手牵手SpringBoot之ORM操作MySql
Springboot
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Spring Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。
Springboot是Spring中的一个成员,可以简化Spring,SpringMVC的核心是IOC容器
使用Springboot开发效率高。
Springboot特点
独立运行的 Spring 项目
Spring Boot 可以以 jar 包的形式独立运行,Spring Boot 项目只需通过命令“ java–jar xx.jar” 即可运行。
可以创建独立的Spring应用程序,并且基于其Maven或Gradle插件,可以创建可执行的JARs和WARs;
内嵌 Servlet 容器
Spring Boot 使用嵌入式的 Servlet 容器(例如 Tomcat、Jetty 或者 Undertow 等),应用无需打成 WAR 包 。
提供 starter 简化 Maven 配置
Spring Boot 提供了一系列的“starter”项目对象模型(POMS)来简化 Maven 配置。
提供了大量的自动配置
Spring Boot 提供了大量的默认自动配置,来简化项目的开发,开发人员也通过配置文件修改默认配置。
尽可能自动配置Spring容器
自带应用监控
Spring Boot 可以对正在运行的项目提供监控。
无代码生成和 xml 配置
Springboot特性
遵循习惯优于配置的原则。使用springboot我们只需要很少的配置,大多数使用默认配置即可
内嵌servlet容器,降低了对环境的要求,可用命令直接执行项目
项目快速搭建。springboot尽可能自动配置spring以及第三方库,帮助开发者快速搭建spring框架,可无需配置的自动整合第三方框架
提供各种starter简化Maven配置。springboot提供了一系列的starter用来简化maven依赖。如:常用的spring-boot-starter-web、spring-boot-starter-tomcat等
独立运行spring项目。springboot可以以jar包的形式进行独立运行,使用java -jar xx.jar 就可以成功运行项目,无需部署war文件
可以完全不使用xml配置,只需要自动配置和Java config
应用监控(SpringBootActuator)
XML与JavaConfig
Spring使用XML作为容器配置文件,在3.0后加入了JavaConfig,使用java类做配置文件使用。
JavaConfig
JavaConfig:是Spring提供使用java类配置容器(代替XML配置。配置Spring IOC容器的纯Java方法。
JavaConfig类可以创建java对象,把java对象放入spring容器中(注入)。
可以使用面向对象方式,一个配置类可以继承配置类,可以重写方法。
避免了繁琐的XML配置
————————————————
总体框架
@Mapper注解
@Mapper注解:放在dao接口上面。表示该接口会由Mybaits创建mapper代理对象
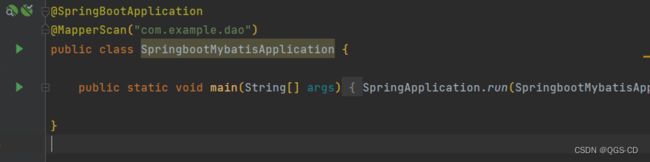
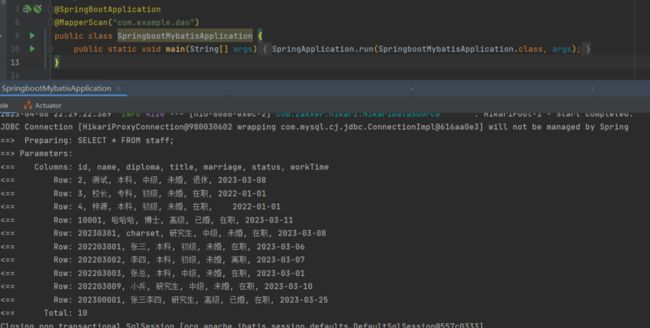
@MapperScan注解
在主类中使用@MapperScan注解,可解决多个dao接口中使用@Mapper注解的繁琐。
@MapperScan("com.example.dao")
或@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.example.dao")Pom.xml配置文件
4.0.0
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
2.7.10
com.example
springboot-Mybatis
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
springboot-Mybatis
springboot-Mybatis
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
2.3.0
com.mysql
mysql-connector-j
runtime
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
src/main/java
**/*.properties
**/*.xml
false
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
创建Dao接口与Mapper文件
dao
//@Mapper //表示该接口会创建mapper代理
public interface StaffDao {
//查询所有
List selectALL();
} Mapper
Pojo类
public class Staff {
private int id;
private String name;
private String diploma;
private String title;
private String marriage;
private String status;
private String workTime; //get+set+toString}Server接口
public interface StaffService {
List selectALL();
} Server实现类
@Service
public class StaffServiceImpl implements StaffService {
@Resource
private StaffDao staffDao;
@Override
public List selectALL() {
List staffs = staffDao.selectALL();
return staffs;
}
} application.properties配置文件
#application.properties配置文件
