【学习IO流】
学习内容:
- 概述
- 字节流
- 字符集
- 字符流
- 缓冲流
- 转换流
- 序列化和反序列化流
- 打印流
- 解压缩/压缩流
- Commons-io
学习产出:
概述
存储和读取数据的解决方案
我们首先要了解File(只能对文件本身做操作)
IO流(可以读写数据,本地文件,网络)
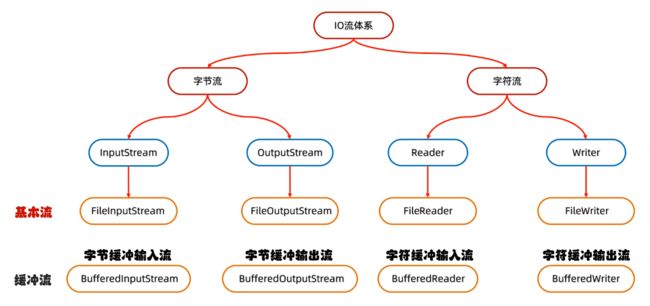
分类:
- 流的方向:输入流,输出流
- 文件类型:字节流(所有文件),字符(纯文本文件,windows自带的记事本能打开读懂的)
字节流
步骤:创建对象,写/读数据,释放资源
字符输出流(OutputStream)
文件字符输出流细节:
//第二个参数,表示续写开关,不传是false
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\a.txt",true);
fos.write(97);
fos.write(new byte[]{98,99});
fos.write(new byte[]{98,99,100,101},2,2);
//换行小知识,在早期dos系统,\r是把光标移动到前面,\n是换行
//windows:\r\n Linux:\n Mac:\r
//java对换行做了优化,上面三个都行
fos.close();
- 创建字符输出流
细节1:参数是路径或者File对象(是路径会去创建文件对象)
细节2:如果文件不存在会创建一个新的文件,但是要保证父级文件是存在的
细节3:如果文件依据存在,会清空文件 - 写数据
write方法写的是整数,但实际写到本地文件是ascii码 - 释放资源
字符输入流(InputStream)
文件字符输入流
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\a.txt");
int ss;
while ((ss=fis.read())!=-1){
System.out.println(ss);
}
fis.close();
//文件拷贝案例
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\b.txt");
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
int ss;
while ((ss=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(ss);
}
//先开的后关闭
fos.close();
fis.close();
- 创建字符输入流
细节1:如果文件不存在,就直接报错。 - 读数据
细节1:一次读取一个子集,读的是ASCLL对象的数字
细节2:读到文件末尾,read方法返回-1,read读一次就相当于移动一次指针 - 释放资源
一次读取多个字节
//一次读取一个字节数组数据,返回的是读取字节的数量,没有读到是-1
public int read(byte[] buffer)
try-catch处理异常
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\a.txt");
fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\b.txt");
byte buffer[] = new byte[1024];
while (fis.read(buffer) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fis != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
上面释放资源代码太麻烦,实现了AutoCloseable接口,可以自动释放资源

FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\b.txt");
try (fis;fos){
byte buffer[] = new byte[1024];
while (fis.read(buffer) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
字符集
计算机的存储规则
在计算机中,任意数据都是二进制来存储的,一个字节是(8bit),字节是计算机存储的最小单元,一个英文字符一个字节
Ascii: ASCII存储不了汉字,我天朝大国汉字怎么能存不了计算机呢?
ASCII存储不了汉字,我天朝大国汉字怎么能存不了计算机呢?
1980年国家发布了GB2312-80字符集,包括了6763个简体汉字。
2000年3.17发布GBK,收录21003个汉字,windows简体系统默认使用的就是GBK(GBK是完全兼容ASCII的)。

