Vue3技术1之Vue3简介、创建Vue3工程、分析工程结构、安装开发者工具与初识setup
Vue3技术1
- Vue3简介
-
- 发展
- 提升
- 创建Vue3工程
-
- 使用vue-cli创建
- 使用vite创建
- 分析工程结构(由vue-cli创建的)
-
- main.js
- vue.config.js
- App.vue
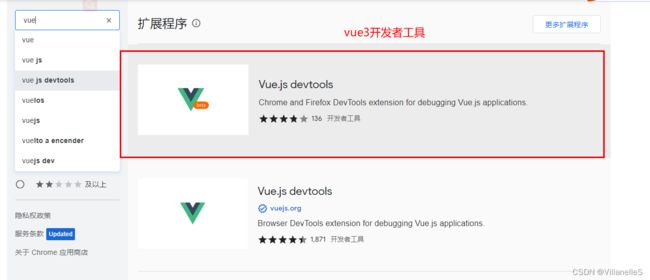
- 安装开发者工具
- 初识setup
-
- setup的两种返回值
-
- 返回一个对象
-
- App.vue
- 返回一个函数
-
- App.vue
- Vue2与Vue3混合使用
-
- App.vue
- 总结
Vue3简介
发展
- 2020年9月18日,Vue.js发布3.0版本,代号:One Piece(海贼王)
- github上的tags地址:https://github.com/vuejs/vue-next/releases/tag/v3.0.0
提升
性能的提升、源码的升级、更好的支持TypeScript、新的特性
创建Vue3工程
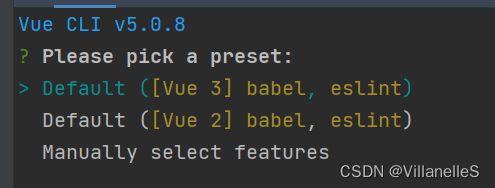
使用vue-cli创建
官方文档
- 确保vue/cli版本在4.5.0以上
vue --version
- 安装或者升级@vue/cli
npm install -g @vue/cli
- 创建
vue create vue-test
- 启动
cd vue_test
npm run serve
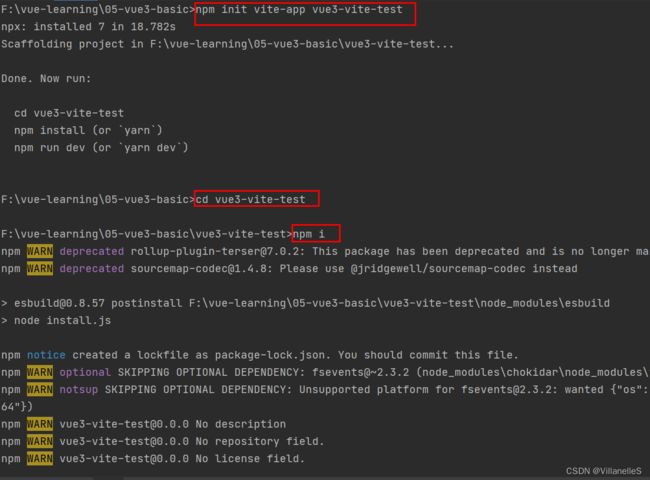
使用vite创建
- 官方文档
- vite官网
- 优势如下
- 开发环境中,无需打包操作,可快速的冷启动。
- 轻量快速的热重载(HMR)。
- 真正的按需编译,不再等待整个应用编译完成。
- 创建工程
npm init vite-app
- 进入工程
cd
- 安装依赖