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/boot
#指定时区
serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
#serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
#连接数据库
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://IP:3306/mysql?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=pwdApplication类启动
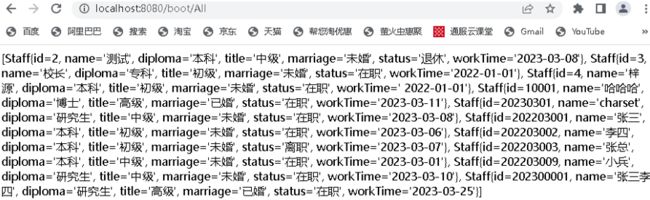
浏览器访问
Dao与mapper分开管理
需要在application.properties配置mapper路径
#指定mapper文件路径
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xmlPom.xml配置
src/main/resources
**/*.*
false
开启Mybatis日志
application.properties配置
#配置mybatis启动日志
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl开启事务控制
事务管理器:DataSourceTransactionManager
Spring实现事务的两种方式
编程式事务:编写代码来实现事务的管理
声明式事务*:基于注解的方式、基于xml配置方式
声明式事务处理
只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程。
事务隔离级别的四个级别:
读未提交:READ_UNCOMMITTEN
这种隔离级别:存在脏读问题,所谓的脏读(dirty read)表示能够读取到其他事务未提交的数据。
读提交:READ_COMMITTED (oracle)
解决了脏读问题,其他事务提交之后才能读到,但存在不可重复读问题
可重复读:REPEATABLE_READ (MYSQL)
解决了不可重复读,可以达到可重复读效果,只要当前事务不结束,读取到的数据移植都是一样的。但存在幻读问题。
序列化:SERIALLZABLE
解决了幻读问题,事务排毒执行。不支持并发。
事务处理方式:1、Spring框架的@Transaction注解。2、aspectj框架xml配置,声明事务控制的内容。
SpringBoot中事务的使用的两种方式:1、业务方法上使用@Transaction注解。2、启动类使用@EnableTransactionManagement
application.properties配置
#application.properties配置文件
server.port=8080
server.servlet.context-path=/boot
#指定时区
serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
#连接数据库
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://IP:3306/mysql?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=pwd
#指定mapper文件路径
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
#配置mybatis启动日志
mybatis.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImplServer层实现
public interface StaffServer {
int insert(Staff staff);
Staff selectById(Integer id);
}@Service
public class StaffServerImpl implements StaffServer {
@Resource
private StaffMapper staffDao;
@Transactional
@Override
public int insert(Staff staff) {
int insert = staffDao.insert(staff);
return insert;
}
@Transactional
@Override
public Staff selectById(Integer id) {
Staff staff = staffDao.selectByPrimaryKey(id);
return staff;
}
}Controller层
@Controller
public class StaffController {
@Resource
private StaffServer staffServer;
@RequestMapping("/selectById")
@ResponseBody
public String selectById(int id){
System.out.println("id:"+id);
Staff staff = staffServer.selectById(id);
System.out.println(staff.toString());
return staff.toString();
}
}使用Mybatis生成器
生成
Application
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableTransactionManagement
@MapperScan("com.example.dao")
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
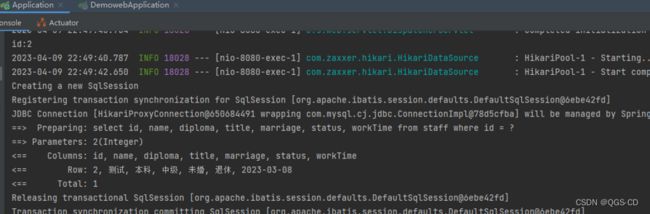
}浏览器访问:
http://localhost:8080/boot/selectById?id=2