JAVA8 最完整的全新的日期和时间API介绍
目录
- 一、介绍
-
- 1.1 java的日期处理API
- 1.2 我们这个世界的时间线
- 二、LocalDate 本地日期
-
- 2.1 为什么要有去时区的日期
- 2.2 创建localDate
- 2.3 LocalDate的常用方法
- 2.4 LocalDate的距离-Period
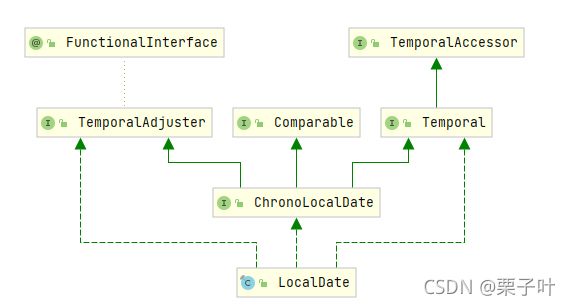
- 2.5 日期校正器 TemporalAdjuster
- 三、LocalTime 本地时间
-
- 3.1 LocalTime 介绍
- 3.2 LocalTIme的常用方法
- 四、ZoneDateTime 带时区的时间
-
- 4.1 什么是时区
- 4.2 为什要有夏令时DST(Daylight Saving Time)
- 4.3 CST和GMT是什么意思
- 4.4 java对夏令时的处理
- 4.5 ZoneDateTime 的常见用法
- 4.6 ZoneDateTime 的常用方法
- 五、DateTimeFormatter 格式化和解析
-
- 5.1 DateTimeFormatter 的三种转换方式
- 5.2 标准格式化解析(时间戳)
- 5.3 语言环境相关的格式化风格
- 5.4 指定模式来自定义日期格式
- 5.5 示例代码
- 六、与旧API相互转换
-
- 互相转换表
JAVA8新特性指路:
0.理解代码参数化和函数式编程
1.全新的时间API
2. optinal的用法
3. lambda表达式
4.Stream流
一、介绍
1.1 java的日期处理API
- 从Java 1.0 开始,就引入了Date类,但是API不好用,并且无法处理闰秒
- Java1.1 引入Calendar类
- 第三次引入的API 最成功,就是 java8的 Java.time API,它纠正了过去的缺陷
java8的 java.time API
- java.time对象都是不可变的
- 一个瞬间(Instant) 是时间线上的一个点
- java时间中,每天都是86400秒 没有闰秒
- 持续时间 Duration 是两个瞬间之间的时间
- localDateTime 没有时区信息
- TemporalAdjuster(时间调节器)方法,可以处理常用的日历计算
1.2 我们这个世界的时间线
秒的定义:
是地球完成一次自转的86400分之一,但是地球自传时间并不完全不变,所以秒,需要更精确的定义,在1967年,秒被定义为,铯133原子的固有属性定义出秒,此后官方时间根据原子钟网络同步。
问题:绝对时间需要与地球自转同步,从1972年喀开始,采取的措施改为插入“闰秒”,这样一天就并非为86400秒了
JAVA时间规范:
- 一天86400秒
- 每天正午与官方世界时间精确匹配
- 其他时间也要以精确方式与其匹配
- 原点: 1970年的1月1日的午夜,与unix/posix时间一样的约定,向前向后分别以纳秒为单位。Instant表示时间线上的时间点,Instant.MIN可以退回10亿年之前。Instant.MAX标识 10000000000年的12月31日。Instant重写了equals和compareTo方法,可以进行比较
- 计算两个,Instant差值,可以使用静态方法Duration.between()
- Instant.now() 可以获取到当前时间,两个Instan的差值,可以用Duration保存
//时间线德一个点 从1970-01 00:00:00 作为起点 Instant now= Instant.now(); System.out.println(now); Instant nextDay=now.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS); Duration dayDuration=Duration.between(now,nextDay); System.out.println(dayDuration); System.out.println(dayDuration.toDays()); System.out.println(dayDuration.toHours()); System.out.println(dayDuration.toMinutes()); System.out.println(dayDuration.toMillis()); Millis()); System.out.println(dayDuration.toNanos());
二、LocalDate 本地日期
2.1 为什么要有去时区的日期
- 在新的API中,人类的时间分为两种 1、本地日期/时间 2、带时区的时间和日期
- 有些计算不需要时区,例如每周一10点,此时如果不同地区的人用带时区时间点加上七天对应的秒,反而可能会由于时区的原因导致时间不准。
- 如果不是非要确定绝对的瞬时点,不推荐使用带时区的时间。
- 除了LocalDate之外 java8还有许多的分日期。例如 MonthDay YearMonth Year
