8.Java基础之多线程
1. 回顾
-
接口
①方法(分jdk版本)
②多继承
③变量特点
④多态的前提之一
⑤工厂设计模式,起码要知道简单工厂
⑥vs 抽象类
-
异常
①异常的祖宗类:
Throwable②异常的分类:编译(受检)+运行(非受检)
③error:处理不了
④常见异常(至少5个):算术、下标越界、空指针、类型转换、输入不匹配
⑤异常的处理机制:捕获(try…catch…finally)+抛出(交给调用者处理)
⑥throw和throws的使用区别
⑤会自定义异常
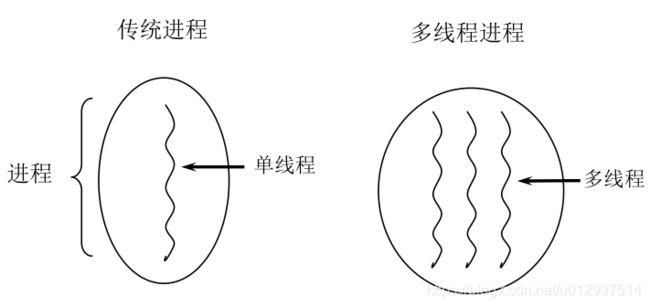
2. 线程
2.1 线程引入【了解】
2.1.1 基础知识
- 程序:静态的代码集合
- 进程:正在执行的程序,CPU分配资源的单位
- 线程:是进程的一条执行路径,是进程的一个子集。以迅雷为例,使用迅雷可以执行多个下载任务,好处:提高程序的执行效率
2.1.2 单核CPU 和多核CPU 的理解
- 单核CPU,其实是一种假的多线程,因为在一个时间单元内,也只能执行一个线程的任务。例如:虽然有多车道,但是收费站只有一个工作人员在收费,只有收了费才能通过,那么CPU就好比收费人员。如果有某个人不想交钱,那么收费人员可以把他“挂起”(晾着他,等他想通了,准备好了钱,再去收费)。但是因为CPU时间单元特别短,因此感觉不出来。
- 如果是多核的话,才能更好的发挥多线程的效率。(现在的服务器都是多核的)
- 一个Java应用程序java.exe,其实至少有三个线程:main()主线程,gc()垃圾回收线程,异常处理线程。当然如果发生异常,会影响主线程。
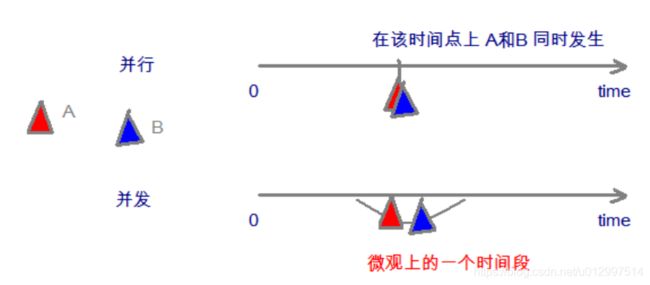
2.1.3 并发和并行
举例:一个食堂,有8个窗口,同一时刻,有8个人在不同的窗口打饭,则称为并行度为8
并发:指两个或多个事件在同一个时间段内发生。8个窗口,每个人打饭花30s,则1分钟内,并发度为16
一个CPU(采用时间片)同时执行多个任务。比如:秒杀、多个人做同一件事。
并行:指两个或多个事件在同一时刻发生(同时发生)。多个CPU同时执行多个任务。
在单核CPU中,我们的感觉是多个任务在同时执行,其实不然,CPU采用的分时轮询机制,即它的切换速度较快,感觉不出来。
简而言之:一个程序运行后至少有一个进程,一个进程中可以包含多个线程
2.1.4 何时需要多线程
- 程序需要同时执行两个或多个任务。
- 程序需要实现一些需要等待的任务时,如用户输入、文件读写操作、网络操作、搜索等。
- 需要一些后台运行的程序时。
2.1.5 高并发编程的意义、好处和注意事项
2.1.5.1 多线程好处
提高cpu的利用率
单线程:
5 seconds reading file A
2 seconds processing file A
5 seconds reading file B
2 seconds processing file B
-----------------------
14 seconds total
多线程
5 seconds reading file A
5 seconds reading file B + 2 seconds processing file A
2 seconds processing file B
-----------------------
12 seconds total
一般来说,在等待磁盘IO,网络IO或者等待用户输入时,CPU可以同时去处理其他任务。
更高效的响应
多线程技术使程序的响应速度更快 ,因为用户界面可以在进行其它工作的同时一直处于活动状态,不会造成无法响应的现象。
公平使用CPU资源
当前没有进行处理的任务,可以将处理器时间让给其它任务;占用大量处理时间的任务,也可以定期将处理器时间让给其它任务;通过对CPU时间的划分,使得CPU时间片可以在多个线程之间切换,避免需要长时间处理的线程独占CPU,导致其它线程长时间等待。
2.1.5.2 多线程的代价
更复杂的设计
共享数据的读取,数据的安全性,线程之间的交互,线程的同步等;
上下文环境切换
线程切换,cpu需要保存本地数据、程序指针等内容;
更多的资源消耗
每个线程都需要内存维护自己的本地栈信息,操作系统也需要资源对线程进行管理维护;
2.2 创建线程的方式【高频面试】
前两种最基础,必须会
线程的启动,需要调用start方法,而不是run方法【调用run其实就是一个普通的方法调用】
继承Thread类,实际上还是在实现Runnable接口
public class Thread implements Runnable继承Thread 和 实现Runnable接口的区别
①可以避免java中的单继承的局限性
②多个线程可以共享同一个接口实现类的对象,非常适合多个相同线程来处理同一份资源。
③实现解耦操作,代码可以被多个线程共享,代码和线程独立【耦合和解耦】
④线程池只能放入实现Runable或Callable类线程,不能直接放入继承Thread的类
Callable接口 vs Runnable的区别
①共同点:都可以实现线程
②Callable的call方法有返回值,Runnable的run方法无返回值
③Callable的call抛出异常,run没有抛出异常
④或想获取执行结果,需要使用Callable,
futureTask.get()
2.2.1 继承Thread
常用的构造方法:
- Thread() :创建新的Thread对象
- Thread(String threadname): :创建线程并指定线程实例名
- Thread(Runnable target) :指定创建线程的目标对象,它实现了Runnable接口中的run方法
- Thread(Runnable target, String name) :创建新的Thread对象
- Thread(FutureTask target) :以FutureTask为参数,FutureTask是对Callable的包装
- 写一个类,继承Thread
- 重写run方法
- 创建Thread子类对象,即创建了线程对象。
- 调用线程对象start方法:启动线程,调用run方法。
/**
* 创建线程方式一:
* 1、创建:继承Thread+重写run
* 2、启动: 创建子类对象 + start
*
*/
public class StartThread extends Thread{
/**
* 线程入口点
*/
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
System.out.println("一边听歌");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建子类对象
StartThread st =new StartThread();
//启动
st.start(); //不保证立即运行 cpu调用
//st.run(); //普通方法调用
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
System.out.println("一边coding");
}
}
}
注意:
- 如果自己手动调用run()方法,那么就只是普通方法,没有启动多线程模式。
- run()方法由JVM调用,什么时候调用,执行的过程控制都有操作系统的CPU调度决定。
- 想要启动多线程,必须调用start方法。
- 一个线程对象只能调用一次start()方法启动,如果重复调用了,则将抛出异常
IllegalThreadStateException。
2.2.2 实现Runnable接口
步骤:
- 定义子类,实现Runnable接口
- 子类中重写Runnable接口中的run方法
- 通过Thread类含参构造器创建线程对象
- 将Runnable接口的子类对象作为实际参数传递给Thread类的构造器中
- 调用Thread类的start方法:开启线程,调用Runnable子类接口的run方法
public class TestMyTread2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//创建一个线程对象
MyThread2 myThread = new MyThread2();
Thread thread = new Thread(myThread,"win1");
thread.start();
//使用lambda创建一个Runnable对象
Runnable r1 = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":" + i);
}
};
//使用匿名对象 启动线程
new Thread(r1,"win2").start();
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i);
// Thread.sleep(100);
}
}
}
class MyThread2 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":" + i);
}
}
}
/**
* lambda推导
* @author azzhu
*/
public class LambdaTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.println("一边学习lambda");
}
}) .start();
new Thread(()-> System.out.println("一边学习奔溃")) .start();
}
}
2.2.3 实现Callable接口–拔高
JDK5.0:新增方式一,且是JUC包中的
-
写一个类,实现Callable接口
-
启动线程
①创建一个FutureTask对象 ft,
new FutureTask(Callable类型的对象)②创建一个线程类,去启动线程。
new Thread(ft).start注意:FutureTask
public class FutureTask<V> implements RunnableFuture<V> //============== public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V>③在需要获取值的时候,去获取
ft.get(); //该方法有返回值public class TestMyCallable { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { MyThread3 myThread3 = new MyThread3(); //Integer sum = myThread3.call(); //System.out.println(sum); FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(myThread3); new Thread(futureTask).start(); //启动线程 Integer result = futureTask.get(); System.out.println("====>" + result); } } class MyThread3 implements Callable<Integer> { @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { return 100; } }
2.2.4 练习
-
创建两个分线程,让其中一个线程输出1-100之间的偶数,另一个线程输出1-100之间的奇数。
-
分别使用以上三种方式,模拟迅雷下载任务
工具类:
import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.net.URL; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; /** * 下载图片 */ public class WebDownloader { /** * 下载 * @param url * @param name */ public void download(String url,String name) { try { FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name)); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("不合法的url"); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.out.println("下载失败"); } } }- 继承Thread
public class TDownloader extends Thread { private String url; //远程路径 private String name; //存储名字 public TDownloader(String url, String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { WebDownloader wd =new WebDownloader(); wd.download(url, name); System.out.println(name); } public static void main(String[] args) { TDownloader td1 =new TDownloader("http://upload.news.cecb2b.com/2014/0511/1399775432250.jpg","phone.jpg"); TDownloader td2 =new TDownloader("http://p1.pstatp.com/large/403c00037462ae2eee13","spl.jpg"); TDownloader td3 =new TDownloader("http://5b0988e595225.cdn.sohucs.com/images/20170830/d8b57e0dce0d4fa29bd5ef014be663d5.jpeg","success.jpg"); //启动三个线程 td1.start(); td2.start(); td3.start(); } }- 实现Runnable
public class IDownloader implements Runnable{ private String url; //远程路径 private String name; //存储名字 public IDownloader(String url, String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public void run() { WebDownloader wd =new WebDownloader(); wd.download(url, name); System.out.println(name); } public static void main(String[] args) { IDownloader td1 =new IDownloader("http://upload.news.cecb2b.com/2014/0511/1399775432250.jpg","phone.jpg"); IDownloader td2 =new IDownloader("http://p1.pstatp.com/large/403c00037462ae2eee13","spl.jpg"); IDownloader td3 =new IDownloader("http://5b0988e595225.cdn.sohucs.com/images/20170830/d8b57e0dce0d4fa29bd5ef014be663d5.jpeg","success.jpg"); //启动三个线程 new Thread(td1).start(); new Thread(td2).start(); new Thread(td3).start(); } }- 实现Callable
import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.Future; /** * 了解创建线程的方式三: * * @author azzhu * */ public class CDownloader implements Callable<Boolean>{ private String url; //远程路径 private String name; //存储名字 public CDownloader(String url, String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public Boolean call() throws Exception { WebDownloader wd =new WebDownloader(); wd.download(url, name); System.out.println(name); return true; } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CDownloader cd1 =new CDownloader("http://upload.news.cecb2b.com/2014/0511/1399775432250.jpg","phone.jpg"); CDownloader cd2 =new CDownloader("http://p1.pstatp.com/large/403c00037462ae2eee13","spl.jpg"); CDownloader cd3 =new CDownloader("http://5b0988e595225.cdn.sohucs.com/images/20170830/d8b57e0dce0d4fa29bd5ef014be663d5.jpeg","success.jpg"); //创建执行服务: 线程池 ExecutorService ser=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); //提交执行: Future<Boolean> result1 =ser.submit(cd1) ; Future<Boolean> result2 =ser.submit(cd2) ; Future<Boolean> result3 =ser.submit(cd3) ; //获取结果: boolean r1 =result1.get(); boolean r2 =result1.get(); boolean r3 =result1.get(); System.out.println(r3); //关闭服务: ser.shutdownNow(); } }
