日撸 Java 三百行day11-13
文章目录
- 说明
- day11-day12 顺序表
-
- 1.面向过程面向对象区别
- 2.代码
-
- 2.1 面向过程
- 2.2 面向对象
- day13 链表
-
- 1.成员内部类
- 2.链表的插入删除
- 3.代码
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
day11-day12 顺序表
1.面向过程面向对象区别
面向过程更关注的是过程(函数),每个函数会完成特定的功能,函数可以通过传参数来控制数据。
面向对象更关注的是对象,每一个对象都有自己的属性和方法,相应的数据和方法都封装在对象内部,一般是通过方法去访问对象内部的数据。
2.代码
正如文章所说,在面向对象的设计中,用对象来存储数据及其上的操作。我们现实生活中的所有事物都可以被看做是对象。在今天写的这个例子中,首先,对于顺序表的操作,我们采用面向过程的思想和面向对象的区别
2.1 面向过程
(参考了PTA中的数据结构与算法题目集):
- 1.对顺序表的构造是通过结构体的形式来声明的
- 2.创建一个空的线性表
- 3 对顺序表的操作就调不同的方法即可
#include
#include
#define MAXSIZE 5
typedef char element;
typedef struct LNode *List;
struct LNode {
element Data[MAXSIZE];
int Last; /* 线性表长度*/
};
//创建了一个空的线性表
List MakeEmpty(){
List list = (List)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
list->Last= -1;
return list;
}
//返回线性表中X的位置。若找不到则返回ERROR;
Position Find( List L, ElementType X ){
for(int i = 0; i <= L->Last; i++){
if(L->Data[i] == X){
return i;
}
}
return ERROR;
}
//将X插入在位置P并返回true。若空间已满,则打印“FULL”并返回false;如果参数P指向非法位置,则打印“ILLEGAL POSITION”并返回false;
bool Insert( List L, ElementType X, Position P ){
if(L->Last+1>= MAXSIZE){
printf("FULL");
return false;
}
if(P<0 || P>L->Last + 1 || P>=MAXSIZE){
printf("ILLEGAL POSITION");
return false;
}
for(int i = L->Last; i >= P; i--){
L->Data[i+1] = L->Data[i];
}
L->Data[P]= X;
L->Last++;
//printf("%d-%d\n", L->Last, MAXSIZE);
return true;
}
//将位置P的元素删除并返回true。若参数P指向非法位置,则打印“POSITION P EMPTY”(其中P是参数值)并返回false
bool Delete( List L, Position P ){
if(P<0 || P>L->Last){
printf("POSITION %d EMPTY", P);
return false;
}
for(int i = P; i < L->Last; i++){
L->Data[i] = L->Data[i+1];
}
L->Last--;
return true;
}
int main()
{
List L;
ElementType X;
Position P;
int N;
L = MakeEmpty();
scanf("%d", &N);
while ( N-- ) {
scanf("%d", &X);
if ( Insert(L, X, 0)==false )
printf(" Insertion Error: %d is not in.\n", X);
}
scanf("%d", &N);
while ( N-- ) {
scanf("%d", &X);
P = Find(L, X);
if ( P == ERROR )
printf("Finding Error: %d is not in.\n", X);
else
printf("%d is at position %d.\n", X, P);
}
scanf("%d", &N);
while ( N-- ) {
scanf("%d", &P);
if ( Delete(L, P)==false )
printf(" Deletion Error.\n");
if ( Insert(L, 0, P)==false )
printf(" Insertion Error: 0 is not in.\n");
}
return 0;
}
2.2 面向对象
大部分顺序表都会有一个数组和相应数组的长度,也都会初始化顺序表;我们则可以给它抽象为一个类,即顺序表类;在这个类中,包含的属性即数组和数组长度(可能根据不同的情况可能会有不同,我们可以通过继承等来扩展这个类),也应该有初始化数组的方法,以及每个数组可能会用到的方法:如将数组转化为字符串输出,插入,删除,查找以及重置顺序表等。当我们想要使用顺便表时,就可以用new实例化一个顺序表对象,而生成的实例化对象也就拥有了这个顺表类中所对应的属性已经方法等。所以面向
-
类
如下面的例子 SequentialList 就是一个抽象出来的一个顺序表类 -
构造函数作用
构造函数名与类名一样,无返回值,可多个。如果类中没有构造函数,其实在未定义构造函数时会有一个缺省无参构造函数。构造函数最大的作用是:在创建对象时(new)初始化对象 -
对象
通过new来实例化对象。
通SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray); //带参数初始化对象
SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(); //不带参数的初始化对象 -
Object类
Object类是所有类的超类(一般我们创建的类都是隐式继承),所有类都可以使用Object类中的成员方法和变量,也可以重写其中的方法,例如今天的代码就重写了toString.若不重写toString方法,则会返回类名+hash值
package datastructure.list;
public class SequentialList {
/**
* The maximal length of the list. It is a constant.
*/
public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
/**
* The actual length not exceeding MAX_LENGTH. Attention: length is not only the member variable of Sequential list,
* but also the member variable of Array. In fact, a name can be the member variable of different classes.
*/
int length;
/**
* The data stored in an array.
*/
int[] data;
/**
* Construct an empty sequential list.
*/
public SequentialList(){
length = 0;
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
}
/**
* Construct a sequential list using an array.
* @param paraArray The given array. Its length should not exceed MAX_LENGTH. For simplicity now we do not check it.
*/
public SequentialList(int[] paraArray){
data = new int[MAX_LENGTH];
length = paraArray.length;
for (int i = 0; i < paraArray.length; i++) {
data[i] = paraArray[i];
}
}
/**
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
* @return
*/
public String toString(){
String resultString = "";
if (length == 0){
return "empty";
}
for (int i = 0; i length){
System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of bounds.");
return false;
}
for (int i = length; i > paraPosition; i--){
data[i] = data[i-1];
}
data[paraPosition] = paraValue;
length++;
return true;
}
/**
* Delete a value at a position.
