【Linux】多线程协同
目录
生产消费模型
BlockQueue阻塞队列模型
BlockQueue.hp
Task.hpp
mypc.cc
RingQueue循环队列模型
POSIX信号量
RingQueue.hpp
Task.hpp
main.cc
生产消费模型
消费者与消费者之间关系:互斥(竞争)
生产者和消费者之间关系:互斥(不能同时访问同一个资源)&& 同步(生产与消费可同时进行)
BlockQueue阻塞队列模型
生产消费模型的任务存取由于加锁解锁过程是串行执行的,所以从阻塞队列中存入和取出任务并不高效,而高效之处体现在生产任务之前和消费任务之后的多线程并发执行
先加锁、再检测生产或消费条件是否满足、再操作、再解锁
当阻塞队列满的时候,生产者进行阻塞等待,当阻塞队列空的时候,消费者进行阻塞等待
BlockQueue.hp
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
const int g_maxCap = 5;
template
class BlockQueue {
public:
BlockQueue(const int& maxCap = g_maxCap)
: _maxCap(maxCap) {
pthread_mutex_init(&_mutex, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_pcond, nullptr);
pthread_cond_init(&_ccond, nullptr);
}
void push(const T& in) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
while (is_full()) {
//pthread_cond_wait这个函数的第二个参数,必须是正在使用的互斥锁
//pthread_cond_wait该函数调用的时候,以原子性的方式,将锁释放,并将自己挂起
//pthread_cond_wait该函数被唤醒返回的时候,会自动重新获取你传入的锁
pthread_cond_wait(&_pcond, &_mutex);
}
_q.push(in);
//pthread_cond_signal这个函数可以放在临界区内部,也可以放在外部
pthread_cond_signal(&_ccond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
void pop(T* out) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&_mutex);
while (is_empty()) {
pthread_cond_wait(&_ccond, &_mutex);
}
*out = _q.front();
_q.pop();
pthread_cond_signal(&_pcond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_mutex);
}
~BlockQueue() {
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_pcond);
pthread_cond_destroy(&_ccond);
}
private:
bool is_empty() {
return _q.empty();
}
bool is_full() {
return _q.size() == _maxCap;
}
private:
std::queue _q;
int _maxCap;
pthread_mutex_t _mutex;
pthread_cond_t _pcond; //生产者对应的条件变量
pthread_cond_t _ccond; //消费者对应的条件变量
};
Task.hpp
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
class CalTask {
using func_t = std::function;
public:
CalTask() {}
CalTask(int x, int y, char op, func_t func)
: _x(x), _y(y), _op(op), _callbask(func) {}
std::string operator()() {
int result = _callbask(_x, _y, _op);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = %d", _x, _op, _y, result);
return buffer;
}
std::string toTaskString() {
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = ?", _x, _op, _y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x, _y;
char _op;
func_t _callbask;
};
const std::string oper = "+-*/%";
int myMath(int x, int y, int op) {
if (y == 0 && (op == '/' || op == '%')) {
std::cerr << "div zero error!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
switch (op) {
case '+': return x + y;
case '-': return x - y;
case '*': return x * y;
case '/': return x / y;
case '%': return x % y;
default:
std::cerr << "oper erro!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
}
class SaveTask {
typedef std::function func_t;
public:
SaveTask() {}
SaveTask(const std::string& message, func_t func)
: _message(message), _func(func) {}
void operator()() {
_func(_message);
}
private:
std::string _message;
func_t _func;
};
void Save(const std::string& message) {
FILE* pf = fopen("./log.txt", "a");
if (!pf) {
std::cerr << "fopen error" << std::endl;
return;
}
fputs(message.c_str(), pf);
fputs("\n", pf);
fclose(pf);
}
mypc.cc
#include "BlockQueue.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
//C:计算
//S:存储
template
class BlockQueues {
public:
BlockQueue* c_bq;
BlockQueue* s_bq;
};
void* productor(void* _bqs) {
BlockQueue* bq = (static_cast*>(_bqs))->c_bq;
while (true) {
// sleep(2);
int x = rand() % 100 + 1;
int y = rand() % 10;
int operCode = rand() % oper.size();
CalTask t(x, y, oper[operCode], myMath);
bq->push(t);
std::cout << "productor thread, 生产计算任务: " << t.toTaskString() << std::endl;
}
return nullptr;
}
void* consumer(void* _bqs) {
BlockQueue* bq = (static_cast*>(_bqs))->c_bq;
BlockQueue* save_bq = (static_cast*>(_bqs))->s_bq;
while (true) {
CalTask t;
bq->pop(&t);
std::string result = t();
std::cout << "cal thread, 完成计算任务: " << result << "...done" << std::endl;
SaveTask save(result, Save);
save_bq->push(save);
std::cout << "cal thread, 推送存储任务完成..." << std::endl;
sleep(1);
}
return nullptr;
}
void* Saver(void* _bqs) {
BlockQueue* save_bq = (static_cast*>(_bqs))->s_bq;
while (true) {
SaveTask t;
save_bq->pop(&t);
t();
std::cout << "save thread, 保存任务完成..." << std::endl;
}
return nullptr;
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned long)time(nullptr) ^ getpid());
BlockQueues bqs;
bqs.c_bq = new BlockQueue();
bqs.s_bq = new BlockQueue();
pthread_t p[3], c[2], s;
