Spring - 手把手分析 IoC 容器创建过程
概述
这里我们以 Spring 5.2.8.RELEASE 版本为例,看一下 IoC 容器 的创建过程。同时我们使用 java-based 的方式实例化 IoC 容器,即使用 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext + @Configuration 的方式配置容器需要的组件。
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
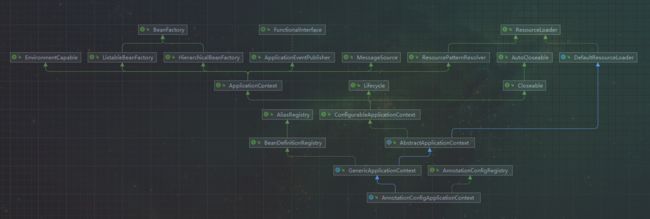
查看 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的继承关系,可以看到这个继承关系还是很复杂的,其中重要的接口有 BeanFactory、ApplicationContext、ResourceLoader、BeanDefinitionRegistry、AnntationConfigRegistry 等:
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
...
}
查看创建 IoC 容器 所使用的 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的构造函数:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
// 1、初始化 IoC 容器和一些底层 Bean
this();
// 2、注册配置类到容器中
register(componentClasses);
// 3、核心流程
refresh();
}
1、首先查看 this() 方法,即无参构造:
这里有一个细节就是如果你了解
Java的类初始化顺序和实例初始化顺序的话,你会知道这里首先会初始化父类,不明白的可以先看一下Java - 详细分析 【类初始化】 和 【实例初始化】 的过程及顺序 这篇文章
首先执行父类 GenericApplicationContext 的初始化方法:
public GenericApplicationContext() {
// 初始化了 BeanFactory
this.beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
}
接着执行了自己的初始化方法:
再一次感叹
Spring的命名,用词很准确、很严谨,基本上都可以做到见名知意,我们在开发中的命名也要尽量做到见名知意
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry {
private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader;
private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner;
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
// 1、注解形式的 BeanDefinition 读取器,用来识别 @Autowired、@Resource 等注解
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
// 2、用来扫描类路径下的 BeanDefinition
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
...
}
1.1、查看 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 的构造函数:
// 这里的 registry 是 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, getOrCreateEnvironment(registry));
}
public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
// 核心流程
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
接着查看 AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry) 源码:
public static void registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(registry, null);
}
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
// 首先获取到 DefaultListableBeanFactory,其实就是 IoC 容器
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
...
// 这里初始化一些底层的 BeanDefinition,比如处理 @Autowired、@Resource 注解的底层 Bean
// 默认会初始化 5 个
//org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor
//org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor
//org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor
//org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerProcessor
//org.springframework.context.event.internalEventListenerFactory
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
...
return beanDefs;
}
1.2、查看 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner 的构造函数
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
this(registry, true);
}
public ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean useDefaultFilters,
Environment environment, @Nullable ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
if (useDefaultFilters) {
// 1、注册默认的过滤器
registerDefaultFilters();
}
// 2、设置 environment
setEnvironment(environment);
// 3、初始化 resourceLoader
setResourceLoader(resourceLoader);
}
1.2.1、查看 registerDefaultFilters() 方法,主要是为了过滤 @Component、@ManagedBean、@Named 注解:
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false));
...
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false));
...
}
1.2.2、设置 environment 信息
// 这里的 BeanDefinitionRegistry 为 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
private static Environment getOrCreateEnvironment(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
// 从最上面的 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 类图中可以看到这里为 true
if (registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
// 这里会进入到 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 的父类 AbstractApplicationContext 中的实现方法
return ((EnvironmentCapable) registry).getEnvironment();
}
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
// AbstractApplicationContext
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
2、查看 register(componentClasses),注册配置类信息
由此可知,配置类也会作为一个
Bean被注册到容器中
@Override
public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) {
Assert.notEmpty(componentClasses, "At least one component class must be specified");
// 这里的 reader 就是上一步初始化的 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader
this.reader.register(componentClasses);
}
// 重载方法
public void registerBean(Class<?> beanClass) {
doRegisterBean(beanClass, null, null, null, null);
}
查看 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader 的 register 方法:
private <T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> beanClass, @Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers, @Nullable Supplier<T> supplier,
@Nullable BeanDefinitionCustomizer[] customizers) {
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(beanClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(supplier);
// 处理 Bean 上面是否有 @Scope 注解
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
// 处理其他注解,比如 @Lazy、@Primary、@DependsOn 等
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
...