npm install
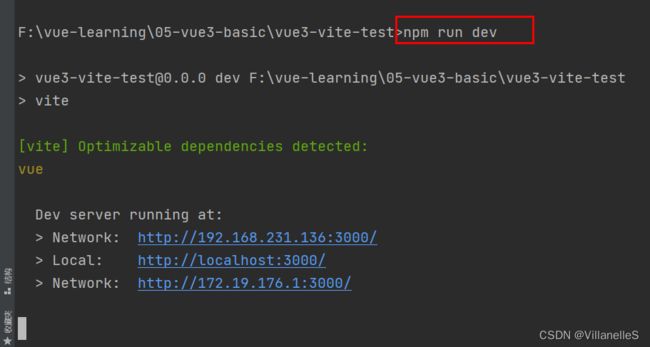
- 运行
npm run dev
分析工程结构(由vue-cli创建的)
main.js
//引入的不再是Vue构造函数了,引入的是一个名为createApp的工厂函数
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// createApp(App).mount('#app')
//创建应用实例对象-app(类似于vue2中的vm,但app比vm更“轻”)
const app=createApp(App)
console.log("app",app)
//挂载
app.mount('#app')
setTimeout(()=>{
//卸载
app.unmount("#app")
},5000)
//对比:vue2中的写法
/*const vm=new Vue({
render:h=>h(App)
})
vm.$mount("#app")*/
vue.config.js
const { defineConfig } = require('@vue/cli-service')
module.exports = defineConfig({
transpileDependencies: true,
lintOnSave: false, //关闭语法检查
})
App.vue
<template>
<img alt="Vue logo" src="./assets/logo.png">
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
HelloWorld
}
}
script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
style>
安装开发者工具
初识setup
setup的两种返回值
返回一个对象