2.3 线程的分类
线程分两类:
- user thread:用户线程
- daemon thread:守护线程。和主线程共死
守护线程:支持性工作,内存资源的回收、调度等。finally不能保证一定执行。【System.exit()】
形象理解:兔死狗烹,鸟尽弓藏
设置某个线程为守护线程:需要在线程启动之前设置
Java垃圾回收就是一个典型的守护线程。
myThread.setDaemon(true);
/**
* 守护线程:是为用户线程服务的;jvm停止不用等待守护线程执行完毕
* 默认:用户线程 jvm等待用户线程执行完毕才会停止
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class DaemonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
You you = new You();
Thread t =new Thread(god);
t.setDaemon(true);//将用户线程调整为守护
t.start();
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(int i=1;i<=365*100;i++) {
System.out.println("happy life...");
}
System.out.println("ooooo.....");
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for(;true;) {
System.out.println("bless you...");
}
}
}
public class OnlyMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//虚拟机线程管理的接口
ThreadMXBean threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
/*
[6] Monitor Ctrl-Break
[5] Attach Listener 负责获取当前主程序运行时相关的各种信息
[4] Signal Dispatcher 分发处理发给虚拟机信号的线程
[3] Finalizer 调用对象的finalize方法的线程
[2] Reference Handler 清除引用的线程
[1] main
* */
ThreadInfo[] threadInfos = threadMXBean.dumpAllThreads(false, false);
for (ThreadInfo threadInfo : threadInfos) {
System.out.println("["+threadInfo.getThreadId()+"]"+" "+threadInfo.getThreadName());
}
}
}
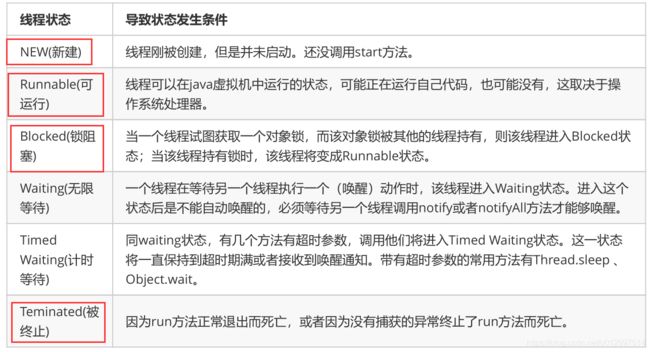
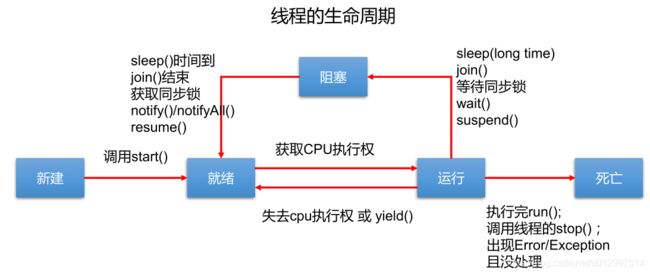
2.4 线程的状态/生命周期【高频面试】
public class Demo2 {
public static Thread thread1;
public static Demo2 obj;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 第一种状态切换 - 新建 -> 运行 -> 终止
System.out.println("#######第一种状态切换 - 新建 -> 运行 -> 终止################################");
Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("thread1当前状态:" + Thread.currentThread().getState().toString());
System.out.println("thread1 执行了");
}
});
System.out.println("没调用start方法,thread1当前状态:" + thread1.getState().toString());
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(2000L); // 等待thread1执行结束,再看状态
System.out.println("等待两秒,再看thread1当前状态:" + thread1.getState().toString());
// thread1.start(); TODO 注意,线程终止之后,再进行调用,会抛出IllegalThreadStateException异常
System.out.println();
System.out.println("############第二种:新建 -> 运行 -> 等待 -> 运行 -> 终止(sleep方式)###########################");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {// 将线程2移动到等待状态,1500后自动唤醒
Thread.sleep(1500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread2当前状态:" + Thread.currentThread().getState().toString());
System.out.println("thread2 执行了");
}
});
System.out.println("没调用start方法,thread2当前状态:" + thread2.getState().toString());
thread2.start();
System.out.println("调用start方法,thread2当前状态:" + thread2.getState().toString());
Thread.sleep(200L); // 主线程等待200毫秒,再看状态
System.out.println("等待200毫秒,再看thread2当前状态:" + thread2.getState().toString());
Thread.sleep(3000L); // 主线程再等待3秒,让thread2执行完毕,再看状态
System.out.println("等待3秒,再看thread2当前状态:" + thread2.getState().toString());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("############第三种:新建 -> 运行 -> 阻塞 -> 运行 -> 终止###########################");
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (Demo2.class) {
System.out.println("thread3当前状态:" + Thread.currentThread().getState().toString());
System.out.println("thread3 执行了");
}
}
});
synchronized (Demo2.class) {
System.out.println("没调用start方法,thread3当前状态:" + thread3.getState().toString());
thread3.start();
System.out.println("调用start方法,thread3当前状态:" + thread3.getState().toString());
Thread.sleep(200L); // 主线程等待200毫秒,再看状态
System.out.println("等待200毫秒,再看thread3当前状态:" + thread3.getState().toString());
}
Thread.sleep(3000L); // 主线程再等待3秒,让thread3执行完毕,再看状态
System.out.println("等待3秒,让thread3抢到锁,再看thread3当前状态:" + thread2.getState().toString());
}
}
2.5 线程同步/安全【高频面试】
2.5.1 问题引出
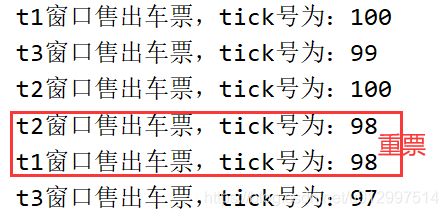
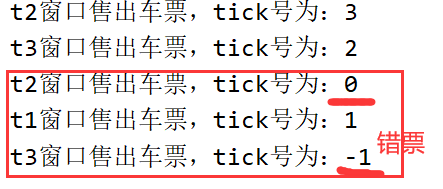
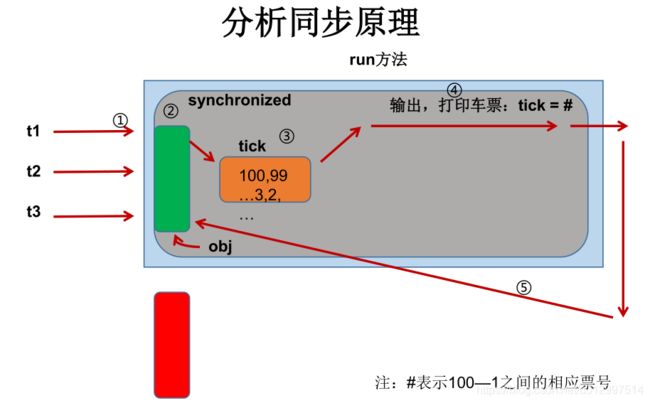
模拟火车站售票程序,开启三个窗口售票。
class Ticket implements Runnable {
private int tick = 100;
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (tick > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "售出车票,tick号为:" +tick--);
} else
break;
}
}
}
class TicketDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket t = new Ticket();
Thread t1 = new Thread(t);
Thread t2 = new Thread(t);
Thread t3 = new Thread(t);
t1.setName("t1窗口");
t2.setName("t2窗口");
t3.setName("t3窗口");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
-
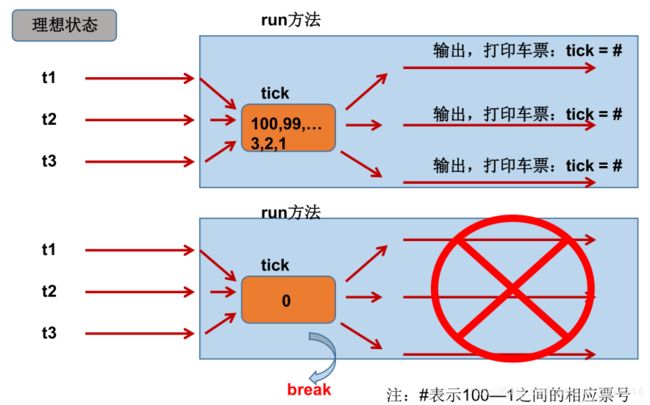
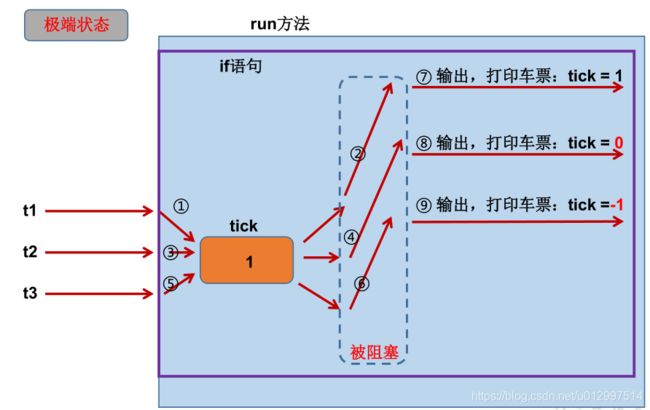
多线程出现了安全问题
-
问题的原因
当多条语句在操作同一个线程共享数据时,一个线程对多条语句只执行了一部分,还没有执行完,另一个线程参与进来执行。导致共享数据的错误。如果数据是每个线程独立拥有的,不会出现线程安全的问题。
-
解决方案:使用锁机制
对多条操作共享数据的语句,只能让一个线程都执行完,在执行过程中,其他线程不可以参与执行,即同步机制,使用锁。
synchronized:锁方法或代码块
lock接口:手动上锁和解锁 ReentrantLock类
2.5.2 同步方法
粒度【粗粒度】比较大,将整个方法锁起来
private synchronized void sellTicket() {
if(i > 0) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+"售出第:"+(50-i+1)+",还剩第:"+(--i));
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.5.3 同步代码块
在可能出现线程安全的代码块外,使用锁锁住,
synchronized(this获取其他任意对象),保证是一把锁对象锁
synchronized (Ticket.class) {}类锁
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000017766364 并发中的各种锁
synchronized (this) {
if(i > 0) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+"售出第:"+(50-i+1)+",还剩第:"+(--i));
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.5.4 Lock锁
- 从JDK 5.0开始,Java提供了更强大的线程同步机制——通过显式定义同步锁对象来实现同步。同步锁使用Lock对象充当。
- java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock接口是控制多个线程对共享资源进行访问的工具。锁提供了对共享资源的独占访问,每次只能有一个线程对Lock对象加锁,线程开始访问共享资源之前应先获得Lock对象。
- ReentrantLock 类实现了 Lock ,它拥有与 synchronized 相同的并发性和内存语义,在实现线程安全的控制中,比较常用的是ReentrantLock,可以显式加锁、释放锁。
//手动加锁+解锁
try {
lock.lock();
if(i > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+"售出第:"+(50-i+1)+",还剩第:"+(--i));
Thread.sleep(10);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
2.5.5 关于ArrayList的线程安全替代品
ArrayList线程不安全:
public class UnsafeTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) {
new Thread(()->{
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}) .start();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
加锁:
public class SynBlockTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) {
new Thread(()->{
//同步块
synchronized(list) {
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}) .start();
}
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
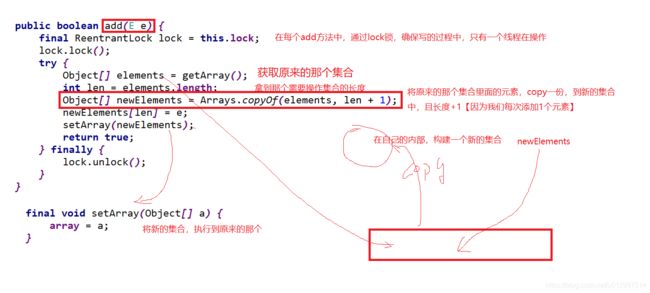
CopyOnWriteArrayList
以add方法的源码为例,我们发现,凡是涉及到关于写【增加、删除的操作】都加了lock锁【显示锁】:
public boolean add(E e) { final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; //lock锁 lock.lock(); try { Object[] elements = getArray(); int len = elements.length; Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1); newElements[len] = e; setArray(newElements); return true; } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
public class SynContainer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++) {
new Thread(()->{
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}) .start();
}
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
你能说一说CopyOnWriteArrayList的原理吗?
参照:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/84485589
2.5.6 单例设计模式之懒汉式( 线程安全)
class Singleton {
//没有volatile其他线程可能访问一个没有初始化的对象
private static volatile Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
//再次检测,避免不必要的同步 ,已经存在对象
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (instance == null) {
//1、开辟空间 //2、初始化对象信息 //3、返回对象的地址给引用
instance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
}
public class SingletonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton s1 = Singleton.getInstance();
Singleton s2 = Singleton.getInstance();
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
}
}
2.5.7 线程的死锁问题
