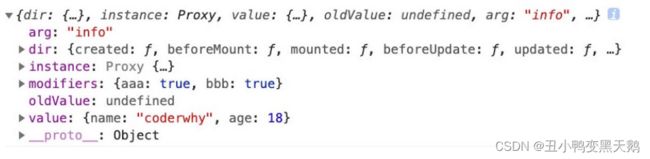
- element实现动态路由+面包屑
软件技术NINI
vue案例vue.js前端
el-breadcrumb是ElementUI组件库中的一个面包屑导航组件,它用于显示当前页面的路径,帮助用户快速理解和导航到应用的各个部分。在Vue.js项目中,如果你已经安装了ElementUI,就可以很方便地使用el-breadcrumb组件。以下是一个基本的使用示例:安装ElementUI(如果你还没有安装的话):你可以通过npm或yarn来安装ElementUI。bash复制代码npmi
- Long类型前后端数据不一致
igotyback
前端
响应给前端的数据浏览器控制台中response中看到的Long类型的数据是正常的到前端数据不一致前后端数据类型不匹配是一个常见问题,尤其是当后端使用Java的Long类型(64位)与前端JavaScript的Number类型(最大安全整数为2^53-1,即16位)进行数据交互时,很容易出现精度丢失的问题。这是因为JavaScript中的Number类型无法安全地表示超过16位的整数。为了解决这个问
- DIV+CSS+JavaScript技术制作网页(旅游主题网页设计与制作)云南大理
STU学生网页设计
网页设计期末网页作业html静态网页html5期末大作业网页设计web大作业
️精彩专栏推荐作者主页:【进入主页—获取更多源码】web前端期末大作业:【HTML5网页期末作业(1000套)】程序员有趣的告白方式:【HTML七夕情人节表白网页制作(110套)】文章目录二、网站介绍三、网站效果▶️1.视频演示2.图片演示四、网站代码HTML结构代码CSS样式代码五、更多源码二、网站介绍网站布局方面:计划采用目前主流的、能兼容各大主流浏览器、显示效果稳定的浮动网页布局结构。网站程
- 【加密社】Solidity 中的事件机制及其应用
加密社
闲侃区块链智能合约区块链
加密社引言在Solidity合约开发过程中,事件(Events)是一种非常重要的机制。它们不仅能够让开发者记录智能合约的重要状态变更,还能够让外部系统(如前端应用)监听这些状态的变化。本文将详细介绍Solidity中的事件机制以及如何利用不同的手段来触发、监听和获取这些事件。事件存储的地方当我们在Solidity合约中使用emit关键字触发事件时,该事件会被记录在区块链的交易收据中。具体而言,事件
- 关于城市旅游的HTML网页设计——(旅游风景云南 5页)HTML+CSS+JavaScript
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业javascripthtmlcss旅游风景
⛵源码获取文末联系✈Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业|游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作|HTML期末大学生网页设计作业,Web大学生网页HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScrip
- HTML网页设计制作大作业(div+css) 云南我的家乡旅游景点 带文字滚动
二挡起步
web前端期末大作业web设计网页规划与设计htmlcssjavascriptdreamweaver前端
Web前端开发技术描述网页设计题材,DIV+CSS布局制作,HTML+CSS网页设计期末课程大作业游景点介绍|旅游风景区|家乡介绍|等网站的设计与制作HTML期末大学生网页设计作业HTML:结构CSS:样式在操作方面上运用了html5和css3,采用了div+css结构、表单、超链接、浮动、绝对定位、相对定位、字体样式、引用视频等基础知识JavaScript:做与用户的交互行为文章目录前端学习路线
- node.js学习
小猿L
node.jsnode.js学习vim
node.js学习实操及笔记温故node.js,node.js学习实操过程及笔记~node.js学习视频node.js官网node.js中文网实操笔记githubcsdn笔记为什么学node.js可以让别人访问我们编写的网页为后续的框架学习打下基础,三大框架vuereactangular离不开node.jsnode.js是什么官网:node.js是一个开源的、跨平台的运行JavaScript的运行
- vue3中el-table中点击图片放大时,被表格覆盖
叫我小鹏呀
vue.jsjavascript前端
问题:vue3中el-table中点击图片放大时,被表格覆盖。解决方法:el-image添加preview-teleported
- vue项目element-ui的table表格单元格合并
酋长哈哈
vue.jselementuijavascript前端
