C++11——lambda表达式
目录
前言
一.lambda表达式用法
二.lambda表达式语法
三.lambda表达式的原理
前言
在显示生活中,我们在用手机购物时。总是可以在页面上看到下面这样的选项。
我们知道底层这是通过排序来完成的,但是当我们实现时,要写多个排序算法,写多个仿函数来实现不同变量的比较。
比如下面代码:
struct CompareNameSmall;
struct CompareNameBig;
struct ComparePriceSmall;
struct ComparePriceBig;
class Goods{
friend struct CompareNameSmall;
friend struct CompareNameBig;
friend struct ComparePriceSmall;
friend struct ComparePriceBig;
private:
string _name;
double _price;
public:
Goods(string name, double price)
:_name(name)
,_price(price)
{}
};
//仿函数
struct CompareNameSmall{
bool operator()(const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2){
return g1._name < g2._name;
}
};
struct CompareNameBig{
bool operator()(const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2){
return g1._name > g2._name;
}
};
struct ComparePriceSmall{
bool operator()(const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2){
return g1._price < g2._price;
}
};
struct ComparePriceBig{
bool operator()(const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2){
return g1._price > g2._price;
}
};
int main(){
Goods gds[] = { { "苹果", 2.5 }, { "香蕉", 3.0 }, { "梨", 3.5 } };
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), CompareNameSmall());
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), CompareNameBig());
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), ComparePriceSmall());
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), ComparePriceBig());
system("pause");
return 0;
}随着C++的发展,人们开始觉得上面的写法太复杂了。每次为了实现一个比较算法,都需要重新定义一个类,如果每次的比较逻辑不一样,还要实现多个类,特别是在相同类的命名上。并且如果不能达到见名知义,我们还得去找对应的仿函数,才能知道它的功能,这给编程者带来了极大的不便。
因此在C++11语法中出现了lambda表达式。
一.lambda表达式用法
class Goods{
public:
string _name;
double _price;
Goods(string name, double price)
:_name(name)
, _price(price)
{}
};
int main(){
Goods gds[] = { { "苹果", 2.5 }, { "香蕉", 3.0 }, { "梨", 3.5 } };
//使用lambda表达式
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), [](const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2)->bool{return g1._name < g2._name; });
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), [](const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2)->bool{return g1._name > g2._name; });
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), [](const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2)->bool{return g1._price < g2._price; });
sort(gds, gds + (sizeof(gds) / sizeof(gds[0])), [](const Goods& g1, const Goods& g2)->bool{return g1._price > g2._price; });
system("pause");
return 0;
}可以实现和上面一样的效果。虽然一样要写这么多函数,但是不需要面临去定义很多类和命名问题,并且不需要在去找函数。
但是我们发现lambda表达式的格式还是很奇怪的,下面来介绍一下lambda表达式的写法。
二.lambda表达式语法
lambda表达式书写格式:[捕捉列表](参数)mutable—>返回值类型{ 函数体 }
- [捕捉列表]:该列表总是出现在lambda表达式的起始位置,编译器根据[]来判断接下来的代码是否为lambda表达式,捕捉列表能够捕捉当前作用域中的变量,供lambda函数使用。
- [val]:表示以传值方式捕捉变量val
