pinia状态管理
个人主页:爱吃炫迈
系列专栏:VUE
座右铭:道阻且长,行则将至
文章目录
- 什么是pinia
- pinia的优势
- Pinia基本使用
- Pinia核心一:State
- Pinia核心二:Getters
- Pinia核心三:Actions
什么是pinia
Pinia本质上是一个状态管理的库,用于跨组件、页面进行状态共享(这点和Vuex、Redux一样),是Vuex的代替者。
pinia的优势
-
Vue2 和 Vue3 都能支持
-
抛弃传统的
Mutation,只有state, getter和action,简化状态管理库 -
不再有modules的嵌套结构,符合 Vue3 的 Composition api,让代码扁平化
-
更友好的TypeScript支持
-
不再有命名空间的概念,不需要记住它们的复杂关系;
-
代码简介,很好的代码自动分割
Pinia基本使用
1. 初始化项目:npm init vite@latest
2. 安装pinia:npm install pinia / yarn add pinia
3. 挂载pinia:
// src/main.js
import { createApp } from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import { createPinia } from "pinia";
const pinia = createPinia();
const app = createApp(App);
app.use(pinia);
app.mount("#app");
4. 定义Store:
Store是神马
一个 Store (如 Pinia)是一个实体,它会持有为绑定到你组件树的状态和业务逻辑,也就是保存了全局的状态;
它始终存在,并且每个人都可以读取和写入的组件;
你可以在你的应用程序中定义任意数量的Store来管理你的状态;
Store有三个核心概念
state、getters、actions;
等同于组件的data、computed、methods;
一旦 store 被实例化,你就可以直接在 store 上访问 state、getters 和 actions 中定义的任何属性;
// src/store/index.js
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
export const useMain = defineStore("main", {
state: () => {
return {
count: 0,
message: 'hello word'
};
},
getters: {},
actions: {},
});
Store的唯一名称
这个名称是必要的,Pinia 使用它来将 store 连接到 devtools。
返回的函数统一使用useX作为命名方案,这是约定的规范;
5. 使用Store:
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h2>{{ store.count }}</h2>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped></style>
6. 解构store:
Store获取到后不能被解构,那么会失去响应式;
为了从 Store 中提取属性同时保持其响应式,需要使用storeToRefs()/toRefs()。
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<template>
//传统方式解构
<h2>count:{{ count }}</h2>
//toRefs方式解构
<h2>count2:{{ count2 }}</h2>
//storeToRefs方式解构
<h2>count3:{{ count3 }}</h2>
//定义一个按钮,用于点击时,令count+1
<button @click="changecount">count</button>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
import { toRefs } from "vue";
import { storeToRefs } from "pinia";
const store = useMain();
// 传统的解构方式
const { count } = store;
// toRefs方式
const { count: count2 } = toRefs(store);
// storeToRefs方式
const { count: count3 } = storeToRefs(store);
//令count+1
const changecount = () => {
store.count++;
};
</script>
<style lang="less" scoped></style>
Pinia核心一:State
state 是 store 的核心部分,因为store是用来帮助我们管理状态的。
在 Pinia 中,状态被定义为返回初始状态的函数;
上文已经演示过State的定义啦,下面写写怎么操作state!!!
