Linux基础部分的学习(7)- 进程间通信
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、进程间的通信
-
- 1.管道:
-
- 1.无名管道
-
- a.特点:
- b.原型:
- c.示例
- d.代码实现:
- 2.命名管道:
-
- a.特点:
- b.原型:
- c.代码示例:
- 2.消息队列:
-
- 1.简介:
- 2.原型:
- 3.代码
- 3.共享内存:
-
- 1、特点:
- 2.原型:
- 3.代码实现:
- 4.信号
-
- 1.概述:
- 2.信号携带消息编程
-
- 原型:
- 5.信号量
-
- 1.简述:
- 2.原型:
- 3.代码实战:
前言
坚志者,功名之主也。不惰者,众善之师也。——《抱朴子》
一、进程间的通信
前面介绍的创建进程,且进程之间交换信息的方法是经过fork,exec传送打开文件,或者通过文件系统进行通信,有点繁杂和残缺。现在我们学习一种进程间相互通信的其他技术 –LINUX IPC继承了(System V IPC 和 基于 Socket IPC)
IPC的几种主要手段有:管道(无名管道和命名管道)、消息队列、信号量、共享存储、Socket、Streams等、其中后二者支持在不同主机上的两个进程IPC。
1.管道:
1.无名管道
a.特点:
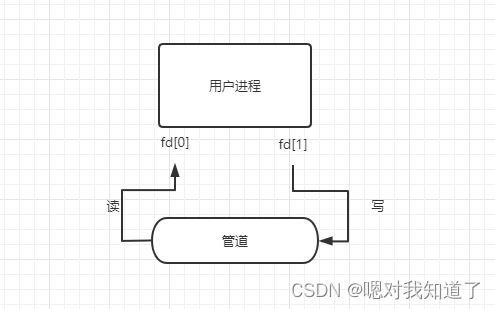
1.半双工,有固定的读、写端
2.只能在具有亲缘关系的进程间进行通信
3.管道中不储存数据,读取后消失
4.可以把它看成是一个特殊的文件,对他的读写可以使用read,write等函数,但它不是普通文件,并且不属于任何文件系统,只存在于内存之中。
b.原型:
#include 当一个管道建立的时候,会返回俩个描述符: fd[0] 读打开
fd[1] 写打开
关闭管道即关闭两个文件描述符
c.示例
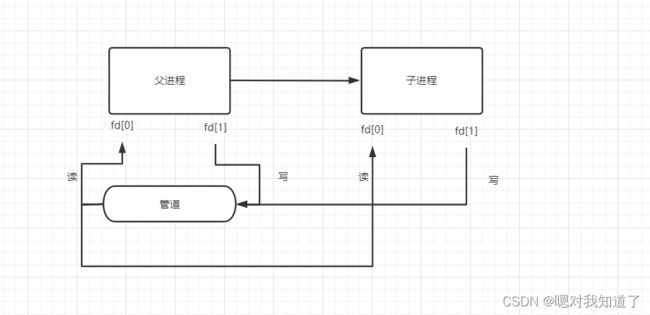
在父进程创建子进程,两个进程之间IPC通信
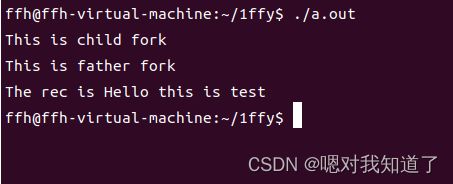
d.代码实现:
#include 2.命名管道:
a.特点:
除了无名管道的功能外,他还允许无亲缘关系进程间的通信
b.原型:
#include mode参数和open参数相同,创建一个fifo可以一般文件I/O函数操作它
当打开一个FIFO时候
若没有指定O_NONBLIOCK(默认),只读open会阻塞到某个进程为写而打开此FIFO,类似只写open会阻塞到某个进程为读而打开
若指定了O_NONBLOCK,则只读open立即返回,而只写open将出错返回-1,如果没有进程已经为读而打开该FIFO,其errno置ENXIO
