吴恩达机器学习作业笔记(线性回归)
零基础知识
1.DataFrame结构
Pandas DataFrame入门教程(图解版)
DataFrame 一个表格型的数据结构,既有行标签(index),又有列标签(columns),它也被称异构数据表,所谓异构,指的是表格中每列的数据类型可以不同,比如可以是字符串、整型或者浮点型等
pd.DataFrame( data, index, columns, dtype, copy)
data可以是多种类型
index和columns传入相应的一维数组作为标签,默认np.arange(n),这里传入一维,不区分列表list和numpy的ndarray数组类型。
copy默认为false
1.1掌握一维列表与二维列表创建DataFrame结构
import pandas as pd
data = [1,2,3,4,5]
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
输出如下
0
0 1
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
import pandas as pd
data = [['Alex',10],['Bob',12],['Clarke',13]]
df = pd.DataFrame(data,columns=['Name','Age'],dtype=float)
print(df)
Name Age
0 Alex 10.0
1 Bob 12.0
2 Clarke 13.0
1.2了解字典创建DataFrame结构
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'Jack', 'Steve', 'Ricky'],'Age':[28,34,29,42]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['rank1','rank2','rank3','rank4'])
print(df)
输出如下
Age Name
rank1 28 Tom
rank2 34 Jack
rank3 29 Steve
rank4 42 Ricky
1.3Pandas csv读写文件
2.Numpy相关知识
NumPy ndarray对象
NumPy 定义了一个 n 维数组对象,简称 ndarray 对象,它是一个一系列相同类型元素组成的数组集合
2.1掌握创建ndarray对象,和.shape函数
import numpy
a=numpy.array([1,2,3])#使用列表构建一维数组
print(a)
[1 2 3]
print(type(a))
#ndarray数组类型
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
b=numpy.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(b)
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
c=numpy.array([[1,2,3]])
print(a.shape)
输出(3,)
print(b.shape)
输出(2,3)
print(c.shape)
输出(1,3)
2.2掌握reshape数组变维
import numpy as np
e = np.array([[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]])
print("原数组",e)
e=e.reshape(2,3)
print("新数组",e)
原数组
[[1 2]
[3 4]
[5 6]]
新数组
[[1 2 3]
[4 5 6]]
2.3数组的区间创建:
numpy.arange(start, stop, step, dtype)
不包含终止值
np.linspace(start, stop, num=50, endpoint=True, retstep=False, dtype=None)
形成num个均匀的样本,endpoint为False时不包含终止值
掌握numpy的索引与切片
通过冒号:来分割参数,[起始值:终止值:间隔]
np.hstack用法
np.hstack将参数元组的元素数组按水平方向进行叠加
2.4Numpy的矩阵乘法
X.dot(Y)
np.dot(X,Y)
numpy矩阵乘法中的multiply,matmul和dot
正文
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = pd.read_csv("ex1data1.txt",names=["population","profit"])
print(data.head())
X = data.population
y = data.profit
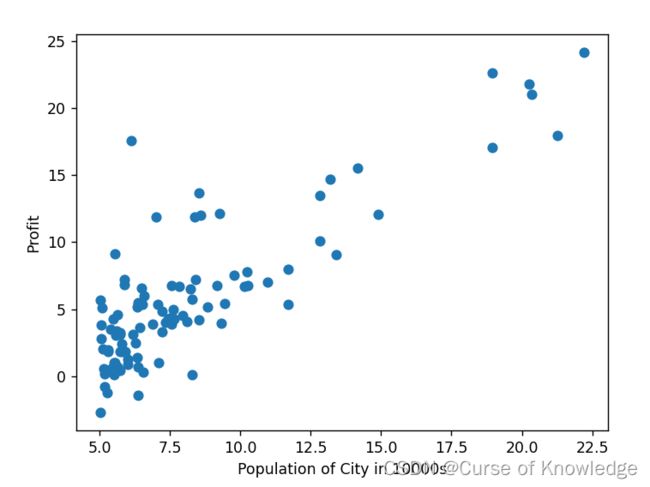
plt.scatter(X,y)
