【C++初阶】4. Date类的实现
如果下面博客有不理解的地方,可以查看源码:代码提交:日期类的实现
1. 构造函数的实现
由于系统实现的默认构造函数即便采用默认值的形式也只能存在1个固定的默认日期(例如:1997-1-1)。所以,构造函数需要显示实现
//判断日期是否正确
bool Date::IsTrueDate(int year, int month, int day)
{
static int arr[13] = { 0,31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month > 12)
return false;
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0) && month == 2)
{
if (day > 28)
{
return false;
}
}
if (day > arr[month])
return false;
return true;
}
class Date
{
public:
// 声明定义分离
bool IsTrueDate(int year, int month, int day);
Date(int year = 2023,int month = 3,int day = 18)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
默认构造函数有三类:无参,全缺省参数,系统默认生成
这边采用的是全缺省的方式:要根据传递过来的参数来实现不同的日期
声明与定义是否需要分离?
对于频繁调用的接口(例如:构造函数),推荐声明与定义不分离,编译器将其转化为内联函数(inline),在调用的地方直接展开(减少拷贝,提高效率)
对于不频繁调用且冗余的接口,推荐分离,因为不方便展开(展开会显得代码太长)
2. 析构函数
由于没有资源的申请,所以不需要手动实现析构函数,采用系统默认的即可
3. 拷贝构造函数
因为编译器默认生成的拷贝为浅拷贝,可以满足需求,所以可以不需要实现 但是日期类的
//隐藏的this指针 Date(Date* const this,const Date& d)
//Date d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
4. 赋值重载
因为编译器默认生成的拷贝为浅拷贝,可以满足需求,所以可以不需要实现
5. Print
void Print()
{
cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl;
}
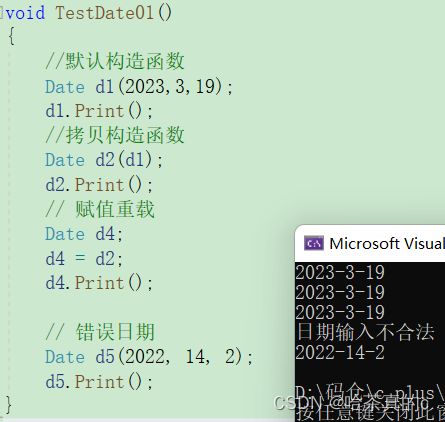
TestDate01
6. 重载 == (operator==)
bool operator==(const Date& d) const
{
return _year == d._year
&& _month == d._month
&& _day == d._day;
}
为啥末尾要加const修饰呢?
末尾加上const修饰其实修饰的是隐藏的this指针,因为==的运算符重载不会改变this指针所指向的内容。
加上const修饰之后,可以保护数据不被修改,增加代码的健壮性。
7. 重载 > (operator>)
声明与定义分离
bool operator>(const Date& d) const;
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{
if (_year > d._year)
return true;
if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
return true;
if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day)
return true;
return false;
}
8. 重载 >= (operator>=)
bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{
// 接口的复用 operator== 和 operator>
return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}
9. 重载 != (operator!=)
bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
10. 重载 < (operator<)
bool operator<(const Date& d) const;
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
11. 重载 <= (operator<)
bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{
return (*this < d) && (*this == d);
}
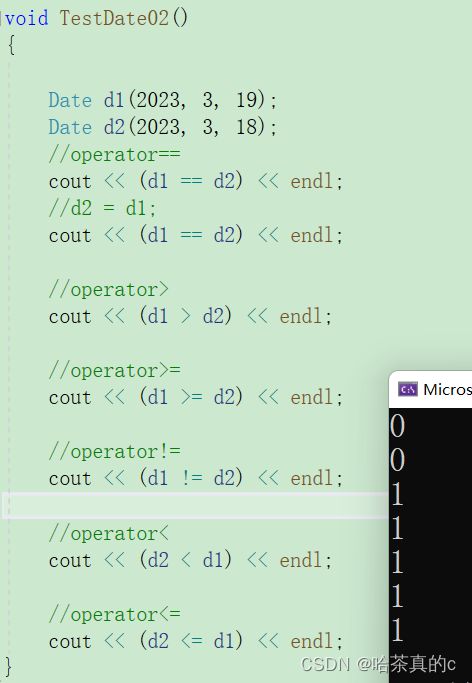
TestDate02
12. 重载 += (operator+=)
//在Date.cpp中定义
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int monthDayArray[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return monthDayArray[month];
}
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
//加个判断
if (day < 0)
{
// 接口复用 operator-=
// 因为天数小于0,所以带负号
*this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
_month++;
if (_month > 12)
{
_year++;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
13. 重载 -= (operator-=)
Date& operator-=(int day);
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
//加个判断
if (day < 0)
{
// 接口复用 operator+=
// 因为天数小于0,所以带负号
*this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day < 0)
{
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month-1);
_month--;
if (_month < 1)
{
_year--;
_month = 13;
}
}
return *this;
}
14. 重载 - (operator-)
Date operator-(int day);
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
//拷贝构造 ret对象
Date ret = *this;
//重载-=
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
为啥这边operator-的返回值是Date(传值返回) 而不是传引用返回呢?