c.代码示例:
write.c
#include read.c
#include 2.消息队列:
1.简介:
消息队列是消息的链接表,存放在内核中,一个队列由一个标识符(即队列ID)来标识
消息队列克服了信号承载信号量少、管道只能承载无格式字节流以及缓冲区大小受限的缺点
2.原型:
#include 3.代码
msgwrite.c
#include msgread.c
#include 3.共享内存:
共享内存(Shared Memory),指两个或多个进程共享一个给定的存储区
1、特点:
共享内存是最快的一种 IPC,因为进程是直接对内存进行存取。
因为多个进程可以同时操作,所以需要进行同步。
信号量+共享内存通常结合在一起使用,信号量用来同步对共享内存的访问。
2.原型:
#include 3.代码实现:
shmwrite.c
#include shmread.c
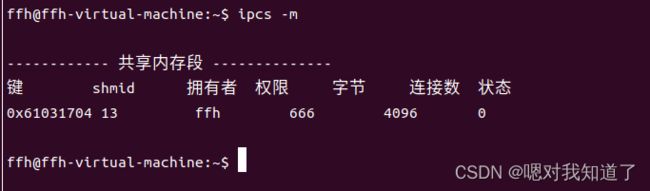
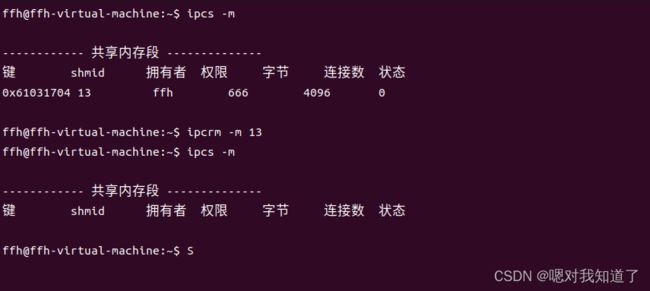
#include 将shmwrite.c中释放共享内存注释,利用 ipcs -m 指令观察当前的共享内存段
利用 ipcrm -m 共享内存的id号码 可以关闭共享内存
4.信号
1.概述:
信号是进程在运行的过程中,有自身产生或进程外部发过来的,
用来通知进程发生了异步事件的通信机制,是硬件中断的软件模拟(软中断),是进程间通信机制中唯一的异步通信机制。
kill -l显示所有信号
信号处理方法: 忽略、捕捉、和默认动作
将传入的ctrl+c信号进行修改,让其执行设定好的函数
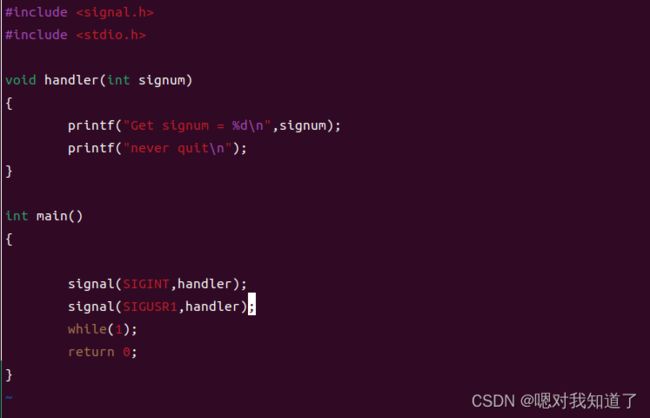
2.信号携带消息编程
原型:
int sigaction(int signum,const struct sigaction*act,struct sigaction *oldact)
signum 是信号
act是struct sgaction指针
包括:1,sa_sigaction:指定要处理的函数
2,sa_flags:指定处理信号的方式
3,sa_mask:阻塞信号集
sigproread.c
#include sigprowrite.c
#include 5.信号量
1.简述:
信号量是一个计数器。信号量用于实现进程间的互斥与同步,而不是用于存储进程间的通信数据
用于进程间的永不,若在进程间要传递数据要结合共享内存实现
信号量基于操作系统的PV操作,程序对信号量的操作都是原子操作
支持信号量组
2.原型:
#include 3.代码实战:
先让子进程释放信号量,再让父进程运行
#include