动态顺序表(C语言实现)
坚持学习
目录
1.顺序表的概念
2.顺序表的定义
3.顺序表的接口函数
3.1顺序表初始化
3.2检查顺序表是否需要扩容
3.3尾插数据
3.4尾删数据
3.5头插数据
3.6头删数据
3.7打印顺序表的数据
3.8销毁顺序表
3.9在指定位置插入数据
3.10删除指定位置的数据
3.11查找指定数据
4.完整的顺序表代码
1.顺序表的概念
顺序表是在计算机内存中以数组的形式保存的线性表,线性表的顺序存储是指用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存储线性表中的各个元素、使得线性表中在逻辑结构上相邻的数据元素存储在相邻的物理存储单元中,即通过数据元素物理存储的相邻关系来反映数据元素之间逻辑上的相邻关系,采用顺序存储结构的线性表通常称为顺序表。顺序表是将表中的结点依次存放在计算机内存中一组地址连续的存储单元中。
通俗的来讲,顺序表就是数组,但在数组的基础上,它还要求数据是从头开始连续存储的,不能 跳跃间隔
2.顺序表的定义
用一个结构体构造顺序表:
这里用 SLDataType 来替换 int ,可以方便我们修改顺序表的数据类型
同时用 SL 来替换 struct SeqList,方便写代码(在后面的函数中可以直接用SL来代替struct SeqList)
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;
int size;//表示数组存了多少个数据
int capacity;//数组实际能存数据的空间容量是多大
}SL;3.顺序表的接口函数
所有的接口函数一览:
void SeqListInit(SL* ps);//初始化
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//检查容量
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾插
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删
void SeqListPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//头插
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps);//头删
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps);//打印
void SeqListDestory(SL* ps);//销毁
//在指定的下标位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
//删除指定位置的数据
void SeqListErase(SL* ps, int pos);
//找到了返回x的下标,没有找到返回-1;
int SeqListFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x);这些接口函数实现了顺序表增删查改等基本功能 ,下面对这些接口函数一一进行讲解:
3.1顺序表初始化
初始化就是将顺序表中的值置为0
void SeqListInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}3.2检查顺序表是否需要扩容
判断是否需要扩大容量的方法就是看size和capacity是否已经相等,相等就说明容量以经达到最大值,我们就需要扩大顺序表的容量。可以在原来顺序表容量的基础上扩大一倍,也就是将capacity乘以2,当以也可以乘以其他值如1.5,3,4(合理即可)。这里扩容用到的动态内存分配——realloc函数(头文件是#include
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
//如果没有空间或空间不足就扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
3.3尾插数据
尾插就是在顺序表的末端插入数据,同时将size加一,请注意:一定要检查顺序表的容量大小和实际存储数据个数是否相等,如果相等了,要先进行扩容 。使用上面3.2所讲的函数就可以实现检查和扩容这两部操作
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
//如果没有空间或空间不足就扩容
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
3.4尾删数据
尾删这部分实现起来很简单,直接将数组长度减一即可,但是一定要保证size大于或着等于0,否则后果很严重(在后面销毁数据时可能引起程序崩溃)最后别忘了将size减一
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps)
{
//保证size大于0
if (ps->size > 0)
{
ps->size--;
}
}
3.5头插数据
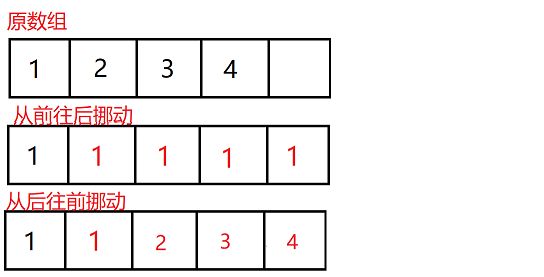
头插数据要先将所有的数据向后挪动一位,然后在第一个位置赋上要插入的值,同时size加一
请注意数据的挪动方式:
数据要从后往前依次挪动,不要从前向后挪,这一点非常重要,因为从前往后挪数组中的值会被覆盖掉
void SeqListPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
//挪动数据
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}3.6头删数据
头删数据和头插数据类似,只要将数组整体向前挪动一位,覆盖第一个元素即可,也要注意从后往前挪动,不再做更多赘述了
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size > 0);
int begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}3.7打印顺序表的数据
这一步非常简单,代码能直接说明
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}3.8销毁顺序表
由于我们用到了动态内存分配,如果空间用完后如果没有即使销毁,会存在内存泄漏的风险。
void SeqListDestory(SL* ps)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}3.9在指定位置插入数据
在指定位置插入数据的原理是将指定位置后面的所有数据向后挪动一,再给指定位置赋新值,请注意:要保证指定位置的合法性
void SeqListInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
if (pos >ps->size || pos < 0)
{
printf("pos invalid\n");
return ;
}
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}头插数据和尾插数据可以用这串代码来替换
头插可以替换为:
void SeqListPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, 0, x);
}尾插可以替换为:
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, ps->size, x);
}3.10删除指定位置的数据
将指定位置后面的所有数据向前挪动覆盖指定位置即可,同时size减一,记得要确保指定位置是数组的大小之类,这里用到了assert断言。
void SeqListErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}3.11查找指定数据