但是操作系统显示的是ANSI(ANSI是很多字符集的通称,我们用的简体中文,所以就当作GBK)。
Unicode字符集:国际标准字符集,他将世界各种语言的每个字符定义一个唯一的编码,以满足跨语言,跨平台的文本信息转换。
GBK编码规则
- 汉字是两个字节存储
- 高位字节二进制一定以1开头,转成十进制后是一个负数
Unicode的编码方式
- UTF-16:使用两个字节(16个比特位进行存储)
- UTF-32:使用四个字节(32个比特位进行存储)
- UTF-8:使用1-4个字节保存(ASCII使用一个字节,简体中文三个字节)(UTF-8是Unicode一种编码方式 )

byte a[]=new byte[10];
String sss="";
//使用指定的字符集
sss.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
sss=new String(a,StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
字符流
字符流底层就是字节流
输入流:一次读取一个字节,遇到中文时,一次读多个字节(一次读取一个字符)
输出流:底层会把数据按照指定的编码方式进行编码,变成字节在写到文件中。
字符输入流(Reader)
看子类 FileReader
//一次一个字节,遇到中文就会一次读取多个
//在读取之后,方法底层还会进行解码并转成10进制
//返回为int
read()
//一次读取一个char数组,相当于,每一次相当与read()之后强转成char
read(char[])
字符输出流(Writer)
看子类FileWrite
//构造方法和字节流是一样的
//写出一个字符
void write(int c)
//写出一个字符申
void write(string str)
//写出一个字符串的一部分
void write(String str, int off, int len)
//写出一个字符数组
void write(char[] cbuf)
//写出字符数组的一部分
void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len)
字符输入流有一在第一次读取的时候会创建一个8192的缓冲区
字符输入出流:在写时候也是先写到缓存区,在以下几种情况才会写到目的地
- 缓冲区充满了
- 手动调用刷新 fos.flush();
- 关闭资源
缓冲流
字节缓冲流
真正读取数据的还是基本流
//把基本流保证成缓冲流,也是会创建一个8192的缓冲区
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in)
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out)
BufferedInputStream inputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(""));
//在关闭的时候只要关闭包装流就可以了
inputStream .close();
字符缓冲流
要知道字符流中已经有8192字节缓冲区了,那是不是没有学习必要了?
不是,字符缓冲流中有两个个非常好用的方法
字符缓冲流有8192的字符数。(字符自带的是byte类型的8192,而字符缓冲是char的8192)
//字符缓冲输入流
// reader.readLine()一次可以读取一行,但是不会把回车和换行读出来
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:\\Users\\Xiao\\Desktop\\find-job\\a.txt"));
String s;
try (reader){
while ((s= reader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("",true));
bw.write("123");
//写出回车换行,会根据操作系统不同,自动写出对于的换行
bw.newLine();
转换流
是字节流和字符流直接的桥梁(是Reader和Writer的子类)
转换输入流:InputStreamReader
转换输入流:OutputStreamWriter
/*
* 利用转换流按照指定字符编码读取
* */
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(""), "GBK");
int ch;
while ((ch= reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) ch);
}
reader.close();
//在jdk11提供的方法,实际还是创建了一个转换流
FileReader reader1 = new FileReader("", Charset.forName("GBK"));
while ((ch= reader1.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char) ch);
}
reader1.close();
//字节流读取一行中文
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(""), "UTF-8");
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(reader);
System.out.println(br.readLine());
br.close();
//获取可以这么写
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(""), "UTF-8"));
序列化和反序列化流
是InputStream和OutputStream的子类
ObjectOutputStream:对象操作输出流,序列化流,可以把java对象写到本地文件中
//创建对象
People people = new People("wx", "18");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(""));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(people);
objectOutputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream:对象操作输入流,反序列化流,可以把文件中的java对象读取
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(""));
Object o = objectInputStream.readObject();
objectInputStream.close();
System.out.println(o.toString());
这里需要注意的是实现了Serializable接口的对象,系统会自动生成serialVersionUID,当我们类发生改变的时候这个也会变,所以我们需要自己取确定这个serialVersionUID,在idea中可以做如下设置
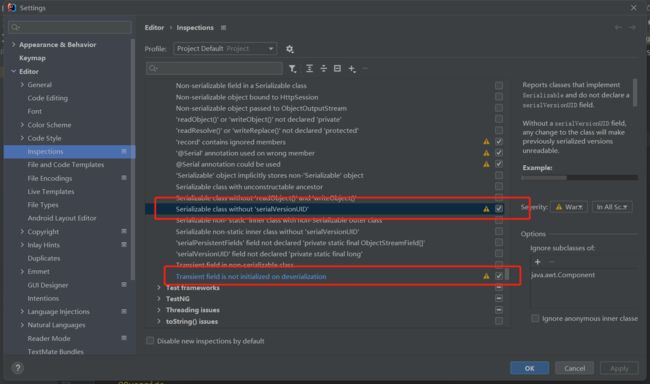

