最短路径三大算法——2,迪杰斯特拉算法dijkstra (复杂度O(n^2))
目前已经更新:
1,弗洛伊德算法floyd(复杂度O(n^3))
2,迪杰斯特拉算法dijkstra (复杂度O(最坏n^2))
3,SPFA算法(复杂度O(n*m))
当然,最短路径有通用的bfs,dfs大神,但是我们这里特别介绍floyd,dijkstra还有spfa,本系列分为三篇
思想
dijkstra本质是贪心,即要求我走的每一步是局部最优就好,什么叫局部最优——我每次都去离我(起点)最近的点,然后更新其他点到起点的距离,当然,原来走过的点要标记一下,不能回去
为什么可以这么贪心呢:当我们每次选择dis[i]最小的点时,我们保证,因为其他点x离起点较远,即使通过i点可以缩小到起点的距离,那么仍然dis[x]>dis[i]+arr[i][x]>dis[i],即更新前后在所有未标记的点中dis[i]离起点更近成立,不会有后效性。
但是dijkstra也有缺点,无法处理负值点(需要用到spfa),但是对于全为正边,他无疑是相当优秀的
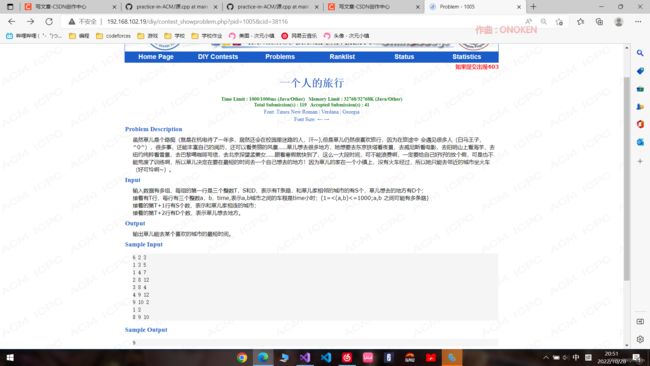
HDU一道例题
多个起点,多个终点,但是不用害怕,聪明的你一定会联想到,我们可以设置一个超级起点(各个起点到他距离为0)和一个超级终点(各个终点到他距离为0),这样只需要跑一遍dijkstra
我们每次都求每个更新后的点中到达起点最近的点,一直到终点,这样我们最后得到的就是终点到起点最近
ACcode
#include
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 1100;
struct city
{
int cit, p;//cit表示指向的城市,p表示路程
};
vectorarr[N];
bool vis[N];//标记是否访问过
ll dis[N];//dis[x]表示x到超级起点距离
void dijkstra()
{
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
priority_queue < pair, vector< pair >, greater>>q;
dis[0] = 0;
q.push({0, 0});//第一个是距离(用于排序构建最小堆,第二个是城市
while (!q.empty())
{
int tmp = q.top().second;//存入城市
q.pop();
if (vis[tmp])continue;
vis[tmp] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)arr[tmp].size(); ++i)//只对跟我邻接的边操作,其余操作也是无意义
{
if (dis[arr[tmp][i].cit] > dis[tmp] + arr[tmp][i].p)
{
dis[arr[tmp][i].cit] = dis[tmp] + arr[tmp][i].p;
if (!vis[arr[tmp][i].cit])//避免重复标记
q.push({dis[arr[tmp][i].cit], arr[tmp][i].cit});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t, s, d;
while (cin >> t >> s >> d)
{
int maxn = -1;
int a, b, time;
for (int i = 1; i <= t; ++i)
{
cin >> a >> b >> time;
maxn = max(maxn, max(a, b));
arr[a].push_back({b, time});
arr[b].push_back({a, time});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= s; ++i)
{
cin >> a;
arr[0].push_back({a, 0});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= d; ++i)
{
cin >> a;
arr[a].push_back({maxn + 1, 0});
}
dijkstra();
cout << dis[maxn + 1] << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <= maxn + 1; ++i)arr[i].clear(); //多组数据不要忘记清空数组
}
} 聪明的你可能会想,为什么我一定要跑最坏复杂度呢,对啊,所以明显可以用优先队列来优化(这样每次筛选最小也比上面方法快)
优先队列的使用可以参考优先队列priority_queue
#include
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 1100;
struct city
{
int cit, p;//cit表示指向的城市,p表示路程
};
vectorarr[N];
bool vis[N];//标记是否访问过
ll dis[N];//dis[x]表示x到超级起点距离
void dijkstra()
{
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
memset(dis, 0x3f, sizeof(dis));
priority_queue < pair, vector< pair >, greater>>q;
dis[0] = 0;
q.push({dis[0], 0});//第一个是距离(用于排序构建最小堆,第二个是城市
while (!q.empty())
{
int tmp = q.top().second;//存入城市
q.pop();
if (vis[tmp])continue;
vis[tmp] = 1;//我们在进来是标记访问,而不是在更新点时标记访问,因为我们有可能在tmp点还未进入while时,被更新了几次,那么我们必须一直vis[tmp]=0才可以存入这些更新的值
//因为优先队列保证同一个点,在多个更新的值中,肯定是离起点最近的最先访问,所以当他进来时,我们才标记访问,后续那些点进来,也会因为已经进来过一次直接跳过
for (int i = 0; i < (int)arr[tmp].size(); ++i)//只对跟我邻接的边操作,其余操作也是无意义
{
if (dis[arr[tmp][i].cit] > dis[tmp] + arr[tmp][i].p)
{
dis[arr[tmp][i].cit] = dis[tmp] + arr[tmp][i].p;
if (!vis[arr[tmp][i].cit])//避免重复标记
q.push({dis[arr[tmp][i].cit], arr[tmp][i].cit});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int t, s, d;
while (cin >> t >> s >> d)
{
int maxn = -1;
int a, b, time;
for (int i = 1; i <= t; ++i)
{
cin >> a >> b >> time;
maxn = max(maxn, max(a, b));
arr[a].push_back({b, time});
arr[b].push_back({a, time});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= s; ++i)
{
cin >> a;
arr[0].push_back({a, 0});
}
for (int i = 1; i <= d; ++i)
{
cin >> a;
arr[a].push_back({maxn + 1, 0});
}
dijkstra();
cout << dis[maxn + 1] << endl;
for (int i = 0; i <= maxn + 1; ++i)arr[i].clear(); //多组数据不要忘记清空数组
}
}