本地日期的理解: 对于各个不同地区的人来说,日常没有时区的概念,而且对于各个时区的人来说,每年都是一样得365/366个日期。所以如果不是确定不同时区的同一时间点,一般不需要使用时区这一概念。
2.2 创建localDate
-
通过LocalDate.now() 可获得不包含时区的本地日期。为了确定本地的日期创建LocalDate需要当前的时区信息才能初始化。如果不指定,则是根据操作系统确定。Clock.systemDefaultZone()
LocalDate now = LocalDate.now(); now=LocalDate.now(Clock.systemDefaultZone()); -
指定年月日来手动创建,localDate 抛弃了UNIX时间系统中,从0开始的反人类做法,月份从1开始。月份信息除了用数字,也可以用月份的枚举表示-java.time.Month
LocalDate birthday=LocalDate.of(1998,1,6); birthday=LocalDate.of(1998, Month.JANUARY,6);
2.3 LocalDate的常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| now、of | 静态方法,获取LocalDate实例 |
| plusDays,plusWeek,plusMonth,plusYear | 为当前LocalDate对象,增加年月日周 |
| minusDays,minusWeek,minusMonth,minusYear | 为当前LocalDate对象,减去年月日周 |
| plus,minus | 添加或者减少一个Duration或Period |
| withDayOfMonth,withDayOfYear,withMonth,withYear | 将月份、天数、年份、修改为指定的值,并且返回一个新的LocalDate对象 |
| with | 传入TemporalAdjuster 来调整时间。LocalDate也是TemporalAdjuster 的实现类。其实是对当前Temporal使用TemporalAdjuster的adjustInto方法 |
| adjustInto | 传入 Temporal对象(例如LocalDate) 继承自TemporalAdjuster 的方法,将传入的对象,调整为和当前对象一样的日期。大多数情况下用反转调用模式With方法 更清楚。 |
| getDayOfMonthgetDayOfYeargetDayOfWeek | 返回月份的天数返回年份的天数返回星期返回一个DayOfWeek的枚举值 |
| getMonth、getMonthValue | 获取当前月份、返回1-12的整形,或者Month枚举 |
| getYear | 获取年份-9999999999~999999999 |
| Util | 获取两个日期之间的Period周期,或者指定ChronoUnits,返回整形。 |
| isBefore、isAfter | 比较两个日期哪个更早 |
| isLeapYear | 按照能被4或者400整除,但不能被100整除 判断是否是闰年。返回布尔值 |
2.4 LocalDate的距离-Period
-
LocalDate的距离类似时间线上的Duration
-
有些时候,直接使用Duration可能并不准确,对于并不确定时长的时间例如 月份(不同月的月份和相同的月份对应的Duration有可能不相同)
-
Period存储的结果,包含了年相差的数字 月相差的数字 日相差的数字
-
Peroid可以由两个LocalDate得出差值,也可以使用其预定义的of方法来生成
//生成Period //其预定义的方法 birthday.plus(Period.ofYears(1)); //上方LocalDate的plus(Duration/Peroid) 等效下方 birthday.plusYears(1); //LocalDate的until方法能快速计算两个本地日期之间的距离 计算本身到目标日期的时间距离。 LocalDate christmas=LocalDate.of(2021,12,25); //period可以理解为 now 加上多少年 加上多少月 再加上多少天 正好等于christmas Period period= now.until(christmas); -
Peroid对象,可以分别获取其包含的 年月日的差值但是并不常用,因为无法衡量差距的具体时间长度
-
Peroid可以转化为指定的的** TemporalUnit(实现类为ChronoUnits)**
-
Peroid也可以进行加减调整
