Three.js-材质纹理详解
目录
1.基础网格材质(MeshBasicMaterial)
1.1 构造函数(Constructor)
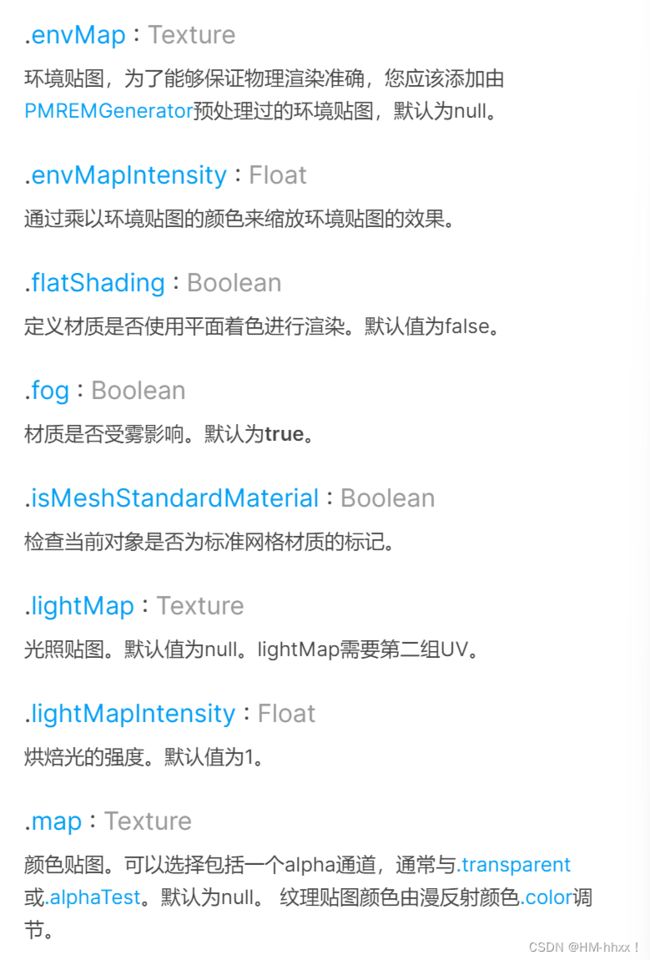
1.2 属性(Properties)
1.3 纹理加载案例
1.4 纹理常用属性
1.5 透明纹理
1.6 AO环境遮挡贴图
2.标准网格材质(MeshStandardMaterial)
2.1 构造函数(Constructor)
2.2 属性(Properties)
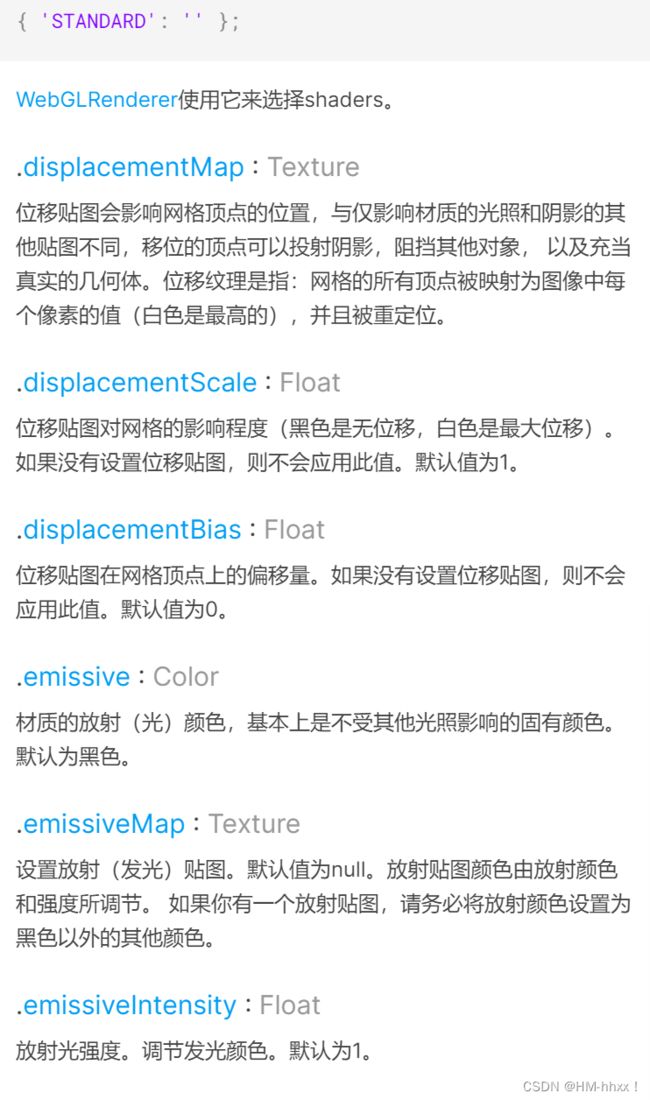
2.3 位移贴图
2.4 粗糙度与粗糙度贴图
2.5 金属贴图
2.6 法线贴图
1.基础网格材质(MeshBasicMaterial)
一个以简单着色(平面或线框)方式来绘制几何体的材质。这种材质不受光照的影响。
1.1 构造函数(Constructor)
MeshBasicMaterial( parameters : Object )
parameters - (可选)用于定义材质外观的对象,具有一个或多个属性。材质的任何属性都可以从此处传入(包括从Material继承的任何属性)。
属性color例外,其可以作为十六进制字符串传递,默认情况下为 0xffffff(白色),内部调用Color.set(color)。
1.2 属性(Properties)
共有属性请参见其基类Material。
 1.3 纹理加载案例:
1.3 纹理加载案例:
import * as THREE from "three";
// 导入轨道控制器
import { OrbitControls } from "three/examples/jsm/controls/OrbitControls";
// 目标:基础材质与纹理
// 1、创建场景
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
// 2、创建相机
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(
75,
window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,
0.1,
1000
);
// 设置相机位置
camera.position.set(0, 0, 10);
scene.add(camera);
// 导入纹理
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
const doorColorTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/color.jpg");
// 添加物体
const cubeGeometry = new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(1, 1, 1);
// 材质设置
const basicMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: "#ffff00",
map: doorColorTexture,//.map颜色贴图
});