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
// 注册 BeanDefinition
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
查看 BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry) 方法:
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
// 注册 BeanDefinition 到 BeanFactory
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
这里使用的 registerBeanDefinition 方法是在 GenericApplicationContext 中重写的方法:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// 这个 beanFacory 就是 this() 方法中初始化的 DefaultListableBeanFactory
this.beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
3、接下来就是最重要的 refresh() 方法
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 1、做一些 refresh 前的准备工作
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 2、让子类刷新内部 Bean 工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 3、BeanFactory 的一些准备工作,上一步并没有做太多,只是获取到了 BeanFactory
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 4、BeanFactory 准备工作完成后进行的后置处理
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 5、执行 BeanFactoryProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 6、注册 BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 7、初始化MessageSource
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 8、初始化事件派发器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 9、添加一些额外的 refresh 工作
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 10、注册监听器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 11、完成 BeanFactory 的初始化
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 12、完成 refresh 方法
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
...
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
3.1、prepareRefresh() 刷新前的准备工作
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
// 记录 Ioc 容器初始化开始时间戳,并设置当前状态是 close 还是 active
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
...
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
// 由子类实现,加载 PropertySource 到 context 环境中
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
// 校验属性是否合法等
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// 保存一些 refresh 之前的 Listener 和 Event
...
}
3.2、obtainFreshBeanFactory() 刷新并返回 BeanFactory
这两个方法都是抽象方法,又因为 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext 继承了 GenericApplicationContext,所以调用的是 GenericApplicationContext 中的 refreshBeanFactory 方法
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 核心流程,刷新 BeanFactory
refreshBeanFactory();
// 返回刷新后的 BeanFactory
return getBeanFactory();
}
protected abstract void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
@Override
public abstract ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
查看 GenericApplicationContext 中的实现:
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.refreshed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"GenericApplicationContext does not support multiple refresh attempts: just call 'refresh' once");
}
// 只是设置了一下 serializationId
this.beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
}
getBeanFactory() 方法返回的是第 1 步中初始化的 DefaultListableBeanFactory。
3.3、prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory) 进行一些属性设置
设置了很多属性,但是这里与主流程无关,就没有详细说明每一项属性的含义,感兴趣的可以查看官方文档。其实代码中的注释已经说的很清楚了,
Spring的撰写文档能力毋庸置疑,英语要学好啊。
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
// 设置类加载器
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 表达式解析器
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
// 添加一个 BeanPostProcessor:ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 忽略各种 Aware
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
// 注册可识别的依赖,使我们可以在任何组件中自动注入
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Register early post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners.
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
// 注册了一些默认的 bean
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
3.4、postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory)
BeanFactory 准备工作完成后进行的后置处理工作,由子类重写这个方法来自定义具体的逻辑
protected void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
}
以上步骤主要完成了
BeanFactory的创建以及预准备工作
3.5、invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)
执行 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,执行时机是在 BeanFactory 的标准初始化之后,所有的 BeanDefinition 已经被加载,但是还没有 Bean 被初始化。
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 核心流程
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 有一个子类 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,在 PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() 方法中,优先执行实现了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 的实现类,再执行实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现类,在 Spring - IoC 容器之拓展点 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 这篇文章中,有分析过,这里就不再赘述了。
3.6、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory)
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
...
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
...
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
...
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
首先获取到实现了 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanPostProcessor 并注册到 BeanFactory 中,其次获取实现了 Ordered 接口的并注册,之后注册没有排序规则的,最后注册实现了 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 接口的。
3.7、initMessageSource()
用来做国际化、消息处理、消息解析等功能,SpringMVC 中再详细分析这一块的源码
3.8、initApplicationEventMulticaster()
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {
...
}
else {
this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);
// 将 applicationEventMulticaster 添加到 IoC 容器中,以便其他组件可以引用
beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);
...
}
}
3.9、onRefresh()
由子类实现自定义的逻辑,是为了添加一些特殊的 refresh 工作,比如:初始化一些特殊的 Bean
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException {
// For subclasses: do nothing by default.
}
3.10、registerListeners()
注册实现了 ApplicationListener 的监听器
protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!
String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);
}
// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...
Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;
this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {
for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {
getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);
}
}
}
3.11、【重要】finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 非核心流程这里就省略了
...
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
在前面的流程中,有一些 Bean 已经被初始化,这里的 preInstantiateSingletons() 是用来初始化剩下的单实例 Bean,这里的 getBean(beanName) 就是创建 Bean 的过程,由于篇幅过长这里就不分析了,在 Spring - 分析 IoC 容器中 Bean 的创建过程 这篇文章中详细分析。
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
...
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Boolean>) ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
// 核心流程
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
3.12、finishRefresh()
完成 IoC 容器 创建的收尾工作
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}