Period period= now.until(christmas); //间隔的年月都无法得到准确的天数,所以一般不常用。 System.out.println(period.getYears()+"年 "+period.getMonths()+"月 "+period.getDays()); //获取period的天数 System.out.println(now.until(christmas,ChronoUnit.DAYS)); System.out.println(period.get(ChronoUnit.DAYS));
2.5 日期校正器 TemporalAdjuster
介绍
- 对于有时候,需要
按照时间调度执行的程序,可能回有一些需求,类似 每月第一个周二,这种日期。 - TemporalAdjusters 类,提供了许多静态方法获取TemporalAdjuster
- Locadate newlocaldate=oldLocalDate.with(TemporalAdjusters)
- LocalDate本身也是TemporalAdjuster的一种
TemporalAdjuster
-
TemporalAdjuster是一个函数式接口 Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal);
-
Locadate也实现了TemporalAdjuster,作用是将传入的日期调整到和当前对象同样的日期相当于使用Temporal.with(TemporalField, long)传递ChronoField.EPOCH_DAY作为字段更推荐使用with方法。
public LocalDate with(TemporalAdjuster adjuster) { // optimizations if (adjuster instanceof LocalDate) { return (LocalDate) adjuster; } return (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(this); } -
自定义TemporalAdjuster的时候,表达式参数类型为 Temporal,如果需要用于LocalDate则需要进行强制转换。可以使用TemporalAdjusters.UnaryOperator() 来避免强制转换。
三、LocalTime 本地时间
3.1 LocalTime 介绍
- 和LocalDate类似,可以通过LocalTime.now() 来获取当前时间的实例 或者通过,localTime.of(时,分,秒) 来获得一个LocalTime实例
3.2 LocalTIme的常用方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| now、of | 创建LocaTime实例的静态方法 |
| plusHours、plusMinutesplusSeconds、plusNanos | 向当前LocalTime对象添加几小时、几分钟、几秒钟、几微秒 |
| minusHours、minusMinutesminusSeconds、minusNanos | 向当前LocalTime对象减去几小时、几分钟、几秒钟、几微秒 |
| plus、minus | 当前LocalTime增加或减少指定的时间单位的时间 |
| winthHour、withMinutewithSecond、withNano | 单独调整某个时间单位至制定的值 |
| getHour,getMinutegetSecond,getNano | 单独获取某个时间部位的值 |
| toSecondOfDaytoNanoOfDay | 返回从零点开始,至当前时间经过的秒数或者微秒数 |
| isBefore、isAfter | 两个LocaTime进行比较 |
四、ZoneDateTime 带时区的时间
4.1 什么是时区
由于地球的自传公转决定了,我们生活在地球上,无法完全按照同一个时间来安排生活和社会活动。否则的话,可能有人在12:00吃午饭,但是对于另一地区来说,他们可能02:00 才对应着真正的太阳直射时间。
所以人们便自己创建了时区机制、来保证能更合理的安排生产生活。时区机制,比自传公转这些问题更加复杂。目前世界时区的数据库,由因特网编号管理局(Interent Assigned Number Authority) IANA 来维护,每年会更新几次,来处理夏令时规则的变化。JAVA便是使用了IANA的数据库。
4.2 为什要有夏令时DST(Daylight Saving Time)
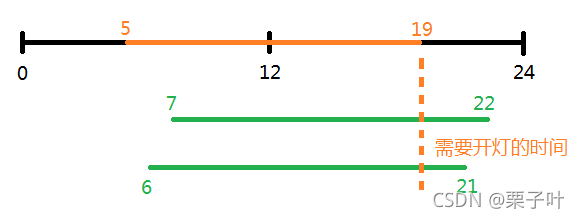
什么是夏令时: 夏令时一般是在昼长夜短的夏季,人为的将时钟拨快一小时。假如夏天5点天亮,如果作息习惯不变,按照原来的习惯,早上6点关灯的话,就浪费了一小时的电量。所以当夏天来临,就实行夏令时机制,将始终拨快,这样的话,原本五点天亮,六点关灯,就变成了,五点天亮,五点关灯,因为始终拨快后的六点,便对应着原来的五点了。
我国停止使用夏令时: 我们在1986年开始使用夏令时,在1991年宣布不再使用。夏令时有种掩耳盗铃的意味,在不同的季节,调整作息时间比起粗暴的波动时针可能更合理 1、夏令时相当于强制改变人的作息习惯 2、夏令时造成某些时间出现两次极其混乱 3、我国横跨五个时区,夏令时并不够通用 4、节约的照明电量有限,反而会增加制冷耗电
