Python-Utils
plt直接显示一张或者多张图片
import os
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 自己简单封装一下图片显示函数
def cv_show(img,name='img'):
cv2.imshow(name,img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 封装一下 直接展示多张图片 可以读好再传进来 但是得plt.imread()读 不能cv2.imread()因为二者RGB通道顺序不一样
def plt_shows(M,imgs):
''' 传入文件路径即可
参数M表示一行几个
'''
N = int(np.ceil(len(imgs)/M))
#形成NxM大小的画布
for i in range(len(imgs)):
img = imgs[i]
if type(img) is str: img = plt.imread(imgs[i])
plt.subplot(N,M,i+1)#表示第i张图片,下标只能从1开始,不能从0,
plt.imshow(img)
#下面两行是消除每张图片自己单独的横纵坐标,不然每张图片会有单独的横纵坐标,影响美观
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
# 封装一下 直接展示1张图片 可以读好再传进来 但是得plt.imread()读 不能cv2.imread()因为二者RGB通道顺序不一样
def plt_show(img):
if type(img) is str: img = plt.imread(img)
plt.subplot(1,1,1)#表示第i张图片,下标只能从1开始,不能从0,
plt.imshow(img)
#下面两行是消除每张图片自己单独的横纵坐标,不然每张图片会有单独的横纵坐标,影响美观
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
目录相关
重新创建目录
def reMakeDir(dir):
if os.path.exists(dir):
shutil.rmtree(dir)
os.mkdir(dir)
单个目录下的全路径名
def allPath(dir):
files = []
for name in os.listdir(dir):
file = os.path.join(dir,name)
files.append(file)
return files
从一个目录中随机抽取出xx%的样本
import cv2
import shutil
import os
import random
def copyFile(srcfile, dstpath):
'''
:param srcfile: 被复制文件名
:param dstpath: 复制到的路径
:return:
'''
if not os.path.isfile(srcfile):
print("%s not exist!" % (srcfile)) # 文件不存在
else:
fpath, fname = os.path.split(srcfile) # 分离文件名和路径
if not os.path.exists(dstpath):
os.makedirs(dstpath) # 创建路径(多级路径都可以创建)
newname = fname
spl = fname.split('.')
i = 1
while os.path.exists(os.path.join(dstpath, newname)):
newname = f'{spl[0]}-{i}.{spl[1]}' # 重名就重命名
i += 1
shutil.copy(srcfile, os.path.join(dstpath, newname)) # 复制文件
## main
file_dir = 'C:/data/task1and4new/version01'
out_dir = 'C:/data/task1and4new/version01_0.1'
count = 0
for dir in os.listdir(file_dir):
files = os.listdir(file_dir+'/'+dir)
n = int(len(files)*0.1) # 随机抽取数量 10%
print('-----------',dir)
randomFiles = random.sample(files,n) # list(files)中随机抽取n个元素
for file in randomFiles:
filepath = os.path.join(file_dir,dir,file)
copyFile(filepath,out_dir+'/'+dir)
print('copy',filepath,'to',copypath,'successfully!')
print(count)
二分法,失败时严格返回应该插入的位置下标
# 二分法本身可以没有递归 失败就返回该插入的位置
def binarySearch(data, k):
i, j = 0, len(data) - 1 # i,j是严格合法下标的上下限值
while i <= j: # 等号不能少 否则比最大的值还大时返回 len(data)-1 而非 len(data)
mid = (i + j) // 2
if data[mid] == k:
return mid
elif k < data[mid]:
j = mid - 1
else:
i = mid + 1
return i # 失败的位置就是该插入的位置 #此时 i>j即i=j+1 也就是应该插入的位置
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = [1, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5]
k = 6
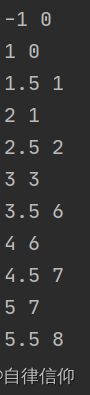
test = [-1, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5, 5, 5.5]
for i in test:
print(i, binarySearch(data, i))
Permutation 全排列
python 全排列,permutations函数
itertools.permutations(iterable, r=None)
连续返回由 iterable 元素生成长度为 r 的排列。
import itertools
n = 3
for i in itertools.permutations(range(1,n+1)):
print(i)
import itertools
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = 'abc'
for i in itertools.permutations(data):
print(i)
import itertools
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = 'abcd'
for i in itertools.permutations(data, 3):
print(i)
('a', 'b', 'c')
('a', 'b', 'd')
('a', 'c', 'b')
('a', 'c', 'd')
('a', 'd', 'b')
('a', 'd', 'c')
('b', 'a', 'c')
('b', 'a', 'd')
('b', 'c', 'a')
('b', 'c', 'd')
('b', 'd', 'a')
('b', 'd', 'c')
('c', 'a', 'b')
('c', 'a', 'd')
('c', 'b', 'a')
('c', 'b', 'd')
('c', 'd', 'a')
('c', 'd', 'b')
('d', 'a', 'b')
('d', 'a', 'c')
('d', 'b', 'a')
('d', 'b', 'c')
('d', 'c', 'a')
('d', 'c', 'b')