由QCustomplot引发drawPolyline和drawLine的区别
QPainter drawPolyline和drawLine
- 一、起因
- 二、原因分析
-
- 2.1 测试
- 2.1 查看QCustomplot中绘制源码
- 三、解决方法
- 四、drawPolyline和drawLine的区别
- 五、对QCharts进行测试
一、起因
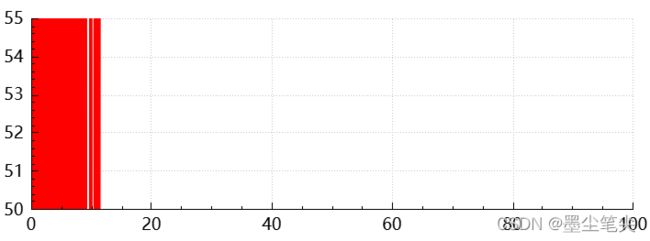
最近在使用QCustomplot绘制曲线图时,遇到性能低下(卡顿甚至无响应)。测试的功能为用rand()函数动态生成1000个数据点,其数据值范围为0<=X<1000, 0<=Y<100, X步进=0.1,其代码如下:
#include 注意代码中的第19行和21行(line->setPen(QPen(Qt::red, 2));, plot_->yAxis->setRange(50, 55);)。设置了Y轴范围为50~55,即只能显示部分图像。其运行结果如下,当数据点数为100个左右开始出现明显卡顿,且CPU占用高。
二、原因分析
2.1 测试
测试环境如下:
- 开发环境:Qt6.2、vs2022;
- CPU:Core i5-1135G7、4核8线程;
| 画笔宽度 | Y轴范围 | 窗口大小 | CPU占用 | 测试现象 | Y轴取值对应像素高度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPen(Qt::red, 2) | (50,55) | 754*347 | 12.4% | 非常卡顿 | 100 / (55 - 50) * 347 = 6940 |
| QPen(Qt::red, 2) | (0,100) | 2160x1440 | 12% | 卡顿 | 100 / (100 - 0) * 1440 = 1440 |
| QPen(Qt::red, 2) | (0,100) | 754*347 | 8% | 较为卡顿 | 100 / (100 - 0) * 347 = 347 |
| QPen(Qt::red, 1) | (50,55) | 754*347 | 1% | 流畅 | 100 / (55 - 50) * 347 = 6940 |
| QPen(Qt::red, 1) | (0,100) | 754*347 | 0.6% | 流畅 | 100 / (100 - 0) * 347 = 347 |
经过上述测试可以看出当画笔宽度大于1且点坐标映射到像素坐标后像素坐标取值范围较大时将出现卡顿现象,也可以理解为将图放大到一定程度。
2.1 查看QCustomplot中绘制源码
- 调用plot_->replot()后,在replot中将对各个图层进行绘制,如坐标轴、曲线、文字、图例等;
void QCustomPlot::replot(QCustomPlot::RefreshPriority refreshPriority)
{
...
//绘制各个图层
foreach (QCPLayer *layer, mLayers)
layer->drawToPaintBuffer();
...
}
void QCPLayer::drawToPaintBuffer()
{
...
if (painter->isActive())
draw(painter);//利用多态调用相应绘制函数
...
}
void QCPGraph::draw(QCPPainter *painter)
{
...
getLines(&lines, lineDataRange);//转换为像素坐标
...
drawLinePlot(painter, lines); //绘制曲线
...
}
void QCPGraph::drawLinePlot(QCPPainter *painter, const QVector<QPointF> &lines) const
{
...
drawPolyline(painter, lines);
...
}
- 下面来看drawPolyline函数,此函数位于qcustomplot.h中,其中根据绘制标志不同,选择drawLine或者drawPolyline函数。而上述测试代码则默认选择的drawPolyline函数。
template <class DataType>
void QCPAbstractPlottable1D<DataType>::drawPolyline(QCPPainter *painter, const QVector<QPointF> &lineData) const
{
...
if (mParentPlot->plottingHints().testFlag(QCP::phFastPolylines) && painter->pen().style() == Qt::SolidLine &&
!painter->modes().testFlag(QCPPainter::pmVectorized) && !painter->modes().testFlag(QCPPainter::pmNoCaching))
{
...
while (i < lineDataSize) {
...
painter->drawLine(lineData.at(i-1), lineData.at(i));
...
