springboot整合线程池
最近项目中做到一个关于批量发短信的业务,如果用户量特别大的话,不能使用单线程去发短信,只能尝试着使用多任务来完成!我们的项目使用到了方式二,即Future的方案
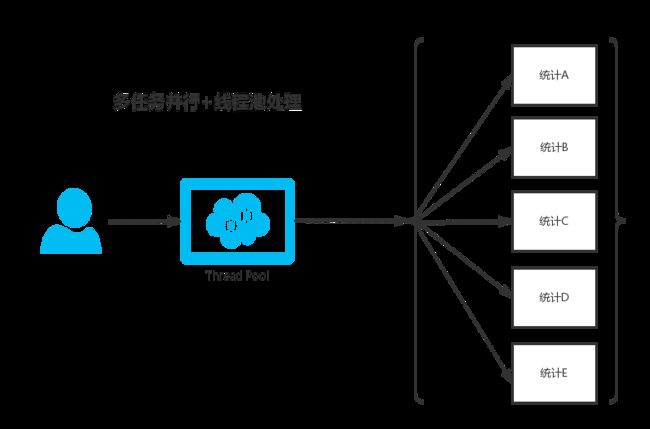
Java 线程池
Java通过Executors提供四种线程池,分别为:
newCachedThreadPool创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。
newFixedThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在队列中等待。
newScheduledThreadPool 创建一个定长线程池,支持定时及周期性任务执行。
newSingleThreadExecutor 创建一个单线程化的线程池,它只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务按照指定顺序(FIFO, LIFO, 优先级)执行。
优点
重用存在的线程,减少对象创建、消亡的开销,性能佳。
可有效控制最大并发线程数,提高系统资源的使用率,同时避免过多资源竞争,避免堵塞。
提供定时执行、定期执行、单线程、并发数控制等功能。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
方式一(CountDownLatch)
public class StatsDemo {
final static SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
final static String startTime = sdf.format(new Date());
/**
* IO密集型任务 = 一般为2*CPU核心数(常出现于线程中:数据库数据交互、文件上传下载、网络数据传输等等)
* CPU密集型任务 = 一般为CPU核心数+1(常出现于线程中:复杂算法)
* 混合型任务 = 视机器配置和复杂度自测而定
*/
private static int corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
/**
* public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,int maximumPoolSize,long keepAliveTime,
* TimeUnit unit,BlockingQueue workQueue)
* corePoolSize用于指定核心线程数量
* maximumPoolSize指定最大线程数
* keepAliveTime和TimeUnit指定线程空闲后的最大存活时间
* workQueue则是线程池的缓冲队列,还未执行的线程会在队列中等待
* 监控队列长度,确保队列有界
* 不当的线程池大小会使得处理速度变慢,稳定性下降,并且导致内存泄露。如果配置的线程过少,则队列会持续变大,消耗过多内存。
* 而过多的线程又会 由于频繁的上下文切换导致整个系统的速度变缓——殊途而同归。队列的长度至关重要,它必须得是有界的,这样如果线程池不堪重负了它可以暂时拒绝掉新的请求。
* ExecutorService 默认的实现是一个无界的 LinkedBlockingQueue。
*/
private static ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, corePoolSize+1, 10l, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue(1000));
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5);
//使用execute方法
executor.execute(new Stats("任务A", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务B", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务C", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务D", 1000, latch));
executor.execute(new Stats("任务E", 1000, latch));
latch.await();// 等待所有人任务结束
System.out.println("所有的统计任务执行完成:" + sdf.format(new Date()));
}
static class Stats implements Runnable {
String statsName;
int runTime;
CountDownLatch latch;
public Stats(String statsName, int runTime, CountDownLatch latch) {
this.statsName = statsName;
this.runTime = runTime;
this.latch = latch;
}
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(statsName+ " do stats begin at "+ startTime);
//模拟任务执行时间
Thread.sleep(runTime);
System.out.println(statsName + " do stats complete at "+ sdf.format(new Date()));
latch.countDown();//单次任务结束,计数器减一
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
结果
方式二(Future)
重点是和springboot整合,采用注解bean方式生成ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
@Bean
//spring依赖包
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
@Configuration
public class GlobalConfig {
/**
* 默认线程池线程池
*
* @return Executor
*/
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor defaultThreadPool() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//核心线程数目
executor.setCorePoolSize(16);
//指定最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(64);
//队列中最大的数目
executor.setQueueCapacity(16);
//线程名称前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("defaultThreadPool_");
//rejection-policy:当pool已经达到max size的时候,如何处理新任务
//CALLER_RUNS:不在新线程中执行任务,而是由调用者所在的线程来执行
//对拒绝task的处理策略
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//线程空闲后的最大存活时间
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
//加载
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
使用
//通过注解引入配置
@Resource(name = "defaultThreadPool")
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor;
- 1
- 2
- 3
//使用Future方式执行多任务
//生成一个集合
List futures = new ArrayList<>();
//获取后台全部有效运营人员的集合
List adminUserDOList = adminManagerService.GetUserToSentMsg(null);
for (AdminUserMsgResponse response : adminUserDOList) {
//并发处理
if (response.getMobile() != null) {
Future future = executor.submit(() -> {
//发送短信
mobileMessageFacade.sendCustomerMessage(response.getMobile(), msgConfigById.getContent());
});
futures.add(future);
}
}
//查询任务执行的结果
for (Future future : futureList) {
while (true) {//CPU高速轮询:每个future都并发轮循,判断完成状态然后获取结果,这一行,是本实现方案的精髓所在。即有10个future在高速轮询,完成一个future的获取结果,就关闭一个轮询
if (future.isDone()&& !future.isCancelled()) {//获取future成功完成状态,如果想要限制每个任务的超时时间,取消本行的状态判断+future.get(1000*1, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)+catch超时异常使用即可。
Integer i = future.get();//获取结果
System.out.println("任务i="+i+"获取完成!"+new Date());
list.add(i);
break;//当前future获取结果完毕,跳出while
} else {
Thread.sleep(1);//每次轮询休息1毫秒(CPU纳秒级),避免CPU高速轮循耗空CPU---》新手别忘记这个
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31