改变State:修改简单数据
直接通过在方法中操作store.属性名修改
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
store.count++
</script>
改变State:多条数据修改
通过基础数据修改方式去修改多条数据也是可行的,但是在
pinia官网中,已经明确表示$patch的方式是经过优化的,会加快修改速度,对性能有很大好处,所以在进行多条数据修改的时候,更推荐使用$patch
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
store.$patch({
count: 200,
message: "hello pinia",
});
</script>
重置State:$reset
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
store.$reset();
</script>
替换State:$state
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
store.$state = {
name: "jack",
age: 19,
};
</script>
Pinia核心二:Getters
Getters相当于Store的计算属性,在获取 State值之前做一些逻辑处理
定义Getters
它们可以用
defineStore()中的 getters 属性定义;getters中可以定义接受一个
state作为参数的函数;getters还可以使用
this来改变数据
// src/store/index.js
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
export const useMain = defineStore("main", {
state: () => {
return {
count: 0,
message: "hello word",
firstname: "jack",
lastname: "bryant",
age: 19,
};
},
getters: {
doubleCounter: function (state) {
return state.count * 2;
//return this.count * 2;
},
doublePlusOne: function (state) {
return state.count * 2 + 1
//return this.count * 2 + 1
},
fullname: function (state) {
return state.firstname + state.lastname;
//return this.firstname + this.lastname;
},
},
});
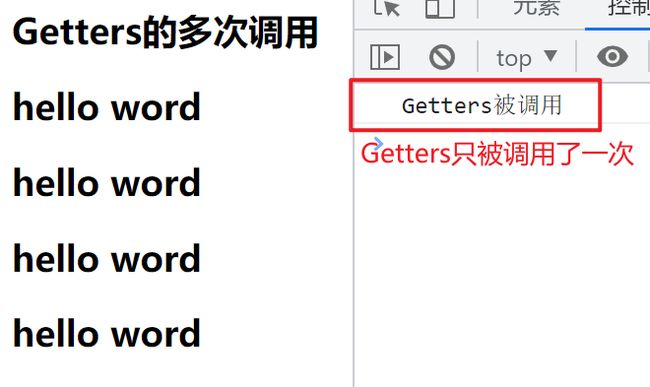
Getters特性
getter 中的值有缓存特性,如果值没有改变,多次使用也只会调用一次。
// src/store/index.js
getters: {
foo: (state) => {
console.log("Getters被调用");
return state.message;
}
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h2>Getters的多次调用</h2>
<h2>{{ store.doubleCounter }}</h2>
<h2>{{ store.doubleCounter }}</h2>
<h2>{{ store.doubleCounter }}</h2>
<h2>{{ store.doubleCounter }}</h2>
</template>
操作Getters
1.访问当前store的Getters:
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h2>{{ store.doubleCounter }}</h2>
<h2>{{ store.doublePlusOne }}</h2>
<h2>{{ store.fullname }}</h2>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
</script>
2.Getters中访问自己的其他Getters:
// src/store/index.js
getters: {
doubleCounter: function (state) {
return state.count * 2;
},
doublePlusOne: function (state) {
// state.count * 2 + 1
//访问了Getters中的doubleCounter
return this.doubleCounter + 1;
},
fullname: function (state) {
return state.firstname + state.lastname;
},
},
3.访问其他store中的Getters
// src/store/index.js
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
import { useInfo } from "./index1";
export const useMain = defineStore("main", {
state: () => {
return {
count: 0,
message: "hello word",
firstname: "jack",
lastname: "bryant",
age: 19,
};
},
getters: {
message: function (state) {
const useInfoStore = useInfo();
//访问了useInfoStore中的Getters中的heightInfo属性
return this.fullname + ":" + useInfoStore.heightInfo;
},
},
});
//新建一个store
// src/store/index1.js
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
export const useInfo = defineStore("info", {
state: () => {
return {
height: 1.89,
};
},
getters: {
heightInfo: function (state) {
return state.height * 2;
},
},
});
4.Getters也可以返回一个函数,这样就可以接受参数:
// src/store/index.js
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
export const useMain = defineStore("main", {
state: () => {
return {
user: [
{ id: 111, name: "jack" },
{ id: 222, name: "kobe" },
],
};
},
getters: {
getById: function (state) {
return (userId) => {
return state.user.find((item) => item.id === userId);
};
},
},
});
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h2>{{ getUserById(111) }}</h2>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
const getUserById = store.getById;
</script>
Pinia核心三:Actions
定义Actions
Actions 相当于组件中的 methods。
- 可以使用 defineStore() 中的 actions 属性定义,并且它们非常适合定义业务逻辑;
- 和getters一样,在action中可以通过this访问整个store实例的所有操作;
操作Actions
// src/store/index.js
import { defineStore } from "pinia";
export const useMain = defineStore("main", {
state: () => {
return {
count: 0,
};
},
getters: {},
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++;
},
randomCount() {
this.count = Math.random();
},
},
});
//src/components/HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h2>{{ store.count }}</h2>
<button @click="actionClick">actions</button>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useMain } from "../store/index";
const store = useMain();
const actionClick = () => {
store.increment();
};
</script>
异步Actions
action 可以像写一个简单的函数一样支持 async/await 的语法,让你愉快的应付异步处理的场景。
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user',
actions: {
async login(account, pwd) {
const { data } = await api.login(account, pwd)
return data
}
}
})