一、合并效果二全部代码exportdefault{name:'CellMerge',data(){return{tableData:[{id:'1',name:'王小虎',amount1:'165',amount2:'3.2',amount3:10},{id:'1',name:'王小虎',amount1:'162',amount2:'4.43',amount3:12},{id:'1',name:'
- Vue中table合并单元格用法
weixin_30613343
javascriptViewUI
地名结果人名性别{{item.name}}已完成未完成{{item.groups[0].name}}{{item.groups[0].sex}}{{item.groups[son].name}}{{item.groups[son].sex}}exportdefault{data(){return{list:[{name:'地名1',result:'1',groups:[{name:'张三',sex
- springboot+vue项目实战一-创建SpringBoot简单项目
苹果酱0567
面试题汇总与解析springboot后端java中间件开发语言
这段时间抽空给女朋友搭建一个个人博客,想着记录一下建站的过程,就当做笔记吧。虽然复制zjblog只要一个小时就可以搞定一个网站,或者用cms系统,三四个小时就可以做出一个前后台都有的网站,而且想做成啥样也都行。但是就是要从新做,自己做的意义不一样,更何况,俺就是专门干这个的,嘿嘿嘿要做一个网站,而且从零开始,首先呢就是技术选型了,经过一番思量决定选择-SpringBoot做后端,前端使用Vue做一
- JavaScript 中,深拷贝(Deep Copy)和浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)
跳房子的前端
前端面试javascript开发语言ecmascript
在JavaScript中,深拷贝(DeepCopy)和浅拷贝(ShallowCopy)是用于复制对象或数组的两种不同方法。了解它们的区别和应用场景对于避免潜在的bugs和高效地处理数据非常重要。以下是对深拷贝和浅拷贝的详细解释,包括它们的概念、用途、优缺点以及实现方式。1.浅拷贝(ShallowCopy)概念定义:浅拷贝是指创建一个新的对象或数组,其中包含了原对象或数组的基本数据类型的值和对引用数
- Vue( ElementUI入门、vue-cli安装)
m0_l5z
elementuivue.js
一.ElementUI入门目录:1.ElementUI入门1.1ElementUI简介1.2Vue+ElementUI安装1.3开发示例2.搭建nodejs环境2.1nodejs介绍2.2npm是什么2.3nodejs环境搭建2.3.1下载2.3.2解压2.3.3配置环境变量2.3.4配置npm全局模块路径和cache默认安装位置2.3.5修改npm镜像提高下载速度2.3.6验证安装结果3.运行n
- 博客网站制作教程
2401_85194651
javamaven
首先就是技术框架:后端:Java+SpringBoot数据库:MySQL前端:Vue.js数据库连接:JPA(JavaPersistenceAPI)1.项目结构blog-app/├──backend/│├──src/main/java/com/example/blogapp/││├──BlogApplication.java││├──config/│││└──DatabaseConfig.java
- vue+el-table 可输入表格使用上下键进行input框切换
以对_
vue学习记录vue.jsjavascript前端
使用上下键进行完工数量这一列的切换-->//键盘触发事件show(ev,index){letnewIndex;letinputAll=document.querySelectorAll('.table_inputinput');//向上=38if(ev.keyCode==38){if(index==0){//如果是第一行,回到最后一个newIndex=inputAll.length-1}elsei
- vue + Element UI table动态合并单元格
我家媳妇儿萌哒哒
elementUIvue.js前端javascript
一、功能需求1、根据名称相同的合并工作阶段和主要任务合并这两列,但主要任务内容一样,但要考虑主要任务一样,但工作阶段不一样的情况。(枞向合并)2、落实情况里的定量内容和定性内容值一样则合并。(横向合并)二、功能实现exportdefault{data(){return{tableData:[{name:'a',address:'1',age:'1',six:'2'},{name:'a',addre
- vue 创建项目报错:command failed: npm install --loglevel error
那鱼、会飞
vue.jsvue-cli3
这个问题其实很好解决,只是很多种情况,逐一排除即可。稳下心来~vuecli3创建项目我的node版本是node14.15.0,(永远不要尝试最新版本)node各种版本下载地址:以往的版本|Node.js(nodejs.org)vue/