如果我们有成员变量不想序列化,只需要添加transient 关键字修饰即可
序列化多个对象
在反序列化时,如果已经读取到最后一个对象,在读取会报异常。
所以我们序列化多个对象的时候,一般是把多个对象放到一个集合里面,然后序列化这个集合
打印流
打印流只能写不能读取
打印流一般指:PrintStream(字节打印流),PrintWriter(字符打印流)

字节打印流
//构造方法有很多
PrintStream printStream=new PrintStream("",Charset.forName("GBK"));
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("");
//第二个参数为自动刷新,但是字节打印流没有缓冲区,默认是开的,但是开不开没有区别
new PrintStream(fileOutputStream,true,Charset.forName("GBK"));
//下面是特有方法,可以自动换行的原样写出,还支持占位符输出
printStream.println(97);
printStream.print(true);
printStream.printf("%s爱上了%s","啊伟","阿强");
字符打印流
//默认不是自动刷新的,这里如果不开自动刷新,就会先写到缓冲区
PrintWriter printWriter=new PrintWriter(new FileWriter(""),true);
System.out.println(“”);
//获取到打印流对象,此打印流在虚拟机启动的时候由虚拟机创建,默认指向控制台
//特殊打印流,系统中的标准输出流,在系统中是唯一的,如果out.close()关掉了,就不能输出了,只有重启虚拟机
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.print("dddd");
//System是java提供的uog
解压缩/压缩流
.zip文件在Java中是一个ZipEntry对象
解压本质:把每一个zipEntry按层级拷贝到本地的另一个文件夹中
//解压
public static void unzip(File src,File dest) throws IOException {
//创建一个解压缩流
ZipInputStream zip = new ZipInputStream(new FileInputStream(src));
ZipEntry nextEntry ;
while ((nextEntry = zip.getNextEntry())!=null){
if (nextEntry.isDirectory()){
//文件夹:在目标处创建一个同样的文件夹=
File file=new File(dest,nextEntry.toString());
file.mkdir();
}else {
//读取文件
File file=new File(dest,nextEntry.toString());
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream(file);
int b;
while ((b=zip.read())!=-1){
fos.write(b);
}
fos.close();
//表示压缩包中的一个文件处理完毕
zip.closeEntry();
}
}
zip.close();
}
//压缩
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//创建要压缩的文件
File file=new File("");
//目的地,要压缩文件的父级路径,同名
File file1=new File(file.getParentFile(),file.getName()+".zip");
//创建压缩流关联压缩包
ZipOutputStream zipOutputStream = new ZipOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file1));
//获取到file里面的所有文件,变成zipEntry,放到压缩包中
toZip(file,zipOutputStream,"");
zipOutputStream.close();
}
/*
数据源
压缩流
压缩包内部路径
* */
public static void toZip(File src,ZipOutputStream zos,String name) throws IOException {
File[] files = src.listFiles();
for(File file:files){
if (file.isFile()){
//这个构造方法是压缩包内部的路径
ZipEntry zipEntry=new ZipEntry(name+"\\"+file.getName());
zos.putNextEntry(zipEntry);
//读取数据,写道压缩包
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
int a;
while ((a=inputStream.read())!=-1){
zos.write(a);
}
inputStream.close();
zos.closeEntry();
}else {
//文件夹,递归
toZip(file,zos,name+"\\"+file.getName());
}
}
}
Commons-io和Hutool
Hutool
下载 百度网盘
官网:
https://hutool.cn/
API文档:
https://apidoc.gitee.com/dromara/hutool/
中文使用文档:
https://hutool.cn/docs/#/