- 死锁
- 不同的线程分别占用对方需要的同步资源不放弃,都在等待对方放弃自己需要的同步资源,就形成了线程的死锁
- 出现死锁后,不会出现异常,不会出现提示,只是所有的线程都处于阻塞状态,无法继续
- 解决方法
- 专门的算法、原则
- 尽量减少同步资源的定义
- 尽量避免嵌套同步
class A {
public synchronized void foo(B b) {
System.out.println("当前线程名: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " 进入了A实例的foo方法"); // ①
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("当前线程名: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " 企图调用B实例的last方法"); // ③
b.last();
}
public synchronized void last() {
System.out.println("进入了A类的last方法内部");
}
}
class B {
public synchronized void bar(A a) {
System.out.println("当前线程名: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " 进入了B实例的bar方法"); // ②
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("当前线程名: " + Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ " 企图调用A实例的last方法"); // ④
a.last();
}
public synchronized void last() {
System.out.println("进入了B类的last方法内部");
}
}
public class DeadLock implements Runnable {
A a = new A();
B b = new B();
public void init() {
Thread.currentThread().setName("主线程");
// 调用a对象的foo方法
a.foo(b);
System.out.println("进入了主线程之后");
}
public void run() {
Thread.currentThread().setName("副线程");
// 调用b对象的bar方法
b.bar(a);
System.out.println("进入了副线程之后");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeadLock dl = new DeadLock();
new Thread(dl).start();
dl.init();
}
}
C:\Users\Administrator>jps
13872 KotlinCompileDaemon
724
12008 RemoteMavenServer
14104 DeadLock
13692 Jps
7852 NailgunRunner
C:\Users\Administrator>jstack -l 14104
2020-06-14 22:29:38
Full thread dump Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (25.131-b11 mixed mode):
"副线程" #12 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000002847a800 nid=0x32a0 waiting for monitor entry [0x00000000291cf000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at cn.azzhu.A.last(DeadLock.java:18)
- waiting to lock <0x000000071628e238> (a cn.azzhu.A)
at cn.azzhu.B.bar(DeadLock.java:33)
- locked <0x00000007162905e8> (a cn.azzhu.B)
at cn.azzhu.DeadLock.run(DeadLock.java:55)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"Service Thread" #11 daemon prio=9 os_prio=0 tid=0x00000000283b6800 nid=0xdb8 runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C1 CompilerThread3" #10 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000002830a000 nid=0x3a54 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread2" #9 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x00000000282dd800 nid=0x36b4 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread1" #8 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x00000000281ef000 nid=0x24d8 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread0" #7 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x00000000281ee800 nid=0x36b0 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Monitor Ctrl-Break" #6 daemon prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x00000000282ab800 nid=0x2264 runnable [0x0000000028ace000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
at java.net.SocketInputStream.socketRead0(Native Method)
at java.net.SocketInputStream.socketRead(SocketInputStream.java:116)
at java.net.SocketInputStream.read(SocketInputStream.java:171)
at java.net.SocketInputStream.read(SocketInputStream.java:141)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamDecoder.readBytes(StreamDecoder.java:284)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamDecoder.implRead(StreamDecoder.java:326)
at sun.nio.cs.StreamDecoder.read(StreamDecoder.java:178)
- locked <0x00000007164e3660> (a java.io.InputStreamReader)
at java.io.InputStreamReader.read(InputStreamReader.java:184)
at java.io.BufferedReader.fill(BufferedReader.java:161)
at java.io.BufferedReader.readLine(BufferedReader.java:324)
- locked <0x00000007164e3660> (a java.io.InputStreamReader)
at java.io.BufferedReader.readLine(BufferedReader.java:389)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.application.AppMainV2$1.run(AppMainV2.java:64)
"Attach Listener" #5 daemon prio=5 os_prio=2 tid=0x0000000027b65800 nid=0x1b58 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Signal Dispatcher" #4 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x0000000027b0c000 nid=0x231c runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Finalizer" #3 daemon prio=8 os_prio=1 tid=0x0000000002c9d800 nid=0x1740 in Object.wait() [0x0000000027fcf000]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0x0000000715f88ec8> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:143)
- locked <0x0000000715f88ec8> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:164)
at java.lang.ref.Finalizer$FinalizerThread.run(Finalizer.java:209)
"Reference Handler" #2 daemon prio=10 os_prio=2 tid=0x0000000002c9c000 nid=0xb34 in Object.wait() [0x0000000027acf000]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0x0000000715f86b68> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Object.java:502)
at java.lang.ref.Reference.tryHandlePending(Reference.java:191)
- locked <0x0000000715f86b68> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.Reference$ReferenceHandler.run(Reference.java:153)
"主线程" #1 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000000243c800 nid=0x1184 waiting for monitor entry [0x00000000029ef000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at cn.azzhu.B.last(DeadLock.java:37)
- waiting to lock <0x00000007162905e8> (a cn.azzhu.B)
at cn.azzhu.A.foo(DeadLock.java:14)
- locked <0x000000071628e238> (a cn.azzhu.A)
at cn.azzhu.DeadLock.init(DeadLock.java:48)
at cn.azzhu.DeadLock.main(DeadLock.java:62)
"VM Thread" os_prio=2 tid=0x0000000025c0a000 nid=0x2f9c runnable
"GC task thread#0 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bbb800 nid=0x38c4 runnable
"GC task thread#1 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bbd000 nid=0x3b1c runnable
"GC task thread#2 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bbe800 nid=0x3960 runnable
"GC task thread#3 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bc1000 nid=0x38ec runnable
"GC task thread#4 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bc3000 nid=0x3a00 runnable
"GC task thread#5 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bc4800 nid=0x3860 runnable
"GC task thread#6 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bc7800 nid=0x2d58 runnable
"GC task thread#7 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bc8800 nid=0x3614 runnable
"VM Periodic Task Thread" os_prio=2 tid=0x000000002830c800 nid=0x17c4 waiting on condition
JNI global references: 33
Found one Java-level deadlock:
=============================
"副线程":
waiting to lock monitor 0x0000000025c13588 (object 0x000000071628e238, a cn.azzhu.A),
which is held by "主线程"
"主线??":
waiting to lock monitor 0x0000000025c12038 (object 0x00000007162905e8, a cn.azzhu.B),
which is held by "副线程"
Java stack information for the threads listed above:
===================================================
"副线程":
at cn.azzhu.A.last(DeadLock.java:18)
- waiting to lock <0x000000071628e238> (a cn.azzhu.A)
at cn.azzhu.B.bar(DeadLock.java:33)
- locked <0x00000007162905e8> (a cn.azzhu.B)
at cn.azzhu.DeadLock.run(DeadLock.java:55)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"主线???":
at cn.azzhu.B.last(DeadLock.java:37)
- waiting to lock <0x00000007162905e8> (a cn.azzhu.B)
at cn.azzhu.A.foo(DeadLock.java:14)
- locked <0x000000071628e238> (a cn.azzhu.A)
at cn.azzhu.DeadLock.init(DeadLock.java:48)
at cn.azzhu.DeadLock.main(DeadLock.java:62)
Found 1 deadlock. //说明发现了死锁
/**
* 死锁: 过多的同步可能造成相互不释放资源
* 从而相互等待,一般发生于同步中持有多个对象的锁
*
* 避免: 不要在同一个代码块中,同时持有多个对象的锁
*
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Markup g1 = new Markup(1,"张柏芝");
Markup g2 = new Markup(0,"王菲");
g1.start();
g2.start();
}
}
//口红
class Lipstick{
}
//镜子
class Mirror{
}
//化妆
class Markup extends Thread{
static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
//选择
int choice;
//名字
String girl;
public Markup(int choice,String girl) {
this.choice = choice;
