboot2.1.x 可以直接使用
//密码编码:passwordEncoder
//在springSecurtiy 5.0+之后 新增了很多的加密方法。
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//我们这里是模拟数据库:添加了三个用户
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("acoffee").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("root").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1","vip2","vip3")
.and()
.withUser("guest").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("vip1");
}
}
index的部分代码:
<div class="ui segment" id="index-header-nav" th:fragment="nav-menu">
<div class="ui secondary menu">
<a class="item" th:href="@{/index}">首页a>
<div class="right menu">
<div sec:authorize="!isAuthenticated()">
<a class="item" th:href="@{/toLogin}">
<i class="address card icon">i> 登录
a>
div>
<div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()">
<a class="item">
用户名: <span sec:authentication="name">span>
a>
div>
<div sec:authorize="isAuthenticated()">
<a class="item" th:href="@{/logout}">
<i class="sign-out icon">i> 注销
a>
div>
div>
div>
div>
通过 SecurityConfig类: controller: login.html的登录表单 controller: 登录表单:
<div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip1')">
<div class="ui raised segment">
<div class="ui">
<div class="content">
<h5 class="content">Level 1h5>
<hr>
<div><a th:href="@{/level1/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-1-1a>div>
<div><a th:href="@{/level1/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-1-2a>div>
<div><a th:href="@{/level1/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-1-3a>div>
div>
div>
div>
div>
<div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip2')">
<div class="ui raised segment">
<div class="ui">
<div class="content">
<h5 class="content">Level 2h5>
<hr>
<div><a th:href="@{/level2/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-2-1a>div>
<div><a th:href="@{/level2/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-2-2a>div>
<div><a th:href="@{/level2/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-2-3a>div>
div>
div>
div>
div>
<div class="column" sec:authorize="hasRole('vip3')">
<div class="ui raised segment">
<div class="ui">
<div class="content">
<h5 class="content">Level 3h5>
<hr>
<div><a th:href="@{/level3/1}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-3-1a>div>
<div><a th:href="@{/level3/2}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-3-2a>div>
<div><a th:href="@{/level3/3}"><i class="bullhorn icon">i> Level-3-3a>div>
div>
div>
div>
div>
定制登录页、注销以及 记住我 功能
//AOP(体现了面向切面):我们没有没有去该原来的代码,就实现了权限分级
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
//首页所有人都可以访问,功能页只有对应有权限的人才能访问
//请求:请求授权的规则
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/level1/**").hasRole("vip1")
.antMatchers("/level2/**").hasRole("vip2")
.antMatchers("/level3/**").hasRole("vip3");
//没有权限我们让其跳向登录页面,仅下面这一行代码就能实现
//如果name不一致,我们也可以指定
//http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin").usernameParameter("user").passwordParameter("pwd").loginProcessingUrl("/login");
http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin");
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能,登录失败可能存在的原因
//开启注销功能
http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
//开启记住我功能
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
}
@Controller
public class RouterController {
@RequestMapping({"/", "/index"})
public String index() {
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin() {
return "/login";
}
<div class="ui form">
<form th:action="@{/toLogin}" method="post">
<div class="field">
<label>Usernamelabel>
<div class="ui left icon input">
<input type="text" placeholder="Username" name="username">
<i class="user icon">i>
div>
div>
<div class="field">
<label>Passwordlabel>
<div class="ui left icon input">
<input type="password" name="password">
<i class="lock icon">i>
div>
div>
<div class="field">
<input type="checkbox" name="remember">记住我
div>
<input type="submit" class="ui blue submit button"/>
form>
div>
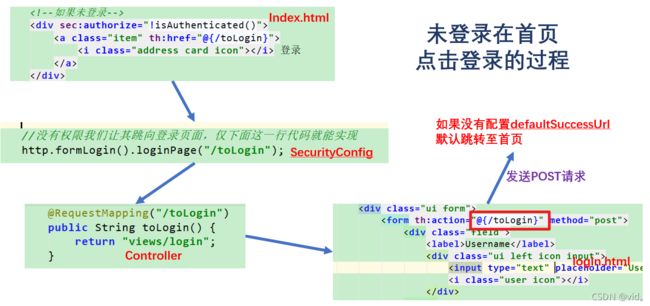
当然上面Config类是简单写法,下面我们展示SecurityConfig较为全面的写法,我们只展示关键部分,主要是展示一些接口的功能: //没有权限我们让其跳向登录页面,仅下面这一行代码就能实现
//如果name不一致,我们也可以指定
//http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin").usernameParameter("user").passwordParameter("pwd").loginProcessingUrl("/login");
http.formLogin() //自定义自己编写的登录页面
.loginPage("/login.html") //登录页面设置,直接设置登录页面的路径
.loginProcessingUrl("/login") //登录访问路径
.defaultSuccessUrl("/LoginSuc") //登录成功后,跳转路径
.and().authorizeRequests()
//设置可以直接访问的路径,不需要权限,这里就是访问登录也不需要权限
.antMatchers("/toLogin").permitAll().anyRequest().authenticated();
http.csrf().disable();//关闭csrf功能,登录失败可能存在的原因
//开启注销功能
http.logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/");
//开启记住我功能
http.rememberMe().rememberMeParameter("remember");
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin() {
return "/login";
}
@RequestMapping("/LoginSuc")
public String toLogin1() {
return "index";
}
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div class="field">
<label>Usernamelabel>
<div class="ui left icon input">
<input type="text" placeholder="Username" name="username">
<i class="user icon">i>
div>
div>