- [=]:表示以传值方式捕捉当前作用域中的变量,包括this指针。
- [&val]:表示以引用方式传递捕捉变量val。
- [&]:表示以引用方式传递捕捉当前作用域中的所有变量,包括this指针。
- [this]:表示以传值方式捕捉当前的this指针。
- (参数):参数列表。与普通函数参数列表使用相同。如果不需要传递参数,可以连同"()"一起省略。
- mutable:默认情况下,lambda函数总是一个const函数,捕捉的传值参数具有常性,mutable可以取消常性。使用mutable修饰符时,参数列表不能省略,即使参数为空。
- —>返回值类型:返回值类型。使用追踪返回类型形式声明函数的返回值类型,没有返回值此部分可省略。返回值类型明确的情况下,也可省略,由编译器推导。
- {函数体}:在函数体内除了可以使用参数外,还能使用捕捉的变量。
注意:在lambda表达式中,参数列表和返回值类型都可省略,而捕捉列表和函数体可以为空。所以最简单的lambda表达式为:[]{},该表达式不能做任何事。
int main(){
//最简单的lambda表达式
[]{};
//捕捉当前作用域的变量,没有参数,编译器推导返回值类型。
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
[=]{return a + b; };
//使用和仿函数差不多
auto fun1 = [&](int c){b = a + c; };
fun1(10);
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
auto fun2 = [&](int c)->int{return a + c; };
fun2(20);
cout << fun2(20) << endl;
//传值捕捉
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
auto add0 = [x, y]()mutable->int{ x *= 2;//捕捉传递传值具有常性
return x + y; };
cout << add0() << endl;
auto add1 = [&x, y]()->int{ x *= 2;//捕捉传递引用不具有常性
return x + y; };
cout << add1() << endl;
auto add2 = [](int s, int m)->int{ s *= 2;//参数不具有常性
return s + m; };
system("pause");
return 0;
}从上面要注意的一点是:捕捉列表传值传递具有常性,要加mutable,传引用传递不具有常性,参数列表不具有常性。
捕捉列表的要和捕捉参数变量名相同,传值传递是当前作用域变量的拷贝。
int main(){
//最简单的lambda表达式
[]{};
//捕捉当前作用域的变量,没有参数,编译器推导返回值类型。
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
//auto fun1 = [x, y]()->int{return x + y; };//编译错误,要和捕捉参数名相同
//传值传递是捕捉变量的拷贝,实际外面的a,b没有交换
auto swap1 = [a, b]()mutable{int z = a; a = b; b = z; };
swap1();//注意还需要调用
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
//传引用才能真正修改
auto swap2 = [&a, &b]{int z = a; a = b; b = z; };
swap2();
cout << a << " " << b << endl;
return 0;
}注意构造完对象后,对象调用,函数才起作用。
注意点:
- 语法上捕捉列表可由多个捕捉项组成,并以逗号隔开。捕捉项不能重复传递,否则会导致编译错误。比如:当前作用域已经有了变量a,捕捉设为[=,a],=已经捕捉过a了,编译时会报错。
- 捕捉列表只能捕捉当前作用域的局部变量,作用域以外的局部变量或者非局部变量都会报错。
- lambda表达式之间不能赋值,即使看起来类型相同。
void (*PF)();
int main(){
auto f1 = []{cout << "hello world" << endl; };
auto f2 = []{cout << "hello world" << endl; };
// 此处先不解释原因,等lambda表达式底层实现原理看完后,大家就清楚了
//f1 = f2; // 编译失败--->提示找不到operator=()
// 允许使用一个lambda表达式拷贝构造一个新的副本
auto f3(f2);
f3();
// 可以将lambda表达式赋值给相同类型的函数指针
PF = f2;
PF();
return 0;
}三.lambda表达式的原理
首先我们先来比较一下仿函数和lambda表达式
我们发现仿函数的使用和lambda表达式差不多。
class Rate
{
public:
Rate(double rate) : _rate(rate)
{}
double operator()(double money, int year)
{
return money * _rate * year;
}
private:
double _rate;
};
int main()
{
// 函数对象
double rate = 0.49;
Rate r1(rate);
r1(10000, 2);
// lamber
auto r2 = [=](double monty, int year)->double{return monty*rate*year; };
r2(10000, 2);
return 0;
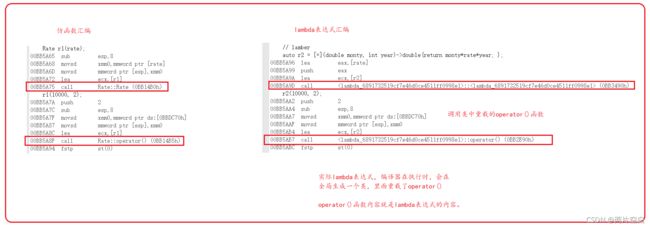
}通过汇编来查看lambda表达式部分:
lambda表达式原理:实际编译器在全局作用域自动生成了一个类,在类中重载了operator(), operator()函数的内容就是lambda表达式的内容。
可以理解成lambda表达式底层还是仿函数。本来时要程序员编写,现在变成了编译器自动生成,我们看起来跟方便了。