this.girl = girl;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//化妆
markup();
}
//相互持有对方的对象锁-->可能造成死锁
private void markup() {
if(choice==0) {
synchronized(lipstick) { //获得口红的锁
System.out.println(this.girl+"涂口红");
//1秒后想拥有镜子的锁
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*
synchronized(mirror) {
System.out.println(this.girl+"照镜子");
}*/
}
synchronized(mirror) {
System.out.println(this.girl+"照镜子");
}
}else {
synchronized(mirror) { //获得镜子的锁
System.out.println(this.girl+"照镜子");
//2秒后想拥有口红的锁
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/*
synchronized(lipstick) {
System.out.println(this.girl+"涂口红");
} */
}
synchronized(lipstick) {
System.out.println(this.girl+"涂口红");
}
}
}
}
2.5.8 synchronized VS Lock
- Lock是显式锁(手动开启和关闭锁,别忘记关闭锁),synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
- Lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
- 使用Lock锁,JVM将花费较少的时间来调度线程,性能更好。并且具有更好的扩展性(提供更多的子类)
synchronized代码简洁,性能较开始有了很大提示
Lock:获取锁可以被中断,超时获取锁,尝试获取锁;读多写少用读写锁
除非有上述3中需求,否则尽量使用synchronized
优先使用顺序:Lock → 同步代码块(已经进入了方法体,分配了相应资源) → 同步方法
(在方法体之外)
2.5.9 ConcurrentHashMap
略
2.5.10 线程安全案例补充
-
快乐火车票
public class Happy12306 { public static void main(String[] args) { Web12306 c = new Web12306(4,"happy sxt"); new Passenger(c,"老高",2).start(); new Passenger(c,"老裴",1).start(); } } //顾客 class Passenger extends Thread{ int seats; public Passenger(Runnable target,String name,int seats) { super(target,name); this.seats = seats; } } //火车票网 class Web12306 implements Runnable{ int available; //可用的位置 String name; //名称 public Web12306(int available, String name) { this.available = available; this.name = name; } public void run() { Passenger p = (Passenger)Thread.currentThread(); boolean flag = this.bookTickets(p.seats); if(flag) { System.out.println("出票成功"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-<位置为:"+p.seats); }else { System.out.println("出票失败"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-<位置不够"); } } //购票 public synchronized boolean bookTickets(int seats) { System.out.println("可用位置为:"+available); if(seats>available) { return false; } available -=seats; return true; } } -
快乐影院
public class HappyCinema { public static void main(String[] args) { Cinema c = new Cinema(2,"happy sxt"); new Thread(new Customer(c,2),"老高").start(); new Thread(new Customer(c,1),"老裴").start(); } } //顾客 class Customer implements Runnable{ Cinema cinema; int seats; public Customer(Cinema cinema, int seats) { this.cinema = cinema; this.seats = seats; } @Override public void run() { synchronized(cinema) { boolean flag = cinema.bookTickets(seats); if(flag) { System.out.println("出票成功"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-<位置为:"+seats); }else { System.out.println("出票失败"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-<位置不够"); } } } } //影院 class Cinema{ int available; //可用的位置 String name; //名称 public Cinema(int available, String name) { this.available = available; this.name = name; } //购票 public boolean bookTickets(int seats) { System.out.println("可用位置为:"+available); if(seats>available) { return false; } available -=seats; return true; } }public class HappyCinema2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //可用位置 List<Integer> available =new ArrayList<Integer>(); available.add(1); available.add(2); available.add(3); available.add(6); available.add(7); //顾客需要的位置 List<Integer> seats1 =new ArrayList<Integer>(); seats1.add(1); seats1.add(2); List<Integer> seats2 =new ArrayList<Integer>(); seats2.add(3); seats2.add(6); SxtCinema c = new SxtCinema(available,"happy sxt"); new Thread(new HappyCustomer(c,seats1),"老高").start(); new Thread(new HappyCustomer(c,seats2),"老裴").start(); } } //顾客 class HappyCustomer implements Runnable{ SxtCinema cinema; List<Integer> seats; public HappyCustomer(SxtCinema cinema, List<Integer> seats) { this.cinema = cinema; this.seats = seats; } @Override public void run() { synchronized(cinema) { boolean flag = cinema.bookTickets(seats); if(flag) { System.out.println("出票成功"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-<位置为:"+seats); }else { System.out.println("出票失败"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-<位置不够"); } } } } //影院 class SxtCinema{ List<Integer> available; //可用的位置 String name; //名称 public SxtCinema(List<Integer> available, String name) { this.available = available; this.name = name; } //购票 public boolean bookTickets(List<Integer> seats) { System.out.println("欢迎光临"+this.name+",当前可用位置为:"+available); List<Integer> copy = new ArrayList<Integer>(); copy.addAll(available); //相减 copy.removeAll(seats); //判断大小 if(available.size()-copy.size() !=seats.size()) { return false; } //成功 available = copy; return true; } } -
模拟取款
账户类
class Account{ int money; //金额 String name; //名称 public Account(int money, String name) { this.money = money; this.name = name; } }/** * 线程安全: 在并发时保证数据的正确性、效率尽可能高 * synchronized * 1、同步方法 * 2、同步块 ,目标更明确 * @author azzhu * */ public class SynBlockTest01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //账户 Account account =new Account(1000,"结婚礼金"); SynDrawing you = new SynDrawing(account,80,"可悲的你"); SynDrawing wife = new SynDrawing(account,90,"happy的她"); you.start(); wife.start(); } } //模拟取款 线程安全 class SynDrawing extends Thread{ Account account ; //取钱的账户 int drawingMoney ;//取的钱数 int packetTotal ; //口袋的总数 public SynDrawing(Account account, int drawingMoney,String name) { super(name); this.account = account; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } @Override public void run() { test() ; } //目标锁定account public void test() { //提高性能 if(account.money<=0) { return ; } //同步块 synchronized(account) { if(account.money -drawingMoney<0) { return; } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } account.money -=drawingMoney; packetTotal +=drawingMoney; System.out.println(this.getName()+"-->账户余额为:"+account.money); System.out.println(this.getName()+"-->口袋的钱为:"+packetTotal); } } }/** * 线程安全: 在并发时保证数据的正确性、效率尽可能高 * synchronized * 1、同步方法 * 2、同步块 * @author azzhu * */ public class SynTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //账户 Account account =new Account(100,"结婚礼金"); SafeDrawing you = new SafeDrawing(account,80,"可悲的你"); SafeDrawing wife = new SafeDrawing(account,90,"happy的她"); you.start(); wife.start(); } } //模拟取款 class SafeDrawing extends Thread{ Account account ; //取钱的账户 int drawingMoney ;//取的钱数 int packetTotal ; //口袋的总数 public SafeDrawing(Account account, int drawingMoney,String name) { super(name); this.account = account; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } @Override public void run() { } //目标不对锁定失败 这里不是锁this 应该锁定 account public synchronized void test() { if(account.money -drawingMoney<0) { return; } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } account.money -=drawingMoney; packetTotal +=drawingMoney; System.out.println(this.getName()+"-->账户余额为:"+account.money); System.out.println(this.getName()+"-->口袋的钱为:"+packetTotal); } }/** * 线程不安全:取钱 * * @author azzhu * */ public class UnsafeTest02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //账户 Account account =new Account(100,"结婚礼金"); Drawing you = new Drawing(account,80,"可悲的你"); Drawing wife = new Drawing(account,90,"happy的她"); you.start(); wife.start(); } } //模拟取款 class Drawing extends Thread{ Account account ; //取钱的账户 int drawingMoney ;//取的钱数 int packetTotal ; //口袋的总数 public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney,String name) { super(name); this.account = account; this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney; } @Override public void run() { if(account.money -drawingMoney<0) { return; } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } account.money -=drawingMoney; packetTotal +=drawingMoney; System.out.println(this.getName()+"-->账户余额为:"+account.money); System.out.println(this.getName()+"-->口袋的钱为:"+packetTotal); } }
2.6 线程的常用方法
yield vs join
①yield方法:礼让,但是不一定成功;join,强行插队
②yield是static方法,调用方式
Thread.yield,而join非静态方法
2.6.1 yeild
- 暂停当前正在执行的线程,把执行机会让给优先级相同或更高的线程
- 若队列中没有同优先级的线程,忽略此方法,即这个时候当前线程就会马上恢复执行!