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry, basicMaterial);
scene.add(cube);
// 初始化渲染器
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
// 设置渲染的尺寸大小
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
// 将webgl渲染的canvas内容添加到body
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement);
// 创建轨道控制器
const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement);
// 设置控制器阻尼,让控制器更有真实效果,必须在动画循环里调用.update()。
controls.enableDamping = true;
// 添加坐标轴辅助器
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(5);
scene.add(axesHelper);
function render() {
controls.update();
renderer.render(scene, camera);
// 渲染下一帧的时候就会调用render函数
requestAnimationFrame(render);
}
render();
// 监听画面变化,更新渲染画面
window.addEventListener("resize", () => {
// console.log("画面变化了");
// 更新摄像头
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
// 更新摄像机的投影矩阵
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
// 更新渲染器
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
// 设置渲染器的像素比
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio);
});
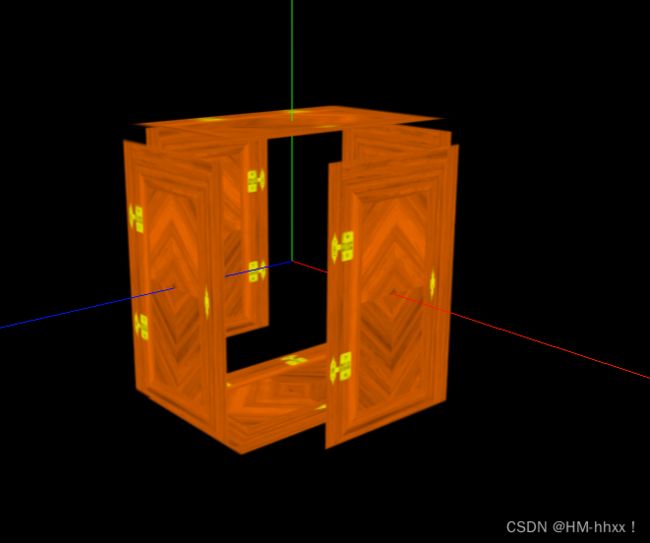
实现效果:
1.4 纹理常用属性
在纹理设置中,可以对其基本属性尽心设置,例如偏移量、旋转、重复等,其基于Textures类,具有Textures的属性。
1)设置纹理偏移
// 设置纹理偏移
// doorColorTexture.offset.x = 0.5;
// doorColorTexture.offset.y = 0.5;
// doorColorTexture.offset.set(0.5, 0.5);2)设置纹理旋转
// 纹理旋转
// 设置旋转的原点
// doorColorTexture.center.set(0.5, 0.5);
// // 旋转45deg
// doorColorTexture.rotation = Math.PI / 4;3)设置纹理重复
// 设置纹理的重复
// doorColorTexture.repeat.set(2, 3);