}
} else
{
...
// draw last segment:
painter->drawPolyline(lineData.constData()+segmentStart, lineDataSize-segmentStart);
}
}
三、解决方法
长上述源码可以看到,使用QCP::phFastPolylines则可以使用drawLine函数绘制,性能将明显提升。设置快速绘制标志的方法为plot_->setPlottingHint(QCP::phFastPolylines);。
设置为QCP::phFastPolylines后,进行性能测试:
| 画笔宽度 | Y轴范围 | 窗口大小 | CPU占用 | 测试现象 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QPen(Qt::red, 2) | (50, 55) | 754*347 | 0.6% | 流畅 |
| QPen(Qt::red, 2) | (50, 55) | 2160x1440 | 7% | 流畅 |
从源码注释也可看出
enum PlottingHint {
phNone = 0x000 /// No hints are set
,phFastPolylines = 0x001 /// Graph/Curve lines are drawn with a faster method. This reduces the quality especially of the line segment joins, thus is most effective for pen sizes larger than 1. It is only used for solid line pens.
,phImmediateRefresh = 0x002 /// causes an immediate repaint() instead of a soft update() when QCustomPlot::replot() is called with parameter QCustomPlot::rpRefreshHint. This is set by default to prevent the plot from freezing on fast consecutive replots (e.g. user drags ranges with mouse).
,phCacheLabels = 0x004 /// axis (tick) labels will be cached as pixmaps, increasing replot performance.
};
phFastPolylines:用更快的方法绘制图形/曲线的线,但是会降低质量,特别是线段连接处的质量,因此对线宽大于1的画笔最有效。 它只用于实线。
四、drawPolyline和drawLine的区别
上面说会降低绘制质量,特别是线段连接处。下面看看drawPolyline和drawLine绘制出的线段的区别。
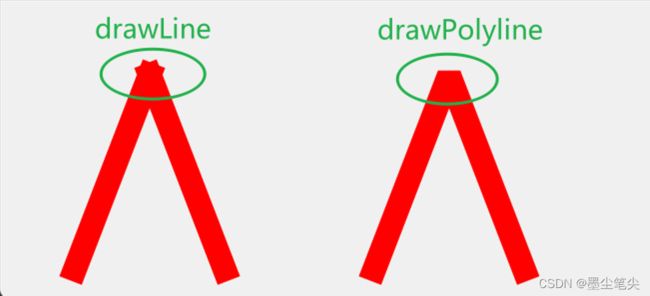
测试代码如下:
#include 从上图可以看出drawPloyline绘制的线段会对连接处进行裁剪等操作,使连接处更加圆滑,这也将增加更多的计算,由此导致性能低下。对上图中的绘制进行耗时测量,测量结果如下(有3~5倍的差距):

五、对QCharts进行测试
对QCharts的测试显示,默认使用drawLine方式进行绘制。
测试结果如下:
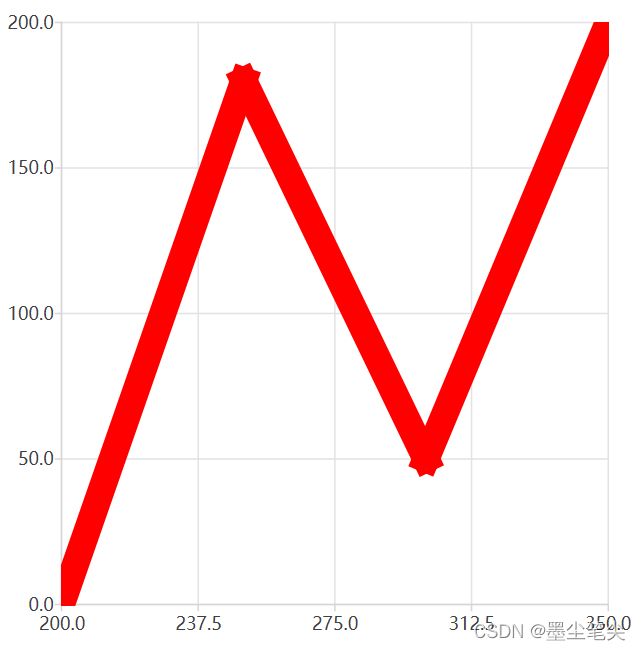
测试代码如下:
#include