plt.xlabel("Population of City in 10000s")
plt.ylabel("Profit")
plt.show()
data.head()输出前五行
population profit
0 6.1101 17.5920
1 5.5277 9.1302
2 8.5186 13.6620
3 7.0032 11.8540
4 5.8598 6.8233
data = np.array(data)
把dataframe转化成了numpy数组
X = data[:,0].reshape(-1,1)
X = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X),1)),X])
y = data[:,1].reshape(-1,1)
theta = np.zeros(X.shape[1]).reshape(-1,1)
到这里,X,y,theta已经初始化完毕
X一个m行2列的矩阵,第一列代表x_0,全部是1,第二列是x_1,是数据Population
y是一个m行1列的矩阵,代表profit
theta代表两个参数
def J(X,y,theta):
cost = np.sum((X.dot(theta)-y)**2)/(2*len(X))
return cost
这是在定义Cost Function
def dJ(X,y,theta):
ans =X.T.dot(X.dot(theta)-y) /len(X)
return ans#返回一个(2,1)矩阵,表示dtheta0,dtheta1
def grad_descend(X,y,theta_init,learning_rate,iters,error):
i=0
theta = theta_init
while i < iters:
grad = dJ(X, y, theta)
theta_old = theta
theta = theta - learning_rate * grad
if (abs(J(X,y,theta) - J(X,y,theta_old))) < error:
print("第{}次梯度下降,达到理想误差".format(i+1))
break
i+=1
return theta
定义梯度下降,当更新theta前后的Cost Function之差绝对值小于error的是时候停止循环
并返回此时的theta值,这就得到了两个参数
theta = grad_descend(X,y,theta,0.01,1e4,1e-8)
print(theta)
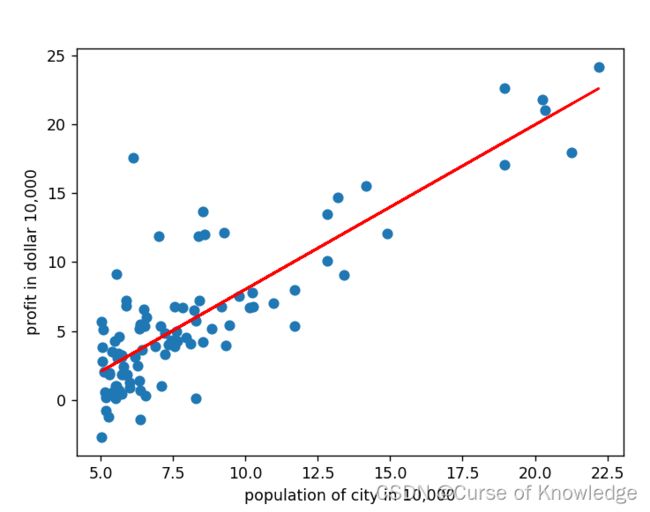
plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1])
plt.plot(X[:,1],X.dot(theta),color="r")
plt.xlabel("population of city in 10,000")
plt.ylabel("profit in dollar 10,000")
plt.show()
输出
第3648次梯度下降,达到理想误差
[[-3.89027341]
[ 1.19248036]]
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = pd.read_csv("D:\BaiduNetdiskDownload\data_sets\ex1data1.txt",names=["population","profit"])
print(data.head())
X = data.population
y = data.profit
data = np.array(data)#把dataframe转化成了numpy数组
X = data[:,0].reshape(-1,1)
X = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X),1)),X])
y = data[:,1].reshape(-1,1)
print("------------------------------------")
def J(X,y,theta):
cost = np.sum((X.dot(theta)-y)**2)/(2*len(X))
return cost
def dJ(X,y,theta):
ans =X.T.dot(X.dot(theta)-y) /len(X)
return ans#返回一个(2,1)矩阵,表示dtheta0,dtheta1
def grad_descend(X,y,theta_init,learning_rate,iters,error):
i=0
theta = theta_init
while i < iters:
grad = dJ(X, y, theta)
theta_old = theta
theta = theta - learning_rate * grad