4.3 CST和GMT是什么意思
GMT (Greenwich Mean Time) 格林威治标准时,用标准世界时UTC表示则为UTC+0
CST
- 在中国表示中国标准时,对应已命名的时区标准就是Asia/Shanghai
- Asia/Shanghai会兼容地区的历史上各个时间节点,例如中国1986~1991实行了夏令时,在1992年开始 CST 就和UTC+8完全一致了。
- 我国虽然横跨五个时区,但是为了方便生产生活,统一只用了一个时区 CST
- JAVA还有个OffsetDateTime类,专门用来处理只带有UTC偏移量的时间,但是没有关联地区的时区规则,一般用来处理不需要时区规则的程序。对于人类的时间,应使用ZonedDateTime
4.4 java对夏令时的处理
- 夏令时开始时,直接把时间往后调一小时,那么对于LocalDate将直接消失1消失,如果使用消失的LocalDate来初始化一个ZoneDateTime 那么生成的ZoneDateTime时间会和尝试设置的不同,但是这是正确的。
- 夏令时结束时,直接把日期往前调整1消失,对于LocalDateTime来说,同样的一个小时,将会出现两遍。用这个重复的时间来初始化ZoneDateTime 那么将会得到第一次的那个时间。对于LocalDateTime来说,一天内的这个重合的时间完全一样,但是对于ZoneDateTime来说,偏移量是有区别的。
- 对于跨夏令时的时间处理,为了和人类的时间一致,不能直接添加Duration对象,而应该使用Period对象来进行处理。
4.5 ZoneDateTime 的常见用法
//1、获取当前所有的时区ID 大约600个
Set<String> availableZoneId = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();
//2、根据时区ID获取ZoneId对象,ZoneId对象能用来初始化TimeZone
ZoneId GMT= ZoneId.of("GMT");
TimeZone timeZone= TimeZone.getTimeZone(GMT);
System.out.println(timeZone);
//3、LocaDateTime能通过atZone(zoneid) 来转化为 ZoneDateTime
LocalDateTime currentTime=LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("本地时区时间:"+currentTime);
System.out.println("GMT带时区时间:"+currentTime.atZone(GMT));
//4、通过手动设置日期、时间、时区来初始化 ZoneDateTime
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime=ZonedDateTime.of(2021,11,28,01,34,00,0,ZoneId.systemDefault());
//5、带时区的时间点都是可以转化为一个Instant对象的,Instant对象也可以转换为对应的时区的时间
Instant instant=zonedDateTime.toInstant();
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime1=instant.atZone(GMT);
//2021-11-28T01:34+08:00[Asia/Shanghai]
System.out.println(zonedDateTime);
//2021-11-27T17:34Z[GMT]
System.out.println(zonedDateTime1);
4.6 ZoneDateTime 的常用方法
ZonedDateTime 和 LocalDateTime 中的方法几乎一样,而且意义都显而易见。只是夏令时带来了一些复杂性。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| now、of、ofInstant | 创建一个ZonedDateTime |
| plusXXX例如 :Day、Weeks、Months、Years、Hours、minutes、Seconds、Nanos | 添加对应时间单位的时间 |
| minusXXX例如 :Day、Weeks、Months、Years、Hours、minutes、Seconds、Nanos | 从当前时间减去对应时间单位的时间 |
| plus、minus | 添加或者减少一个Duration 或者Period |
| withDayOfMonth,withDayOfYear,withMonth,withYear,winthHour、withMinutewithSecond、withNano | 单独调整对应时间单位的值,返回新的ZonedDateTime |