// // 设置纹理重复的模式
// doorColorTexture.wrapS = THREE.MirroredRepeatWrapping;
// doorColorTexture.wrapT = THREE.RepeatWrapping;THREE.LinearFilter效果:
THREE.NearestFilter效果
1.5 透明纹理
// 导入纹理
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
const doorColorTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/color.jpg");
const doorAplhaTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/alpha.jpg");
// 添加物体
const cubeGeometry = new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(1, 1, 1);
// 材质
const basicMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: "#ffff00",
map: doorColorTexture,
alphaMap: doorAplhaTexture,
transparent: true,
//opacity: 0.3,
// side: THREE.DoubleSide,//渲染两面
});
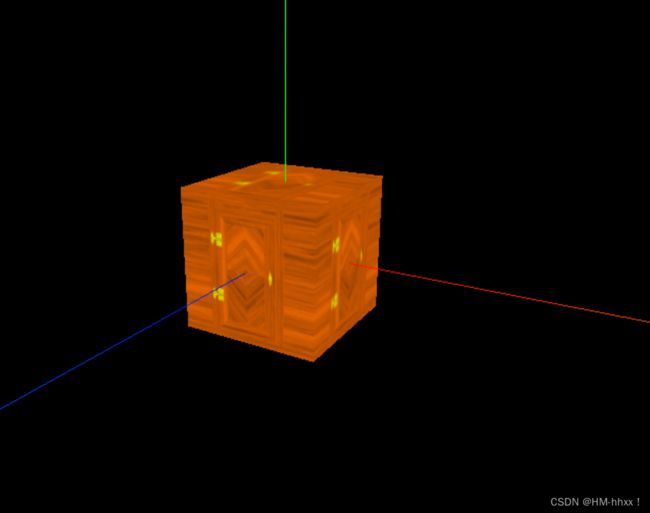
basicMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;//渲染两面
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry, basicMaterial);
scene.add(cube);实现效果:
1.6 AO环境遮挡贴图
// 导入纹理
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
const doorColorTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/color.jpg");//材质贴图
const doorAplhaTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/alpha.jpg");//透明度贴图
const doorAoTexture = textureLoader.load(
"./textures/door/ambientOcclusion.jpg"
);//环境遮挡贴图
// 添加物体
const cubeGeometry = new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(1, 1, 1);
// 材质
const basicMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: "#ffff00",
