canvas系列教程06 ——边界检测、碰撞检测
边界检测
边界检测,即检测一个物体所处“运动环境的范围”(也就是边界)。
边界限制(避免越界)
if (ball.x < ball.radius) {
//小球"碰到"左边界时做什么
} else if (ball.x > cnv.width - ball.radius) {
//小球"碰到"右边界时做什么
}
if (ball.y < ball.radius) {
//小球"碰到"上边界时做什么
} else if (ball.y > cnv.height - ball.radius) {
//小球"碰到"下边界时做什么
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function() {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//初始化数据
var ball = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2);
ball.fill(cxt);
var key = tools.getKey();
//添加键盘事件
window.addEventListener(
"keydown",
function(e) {
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//根据key.direction的值,判断物体移动方向
switch (key.direction) {
case "up":
ball.y -= 3;
checkBorder();
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
case "down":
ball.y += 3;
checkBorder();
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
case "left":
ball.x -= 3;
checkBorder();
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
case "right":
ball.x += 3;
checkBorder();
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
default:
checkBorder();
ball.fill(cxt);
}
},
false
);
//定义边界检测函数
function checkBorder() {
//当小球碰到上边界时
if (ball.y < ball.radius) {
ball.y = ball.radius;
//当小球碰到下边界时
} else if (ball.y > cnv.height - ball.radius) {
ball.y = cnv.height - ball.radius;
}
//当小球碰到左边界时
if (ball.x < ball.radius) {
ball.x = ball.radius;
//当小球碰到右边界时
} else if (ball.x > cnv.width - ball.radius) {
ball.x = cnv.width - ball.radius;
}
}
};
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas
id="canvas"
width="200"
height="150"
style="border:1px solid silver;"
>canvas>
body>
html>
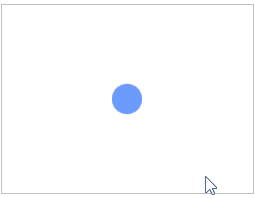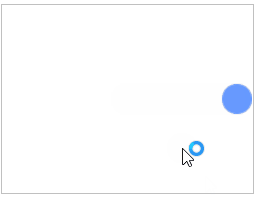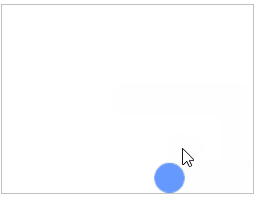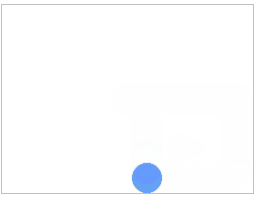
通过键盘中的“↑、↓、←、→”以及“W、S、A、D”这八个键来控制小球的移动方向。然后定义一个边界检测函数checkBorder(),用来限制小球的移动范围,避免其移出画布。
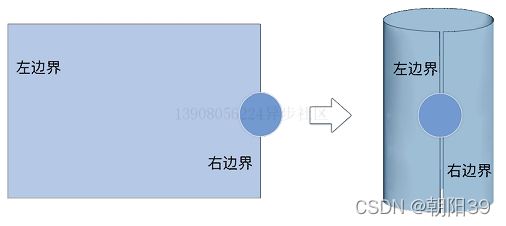
边界环绕
边界环绕,指的是当物体从一个边界消失后,它就会从对立的边界重新出现,从而形成一种环绕效果。简单来说,就是如果物体从左边界消失,然后就会从右边界出现;如果物体从下边界消失,然后就会从上边界出现,以此类推。
if(ball.x < -ball.radius){
//小球"完全超出"左边界时
} else if(ball.x>cnv.width + ball.radius){
//小球"完全超出"右边界时
}
if(ball.y<-ball.radius){
//小球"完全超出"上边界时
} else if(ball.y>cnv.height + ball.radius){
//小球"完全超出"下边界时
}

注意一个关键字:“完全超出”。当小球完全超出边界时,此时小球在画布外面,小球中心与画布边界的距离刚好也是小球的半径。
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//初始化数据
var ball = new Ball(0, cnv.height / 2);
var vx = 2;
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
ball.x += vx;
//当小球"完全超出"右边界时
if (ball.x > cnv.width + ball.radius) {
ball.x = -ball.radius;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
- 添加键盘事件,然后可以根据键盘中的“↑、→、↓、←”以及“W、S、A、D”这八个键来控制小球的移动方向。当小球从一个边界完全消失后,它就会从对面的边界重新生成。
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
var ball = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2);
ball.fill(cxt);
var key = tools.getKey();
//添加键盘事件
window.addEventListener("keydown", function (e) {
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//根据key.direction的值,判断小球移动方向
switch (key.direction) {
case "up":
ball.y -= 3;
//检测上边界
if (ball.y < -ball.radius) {
ball.y = cnv.height + ball.radius;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
case "down":
ball.y += 3;