[email protected]@vue/
[email protected](注意vue/cli2和vue/cli3的下载命名有所改变,2是-形式,3是/形式)其实报错
- JavaScript `Map` 和 `WeakMap`详细解释
跳房子的前端
JavaScript原生方法javascript前端开发语言
在JavaScript中,Map和WeakMap都是用于存储键值对的数据结构,但它们有一些关键的不同之处。MapMap是一种可以存储任意类型的键值对的集合。它保持了键值对的插入顺序,并且可以通过键快速查找对应的值。Map提供了一些非常有用的方法和属性来操作这些数据对:set(key,value):将一个键值对添加到Map中。如果键已经存在,则更新其对应的值。get(key):获取指定键的值。如果键
- 计算机毕业设计PHP仓储综合管理系统(源码+程序+VUE+lw+部署)
java毕设程序源码王哥
php课程设计vue.js
该项目含有源码、文档、程序、数据库、配套开发软件、软件安装教程。欢迎交流项目运行环境配置:phpStudy+Vscode+Mysql5.7+HBuilderX+Navicat11+Vue+Express。项目技术:原生PHP++Vue等等组成,B/S模式+Vscode管理+前后端分离等等。环境需要1.运行环境:最好是小皮phpstudy最新版,我们在这个版本上开发的。其他版本理论上也可以。2.开发
- 最简单将静态网页挂载到服务器上(不用nginx)
全能全知者
服务器nginx运维前端html笔记
最简单将静态网页挂载到服务器上(不用nginx)如果随便弄个静态网页挂在服务器都要用nignx就太麻烦了,所以直接使用Apache来搭建一些简单前端静态网页会相对方便很多检查Web服务器服务状态:sudosystemctlstatushttpd#ApacheWeb服务器如果发现没有安装web服务器:安装Apache:sudoyuminstallhttpd启动Apache:sudosystemctl
- 补充元象二面
Redstone Monstrosity
前端面试
1.请尽可能详细地说明,防抖和节流的区别,应用场景?你的回答中不要写出示例代码。防抖(Debounce)和节流(Throttle)是两种常用的前端性能优化技术,它们的主要区别在于如何处理高频事件的触发。以下是防抖和节流的区别和应用场景的详细说明:防抖和节流的定义防抖:在一段时间内,多次执行变为只执行最后一次。防抖的原理是,当事件被触发后,设置一个延迟定时器。如果在这个延迟时间内事件再次被触发,则重
- 微信小程序开发注意事项
jun778895
微信小程序小程序
微信小程序开发是一个融合了前端开发、用户体验设计、后端服务(可选)以及微信小程序平台特性的综合性项目。这里,我将详细介绍一个典型的小程序开发项目的全过程,包括项目规划、设计、开发、测试及部署上线等各个环节,并尽量使内容达到或超过2000字的要求。一、项目规划1.1项目背景与目标假设我们要开发一个名为“智慧校园助手”的微信小程序,旨在为学生提供一站式校园生活服务,包括课程表查询、图书馆座位预约、食堂
- 切换淘宝最新npm镜像源是
hai40587
npm前端node.js
切换淘宝最新npm镜像源是一个相对简单的过程,但首先需要明确当前淘宝npm镜像源的状态和最新的镜像地址。由于网络环境和服务更新,镜像源的具体地址可能会发生变化,因此,我将基于当前可获取的信息,提供一个通用的切换步骤,并附上最新的镜像地址(截至回答时)。一、了解npm镜像源npm(NodePackageManager)是JavaScript的包管理器,用于安装、更新和管理项目依赖。由于npm官方仓库
- 字节二面
Redstone Monstrosity
前端面试
1.假设你是正在面试前端开发工程师的候选人,面试官让你详细说出你上一段实习过程的收获和感悟。在上一段实习过程中,我获得了宝贵的实践经验和深刻的行业洞察,以下是我的主要收获和感悟:一、专业技能提升框架应用熟练度:通过实际项目,我深入掌握了React、Vue等前端框架的使用,不仅提升了编码效率,还学会了如何根据项目需求选择合适的框架。问题解决能力:在实习期间,我遇到了许多预料之外的技术难题。通过查阅文
- vue render 函数详解 (配参数详解)
你的眼睛會笑
vue2vue.jsjavascript前端
vuerender函数详解(配参数详解)在Vue3中,`render`函数被用来代替Vue2中的模板语法。它接收一个h函数(或者是`createElement`函数的别名),并且返回一个虚拟DOM。render函数的语法结构如下:render(h){returnh('div',{class:'container'},'Hello,World!')}在上面的示例中,我们使用h函数创建了一个div元素
- 前端代码上传文件
余生逆风飞翔
前端javascript开发语言