| withZoneSameInstantwithZoneSameLocal | 获取同一个时间点的另一个时区的ZonedDateTime或者获取同一个本地时间,不同时间点的另一个时区的ZonedDateTime |
| getDayOfMonth getDayOfYeargetDayOfWeek | 获取131之间的月份中的第几天获取1366一年中的天数获取星期几 或者DayOfWeek枚举 |
| getMonth、getMonthValue | 获取月份 或者获取Month的枚举 |
| getYear | 获取年份 |
| getHour 、Minute、Second、Nano | 获取时间信息 |
| getOffset | 获取对应时间点对应的时区的偏移量因为对应地区的时区信息并不是简单地,GMT+n UTC+n ,往往还涉及历史原因或者夏令时制度,所以不同时间点的偏移量是不一样的。一般在-12:00 至 +14之间,涉及夏令时可能还有分钟的区别 |
| toLocalDate 、toLocalTime、toInstant | 转换为本地时间、或者对应的时间点 |
| isBefore isAfter | 比较两个对象 |
五、DateTimeFormatter 格式化和解析
5.1 DateTimeFormatter 的三种转换方式
DateTimeFormatter 提供了三种方式来格式化日期/时间
- 使用预定义的标准格式化时间(fromat方法)
- 语言环境相关的格式
- 自定义格式
如果考虑向后兼容,需要一个 java.util.DateFormat对象,那么可以使用 toFormat() 方法再转换为DateFormat对象。
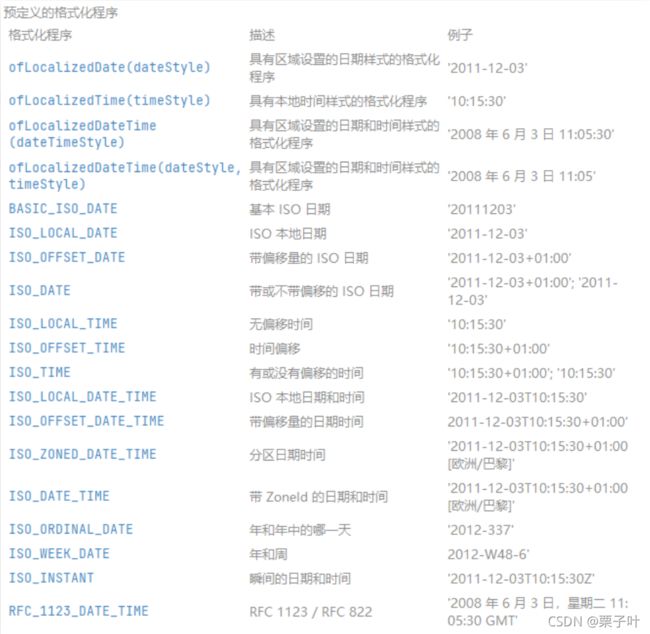
5.2 标准格式化解析(时间戳)
- DateTimeFormatter 预定义了一些静态对象,来用于解析TemporalAccessor 成常用的时间格式
- 预定义格主要用于机器可读的时间戳,如果要让人可读则可以使用预定义的语言环境相关的格式化方式
5.3 语言环境相关的格式化风格
- JAVA 8 对日期和时间各定义了四种风格 SHORT、MEDIUM、LONG 、FULL
- 可以使用ofLocalizedDate、ofLocalizedTime、ofLocalizedDateTime来创建这类格式
- 这些方法,默认使用当前的语言环境,可以使用withLocal(Local.XX) 来改变语言环境
| 风格 | 日期 | 时间 |
|---|---|---|
| SHORT | 7/16/69 | 9:32 AM |
| MEDIUM | Jul 16,1969 | 9:32:00 AM |
| LONG | Jul 16,1969 | 9:32:00 AM EDT |
| FULL | Wendsday,Jul 16,1969 | 9:32:00 AM EDT |
LocalDate localDate=LocalDate.now();
LocalTime localTime=LocalTime.now();
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime=ZonedDateTime.now();
//1、解析成预定义的标准化格式 2021-11-27T19:12:11.623Z
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_INSTANT.format(zonedDateTime));
//2、四种解析风格 SHORT、MEDIUM、LONG 、FULL
// 2021年11月28日 星期日 上午03时15分18秒 CST
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter=DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.FULL);
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(zonedDateTime));
//2021年11月28日 星期日 上午03时19分08秒 CST
dateTimeFormatter=dateTimeFormatter.withLocale(Locale.US);
//Sunday, November 28, 2021 3:19:08 AM CST
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(zonedDateTime));
5.4 指定模式来自定义日期格式
- 例如 DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern( “E yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm” ) 通过自定义的模式字符串,来生成formatter