//检测下边界
if (ball.y > cnv.height + ball.radius) {
ball.y = -ball.radius;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
case "left":
ball.x -= 3;
//检测左边界
if (ball.x < -ball.radius) {
ball.x = cnv.width + ball.radius;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
case "right":
ball.x += 3;
//检测右边界
if (ball.x > cnv.width + ball.radius) {
ball.x = -ball.radius;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
break;
//default值
default:
ball.fill(cxt);
}
}, false);
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
边界生成
边界生成,指的是物体完全超出边界之后,会在最开始的位置重新生成。可用于创建喷泉以及各种粒子特效。例如在喷泉效果中,水滴不断地飞溅出来,飞出Canvas后会重新加入到水流的源头。
边界生成,可以源源不断地为Canvas提供运动物体,而又不用担心Canvas上的物体过多以至于影响浏览器的性能速度,因为物体的数量是固定不变的。
if (ball.x < -ball.radius ||
ball.x > cnv.width + ball.radius ||
ball.y < -ball.radius ||
ball.y > cnv.height + ball.radius) {
……
}
封装【生成随机颜色】的函数,添加到 js/tool.js 中
window.tools.getRandomColor=function(){
return ‘#’ +
(function (color) {
return (color += ‘0123456789abcdef’[Math.floor(Math.random() * 16)])
&& (color.length == 6) ? color : arguments.callee(color);
})(‘’);
}
实战范例:无限爆炸发散
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//定义一个用来存放小球的数组balls
var balls = [];
//n表示小球数量
var n = 50;
//生成n个小球,其中小球的color、vx、vy都是随机值
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
//球心坐标为Canvas中心,color为随机颜色值
var ball = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2, 5, tools.getRandomColor());
//ball.vx和ball.vy取值都是:-1~1之间的任意数
ball.vx = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
ball.vy = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
//添加到数组balls中
balls.push(ball);
}
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//使用forEach()函数遍历数组balls
balls.forEach(function (ball) {
//边界检测,使得小球完全移出画布后会在中心位置重新生成
if (ball.x < -ball.radius ||
ball.x > cnv.width + ball.radius ||
ball.y < -ball.radius ||
ball.y > cnv.height + ball.radius) {
ball.x = cnv.width / 2;
ball.y = cnv.height / 2;
ball.vx = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
ball.vy = Math.random() * 2 - 1;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
ball.x += ball.vx;
ball.y += ball.vy;
})
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
实战范例:爆米花
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//balls表示用来存放小球的数组
var balls = [];
//n表示小球数量
var n = 50;
var gravity = 0.15;
//生成n个小球,其中小球的color、vx、vy取的都是随机值
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var ball = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2, 5, tools.getRandomColor());
//随机生成-3~3之间的数
ball.vx = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
ball.vy = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
balls.push(ball);
}
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//使用forEach()函数遍历数组balls
balls.forEach(function (ball) {
//边界检测,使得小球完全移出画布后会在中心位置重新生成
if (ball.x < -ball.radius ||
ball.x > cnv.width + ball.radius ||
ball.y < -ball.radius ||
ball.y > cnv.height + ball.radius) {
ball.x = cnv.width / 2;
ball.y = cnv.height / 2;
ball.vx = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
ball.vy = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
ball.x += ball.vx;
ball.y += ball.vy;
ball.vy += gravity;
})
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