map: doorColorTexture,
alphaMap: doorAplhaTexture,
transparent: true,
aoMap: doorAoTexture,//AO环境遮挡贴图
aoMapIntensity: 1,//环境遮挡强度
});
basicMaterial.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry, basicMaterial);
scene.add(cube);
// 给cube添加第二组uv
cubeGeometry.setAttribute(
"uv2",
new THREE.BufferAttribute(cubeGeometry.attributes.uv.array, 2)
);
实现效果:
2.标准网格材质(MeshStandardMaterial)
一种基于物理的标准材质,使用Metallic-Roughness工作流程。
基于物理的渲染(PBR)最近已成为许多3D应用程序的标准,例如Unity, Unreal和 3D Studio Max。
这种方法与旧方法的不同之处在于,不使用近似值来表示光与表面的相互作用,而是使用物理上正确的模型。 我们的想法是,不是在特定照明下调整材质以使其看起来很好,而是可以创建一种材质,能够“正确”地应对所有光照场景。
在实践中,该材质提供了比MeshLambertMaterial 或MeshPhongMaterial 更精确和逼真的结果,代价是计算成本更高。
计算着色的方式与MeshPhongMaterial相同,都使用Phong着色模型, 这会计算每个像素的阴影(即在fragment shader, AKA pixel shader中), 与MeshLambertMaterial使用的Gouraud模型相比,该模型的结果更准确,但代价是牺牲一些性能。
请注意,为获得最佳效果,您在使用此材质时应始终指定environment map。
2.1构造函数(Constructor)
MeshStandardMaterial( parameters : Object )
parameters - (可选)用于定义材质外观的对象,具有一个或多个属性。 材质的任何属性都可以从此处传入(包括从Material继承的任何属性)。
属性color例外,其可以作为十六进制字符串传递,默认情况下为 0xffffff(白色),内部调用Color.set(color)。
2.2 属性(Properties)
2.3 位移贴图
一种按深度绘制几何体的材质。深度基于相机远近平面。白色最近,黑色最远。通过导入深度网格材质,可以对其色调的不同,赋予不同的高度,从而实现物体的凹凸起伏效果。位移贴图会影响网格顶点的位置,与仅影响材质的光照和阴影的其他贴图不同,移位的顶点可以投射阴影,阻挡其他对象, 以及充当真实的几何体。位移纹理是指:网格的所有顶点被映射为图像中每个像素的值(白色是最高的),并且被重定位。
// 导入纹理
const textureLoader = new THREE.TextureLoader();
const doorColorTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/color.jpg");
const doorAplhaTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/alpha.jpg");
const doorAoTexture = textureLoader.load(
"./textures/door/ambientOcclusion.jpg"
);
//导入置换贴图
const doorHeightTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/height.jpg");
// 添加物体
const cubeGeometry = new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(1, 1, 1, 100, 100, 100);
// 材质
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: "#ffff00",
map: doorColorTexture,
alphaMap: doorAplhaTexture,
transparent: true,
aoMap: doorAoTexture,
aoMapIntensity: 1,
displacementMap: doorHeightTexture,
displacementScale: 0.1,
// opacity: 0.3,
// side: THREE.DoubleSide,
});
console.log(material);
material.side = THREE.DoubleSide;
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry, material);
scene.add(cube);
// 给cube添加第二组uv
cubeGeometry.setAttribute(
"uv2",
new THREE.BufferAttribute(cubeGeometry.attributes.uv.array, 2)
);
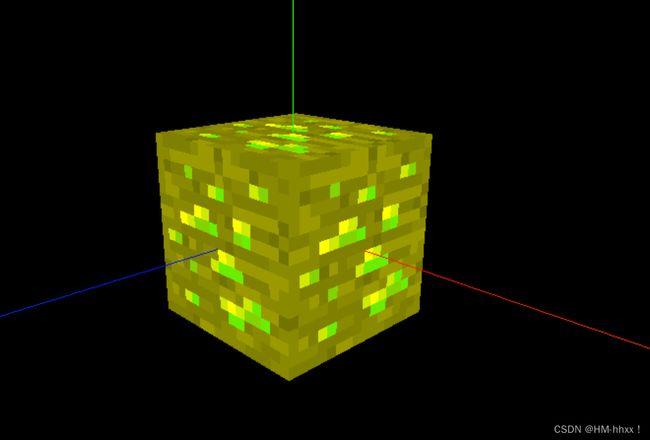
实现效果:
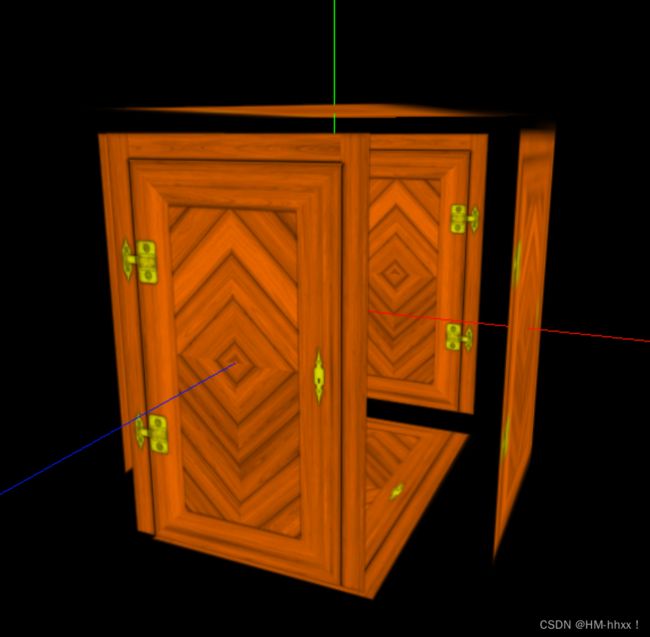
导入位移材质贴图后,会根据该贴图的灰度不同,设置各个部分的位移量,实现立体效果。
2.4 粗糙度与粗糙度贴图
该纹理的绿色通道用于改变材质的粗糙度。
// 导入粗糙度贴图
const roughnessTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/roughness.jpg");// 材质
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: "#ffff00",
map: doorColorTexture,
alphaMap: doorAplhaTexture,
transparent: true,
//AO遮挡材质
aoMap: doorAoTexture,
aoMapIntensity: 1,
//位移材质
displacementMap: doorHeightTexture,
displacementScale: 0.1,
//粗糙度材质
roughness: 1,