App.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息h1>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}h2>
<button @click="sayHello">说话button>
template>
<script>
import {h} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
//此处只是测试一下setup,暂不考虑响应式的问题
setup(){
//数据
let name="张三"
let age=18
//方法
function sayHello(){
alert(`我叫${name},今年${age}岁了~`)
}
//返回一个对象(常用)
return{
name,
age,
sayHello
}
//返回一个函数(渲染函数)
// return ()=>h('h1','个人信息')
}
}
script>
返回一个函数
App.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息h1>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}h2>
<button @click="sayHello">说话button>
template>
<script>
import {h} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
//此处只是测试一下setup,暂不考虑响应式的问题
setup(){
//数据
let name="张三"
let age=18
//方法
function sayHello(){
alert(`我叫${name},今年${age}岁了~`)
}
//返回一个对象(常用)
/*return{
name,
age,
sayHello
}*/
//返回一个函数(渲染函数)
return ()=>h('h1','个人信息')
}
}
script>
Vue2与Vue3混合使用
App.vue
<template>
<h1>一个人的信息h1>
<h2>姓名:{{name}}h2>
<h2>年龄:{{age}}h2>
<h2>性别:{{sex}}h2>
<h2>a:{{a}}h2>
<button @click="sayHello">说话button>
<br>
<br>
<button @click="sayWelcome">说话button>
<br>
<br>
<button @click="test1">测试一下在Vue2的配置中去读取Vue3中的数据、方法button>
<br>
<br>
<button @click="test2">测试一下在Vue3中的setup配置中去读取Vue2的数据、方法button>
template>
<script>
import {h} from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
data(){
return{
sex:"男",
a:100
}
},
methods:{
sayWelcome(){
alert("你好"+this.sex+"士,欢迎光临")
},
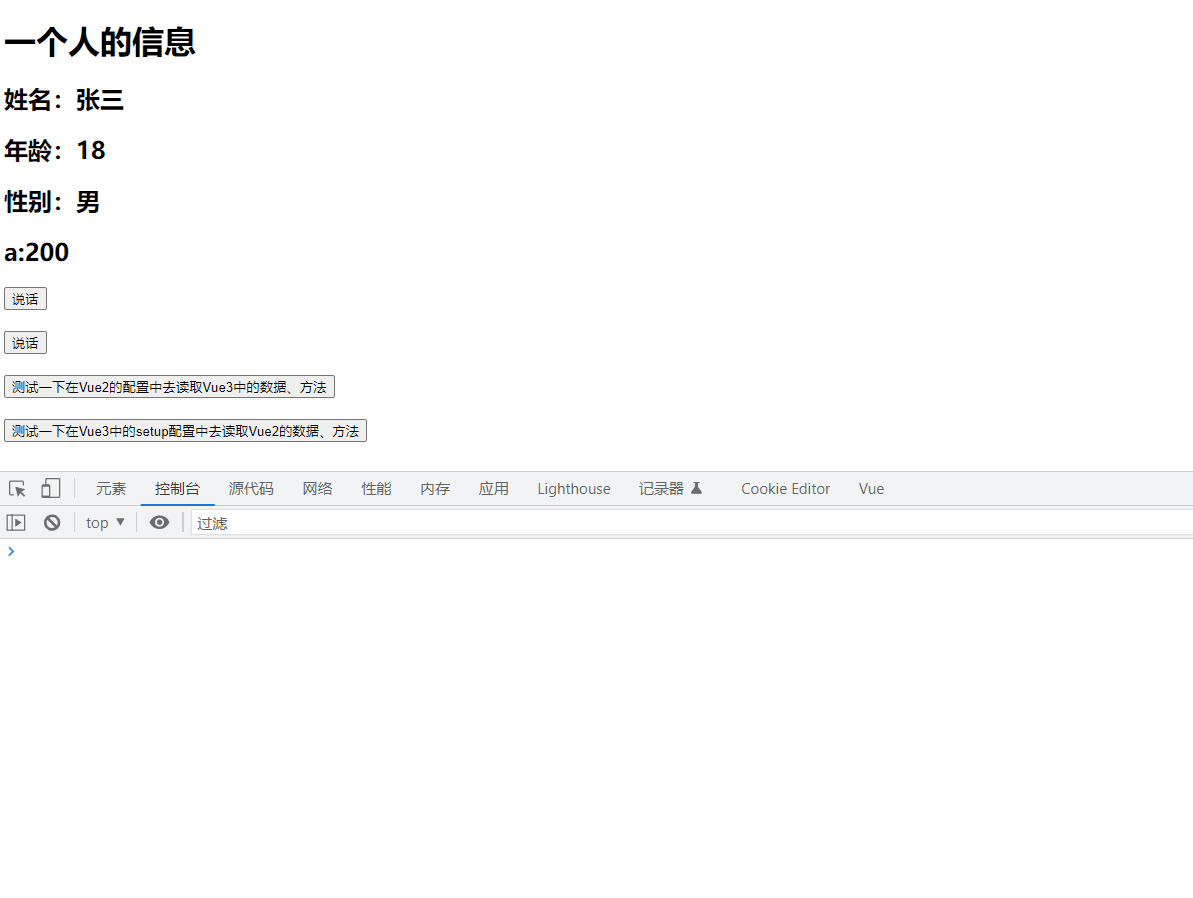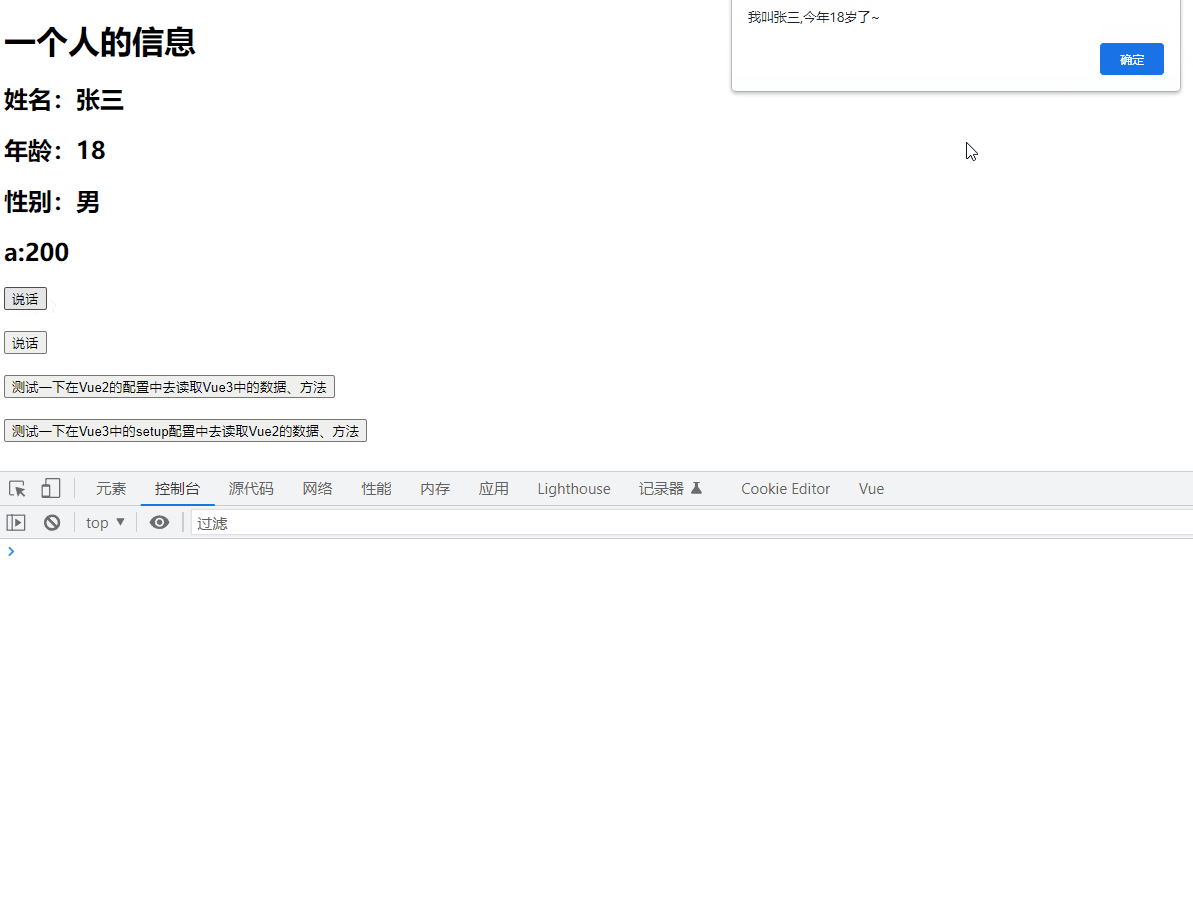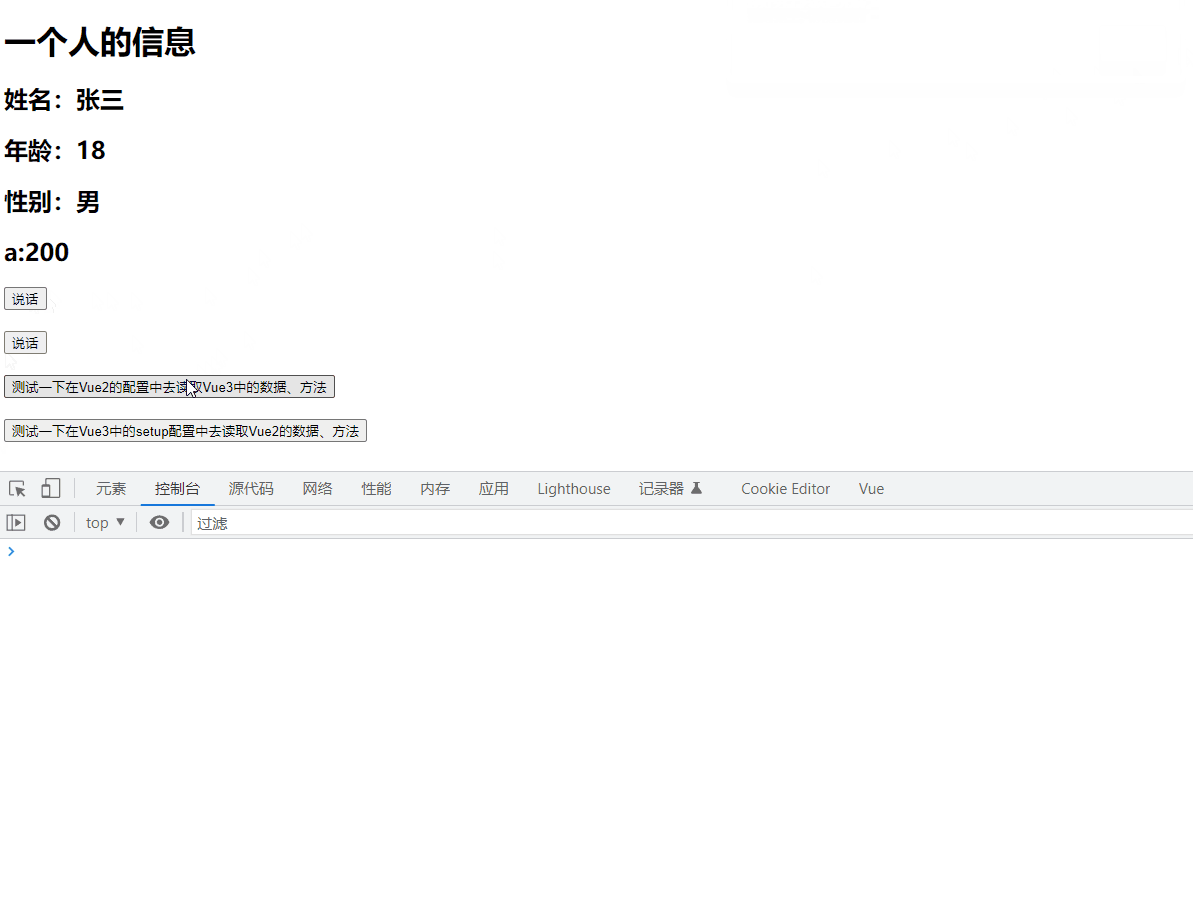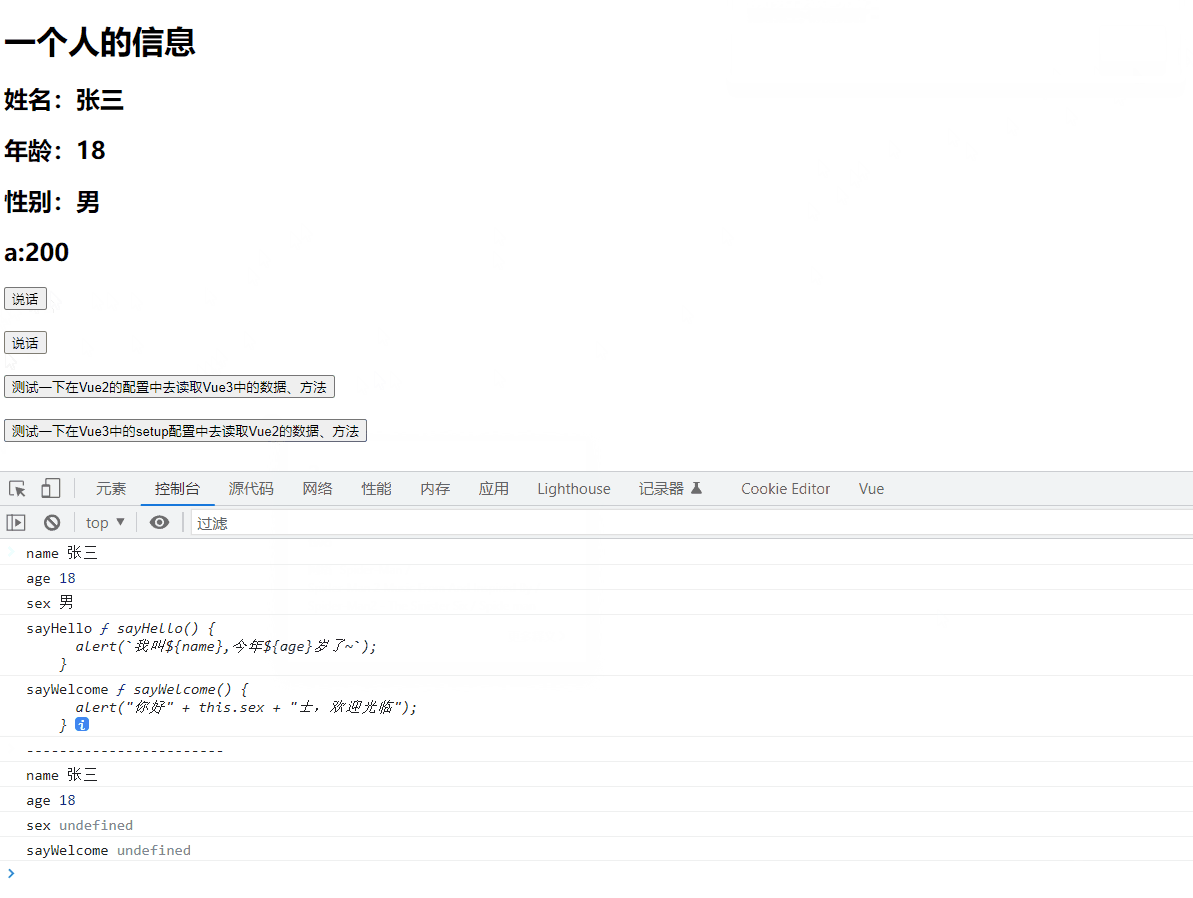
test1(){
console.log("name",this.name)
console.log("age",this.age)
console.log("sex",this.sex)
console.log("sayHello",this.sayHello)