散弹
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//balls表示用来存放小球的数组
var balls = [];
//n表示小球数量
var n = 50;
//生成n个小球,其中小球的color、vx、vy取的都是随机值
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var ball = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2, 5, tools.getRandomColor());
ball.vx = 3;
ball.vy = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
balls.push(ball);
}
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//使用forEach()函数遍历数组balls
balls.forEach(function (ball) {
//当小球移出画布时,会在中心位置重新生成
if (ball.x < -ball.radius ||
ball.x > cnv.width + ball.radius ||
ball.y < -ball.radius ||
ball.y > cnv.height + ball.radius) {
ball.x = cnv.width / 2;
ball.y = cnv.height / 2;
//随机产生3~4之间的任意数
ball.vx = Math.random() + 3;
//随机产生-3~3之间的任意数
ball.vy = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
ball.x += ball.vx;
ball.y += ball.vy;
})
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
边界反弹
边界反弹,指的是物体触碰到边界之后就会反弹回来,就像现实世界中小球碰到墙壁反弹一样。
如果物体碰到左边界或右边界的时候,就对vx(即x轴速度)取反,而vy不变;如果物体碰到上边界或下边界的时候,就对vy(即y轴速度)取反,而vx不变。
//碰到左边界
if (ball.x < ball.radius) {
ball.x = ball.radius;
vx = -vx;
//碰到右边界
} else if (ball.x > canvas.width - ball.radius) {
ball.x = canvas.width - ball.radius;
vx = -vx;
}
//碰到上边界
if (ball.y < ball.radius) {
ball.y = ball.radius;
vy = -vy;
//碰到下边界
} else if (ball.y > canvas.height - ball.radius) {
ball.y = canvas.height - ball.radius;
vy = -vy;
}
单球反弹
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
var ball = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2);
//随机产生-3~3之间的任意数,作为vx、vy的值
var vx = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
var vy = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
(function drawFrame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(drawFrame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
ball.x += vx;
ball.y += vy;
//边界检测
//碰到左边界
if (ball.x < ball.radius) {
ball.x = ball.radius;
vx = -vx;
//碰到右边界
} else if (ball.x > canvas.width - ball.radius) {
ball.x = canvas.width - ball.radius;
vx = -vx;
}
//碰到上边界
if (ball.y < ball.radius) {
ball.y = ball.radius;
vy = -vy;
//碰到下边界
} else if (ball.y > canvas.height - ball.radius) {
ball.y = canvas.height - ball.radius;
vy = -vy;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
多球反弹
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//定义一个用来存放小球的数组balls
var balls = [];
//n表示小球数量
var n = 10;
//生成n个小球,其中小球的color、vx、vy都是随机的
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
var ball = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2, 8, tools.getRandomColor());
//随机产生-3~3之间的任意数,作为vx、vy的值
ball.vx = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
ball.vy = (Math.random() * 2 - 1) * 3;
//添加到数组balls中
balls.push(ball);
}
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//使用forEach()函数遍历数组balls
balls.forEach(function (ball) {
ball.x += ball.vx;
ball.y += ball.vy;
//边界检测
//碰到左边界
if (ball.x < ball.radius) {
ball.x = ball.radius;
ball.vx = -ball.vx;
//碰到右边界
} else if (ball.x > canvas.width - ball.radius) {
ball.x = canvas.width - ball.radius;
ball.vx = -ball.vx;
}
//碰到上边界
if (ball.y < ball.radius) {
ball.y = ball.radius;
ball.vy = -ball.vy;
//碰到下边界
} else if (ball.y > canvas.height - ball.radius) {