* @param paraPosition paraPosition The given position.
* @return Success or not.
*/
public boolean delete(int paraPosition){
if (paraPosition < 0 || paraPosition >= length){
System.out.println("The position " + paraPosition + " is out of bounds.");
return false;
}
for (int i = paraPosition; i < length-1; i++){
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
length--;
return true;
}
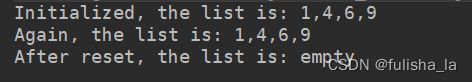
public static void main(String args[]) {
/*int[] tempArray = { 1, 4, 6, 9 };
SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray);
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());
System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempFirstList.reset();
System.out.println("After reset, the list is: " + tempFirstList);*/
int[] tempArray = { 1, 4, 6, 9 };
SequentialList tempFirstList = new SequentialList(tempArray);
System.out.println("After initialization, the list is: " + tempFirstList.toString());
System.out.println("Again, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
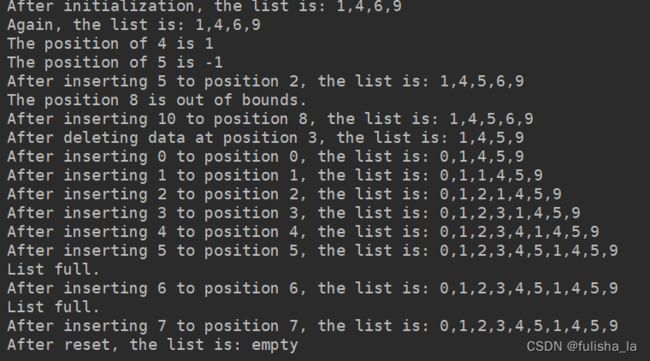
int tempValue = 4;
int tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexOf(tempValue);
System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);
tempValue = 5;
tempPosition = tempFirstList.indexOf(tempValue);
System.out.println("The position of " + tempValue + " is " + tempPosition);
tempPosition = 2;
tempValue = 5;
tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);
System.out.println(
"After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempPosition = 8;
tempValue = 10;
tempFirstList.insert(tempPosition, tempValue);
System.out.println(
"After inserting " + tempValue + " to position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
tempPosition = 3;
tempFirstList.delete(tempPosition);
System.out.println("After deleting data at position " + tempPosition + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
tempFirstList.insert(i, i);
System.out.println("After inserting " + i + " to position " + i + ", the list is: " + tempFirstList);
} // Of for i
tempFirstList.reset();
System.out.println("After reset, the list is: " + tempFirstList);
}
}
day13 链表
1.成员内部类
在c语言中,对链表的数据结构是用结构体来表示,在java中使用内部类来表示链表结构体,成员内部类是定义在另一个类的内部的类,可以访问外部类的成员和方法,包括私有成员和方法。如文章中的Node类可以访问外部类中所有的成员变量和成员方法。
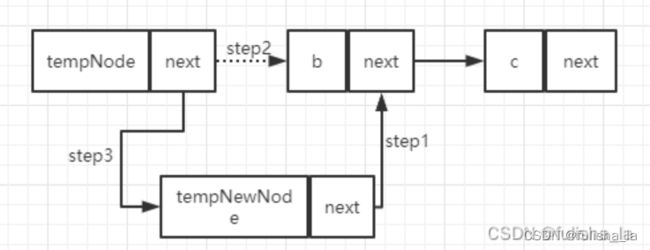
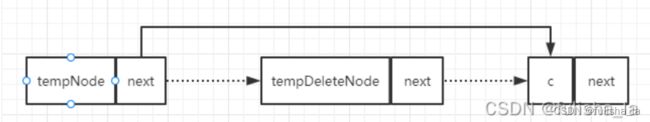
2.链表的插入删除
3.代码
在c中,对链表结构的定义
typedef struct LNode *PtrToLNode;
struct LNode {
ElementType Data;
PtrToLNode Next;
};
typedef PtrToLNode Position;
typedef PtrToLNode List;
在java中
package datastructure.list;
import sun.applet.Main;
import java.util.UUID;
public class LinkedList {
class Node{
int data;
Node next;
/**
* The constructor
* @param paraValue The data.
*/
public Node(int paraValue){
data = paraValue;
next = null;
}
}
Node header;
/**
* Construct an empty linked list.
*/
public LinkedList(){
header = new Node(0);
}
/**
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
* @return
*/
public String toString(){
String resultString = "";
if (header.next == null){
return "empty";
}
Node tempNode = header.next;
while (tempNode != null){
resultString += tempNode.data + ",";
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
return resultString;
}
/**
* Reset to empty. Free the space through garbage collection.
*/
public void reset() {
header.next = null;
}
/**
* Locate the given value. If it appears in multiple positions, simply return the first one.
* @param paraValue The given value.
* @return The position. -1 for not found.
*/
public int locate(int paraValue){
int tempPosition = -1;
Node tempNode = header.next;
int tempCurrentPosition = 0;
while (tempNode != null){
if (tempNode.data == paraValue){
tempPosition = tempCurrentPosition;
break;
}
tempNode = tempNode.next;
tempCurrentPosition++;
}
return tempCurrentPosition;
}
/**
* Insert a value to a position. If the list is already full, do nothing.
* @param paraPosition The given position.
* @param paraValue The given value.
* @return Success or not.
*/
public boolean insert(int paraPosition, int paraValue){
Node tempNode = header;
Node tempNewNode;
//find a preNode
for (int i = 0; i