- 从字符串中解析成时间,可以使用各个时间对象的,parse方法

5.5 示例代码
LocalDate localDate=LocalDate.now();
LocalTime localTime=LocalTime.now();
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime=ZonedDateTime.now();
//1、解析成预定义的标准化格式 2021-11-27T19:12:11.623Z
System.out.println(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_INSTANT.format(zonedDateTime));
//2、四种解析风格 SHORT、MEDIUM、LONG 、FULL
// 2021年11月28日 星期日 上午03时15分18秒 CST
DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter=DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.FULL);
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(zonedDateTime));
//2021年11月28日 星期日 上午03时19分08秒 CST
dateTimeFormatter=dateTimeFormatter.withLocale(Locale.US);
//Sunday, November 28, 2021 3:19:08 AM CST
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(zonedDateTime));
//字符串转换为时间
dateTimeFormatter=DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("世纪: GGGG 时区: zzzz YYYY年 MM月 dd 日");
//世纪: 公元 时区: 中国标准时间 2021年 11月 28 日
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(zonedDateTime));
dateTimeFormatter=dateTimeFormatter.withLocale(Locale.US);
//世纪: Anno Domini 时区: China Standard Time 2021年 11月 28 日
System.out.println(dateTimeFormatter.format(zonedDateTime));
六、与旧API相互转换
- 新的API 的Instant类相当于 java.util.Date类,在java8中 给Date类增加了两个方法,toInstant用来生成Instant对象,静态方法 Date.from(Instant ) 则接收Instant方法,生成Date
- ZoneDateTime 类似于Java.util.GregorianCalendar ,后者也增加了toZoneDateTIme和from静态方法,来互相转换。
- java.text.Format ,也可以通过DateTimeFormatter 的format获得
互相转换表
| 转换的类 | To遗留类 | FROM遗留类 |
|---|---|---|
| Instant和Date | Date.from(instant) | data.toInstant() |
| ZoneDateFormatGregorianCalendar | GregorianCalendar.from() | cal.toZoneDateTime() |
| Instantjava.sql.TimeStamp | Timestamp.from | timestamp.toInstant() |
| LocalDateTimejava.sql.TimeStamp | TimeStamp.valueOf(localDateTime) | timeStamp.toLocalDateTime() |
| LocalDatejava.sql.Time | Date.valueOf(localDate) | data.toLocalDate() |
| LocalTimejava.sql.Time | Time.valueOf(localTime) | time.toLocalTime() |
| DateTimeFormatterjava.text.DateFormat | formatter.toFormat() | 无 |
| java.util.TimeZoneZoneId | TimeZone.getTimeZone(zoneid) | timeZone.toZoneId() |