ball.y = canvas.height - ball.radius;
ball.vy = -ball.vy;
}
ball.fill(cxt);
})
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
碰撞检测
碰撞检测检测的是“物体与物体”之间是否发生碰撞。
实际开发中,什么时候用外接矩形判定法,什么时候用外接圆判定法,取决于物体的形状。—— 哪个方法误差较小,就用哪个。
外接矩形判定法
外接矩形判定法,指的是如果检测物体是一个矩形或者近似矩形,就可以把这个物体抽象成一个矩形,然后用判断两个矩形是否碰撞的方法进行检测。
外接矩形的画法:选择一个物体,在它周围画一个矩形。矩形的上边穿过物体最顶端那个像素,下边穿过物体最底端那个像素,然后左边穿过物体最左端那个像素,右边穿过物体最右端那个像素。

对于五角星、心形这种不规则图形,如果单纯地从它们形状来判断两两之间是否发生碰撞是比较困难的,因此我们都是直接根据它们的外接矩形是否碰撞来判断。从上面也可以知道,使用外接矩形判定法,是存在一定误差的。不过即使这样,这种方法却可以大大减少我们计算的复杂度。
判断两个矩形是否发生碰撞,只需要判断:两个矩形左上角的坐标所处的范围。如果两个矩形左上角的坐标满足一定条件,则两个矩形就发生了碰撞。
在 js/tool.js 中新增 checkRect() 方法,用于判断两个矩形是否发生碰撞,碰撞返回 true。
window.tools.checkRect = function (rectA, rectB) {
return !(rectA.x + rectA.width < rectB.x ||
rectB.x + rectB.width < rectA.x ||
rectA.y + rectA.height < rectB.y ||
rectB.y + rectB.height < rectA.y);
}
在 js/ball.js 中添加 getRect 方法,用于求出小球的外接矩形。此getRect()方法只针对圆形小球而言,对于其他不规则图形如五角星、心形等,则需要根据它们的形状特点,然后定义一个属于它们自己的外接矩形的方法。
Ball.prototype ={
getRect: function () {
var rect = {
x: this.x - this.radius,
y: this.y - this.radius,
width: this.radius * 2,
height: this.radius * 2
};
return rect;
}
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
var msg = document.getElementById("msg");
//定义一个位置固定的小球ballA
var ballA = new Ball(cnv.width / 2, cnv.height / 2, 30);
//获取ballA的外接矩形
var rectA = ballA.getRect();
var mouse = tools.getMouse(cnv);
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//绘制ballA以及它的外接矩形
ballA.fill(cxt);
cxt.strokeRect(rectA.x, rectA.y, rectA.width, rectA.height);
//定义一个位置不固定的小球ballB,小球追随鼠标
var ballB = new Ball(mouse.x, mouse.y, 30);
//获取ballB的外接矩形
var rectB = ballB.getRect();
//绘制ballB以及它的外接矩形
ballB.fill(cxt);
cxt.strokeRect(rectB.x, rectB.y, rectB.width, rectB.height);
//碰撞检测
if (tools.checkRect(rectA, rectB)) {
msg.innerHTML = "撞上了";
} else {
msg.innerHTML = "没撞上";
}
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="270" height="200" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
<p id="msg">p>
body>
html>

ballA位置是固定的,ballB位置是随鼠标位置改变而改变的。使用getRect()方法求出这两个小球的外接矩形,然后使用tools.checkRect()方法对两个外接矩形进行碰撞检测。
实战范例:俄罗斯方块
这里的box有两种状态:正在下落的activeBox();已经停止的box。
当画布中出现第1个box时,此时的activeBox和box都是它,所以boxes.forEach()中不会进行碰撞检测。
当第1个box落到底部后,就会创建第2个box。此时的activeBox就应该是第2个box。之后第2个box(activeBox)在下落的过程中,就会与数组boxes中已有的矩形做碰撞检测,然后以此循环。
在碰撞检测中,方块需要确保检测对象不是自己的,然后用tools.checkRect()方法检测两个方块是否碰撞。
最后,加入键盘控制即可!
详细代码:
添加代码到 js/box.js中,用于定义一个Box类,专门生成大小不一的方块。
function Box(x, y, width, height, color) {
//小球中心的x坐标,默认值为0
this.x = x || 0;
//小球中心的y坐标,默认值为0
this.y = y || 0;
//小球宽度,默认值为80
this.width = width || 80;
//小球高度,默认值为40
this.height = height || 40;
this.color = color || "red";
//x和y速度
this.vx = 0;
this.vy = 0;
}
Box.prototype = {
//绘制"描边"矩形
stroke: function (cxt) {
cxt.save();
cxt.strokeStyle = this.color;
cxt.beginPath();
cxt.rect(this.x, this.y, this.width, this.height);
cxt.closePath();
cxt.stroke();
cxt.restore();
},
//绘制"填充"矩形
fill: function (cxt) {
cxt.save();
cxt.fillStyle = this.color;
cxt.beginPath();
cxt.rect(this.x, this.y, this.width, this.height);
cxt.closePath();
cxt.fill();
cxt.restore();
}
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/box.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//定义一个用来存放方块的数组boxes