public class YieldDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield my =new MyYield();
new Thread(my,"a").start();
new Thread(my,"b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->start");
Thread.yield(); //礼让
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->end");
}
}
public class YieldDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.println("lambda...."+i);
}
}) .start();
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
if(i%20==0) {
Thread.yield(); //main礼让
}
System.out.println("main...."+i);
}
}
}
2.6.2 sleep
静态方法,单位是毫秒
①sleep与锁无关,线程睡眠到期自动苏醒,并返回到Runnable(可运行)状态
②sleep()中指定的时间是线程不会运行的最短时间。因此,sleep()方法不能保证该线程睡眠到期后就
开始立刻执行【要看CPU是否立即调度到】
③令当前活动线程在指定时间段内放弃对CPU控制,使其他线程有机会被执行,时间到后重排队。
模拟倒计时:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* sleep模拟倒计时
*
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class BlockedSleep03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//倒计时
Date endTime=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()+1000*10);
long end = endTime.getTime();
while(true) {
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss").format(endTime));
Thread.sleep(1000);
endTime=new Date(endTime.getTime()-1000);
if(end-10000 >endTime.getTime() ) {
break;
}
}
}
public static void test() throws InterruptedException {
//倒数10个数,1秒一个
int num = 10;
while(true) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
}
}
}
模拟休息:
/**
* sleep模拟休息
*
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class BlockedSleep02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Racer racer = new Racer();
new Thread(racer,"tortoise").start();
new Thread(racer,"rabbit").start();
}
}
class Racer implements Runnable{
private String winner;//胜利者
@Override
public void run() {
for(int steps =1;steps<=100;steps++) {
//模拟休息
if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("rabbit") && steps%10==0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+steps);
//比赛是否结束
boolean flag = gameOver(steps);
if(flag) {
break;
}
}
}
private boolean gameOver(int steps) {
if(winner!=null) { //存在胜利者
return true;
}else {
if(steps ==100) {
winner = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("winner==>"+winner);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
模拟网络延迟:
/**
* sleep模拟网络延时,放大了发生问题的可能性
*
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class BlockedSleep01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//一份资源
Web12306 web =new Web12306();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
//多个代理
new Thread(web,"码畜").start();
new Thread(web,"码农").start();
new Thread(web,"码蟥").start();;
}
}
class Web12306 implements Runnable{
//票数
private int ticketNums = 99;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true) {
if(ticketNums<0) {
break;
}
//模拟延时
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+ticketNums--);
}
}
}
2.6.3 join
哪个线程调用join方法,会阻塞其他线程,让当前线程执行完之后,再执行其他【强行插队,面试】
用处:线程A,执行了线程B的join方法,线程A必须要等待B执行完成了以后,线程A才能继续自己的工作。
public class UseJoin {
static class JumpQueue implements Runnable {
private Thread thread; //用来插队的线程
public JumpQueue(Thread thread) {
this.thread = thread;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
thread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" terminated..");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread previous = Thread.currentThread(); //主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//i=0,previous是主线程;i=1,previous是i=0这个线程
Thread thread = new Thread(new JumpQueue(previous),String.valueOf(i));
System.out.println(previous.getName()+" jump a queue the thread:"+thread.getName());
thread.start();
previous = thread;
}
//休眠2秒
SleepTools.second(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" terminated...");
}
}
public class BlockedJoin01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t=new Thread(()->{
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.println("lambda...."+i);
}
});
t.start();
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
if(i==20) {
t.join(); //插队 main被阻塞了
}
System.out.println("main...."+i);
}
}
}
public class BlockedJoin02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("爸爸和儿子买烟的故事");
new Thread(new Father()).start();
}
}
class Father extends Thread{
public void run() {
System.out.println("想抽烟,发现没了");
System.out.println("让儿子去买中华");
Thread t =new Thread(new Son());
t.start();
try {
t.join(); //father被阻塞
System.out.println("老爸接过烟,把零钱给了儿子");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("孩子走丢了,老爸出去找孩子了。。。");
}
}
}
class Son extends Thread{
public void run() {
System.out.println("接过老爸的钱出去了。。。");
System.out.println("路边有个游戏厅,玩了10秒");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
System.out.println(i+"秒过去了...");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("赶紧买烟去。。。。");
System.out.println("手拿一包中华回家了。。。。");
}
}
2.6.4 优先级
setPriority(1-10):设置优先级,只保证优先执行的概率,并不一定就优先,默认是5,最小是1,最大是10
设置的值,必须在1-10之间,否则会抛出IllegalArgumentException
优先级高的线程分配时间片的数量高于优先级低的线程
2.6.5 其他方法
Thread.currentThread.getName()/getId():获取线程名称或者idpublic State getState():获取线程的状态public final native boolean isAlive():判断线程是否存活public final boolean isDaemon():判断是否是守护线程
2.6.6 调用yield()、sleep()、wait()、notify()等方法对锁有何影响
面试点
- 线程在执行yield()以后,持有的锁是不释放的
- sleep()方法被调用以后,持有的锁是不释放的
- 调用方法之前,必须要持有锁,调用了wait()方法以后,锁就会被释放,当wait()方法返回的时候,线程会重新持有锁
- 调用方法之前,必须要持有锁,调用notify()方法本身不会释放锁
2.7 如何终止线程
①stop():过时,不建议使用,因为,使用stop,即使你的操作中加上了synchronized,也可能导致数据的不一致性
②interrupt():中断线程
③可以使用标记思想去实现
/**
* 终止线程
* 1、线程正常执行完毕-->次数
* 2、外部干涉 -->加入标识
* 不要使用stop destroy
*
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class TerminateThread implements Runnable {
//1、加入标识 标记线程体是否可以运行
private boolean flag = true;
private String name;
public TerminateThread(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
//2、关联标识,true-->运行 false -->停止
while(flag) {
System.out.println(name+"-->"+i++);
}
}
//3、对外提供方法改变标识
public void terminate() {
this.flag = false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TerminateThread tt = new TerminateThread("C罗");
new Thread(tt).start();
for(int i=0;i<=99;i++) {
if(i==88) {
tt.terminate();//线程的终止
System.out.println("tt game over");
}
System.out.println("main-->"+i);
}
}
}
isInterrupted:线程若已经被中断,返回true,否则返回false
interrupted:判断当前线程是否处于中断状态,我们可以根据true,false去执行业务,这个方法是一个静态方法,实际上还是调用了isInterrupted方法,源码如下
public static boolean interrupted() {
return currentThread().isInterrupted(true);
}
public class StopThread extends Thread {
private int i = 0, j = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this) {
// 增加同步锁,确保线程安全
++i;
try {
// 休眠10秒,模拟耗时操作
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
++j;
}
}
/** * 打印i和j */
public void print() {
System.out.println("i=" + i + " j=" + j);
}
}
/**
* 示例3 - 线程stop强制性中止,破坏线程安全的示例
*/
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
StopThread thread = new StopThread();
thread.start();
// 休眠1秒,确保i变量自增成功
Thread.sleep(1000);
// 暂停线程
//thread.stop(); // 错误的终止
thread.interrupt(); // 正确终止
while (thread.isAlive()) {
// 确保线程已经终止
} // 输出结果
thread.print();
}
}
/** 通过状态位来判断 */
public class Demo4 extends Thread {
public volatile static boolean flag = true;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (flag) { // 判断是否运行
System.out.println("运行中");
Thread.sleep(1000L);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
// 3秒之后,将状态标志改为False,代表不继续运行
Thread.sleep(3000L);
flag = false;
System.out.println("程序运行结束");
}
}
3. 等待唤醒机制【掌握原理】
【面试】使用两个线程实现奇数和偶数的交替打印或者实现ABAB…打印
thread-0 1/A
thread-1 2/B
…
涉及到的知识点:锁、等待(wait())、唤醒机制(notify()、notifyAll())
public class ThreadTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Counter counter = new Counter();
new Thread(new PrintOdd(counter)).start();
new Thread(new PrintEven(counter)).start();
}
}
class Counter {
public int value = 1;
public boolean odd = true;
}
class PrintOdd implements Runnable {
public Counter counter;
public PrintOdd(Counter counter) {
this.counter = counter;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter.value <= 100) {
synchronized(counter) {
if (counter.odd) {
System.out.println(counter.value);
counter.value++;
counter.odd = !counter.odd;
//很重要,要去唤醒打印偶数的线程
counter.notify();
}
try {
counter.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
}
}
}
class PrintEven implements Runnable {
public Counter counter;
public PrintEven(Counter counter) {
this.counter = counter;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (counter.value <= 100) {
synchronized (counter) {
if (!counter.odd) {
System.out.println(counter.value);
counter.value++;
counter.odd = !counter.odd;
counter.notify();
}
try {
counter.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {}
}
}
}
}
public class Main{
static class Word {
String s;
public Word(String a) {
s = a;
}
public void setS (String a) {
s = a;
}
public String getS() {
return s;
}
}
static int i = 0;
static Word s = new Word("A");
public static void main(String[] args) {
//A线程
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (i < 100) {
synchronized (s) {
if (s.getS().equals("B")) {
try {
s.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(s.getS());
s.setS("B");
i++;
s.notify();
}
}
}
}
});
//B线程
Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (i < 100) {
synchronized (s) {
if (s.getS().equals("A")) {
try {
s.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println(s.getS());
s.setS("A");
i++;
s.notify();
}
}
}
}
});
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
练习:使用两个线程印 打印 1-100 。线程1, 线程2
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Communication comm = new Communication();
new Thread(comm).start();
new Thread(comm).start();
}
}
class Communication implements Runnable {
int i = 1;
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (this) {
notify();
if (i <= 100) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
":" + i++);
} else
break;