因为-操作并不会影响this指针指向对象的值,所以需要拷贝构造一个临时变量进行操作符运算
15. 重载 + (operator+)
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
//拷贝构造 ret对象
Date ret = *this;
//重载+=
ret += day;
return ret;
}
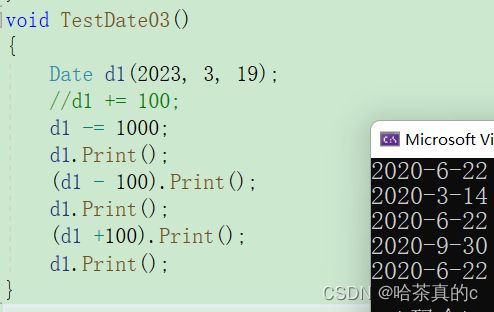
TestDate03
16. 重载 后置++ (operator++)
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date ret = *this;
*this += 1;
return ret;
}
为啥后置++要传值返回呢?前置++可以传引用返回呢
因为后置++是先返回值,再进行++操作。
而前置++是先++,再返回++后的值。
17. 重载 前置++(operator++)(int)
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
18. 重载 后置-- (operator--)
// 后置--
Date operator--(int);
// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date ret = *this;
*this -= 1;
return ret;
}
19. 重载 前置-- (operator--)(int)
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
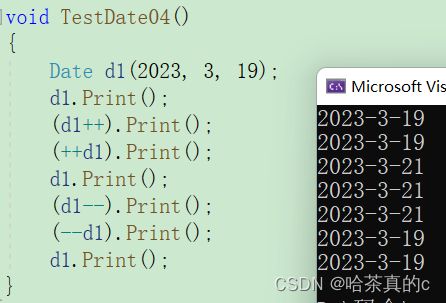
TestDate04
20. 重载- (operator-)
// 日期减
int operator-(const Date& d);
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
//在二者中找一个小的日期类不断++ 直到与大的日期相等即可
int date = 0;
// 假设this大 d小
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
if (max < min)
{
// this小 d大
max = d;
min = *this;
}
while (min != max)
{
++date;
++min;
}
return date;
}
TestDate05
21. 流插入重载 (operator<<)
因为流插入,流提取的操作符是cout<,是将类型流向控制台或者从控制台提取出来,所以不能实现成成员函数,否则就是d1.operator<<(d1<
在类中任意位置声明友元函数即可。
class Date
{
// 友元声明(类的任意位置)
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& out, Date& d);
//....
这里的operator>>参数为啥是Date& 而不是const Date& 呢?
因为流插入就是要修改Date对象的,所以不能拿const修饰
inline ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day << endl;
return out;
}
这里能不能不设计成inline内联呢?
答案是不行的,因为该函数是定义在Date.h文件当中,而Date.h又会在两个文件中都引用,在编译阶段,Date.cpp 和 Test.cpp 两个文件当中的头文件分别展开 那么在链接的过程中,不加inline就会使函数出现在符号表当中,而两份代码会导致两个地址,出现链接错误。
所以必须要inline内联,或者定义成static静态函数,改变其链接属性,使其无法出现在符号表
这里函数要返回值是为啥?ostream&
是因为要连续赋值,cin >>d1>>d2;类似这种场景,如果不传返回值,则无法进行连续操作
22. 流提取重载 (operator>>)
inline istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}