console.log("sayWelcome",this.sayWelcome)
},
},
//此处只是测试一下setup,暂不考虑响应式的问题
setup(){
//数据
let name="张三"
let age=18
let a=200
//方法
function sayHello(){
alert(`我叫${name},今年${age}岁了~`)
}
function test2(){
console.log('------------------------')
console.log('name',name);
console.log('age',age)
console.log('sex',this.sex)
console.log('sayWelcome',this.sayWelcome)
}
//返回一个对象(常用)
return{
name,
age,
sayHello,
test2,
a
}
//返回一个函数(渲染函数)
// return ()=>h('h1','个人信息')
}
}
script>
总结
- 理解:Vue3.0中一个新的配置项,值为一个函数
- setup是所有
Composition API(组合API)“表演的舞台” - 组件中所用到的:数据、方法等等,均要配置在setup中
- setup函数的两种返回值:
(1)若返回一个对象,则对象中的属性、方法,在模板中均可以直接使用(重点关注!)
(2)若返回一个渲染函数,则可以自定义渲染内容(了解) - 注意点:
(1)尽量不要与Vue2.x配置混用
- Vue2.x配置(data、methods、computed…)中
可以访问到setup中的属性、方法 - 但在setup中
不能访问到Vue2.x配置(data、methods、computed…) - 如果有重名,setup优先
(2)setup不能是一个async函数,因为返回值不再是return的对象,而是promise,模板看不到return对象中的属性