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3.1 线程通讯
概念:多个线程在处理同一个资源,但是处理的动作(线程的任务)却不相同。
比如:线程A用来生产包子的,线程B用来吃包子的,包子可以理解为同一资源,线程A与线程B处理的动作,一个是生产,一个是消费,那么线程A与线程B之间就存在线程通信问题
为什么要处理线程间通信:
多个线程并发执行时, 在默认情况下CPU是随机切换线程的,当我们需要多个线程来共同完成一件任务,并且我们
希望他们有规律的执行, 那么多线程之间需要一些协调通信,以此来帮我们达到多线程共同操作一份数据。
如何保证线程间通信有效利用资源:
多个线程在处理同一个资源,并且任务不同时,需要线程通信来帮助解决线程之间对同一个变量的使用或操作。 就是多个线程在操作同一份数据时, 避免对同一共享变量的争夺。也就是我们需要通过一定的手段使各个线程能有效的利用资源。而这种手段即—— 等待唤醒机制。
3.2 等待唤醒机制
什么是等待唤醒机制
这是多个线程间的一种协作机制。谈到线程我们经常想到的是线程间的竞争(race),比如去争夺锁,但这并不是故事的全部,线程间也会有协作机制。就好比在公司里你和你的同事们,你们可能存在在晋升时的竞争,但更多时候你们更多是一起合作以完成某些任务。
就是在一个线程进行了规定操作后,就进入等待状态(wait()), 等待其他线程执行完他们的指定代码过后 再将其唤醒(notify());在有多个线程进行等待时, 如果需要,可以使用 notifyAll()来唤醒所有的等待线程。
wait/notify 就是线程间的一种协作机制。
等待唤醒中的方法
等待唤醒机制就是用于解决线程间通信的问题的,使用到的3个方法的含义如下:
wait:线程不再活动,不再参与调度,进入wait set中,因此不会浪费 CPU 资源,也不会去竞争锁了,这时的线程状态即是 WAITING。它还要等着别的线程执行一个特别的动作,也即是“通知(notify)”在这个对象上等待的线程从wait set 中释放出来,重新进入到调度队列(ready queue)中
-
notify:则选取所通知对象的 wait set 中的一个线程释放;例如,餐馆有空位置后,等候就餐最久的顾客最先入座。 -
notifyAll:则释放所通知对象的 wait set 上的全部线程。
调用wait和notify方法需要注意的细节
- wait方法与notify方法必须要由同一个锁对象调用。因为:对应的锁对象可以通过notify唤醒使用同一个锁对象调用的wait方法后的线程。
- wait方法与notify方法是属于Object类的方法的。因为:锁对象可以是任意对象,而任意对象的所属类都是继承了Object类的。
- wait方法与notify/notifyAll方法必须要在同步代码块或者是同步方法中使用。因为:必须要通过锁对象调用这2个方法。
3.3 生产者与消费者问题
等待唤醒机制其实就是经典的“生产者与消费者”的问题。
就拿生产包子消费包子来说等待唤醒机制如何有效利用资源:
包子铺线程生产包子,吃货线程消费包子。当包子没有时(包子状态为false),吃货线程等待,包子铺线程生产包子
(即包子状态为true),并通知吃货线程(解除吃货的等待状态),因为已经有包子了,那么包子铺线程进入等待状态。
接下来,吃货线程能否进一步执行则取决于锁的获取情况。如果吃货获取到锁,那么就执行吃包子动作,包子吃完(包
子状态为false),并通知包子铺线程(解除包子铺的等待状态),吃货线程进入等待。包子铺线程能否进一步执行则取
决于锁的获取情况。
package test03;
/**
* 生产者和消费者问题
*
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-12-24 15:56:15
*/
public class pc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//等待唤醒案例
BaoZi bz = new BaoZi();
ChiHuo ch = new ChiHuo("吃货",bz);
BaoZiPu bzp = new BaoZiPu("包子铺",bz);
ch.start();
bzp.start();
}
}
//共享资源
class BaoZi {
String pier;
String xianer;
boolean flag = false;//包子资源 是否存在 包子资源状态
}
//消费者
class ChiHuo extends Thread {
private BaoZi bz;
public ChiHuo(String name, BaoZi bz) {
super(name);
this.bz = bz;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
synchronized (bz) {
if (!bz.flag) {//没包子
try {
bz.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("吃货正在吃" + bz.pier + bz.xianer + "包子");
bz.flag = false;
bz.notify();
}
}
}
}
//生产者
class BaoZiPu extends Thread {
//操作的资源
private BaoZi bz;
public BaoZiPu(String name, BaoZi bz) {
super(name);
this.bz = bz;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int count = 0;
//造包子
while (true) {
//同步
synchronized (bz) {
if (bz.flag) {//包子资源 存在
try {
//生产者等待
bz.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 没有包子 造包子
System.out.println("包子铺开始做包子");
if (count % 2 == 0) {
// 冰皮 五仁
bz.pier = "冰皮";
bz.xianer = "五仁";
} else {
// 薄皮 牛肉大葱
bz.pier = "薄皮";
bz.xianer = "牛肉大葱";
}
count++;
//修改状态
bz.flag = true;
System.out.println("包子造好了:" + bz.pier + bz.xianer);
System.out.println("吃货来吃吧");
//唤醒等待线程 (吃货)
bz.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
3.4 练习
3.4.1 生产产品
- 生产者(Productor)将产品交给店员(Clerk),而消费者(Customer)从店员处取走产品,店员一次只能持有固定数量的产品(比如:20),如果生产者试图生产更多的产品,店员会叫生产者停一下,如果店中有空位放产品了再通知生产者继续生产;如果店中没有产品了,店员会告诉消费者等一下,如果店中有产品了再通知消费者来取走产品。
- 这里可能出现两个问题:
- 生产者比消费者快时,消费者会漏掉一些数据没有取到。
- 消费者比生产者快时,消费者会取相同的数据。
售货员类:
class Clerk { // 售货员
private int product = 0;
public synchronized void addProduct() {
if (product >= 20) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
product++;
System.out.println("生产者生产了第" + product + "个产品");
notifyAll();
}
}
public synchronized void getProduct() {
if (this.product <= 0) {
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} else {
System.out.println("消费者取走了第" +
product + "个产品");
product--;
notifyAll();
}
}
}
生产者类:
class Productor implements Runnable { // 生产者
Clerk clerk;
public Productor(Clerk clerk) {
this.clerk = clerk;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("生产者开始生产产品");
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep((int) Math.random() * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
clerk.addProduct();
}
}
}
消费者类:
class Consumer implements Runnable { // 消费者
Clerk clerk;
public Consumer(Clerk clerk) {
this.clerk = clerk;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("消费者开始取走产品");
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep((int) Math.random() * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
clerk.getProduct();
}
}
}
测试类:
public class ProductTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Clerk clerk = new Clerk();
Thread productorThread = new Thread(new Productor(clerk));
Thread consumerThread = new Thread(new Consumer(clerk));
productorThread.start();
consumerThread.start();
}
}
3.4.2 模拟银行取钱
1.定义一个Account类
1)该Account类封装了账户编号(String)和余额(double)两个属性
2)设置相应属性的getter和setter方法
3)提供无参和有两个参数的构造器
4)系统根据账号判断与用户是否匹配,需提供hashCode()和equals()方法的重写
2.提供两个取钱的线程类:小明、小明’s wife
1)提供了Account类的account属性和double类的取款额的属性
2)提供带线程名的构造器
3)run()方法中提供取钱的操作
3.在主类中创建线程进行测试。考虑线程安全问题。
Account类:
class Account {
private String accountId;
private double balance;
public Account() {
}
public Account(String accountId, double balance) {
this.accountId = accountId;
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getAccountId() {
return accountId;
}
public void setAccountId(String accountId) {
this.accountId = accountId;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public String toString() {
return "Account [accountId=" + accountId + ",balance=" + balance + "]";
}
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((accountId == null) ? 0 :
accountId.hashCode());
long temp;
temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(balance);
result = prime * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>>
32));
return result;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Account other = (Account) obj;
if (accountId == null) {
if (other.accountId != null)
return false;
} else if (!accountId.equals(other.accountId))
return false;
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(balance) !=
Double.doubleToLongBits(other.balance))
return false;
return true;
}
}
取款线程:
class WithDrawThread extends Thread {
Account account;
// 要取款的额度
double withDraw;
public WithDrawThread(String name, Account account, double amt) {
super(name);
this.account = account;
this.withDraw = amt;
}
public void run() {
synchronized (account) {
if (account.getBalance() > withDraw) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":取款成功,取现的金额为:" + withDraw);
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
account.setBalance(account.getBalance() - withDraw);
} else {
System.out.println("取现额度超过账户余额,取款失败");
}
System.out.println("现在账户的余额为:" + account.getBalance());
}
}
}
测试类:
public class WithDrawThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account("1234567", 10000);
Thread t1 = new WithDrawThread("小明", account, 8000);
Thread t2 = new WithDrawThread("小明's wife", account, 2800);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
3.5 案例补充
3.5.1 管程法
/**
* 协作模型:生产者消费者实现方式一:管程法
* 借助缓冲区
*
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class CoTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SynContainer container = new SynContainer();
new Productor(container).start();
new Consumer(container).start();
}
}
//生产者
class Productor extends Thread{
SynContainer container ;
public Productor(SynContainer container) {
this.container = container;
}
public void run() {
//生产
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.println("生产-->"+i+"个馒头");
container.push(new Steamedbun(i) );
}
}
}
//消费者
class Consumer extends Thread{
SynContainer container ;
public Consumer(SynContainer container) {
this.container = container;
}
public void run() {
//消费
for(int i=0;i<100;i++) {
System.out.println("消费-->"+container.pop().id+"个馒头");
}
}
}
//缓冲区
class SynContainer{
Steamedbun[] buns = new Steamedbun[10]; //存储容器
int count = 0; //计数器
//存储 生产
public synchronized void push(Steamedbun bun) {
//何时能生产 容器存在空间
//不能生产 只有等待
if(count == buns.length) {
try {
this.wait(); //线程阻塞 消费者通知生产解除
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
//存在空间 可以生产
buns[count] = bun;
count++;
//存在数据了,可以通知消费了
this.notifyAll();
}
//获取 消费
public synchronized Steamedbun pop() {
//何时消费 容器中是否存在数据
//没有数据 只有等待
if(count == 0) {
try {
this.wait(); //线程阻塞 生产者通知消费解除
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
//存在数据可以消费
count --;
Steamedbun bun = buns[count] ;
this.notifyAll(); //存在空间了,可以唤醒对方生产了
return bun;
}
}
//馒头
class Steamedbun{
int id;
public Steamedbun(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
3.5.2 信号灯法
/**
* 协作模型:生产者消费者实现方式二:信号灯法
* 借助标志位
*
* @author azzhu
*
*/
public class CoTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tv tv =new Tv();
new Player(tv).start();
new Watcher(tv).start();
}
}
//生产者 演员
class Player extends Thread{
Tv tv;
public Player(Tv tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
if(i%2==0) {
this.tv.play("奇葩说");
}else {
this.tv.play("太污了,喝瓶立白洗洗嘴");
}
}
}
}
//消费者 观众
class Watcher extends Thread{
Tv tv;
public Watcher(Tv tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) {
tv.watch();
}
}
}
//同一个资源 电视
class Tv{
String voice;
//信号灯
//T 表示演员表演 观众等待
//F 表示观众观看 演员等待
boolean flag = true;
//表演
public synchronized void play(String voice) {
//演员等待
if(!flag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//表演
System.out.println("表演了:"+voice);
this.voice = voice;
//唤醒
this.notifyAll();
//切换标志
this.flag =!this.flag;
}
//观看
public synchronized void watch() {
//观众等待
if(flag) {
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//观看
System.out.println("听到了:"+voice);
//唤醒
this.notifyAll();
//切换标志
this.flag =!this.flag;
}
}
4.线程池【扩展】
JDK5.0:新增创建方式二
4.1 线程池思想概述
我们使用线程的时候就去创建一个线程,这样实现起来非常简便,但是就会有一个问题:
如果并发的线程数量很多,并且每个线程都是执行一个时间很短的任务就结束了,这样频繁创建线程就会大大降低系统的效率,因为频繁创建线程和销毁线程需要时间。
那么有没有一种办法使得线程可以复用,就是执行完一个任务,并不被销毁,而是可以继续执行其他的任务?