这串代码的基本原理是给的要找的数,找到了返回该数的下标位置,找不到返回-1,实现起来也很简单。
int SeqListFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
4.完整的顺序表代码
讲了这么多,来看看完整的代码时什么样吧:
SeqList.h文件:
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* a;
int size;//表示数组存了多少个数据
int capacity;//数组实际能存数据的空间容量是多大
}SL;
//接口函数
void SeqListInit(SL* ps);//初始化
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//尾插
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps);//尾删
void SeqListPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);//头插
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps);//头删
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps);//打印
void SeqListDestory(SL* ps);//销毁
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SL* ps);//检查容量
//在指定的下标位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x);
//删除指定位置的数据
void SeqListErase(SL* ps, int pos);
//找到了返回x的下标,没有找到返回-1;
int SeqListFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x); SeqList.c文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SeqListInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//打印
void SeqListPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//检查容量
void SeqListCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
//如果没有空间或空间不足就扩容
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newcapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
//销毁
void SeqListDestory(SL* ps)
{
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
//如果没有空间或空间不足就扩容
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
ps->a[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SL* ps)
{
//保证size大于0
if (ps->size > 0)
{
ps->size--;
}
}
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
//挪动数据
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= 0)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps->size > 0);
int begin = 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}
//查找
int SeqListFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->a[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//在指定的下标位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
if (pos >ps->size || pos < 0)
{
printf("pos invalid\n");
return ;
}
SeqListCheckCapacity(ps);
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->a[end + 1] = ps->a[end];
--end;
}
ps->a[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//删除指定位置的数据
void SeqListErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin < ps->size)
{
ps->a[begin - 1] = ps->a[begin];
++begin;
}
ps->size--;
}test.c文件:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"SeqList.h"
void TestSeqlidt1()
{
SL sl;
SeqListInit(&sl);
//尾插入五个数据
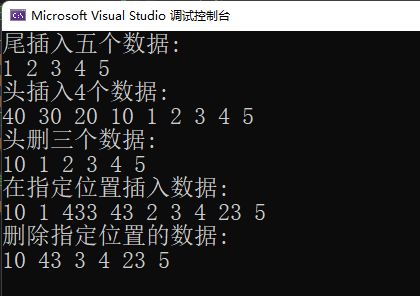
printf("尾插入五个数据:\n");
SeqListPushBack(&sl, 1);
SeqListPushBack(&sl, 2);
SeqListPushBack(&sl, 3);
SeqListPushBack(&sl, 4);
SeqListPushBack(&sl, 5);
//打印
SeqListPrint(&sl);
//头插入4个数据
printf("头插入4个数据:\n");
SeqListPushFront(&sl, 10);
SeqListPushFront(&sl, 20);
SeqListPushFront(&sl, 30);
SeqListPushFront(&sl, 40);
//打印
SeqListPrint(&sl);
//头删三个数据
printf("头删三个数据:\n");
SeqListPopFront(&sl);
SeqListPopFront(&sl);
SeqListPopFront(&sl);
//打印
SeqListPrint(&sl);
//在指定位置插入数据
printf("在指定位置插入数据:\n");
SeqListInsert(&sl, 5, 23);
SeqListInsert(&sl, 2, 433);
SeqListInsert(&sl, 3, 43);
//打印
SeqListPrint(&sl);
//删除指定位置的数据
printf("删除指定位置的数据:\n");
SeqListErase(&sl, 2);
SeqListErase(&sl, 3);
SeqListErase(&sl, 1);
//打印
SeqListPrint(&sl);
//销毁顺序表
SeqListDestory(&sl);
}
int main()
{
TestSeqlidt1();
return 0;
}展示一下运行的效果:
文章到这里就结束啦~~