if (abs(J(X,y,theta) - J(X,y,theta_old))) < error:
print("第{}次梯度下降,达到理想误差".format(i+1))
break
i+=1
return theta
theta = np.zeros(X.shape[1]).reshape(-1,1)
theta = grad_descend(X,y,theta,0.01,1e4,1e-8)
print(theta)
plt.scatter(data[:,0],data[:,1])
plt.plot(X[:,1],X.dot(theta),color="r")
plt.xlabel("population of city in 10,000")
plt.ylabel("profit in dollar 10,000")
plt.show()
不使用正规方程
不适用正规方程的请情况下,可以分别计算每一个特征的梯度,最后组合到一个矩阵中。下面的dj0就代表theta0的梯度,dj1代表theta的梯度,观察dj0和dj1的表达式,他们的括号内的计算式是一样的,都是全部样本的X.dot(theta)-y的求和。
def dJ(X,y,theta):
dj0 = 0
dj1 = 0
for i in range(len(X)):
dj0 += (X[i].dot(theta) - y[i]) * X[i][0]
dj1 += (X[i].dot(theta) - y[i]) * X[i][1]
dj = np.hstack([dj0,dj1]).reshape(-1,1)
return dj
检查梯度下降是否收敛
可以在grad_descend中的循环里加入以下语句,将每一次的Cost值保存到列表里,最后绘图,此时要将空列表传入函数体。
temp=J(X, y, theta)
listJ.append(temp)#将cost的值存到listJ中
#使用append就省去初始化列表,一开始创建一个空列表,追加元素就可以
#如果使用listJ[i] = temp,需要为列表提前开辟空间,但是这里的迭代次数还未知,不方便
plt.plot(listJ)
多变量线性回归
这次使用numpy中的np.load(),直接导入数据,就是二维矩阵的形式。
在求解归一化时,是对特征X归一化,不对y进行处理。同时在验证数据时,验证集数据也要进行处理。
了解python中的广播,掌握
np.std(arr,axis = None)按列进行,计算指定数据 (数组元素)沿指定轴 (如果有)的标准偏差。
np.mean()
np.min() np.max()
np.subtract()矩阵相减
代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = np.loadtxt("ex1data2.txt",delimiter = ',')
X = data[:,0:2]
y = data[:,2].reshape(-1,1)
def norm(x):
mean = np.mean(x,axis=0)
#max = np.max(x,axis=0)
#min = np.min(x, axis=0)
#size = np.subtract(max,min)
std = np.std(x,axis=0)
norm = (x - mean)/std
return mean,std,norm
mean,std,X = norm(X)
X = np.c_[np.ones(len(X)),X]
def J(X,y,theta):
cost = np.sum((X.dot(theta)-y)**2)/(2*len(X))
return cost
def dJ(X,y,theta):
#xtheta = np.dot(X,theta)-y
ans =X.T.dot(X.dot(theta)-y) /len(X)
return ans#返回一个(2,1)矩阵,表示dtheta0,dtheta1
def grad_descend(X,y,theta_init,learning_rate,iters,error,listJ):
i=0
theta = theta_init
while i < iters:
grad = dJ(X, y, theta)
temp=J(X, y, theta)
listJ.append(temp)#将cost的值存到listJ中
theta_old = theta
theta = theta - learning_rate * grad
if (abs(J(X,y,theta) - J(X,y,theta_old))) < error:
print("第{}次梯度下降,达到理想误差".format(i+1))
break
i+=1
return theta
listJ = []
theta = np.zeros(X.shape[1]).reshape(-1,1)
theta = grad_descend(X,y,theta,0.01,1e5,1e-8,listJ)
print(theta)
plt.plot(listJ)