在Java中可以通过线程池来达到这样的效果。今天我们就来详细讲解一下Java的线程池。
4.2 线程池概念
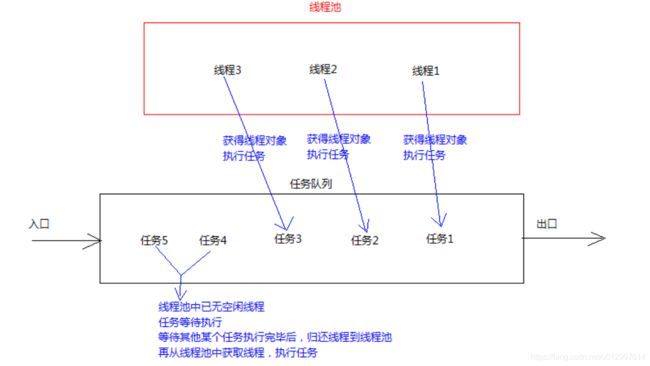
线程池:其实就是一个容纳多个线程的容器,其中的线程可以反复使用,省去了频繁创建线程对象的操作,无需反复创建线程而消耗过多资源。
由于线程池中有很多操作都是与优化资源相关的,我们在这里就不多赘述。我们通过一张图来了解线程池的工作原理:
合理利用线程池能够带来三个好处:【面试】
- **降低资源消耗。**减少了创建和销毁线程的次数,每个工作线程都可以被重复利用,可执行多个任务。
- 提高响应速度(减少了创建新线程的时间)。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要的等到线程创建就能立即执行。
- **提高线程的可管理性。**可以根据系统的承受能力,调整线程池中工作线线程的数目,防止因为消耗过多的内
存,而把服务器累趴下(每个线程需要大约1MB内存,线程开的越多,消耗的内存也就越大,最后死机)。
线程池的应用场合:
- 需要大量线程,并且完成任务的时间短
- 对性能要求苛刻
- 接受突发性的大量请求
4.3 线程池的源码
实际上,我们创建的线程池,都是调用了
ThreadPoolExecutor去创建,所以要是自定义线程池,需要跟``ThreadPoolExecutor`搭上关系。
Java里面线程池的顶级接口是 java.util.concurrent.Executor,但是严格意义上讲 Executor 并不是一个线程池,而只是一个执行线程的工具。真正的线程池接口是 java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService。
要配置一个线程池是比较复杂的,尤其是对于线程池的原理不是很清楚的情况下,很有可能配置的线程池不是较优的,因此在 java.util.concurrent.Executors 线程工厂类里面提供了一些静态工厂,生成一些常用的线程池。官方建议使用**Executors**工程类来创建线程池对象。
Executors类中有个创建线程池的方法如下:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads):返回线程池对象。(创建的是有界线程池,也就是池中的线程个数可以指定最大数量)public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool():用的最多的,可缓存的线程池public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize):可调度的线程池public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor():使用不多public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool():jdk8新增
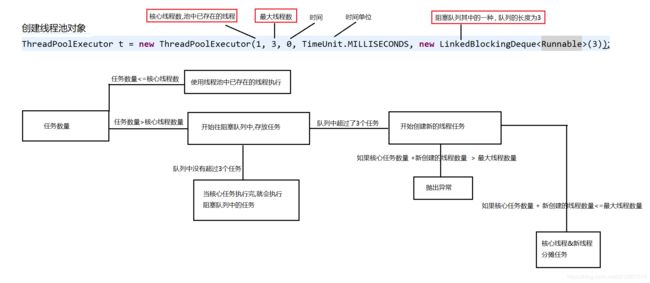
源码【前四个,调用的时候,最终都是new ThreadPoolExecutor】:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
1. int corePoolSize:
这个参数是线程池核心工作线程,就像去银行一样,他所有的窗口不一定都开。默认情况下,创建了线程池后,线程数为0,当有任务来之后,就会创建一个线程去执行任务。
假设银行总共有6个窗口,开了三个,这3个就是我们的核心线程数即corePoolSize。
2. int maximumPoolSize:
这个参数是最大线程数的意思。就像上面的例子说的银行总共开了6个窗口,这6个窗口就是线程池最大承担同时工作的线程的个数。
就是最多可以同时有多少个窗口同时工作。
3. BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue:
这个参数是阻塞队列,当我们在银行办业务时,往往不是所有的窗口都是开的,一般只会开一部分,人多了的话就会进入银行的等待区,线程池也是这么设计,这个阻塞队列就是用来存储因为线程工作空间被占用,而只能等待在等候区的线程。但是当我们的等候区的线程也满了的时候,有工作任务再次被丢进来了,线程池会再次申请开新的线程,就像银行候客区满的时候,银行为了提高工作效率,会增加窗口,这时候打开所有的窗口,及线程池工作线程达到极限,后面的线程会进入阻塞队列。
4.RejectedExecutionHandler handler:
这个是线程池的拒绝策略,当线程池已经达到最大极限,并且队列里面也已经满了,就像银行一样,所有窗口都开了,整个银行里面都是人,为了维护银行的安全,当然需要制定一定的策略处理这种线程非常多的情况,对于拒绝策略,这里暂时不做介绍。
比如抛出异常、直接舍弃、丢弃队列中最旧任务等,默认是直接抛出异常
1、CallerRunsPolicy:如果发现线程池还在运行,就直接运行这个线程
2、DiscardOldestPolicy:在线程池的等待队列中,将头取出一个抛弃,然后将当前线程放进去。
3、DiscardPolicy:什么也不做
4、AbortPolicy:java默认,抛出一个异常:
5.long keepAliveTime
多余的空闲线程的存活时间。就像我们的银行一样,由于人非常多我们把剩下的所有窗口都开了,那么如果我们业务已经处理完了,在非核心线程和队列里面的任务都已经处理完了,那么这个时候这个参数就会有作用了,设置一段时间,如果做完了队列和非核心线程的任务,在这个时间段内没有任务,那么后来新加的窗口,相当于我们的非核心线程数就会慢慢的关闭,直到只剩核心线程数。
6.TimeUnit unit:
这个参数代表这上面非空闲线程存活时间的单位。
7.ThreadFactory threadFactory:
表示生成线程池中工作线程的工厂,用于创建线程,一般用默认的即可。
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43778179/article/details/93750558
4.4 使用
使用线程池中线程对象的步骤:
- 创建线程池对象。
- 创建Runnable接口子类对象。(task)
- 提交Runnable接口子类对象。(take task)
- 关闭线程池(一般不做)
package juc.threadpool;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Description
* @Author DJZ-WWS
* @Date 2019/2/26 16:39
*/
public class ThreadPoolTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 6, 3000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy());
Runnable myRunnable = () -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "run");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
executor.execute(myRunnable);
executor.execute(myRunnable);
executor.execute(myRunnable);
System.out.println("---先开启三个线程---");
System.out.println("核心线程数" + executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("线程池线程数" + executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("队列任务数" + executor.getQueue().size());
executor.execute(myRunnable);
executor.execute(myRunnable);
executor.execute(myRunnable);
System.out.println("---再开启三个线程---");
System.out.println("核心线程数" + executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("线程池线程程数" + executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("队列任务数" + executor.getQueue().size());
Thread.sleep(8000);
System.out.println("----8秒之后----");
System.out.println("核心线程数" + executor.getCorePoolSize());
System.out.println("线程池线程线程池数" + executor.getPoolSize());
System.out.println("队列任务数" + executor.getQueue().size());
executor.shutdown();
}
}
4.5 线程池的工作流程
5.JUC并发工具类
5.1 CountdownLatch
5.1.1 作用
使一个线程等待其他的线程完成工作之后再执行,加强版的join
5.1.2 应用场景
- 比如对于马拉松比赛,进行排名计算,参赛者的排名,肯定是跑完比赛之后,进行计算得出的,翻译成Java识别的预发,就是N个线程执行操作,主线程等到N个子线程执行完毕之后,在继续往下执行
- 在启动各种框架服务,若应用程序的主线程希望在启动框架服务的线程,完成所有框架服务的启动之后,再来执行主线程。
5.1.3 实战
await():用来等待
countDown():负责计数器的减1
源码分析:
1、CountDownLatch:A synchronization aid that allows one or more threads to wait until a set of operations being performed in other threads completes.
大致意思:也就是说主线程在等待所有其它的子线程完成后再往下执行
2、构造函数:CountDownLatch(int count)//初始化count数目的同步计数器,只有当同步计数器为0,主线程才会向下执行
主要方法:void await()//当前线程等待计数器为0
boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)//与上面的方法不同,它加了一个时间限制。
void countDown()//计数器减1
long getCount()//获取计数器的值
3.它的内部有一个辅助的内部类:sync.
package cn.azzhu.ch2.tools;
import cn.azzhu.ch1.util.SleepTools;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
/**
* 有5个初始化线程,6个扣除点【一个线程中可以多次扣除,扣减数 >= 线程数】
* 扣除完之后,主线程和业务线程才能继续自己的工作
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-09-28 21:13:08
*/
public class UseCountDownLatch {
static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(6);
//初始化线程
private static class InitThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+" ready init work ....");
latch.countDown(); //初始化线程完成工作,countDown()只扣减1次
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+" ......continue do its work");
}
}
}
//业务线程
private static class BusiThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
System.out.println("BusiThread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+" do business .....");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//单独的初始化线程:初始化分为2步,需要扣减2次
new Thread(() -> {
SleepTools.ms(1);
System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+" ready init work step 1st.....");
//TODO
latch.countDown(); //每完成一步初始化工作,扣减一次
System.out.println("begin step 2nd.....");
SleepTools.ms(1);
System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+" ready init work step 2nd.....");
//TODO
latch.countDown(); //每完成一步初始化工作,扣减一次
}).start();
new Thread(new BusiThread()).start();
for (int i = 0; i <= 3; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new InitThread());
thread.start();
}
//TODO
latch.await();
System.out.println("Main do its work .....");
}
}
5.2 CyclicBarrier
5.2.1 作用
让一组线程到达某个屏障,被阻塞,一直到组内最后一个线程达到屏障时,屏障开放,所有被阻塞的线程会继续运行。【集齐七龙珠】
public CyclicBarrier(int parties, Runnable barrierAction) //屏障开放,CyclicBarrier定义的任务会执行
5.2.2 应用场景
CyclicBarrier可以用于多线程计算数据,最后合并计算结果的应用场景。比如现在需要计算10个人12个月内的工资详细,可以将线程分为10个,分别计算每个人的工资,最后,再用barrierAction将这些线程的计算结果进行整合,得出最后结果 。
5.2.3 实战
package cn.azzhu.ch2.tools;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.CyclicBarrier;
/**
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-09-29 08:46:18
*/
public class UseCyclicBarrier {
private static CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(5,new CollectThread());
//存放子线程工作信息的容器
private static ConcurrentHashMap<String,Long> resultMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i <= 4 ; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new SubThread());
thread.start();
}
}
//负责屏障开放以后的工作
private static class CollectThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (Map.Entry<String, Long> workResult : resultMap.entrySet()) {
result.append("["+workResult.getValue()+"]");
}
System.out.println(" the result = " + result);
System.out.println("do other business ......");
}
}
//工作线程
private static class SubThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId(); //线程本身的处理结果
resultMap.put(Thread.currentThread().getId()+"",id);
Random r = new Random(); //随机决定工作线程是否睡眠
try {
if(r.nextBoolean()) {
Thread.sleep(1000+id);
System.out.println("Thread_"+id+" .... do something ");
}
//TODO
System.out.println(id+"... is await");
barrier.await();
Thread.sleep(1000+id);
System.out.println("Thread_"+id+" .... do its business ");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
5.2.4 对比CountDownLatch
- CyclicBarrier的某个线程运行到屏障点上之后,该线程立即停止运行,直到所有的线程都到达了这个屏障点,所有线程才依次按顺序被唤醒重新运行;CountDownLatch是某个线程运行到某个点上之后,只是给计数器数值减一,该线程仍继续运行;
- CyclicBarrier唤醒等待线程虽然是唤醒全部,但等待线程是按顺序依次执行的;CountDownLatch是唤醒多个任务,抢占式执行;
- CyclicBarrier可重用的,因为内部计数器可重置;CountDownLatch不可重用,计数器值为0该CountDownLatch就不可再用。
- CountDownLatch放行由第三者控制,CyclicBarrier放行由一组线程本身控制
- CountDownLatch放行条件>=线程数,CyclicBarrier放行条件=线程数
5.3 Semaphone
5.3.1 作用
控制同时访问某个特定资源的线程数量
5.3.2 应用场景
用在流量控制
5.3.3 实战
package cn.azzhu.ch2.tools.semaphore;
import cn.azzhu.ch1.pool.SqlConnectImpl;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
/**
* 一个数据库连接池的实现
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-09-29 09:36:17
*/
public class DBPoolSemaphore {
private final static int POOL_SIZE = 10;
private final Semaphore useful,useless; //useful表示可用的数据库连接,useless表示已用的数据库连接
public DBPoolSemaphore() {
this.useful = new Semaphore(POOL_SIZE);
this.useless = new Semaphore(0);
}
//存放数据库连接的容器
private static LinkedList<Connection> pool = new LinkedList<>();
//初始化池
static {
for (int i = 0; i < POOL_SIZE; i++) {
pool.addLast(SqlConnectImpl.fetchConnection());
}
}
/*归还连接*/
public void returnConn(Connection connection) throws InterruptedException {
if(connection != null){
System.out.println("当前有"+useful.getQueueLength()+"个线程等待数据库连接!!!"