roughnessMap: roughnessTexture,
});实现效果:
导入粗糙度贴图后,可以改变该示例门的粗糙度,使其不产生镜面反射,会发生类似于木制的漫反射效果。
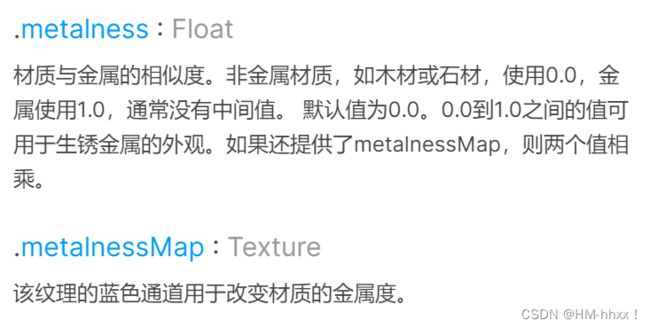
2.5 金属贴图
材质与金属的相似度。非金属材质,如木材或石材,使用0.0,金属使用1.0,通常没有中间值。 默认值为0.0。0.0到1.0之间的值可用于生锈金属的外观。如果还提供了metalnessMap,则两个值相乘。
示例:
// 导入金属贴图
const metalnessTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/metalness.jpg");
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: "#ffff00",
map: doorColorTexture,
alphaMap: doorAplhaTexture,
transparent: true,
//
aoMap: doorAoTexture,
aoMapIntensity: 1,
//
displacementMap: doorHeightTexture,
displacementScale: 0.1,
//粗糙度材质
roughness: 1,
roughnessMap: roughnessTexture,
//金属材质
metalness: 1,
metalnessMap: metalnessTexture,
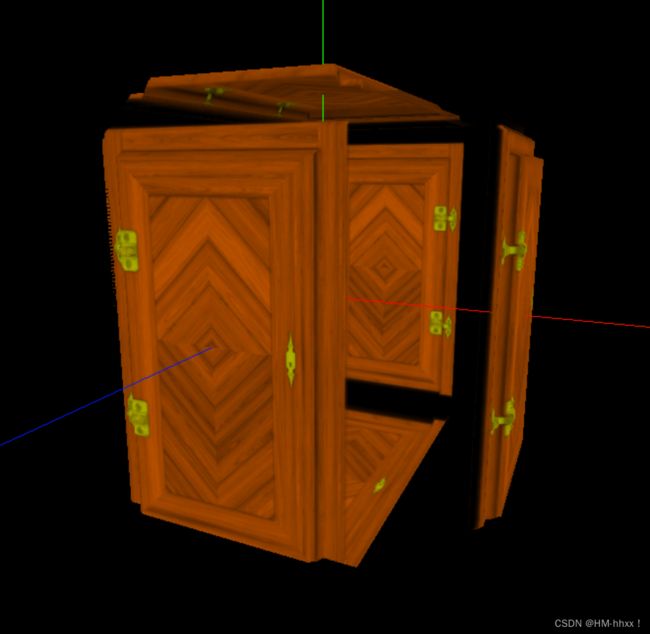
});实现效果:
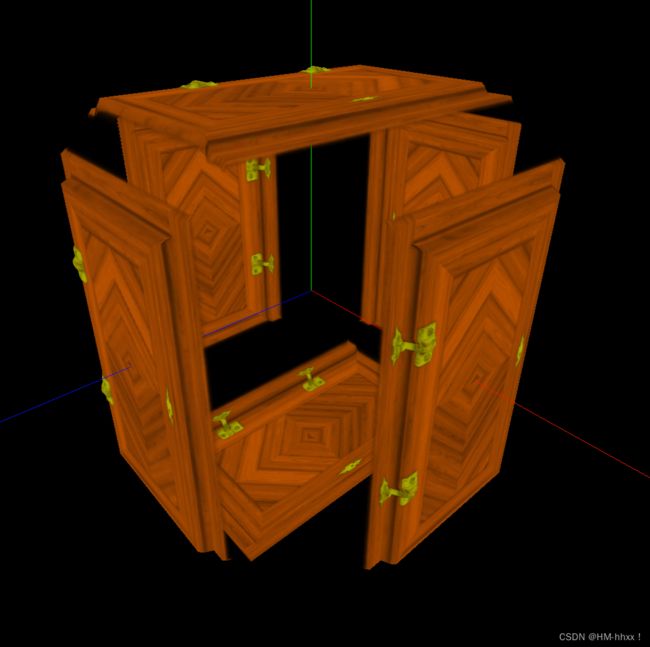
门合页处金属会呈现不同的光照效果。
 2.6 法线贴图
2.6 法线贴图
用于创建法线贴图的纹理。RGB值会影响每个像素片段的曲面法线,并更改颜色照亮的方式。法线贴图不会改变曲面的实际形状,只会改变光照。
示例:
// 导入法线贴图
const normalTexture = textureLoader.load("./textures/door/normal.jpg");
// 材质
const material = new THREE.MeshStandardMaterial({
color: "#ffff00",
map: doorColorTexture,
alphaMap: doorAplhaTexture,
transparent: true,
//
aoMap: doorAoTexture,
aoMapIntensity: 1,
//
displacementMap: doorHeightTexture,
displacementScale: 0.1,
//粗糙度材质
roughness: 1,
roughnessMap: roughnessTexture,
//金属材质
metalness: 1,
metalnessMap: metalnessTexture,
//法线贴图
normalMap: normalTexture,
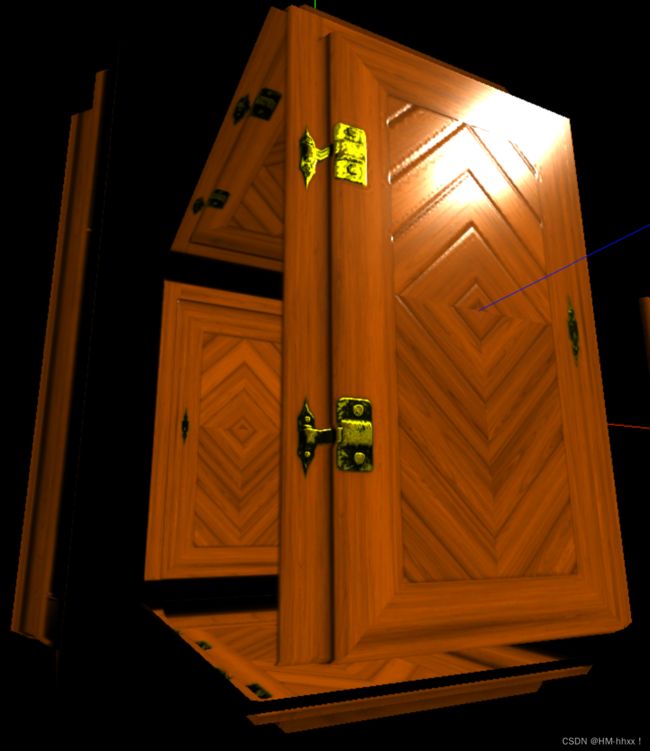
});实现效果:
加入法线贴图后,该示例门的纹路出会出现基于法线的反光效果,实现纹路的设置。