pthread_create(p, nullptr, productor, &bqs);
pthread_create(p + 1, nullptr, productor, &bqs);
pthread_create(p + 2, nullptr, productor, &bqs);
pthread_create(c, nullptr, consumer, &bqs);
pthread_create(c + 1, nullptr, productor, &bqs);
pthread_create(&s, nullptr, Saver, &bqs);
pthread_join(p[0], nullptr);
pthread_join(p[1], nullptr);
pthread_join(p[2], nullptr);
pthread_join(c[0], nullptr);
pthread_join(c[1], nullptr);
pthread_join(s, nullptr);
delete bqs.c_bq;
delete bqs.s_bq;
return 0;
}
RingQueue循环队列模型
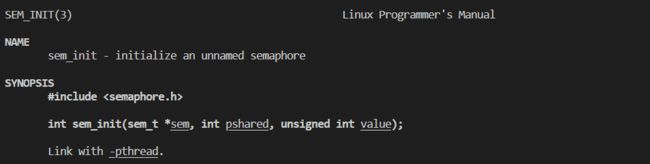
POSIX信号量
信号量本质是一个计数器:衡量临界资源中资源数量的计数器
一份公共资源,运行同时访问不同的区域
不同的线程可以并发访问公共资源的不同区域
只要拥有信号量,就在未来一定拥有临界资源的一部分
申请信号量的本质:对临界资源的特定小块资源的预定机制
通过信号量,在线程真正访问临界资源之前,就已经提前知道了临界资源的使用情况
RingQueue.hpp
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
static const int g_cap = 5;
template
class RingQueue {
private:
void P(sem_t& sem) {
int n = sem_wait(&sem);
assert(n == 0);
}
void V(sem_t& sem) {
int n = sem_post(&sem);
assert(n == 0);
}
public:
RingQueue(const int& cap = g_cap)
: _queue(cap), _cap(cap) {
int n = sem_init(&_spaceSem, 0, _cap);
assert(n == 0);
n = sem_init(&_dataSem, 0, 0);
assert(n == 0);
_productorStep = _consumerStep = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&_pmutex, nullptr);
pthread_mutex_init(&_cmutex, nullptr);
}
//生产者
void Push(const T& in) {
P(_spaceSem); //申请到了空间信号量,表示对空间进行预定
pthread_mutex_lock(&_pmutex);
_queue[_productorStep++] = in;
_productorStep %= _cap;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_pmutex);
V(_dataSem);
}
//消费者
void Pop(T* out) {
P(_dataSem);
pthread_mutex_lock(&_cmutex);
*out = _queue[_consumerStep++];
_consumerStep %= _cap;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&_cmutex);
V(_spaceSem);
}
~RingQueue() {
sem_destroy(&_spaceSem);
sem_destroy(&_dataSem);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_pmutex);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&_cmutex);
}
private:
std::vector _queue;
int _cap;
sem_t _spaceSem; //生产者:根据空间资源生产
sem_t _dataSem; //消费者:根据数据资源消费
int _productorStep;
int _consumerStep;
pthread_mutex_t _pmutex;
pthread_mutex_t _cmutex;
}; Task.hpp
#pragma
#include
#include
#include
#include
class Task {
using func_t = std::function;
// typedef std::function func_t;
public:
Task() {}
Task(int x, int y, char op, func_t func)
: _x(x), _y(y), _op(op), _callback(func) {}
std::string operator()() {
int result = _callback(_x, _y, _op);
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = %d", _x, _op, _y, result);
return buffer;
}
std::string toTaskString() {
char buffer[1024];
snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d %c %d = ?", _x, _op, _y);
return buffer;
}
private:
int _x, _y;
char _op;
func_t _callback;
};
const std::string oper = "+-*/%";
int myMath(int x, int y, char op) {
if (y == 0 && (op == '/' || op == '%')) {
std::cerr << "div zero error!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
switch (op) {
case '+': return x + y;
case '-': return x - y;
case '*': return x * y;
case '/': return x / y;
case '%': return x % y;
default:
std::cerr << "op is wrong!" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
} main.cc
#include "RingQueue.hpp"
#include "Task.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
#include
std::string SelfName() {
char name[128];
snprintf(name, sizeof(name), "thread[0x%x]", pthread_self());
return name;
}
void* ProductorRoutine(void* rq) {
RingQueue* ringqueue = static_cast*>(rq);
while (true) {
int x = rand() % 10;
int y = rand() % 5;
char op = oper[rand() % oper.size()];
Task t(x, y, op, myMath);
//生产任务
ringqueue->Push(t);
std::cout << SelfName() << ", 生产者派发了一个任务: " << t.toTaskString() << std::endl;
// sleep(1);
}
}
void* ConsumerRoutine(void* rq) {
RingQueue* ringqueue = static_cast*>(rq);
while (true) {
Task t;
//消费任务
ringqueue->Pop(&t);
std::string result = t();
std::cout << SelfName() << ", 消费者消费了一个任务: " << result << std::endl;
// sleep(1);
}
}
int main() {
srand((unsigned int)time(nullptr) ^ getpid() ^ pthread_self());
RingQueue* rq = new RingQueue();
pthread_t p[4], c[8];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
pthread_create(p + i, nullptr, ProductorRoutine, rq);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
pthread_create(c + i, nullptr, ConsumerRoutine, rq);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
pthread_join(p[i], nullptr);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
pthread_join(c[i], nullptr);
}
delete rq;
return 0;
}