+"可用连接数:"+useful.availablePermits());
useless.acquire();
synchronized (pool){
pool.addLast(connection);
}
useful.release();
}
}
/*从池子拿连接*/
public Connection takeConn() throws InterruptedException {
useful.acquire();
Connection conn;
synchronized (pool){
conn = pool.removeFirst();
}
useless.release();
return conn;
}
}
package cn.azzhu.ch2.tools.semaphore;
import cn.azzhu.ch1.util.SleepTools;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-09-29 09:47:18
*/
public class AppTest {
private static DBPoolSemaphore dbPool = new DBPoolSemaphore();
private static class BusiThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
Random r = new Random(); //让每个线程持有的连接数不一样
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Connection connection = dbPool.takeConn();
System.out.println("Thread_"+Thread.currentThread().getId()
+"_获取数据库连接共耗时【"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-start)+"】ms");
SleepTools.ms(100+r.nextInt(100)); //模拟业务操作,线程持有连接查询数据
System.out.println("查询数据完成,归还连接!");
dbPool.returnConn(connection);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
BusiThread thread = new BusiThread();
thread.start();
}
}
}
5.4 Exchange
5.4.1 作用
用于两个线程间的数据交换,实际应用较少
5.4.2 实战
package cn.azzhu.ch2.tools;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.Exchanger;
/**
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-09-29 09:57:48
*/
public class UseExchange {
private static final Exchanger<Set<String>> exchange = new Exchanger<>();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
Set<String> setA = new HashSet<>(); //存放数据的容器
try {
/*添加数据
setA.add(...)*/
setA = exchange.exchange(setA); //交换set
/*处理交换后的数据*/
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
Set<String> setB = new HashSet<>(); //存放数据的容器
try {
/*添加数据
setA.add(...)*/
setB = exchange.exchange(setB); //交换set
/*处理交换后的数据*/
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
}
}
6.线程高级
6.1 volatile
最轻量级的同步机制
- 保证了不同线程对这个变量进行操作时的可见性,即一个线程修改了某个变量的值,这新值对其他线程来说是立即可见的。(实现可见性)
- 禁止进行指令重排序。(实现有序性),保证不影响最终结果
- volatile 只能保证对单次读/写的原子性。i++ 这种操作不能保证原子性。
保证线程可见性,但不保证原子性
最适用的场景:只有一个线程写,多个线程读
/**
* volatile用于保证数据的同步,也就是可见性
*/
public class VolatileTest {
private volatile static int num = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(()->{
while(num==0) { //此处不要编写代码
}
}) .start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
num = 1;
}
}
/**
* Volatile无法提供操作的原子性
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-09-26 19:47:59
*/
public class VolatileUnsafe {
private static class VolatileVar implements Runnable {
private volatile int a = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
String threadName = Thread.currentThread().getName();
a = a + 1;
System.out.println(threadName+":======"+a);
SleepTools.ms(100);
a = a+1;
System.out.println(threadName+":======"+a);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
VolatileVar v = new VolatileVar();
Thread t1 = new Thread(v);
Thread t2 = new Thread(v);
Thread t3 = new Thread(v);
Thread t4 = new Thread(v);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}
}
6.2 ThreadLocal栈封闭
确保每个线程使用自己的那份拷贝。【用空间换取线程的安全性】
在连接池中,往往会使用ThreadLocal,保证每个线程拥有的连接互不影响。
public class UseThreadLocal {
static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Integer>(){
@Override
protected Integer initialValue() {
return 1;
}
};
/*运行3个线程*/
public void startThreadArray() {
Thread[] runs = new Thread[3];
for (int i = 0; i < runs.length; i++) {
runs[i] = new Thread(new TestThread(i));
}
for (Thread run : runs) {
run.start();
}
}
//测试线程,线程的工作是将ThreadLocal变量的值变化,并写回。看看线程之间是否互相影响
public static class TestThread implements Runnable {
int id;
TestThread(int id){
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":start");
Integer s = threadLocal.get(); //获得变量的值
s = s + id;
threadLocal.set(s);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+threadLocal.get());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
UseThreadLocal test = new UseThreadLocal();
test.startThreadArray();
}
}
/**
* ThreadLocal:每个线程自身的存储本地、局部区域
* get/set/initialValue
*/
public class ThreadLocalTest01 {
//private static ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<> ();
//更改初始化值
/*private static ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<> () {
protected Integer initialValue() {
return 200;
};
};*/
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(()-> 200);
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取值
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get());
//设置值
threadLocal.set(99);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get());
new Thread(new MyRun()).start();
new Thread(new MyRun()).start();
}
public static class MyRun implements Runnable{
public void run() {
threadLocal.set((int)(Math.random()*99));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+threadLocal.get());
}
}
}
/**
* ThreadLocal:每个线程自身的数据,更改不会影响其他线程
*/
public class ThreadLocalTest02 {
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(()-> 1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
new Thread(new MyRun()).start();
}
}
public static class MyRun implements Runnable{
public void run() {
Integer left =threadLocal.get();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"得到了-->"+left);
threadLocal.set(left -1);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"还剩下-->"+threadLocal.get());
}
}
}
6.3 原子操作CAS
/**
* CAS:比较并交换
*/
public class CAS {
//库存
private static AtomicInteger stock = new AtomicInteger(5);
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
new Thread(()->{
//模拟网络延时
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Integer left = stock.decrementAndGet();
if(left<1) {
System.out.println("抢完了...");
return ;
}
System.out.print(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抢了一件商品");
System.out.println("-->还剩"+left);
}) .start();
}
}
}
6.4 锁
6.4.1 可重入锁
/**
* 可重入锁: 锁可以延续使用
*/
public class LockTest01 {
public void test() {
// 第一次获得锁
synchronized(this) {
while(true) {
// 第二次获得同样的锁
synchronized(this) {
System.out.println("ReentrantLock!");
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new LockTest01().test();
}
}
6.4.2 公平锁和非公平锁
如果在时间上,先对锁进行获取的请求,一定先被满足,这个锁就是公平的;如果不满足就是非公平的。
非公平锁的效率一般来讲更高,非公平锁上允许插队。
公平锁要维护一个队列,后来的线程要加锁,即使锁空闲,也要先检查有没有其他线程在 wait,如果有自己要挂起,加到队列后面,然后唤醒队列最前面的线程。这种情况下相比较非公平锁多了一次挂起和唤醒。
上文说到的线程切换的开销,其实就是非公平锁效率高于公平锁的原因,因为非公平锁减少了线程挂起的几率,后来的线程有一定几率逃离被挂起的开销。
6.4.3 读写锁
ReentrantLock和synchronized,都是排它锁
读写锁:同一时刻允许多个多线程同时访问,但是写线程访问的时候,所有的读和写都被阻塞。最适合于读多写少的情况。
6.4.4 共享锁和独占锁
ReentrantLock和synchronized,都是排它锁
7. 练习
-
银行 有一 个账户。
有两个储户存 分别向同一个账户存3000 元,存 每次存1000, ,存 存3次 次 。每次存完打印账户余额。问题:该程序是否有安全问题,如果有,如何解决?
【提示】
1,明确哪些代码是多线程运行代码,须写入run()方法
2,明确什么是共享数据。
3,明确多线程运行代码中哪些语句是操作共享数据的。 -
使用两个线程实现奇数和偶数的交替打印或者实现ABAB…打印
-
线程的课堂知识点
①线程安全
②线程通讯
③龟兔赛跑【1km,20速度,兔子睡觉】,谁赢
public class Racer implements Runnable{ private String winner;//胜利者 @Override public void run() { for(int steps =1;steps<=100;steps++) { //模拟休息 if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("rabbit") && steps%10==0) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+steps); //比赛是否结束 boolean flag = gameOver(steps); if(flag) { break; } } } private boolean gameOver(int steps) { if(winner!=null) { //存在胜利者 return true; }else { if(steps ==100) { winner = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println("winner==>"+winner); return true; } } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) { Racer racer = new Racer(); new Thread(racer,"tortoise").start(); new Thread(racer,"rabbit").start(); } }public class CRacer implements Callable<Integer>{ private String winner;//胜利者 @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { for(int steps =1;steps<=100;steps++) { //模拟休息 if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("pool-1-thread-1") && steps%10==0) { Thread.sleep(100); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+steps); //比赛是否结束 boolean flag = gameOver(steps); if(flag) { return steps; } } return null; } private boolean gameOver(int steps) { if(winner!=null) { //存在胜利者 return true; }else { if(steps ==100) { winner = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println("winner==>"+winner); return true; } } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { CRacer racer = new CRacer(); //创建执行服务: ExecutorService ser=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); //提交执行: Future<Integer> result1 =ser.submit(racer) ; Future<Integer> result2 =ser.submit(racer) ; //获取结果: Integer r1 =result1.get(); Integer r2 =result2.get(); System.out.println(r1+"-->"+r2); //关闭服务: ser.shutdownNow(); } } -
后续内容
常用类(String【String,两个SB】、Random、System、日期(jdk8+老的且常用、Calendar))+File文件类
流:文件读写等操作
网络编程+反射/注解
JDBC:java操作数据库
推荐书:《并发编程的艺术》
8.附录
8.1 SleepTools
/**
* 线程休眠辅助工具类
* @author azzhu
* @create 2019-09-25 22:14:41
*/
public class SleepTools {
/**
* 按秒休眠
* @param seconds
*/
public static final void second(int seconds) {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(seconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 按毫秒休眠
* @param millSeconds
*/
public static final void ms(int millSeconds) {
try {
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(millSeconds);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}