点击上传文件import{ElNotification}from'element-plus'import{API_CONFIG}from'../config/index.js'import{UploadFilled}from'@element-plus/icons-vue'import{reactive}from'vue'import{BASE_URL}from'../config/index'i
- VUE3 + xterm + nestjs实现web远程终端 或 连接开启SSH登录的路由器和交换机。
焚木灵
node.jsvue
可远程连接系统终端或开启SSH登录的路由器和交换机。相关资料:xtermjs/xterm.js:Aterminalfortheweb(github.com)后端实现(NestJS):1、安装依赖:npminstallnode-ssh@nestjs/websockets@nestjs/platform-socket.io2、我们将创建一个名为RemoteControlModule的NestJS模块,
- 详解“c:/work/src/components/a/b.vue“‘ has no default export报错原因
hw_happy
开发语言前端vue.jsjavascript
前情提要在一个vue文件中需要引入定义的b.vue文件,但是提示b文件没有默认导出,对于vue2文件来说有exportdefault,在中,所有定义的变量、函数和组件都会自动被视为默认导出的组件内容。因此,不需要显式地使用exportdefault来导出组件。但是在我引用这个文件的时候还是提示了这个错误,原来是我的项目使用了ts和vite\webpack,因为TypeScript和Vue的默认导出
- uniapp实现动态标记效果详细步骤【前端开发】
2401_85123349
uni-app
第二个点在于实现将已经被用户标记的内容在下一次获取后刷新它的状态为已标记。这是什么意思呢?比如说上面gif图中的这些人物对象,有一些已被该用户添加为关心,那么当用户下一次进入该页面时,这些已经被添加关心的对象需要以“红心”状态显现出来。这个点的难度还不算大,只需要在每一次获取后端的内容后对标记对象进行状态更新即可。II.动态标记效果实现思路和步骤首先,整体的思路是利用动态类名对不同的元素进行选择。
- 高性能javascript--算法和流程控制
海淀萌狗
-for,while和do-while性能相当-避免使用for-in循环,==除非遍历一个属性量未知的对象==es5:for-in遍历的对象便不局限于数组,还可以遍历对象。原因:for-in每次迭代操作会同时搜索实例或者原型属性,for-in循环的每次迭代都会产生更多开销,因此要比其他循环类型慢,一般速度为其他类型循环的1/7。因此,除非明确需要迭代一个属性数量未知的对象,否则应避免使用for-i
- 怎么样才能成为专业的程序员?
cocos2d-x小菜
编程PHP
如何要想成为一名专业的程序员?仅仅会写代码是不够的。从团队合作去解决问题到版本控制,你还得具备其他关键技能的工具包。当我们询问相关的专业开发人员,那些必备的关键技能都是什么的时候,下面是我们了解到的情况。
关于如何学习代码,各种声音很多,然后很多人就被误导为成为专业开发人员懂得一门编程语言就够了?!呵呵,就像其他工作一样,光会一个技能那是远远不够的。如果你想要成为
- java web开发 高并发处理
BreakingBad
javaWeb并发开发处理高
java处理高并发高负载类网站中数据库的设计方法(java教程,java处理大量数据,java高负载数据) 一:高并发高负载类网站关注点之数据库 没错,首先是数据库,这是大多数应用所面临的首个SPOF。尤其是Web2.0的应用,数据库的响应是首先要解决的。 一般来说MySQL是最常用的,可能最初是一个mysql主机,当数据增加到100万以上,那么,MySQL的效能急剧下降。常用的优化措施是M-S(
- mysql批量更新
ekian
mysql
mysql更新优化:
一版的更新的话都是采用update set的方式,但是如果需要批量更新的话,只能for循环的执行更新。或者采用executeBatch的方式,执行更新。无论哪种方式,性能都不见得多好。
三千多条的更新,需要3分多钟。
查询了批量更新的优化,有说replace into的方式,即:
replace into tableName(id,status) values
- 微软BI(3)
18289753290
微软BI SSIS
1)
Q:该列违反了完整性约束错误;已获得 OLE DB 记录。源:“Microsoft SQL Server Native Client 11.0” Hresult: 0x80004005 说明:“不能将值 NULL 插入列 'FZCHID',表 'JRB_EnterpriseCredit.dbo.QYFZCH';列不允许有 Null 值。INSERT 失败。”。
A:一般这类问题的存在是
- Java中的List
g21121
java
List是一个有序的 collection(也称为序列)。此接口的用户可以对列表中每个元素的插入位置进行精确地控制。用户可以根据元素的整数索引(在列表中的位置)访问元素,并搜索列表中的元素。
与 set 不同,列表通常允许重复
- 读书笔记
永夜-极光
读书笔记
1. K是一家加工厂,需要采购原材料,有A,B,C,D 4家供应商,其中A给出的价格最低,性价比最高,那么假如你是这家企业的采购经理,你会如何决策?
传统决策: A:100%订单 B,C,D:0%
&nbs
- centos 安装 Codeblocks
随便小屋
codeblocks
1.安装gcc,需要c和c++两部分,默认安装下,CentOS不安装编译器的,在终端输入以下命令即可yum install gccyum install gcc-c++
2.安装gtk2-devel,因为默认已经安装了正式产品需要的支持库,但是没有安装开发所需要的文档.yum install gtk2*
3. 安装wxGTK
yum search w
- 23种设计模式的形象比喻
aijuans
设计模式
1、ABSTRACT FACTORY—追MM少不了请吃饭了,麦当劳的鸡翅和肯德基的鸡翅都是MM爱吃的东西,虽然口味有所不同,但不管你带MM去麦当劳或肯德基,只管向服务员说“来四个鸡翅”就行了。麦当劳和肯德基就是生产鸡翅的Factory 工厂模式:客户类和工厂类分开。消费者任何时候需要某种产品,只需向工厂请求即可。消费者无须修改就可以接纳新产品。缺点是当产品修改时,工厂类也要做相应的修改。如:
- 开发管理 CheckLists
aoyouzi
开发管理 CheckLists
开发管理 CheckLists(23) -使项目组度过完整的生命周期
开发管理 CheckLists(22) -组织项目资源
开发管理 CheckLists(21) -控制项目的范围开发管理 CheckLists(20) -项目利益相关者责任开发管理 CheckLists(19) -选择合适的团队成员开发管理 CheckLists(18) -敏捷开发 Scrum Master 工作开发管理 C
- js实现切换
百合不是茶
JavaScript栏目切换
js主要功能之一就是实现页面的特效,窗体的切换可以减少页面的大小,被门户网站大量应用思路:
1,先将要显示的设置为display:bisible 否则设为none
2,设置栏目的id ,js获取栏目的id,如果id为Null就设置为显示
3,判断js获取的id名字;再设置是否显示
代码实现:
html代码:
<di
- 周鸿祎在360新员工入职培训上的讲话
bijian1013
感悟项目管理人生职场
这篇文章也是最近偶尔看到的,考虑到原博客发布者可能将其删除等原因,也更方便个人查找,特将原文拷贝再发布的。“学东西是为自己的,不要整天以混的姿态来跟公司博弈,就算是混,我觉得你要是能在混的时间里,收获一些别的有利于人生发展的东西,也是不错的,看你怎么把握了”,看了之后,对这句话记忆犹新。 &
- 前端Web开发的页面效果
Bill_chen
htmlWebMicrosoft
1.IE6下png图片的透明显示:
<img src="图片地址" border="0" style="Filter.Alpha(Opacity)=数值(100),style=数值(3)"/>
或在<head></head>间加一段JS代码让透明png图片正常显示。
2.<li>标
- 【JVM五】老年代垃圾回收:并发标记清理GC(CMS GC)
bit1129
垃圾回收
CMS概述
并发标记清理垃圾回收(Concurrent Mark and Sweep GC)算法的主要目标是在GC过程中,减少暂停用户线程的次数以及在不得不暂停用户线程的请夸功能,尽可能短的暂停用户线程的时间。这对于交互式应用,比如web应用来说,是非常重要的。
CMS垃圾回收针对新生代和老年代采用不同的策略。相比同吞吐量垃圾回收,它要复杂的多。吞吐量垃圾回收在执
- Struts2技术总结
白糖_
struts2
必备jar文件
早在struts2.0.*的时候,struts2的必备jar包需要如下几个:
commons-logging-*.jar Apache旗下commons项目的log日志包
freemarker-*.jar
- Jquery easyui layout应用注意事项
bozch
jquery浏览器easyuilayout
在jquery easyui中提供了easyui-layout布局,他的布局比较局限,类似java中GUI的border布局。下面对其使用注意事项作简要介绍:
如果在现有的工程中前台界面均应用了jquery easyui,那么在布局的时候最好应用jquery eaysui的layout布局,否则在表单页面(编辑、查看、添加等等)在不同的浏览器会出
- java-拷贝特殊链表:有一个特殊的链表,其中每个节点不但有指向下一个节点的指针pNext,还有一个指向链表中任意节点的指针pRand,如何拷贝这个特殊链表?
bylijinnan
java
public class CopySpecialLinkedList {
/**
* 题目:有一个特殊的链表,其中每个节点不但有指向下一个节点的指针pNext,还有一个指向链表中任意节点的指针pRand,如何拷贝这个特殊链表?
拷贝pNext指针非常容易,所以题目的难点是如何拷贝pRand指针。
假设原来链表为A1 -> A2 ->... -> An,新拷贝
- color
Chen.H
JavaScripthtmlcss
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <HTML> <HEAD>&nbs
- [信息与战争]移动通讯与网络
comsci
网络
两个坚持:手机的电池必须可以取下来
光纤不能够入户,只能够到楼宇
建议大家找这本书看看:<&
- oracle flashback query(闪回查询)
daizj
oracleflashback queryflashback table
在Oracle 10g中,Flash back家族分为以下成员:
Flashback Database
Flashback Drop
Flashback Table
Flashback Query(分Flashback Query,Flashback Version Query,Flashback Transaction Query)
下面介绍一下Flashback Drop 和Flas
- zeus持久层DAO单元测试
deng520159
单元测试
zeus代码测试正紧张进行中,但由于工作比较忙,但速度比较慢.现在已经完成读写分离单元测试了,现在把几种情况单元测试的例子发出来,希望有人能进出意见,让它走下去.
本文是zeus的dao单元测试:
1.单元测试直接上代码
package com.dengliang.zeus.webdemo.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import o
- C语言学习三printf函数和scanf函数学习
dcj3sjt126com
cprintfscanflanguage
printf函数
/*
2013年3月10日20:42:32
地点:北京潘家园
功能:
目的:
测试%x %X %#x %#X的用法
*/
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
printf("哈哈!\n"); // \n表示换行
int i = 10;
printf
- 那你为什么小时候不好好读书?
dcj3sjt126com
life
dady, 我今天捡到了十块钱, 不过我还给那个人了
good girl! 那个人有没有和你讲thank you啊
没有啦....他拉我的耳朵我才把钱还给他的, 他哪里会和我讲thank you
爸爸, 如果地上有一张5块一张10块你拿哪一张呢....
当然是拿十块的咯...
爸爸你很笨的, 你不会两张都拿
爸爸为什么上个月那个人来跟你讨钱, 你告诉他没
- iptables开放端口
Fanyucai
linuxiptables端口
1,找到配置文件
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
2,添加端口开放,增加一行,开放18081端口
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 18081 -j ACCEPT
3,保存
ESC
:wq!
4,重启服务
service iptables
- Ehcache(05)——缓存的查询
234390216
排序ehcache统计query
缓存的查询
目录
1. 使Cache可查询
1.1 基于Xml配置
1.2 基于代码的配置
2 指定可搜索的属性
2.1 可查询属性类型
2.2 &
- 通过hashset找到数组中重复的元素
jackyrong
hashset
如何在hashset中快速找到重复的元素呢?方法很多,下面是其中一个办法:
int[] array = {1,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,8};
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int i = 0
- 使用ajax和window.history.pushState无刷新改变页面内容和地址栏URL
lanrikey
history
后退时关闭当前页面
<script type="text/javascript">
jQuery(document).ready(function ($) {
if (window.history && window.history.pushState) {
- 应用程序的通信成本
netkiller.github.com
虚拟机应用服务器陈景峰netkillerneo
应用程序的通信成本
什么是通信
一个程序中两个以上功能相互传递信号或数据叫做通信。
什么是成本
这是是指时间成本与空间成本。 时间就是传递数据所花费的时间。空间是指传递过程耗费容量大小。
都有哪些通信方式
全局变量
线程间通信
共享内存
共享文件
管道
Socket
硬件(串口,USB) 等等
全局变量
全局变量是成本最低通信方法,通过设置
- 一维数组与二维数组的声明与定义
恋洁e生
二维数组一维数组定义声明初始化
/** * */ package test20111005; /** * @author FlyingFire * @date:2011-11-18 上午04:33:36 * @author :代码整理 * @introduce :一维数组与二维数组的初始化 *summary: */ public c
- Spring Mybatis独立事务配置
toknowme
mybatis
在项目中有很多地方会使用到独立事务,下面以获取主键为例
(1)修改配置文件spring-mybatis.xml <!-- 开启事务支持 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" /> &n
- 更新Anadroid SDK Tooks之后,Eclipse提示No update were found
xp9802
eclipse
使用Android SDK Manager 更新了Anadroid SDK Tooks 之后,
打开eclipse提示 This Android SDK requires Android Developer Toolkit version 23.0.0 or above, 点击Check for Updates
检测一会后提示 No update were found