var boxes = [];
//定义一个"当前活动"的方块
var activeBox = createBox();
//定义方块的y轴速度
var vy = 1.5;
//加入鼠标控制
var key = tools.getKey();
window.addEventListener("keydown", function () {
switch(key.direction)
{
case "down":
activeBox.y += 5;
break;
case "left":
activeBox.x -= 10;
break;
case "right":
activeBox.x += 10;
break;
}
}, false);
//定义一个函数createBox(),用于创建一个新的方块
function createBox() {
var x = Math.random() * cnv.width;
var y = 0;
var width = Math.random() * 40 + 10;
var height = Math.random() * 40 + 10;
var color = tools.getRandomColor();
var box = new Box(x, y, width, height, color);
//添加到数组boxes中
boxes.push(box);
return box;
}
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
activeBox.y += vy;
//边界检测,如果到达底部,则创建一个新的box
if (activeBox.y > cnv.height - activeBox.height) {
activeBox.y = cnv.height - activeBox.height;
activeBox = createBox();
}
//遍历数组boxes,以便单独处理每一个box
boxes.forEach(function (box) {
/*如果当前遍历的box不是"活动方块(activeBox)",并且当前遍历的方块与
"活动方块(activeBox)"碰上了,则创建新的方块*/
if (activeBox !== box && tools.checkRect(activeBox, box)) {
activeBox.y = box.y - activeBox.height;
activeBox = createBox();
}
box.fill(cxt);
});
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="270" height="200" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
外接圆判定法
外接圆判定法:如果检测物体是一个圆或者近似圆,可以把这个物体抽象成一个圆,然后用判断两个圆是否碰撞的方法进行检测。
外接圆的绘制:选择一个物体,在它周围画一个圆,直到外接圆刚好把这个物体圈起来。

判断两个圆是否发生碰撞 —— 如果两个圆心之间的距离大于或等于两个圆的半径之和,则两个圆没有发生碰撞;如果两个圆心之间的距离小于两个圆的半径之和,则两个圆发生了碰撞。
在 js/tool.js 中新增方法checkCircle
window.tools.checkCircle = function (circleB, circleA) {
var dx = circleB.x - circleA.x;
var dy = circleB.y - circleA.y;
var distance = Math.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
if (distance < (circleA.radius + circleB.radius)) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
var txt = document.getElementById("txt");
//定义一个位置固定的小球
var ballA = new Ball(cnv.width/2, cnv.height / 2, 20, "#FF6699");
var mouse = tools.getMouse(cnv);
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//定义一个位置不固定的小球,小球追随鼠标
var ballB = new Ball(mouse.x, mouse.y, 20, "#66CCFF");
//碰撞检测
if(tools.checkCircle(ballB, ballA)){
txt.innerHTML = "撞上了";
} else{
txt.innerHTML = "没撞上";
}
ballA.fill(cxt);
ballB.fill(cxt);
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="200" height="150" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
<p id="txt">p>
body>
html>
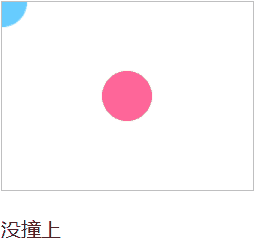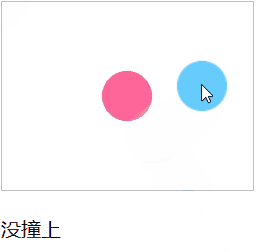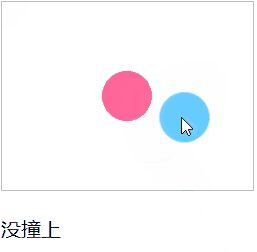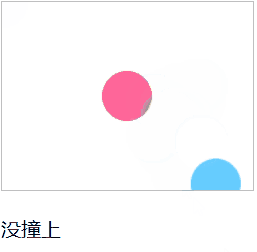
ballA的位置是固定的,ballB位置是随鼠标位置改变而改变的。使用tools.checkCircle()方法对两个小球进行碰撞检测。
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function () {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
//定义两个小球:ballA和ballB
var ballA = new Ball(0, cnv.height / 2, 12, "#FF6699");
var ballB = new Ball(cnv.width, cnv.height / 2, 12, "#66CCFF");
//定义小球x轴速度
var vx = 2;
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
ballA.x += vx;
ballB.x += -vx;
//如果发生碰撞,则速度取反
if(tools.checkCircle(ballB, ballA)){
vx = -vx;
}
ballA.fill(cxt);
ballB.fill(cxt);
})();
}
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas id="canvas" width="270" height="200" style="border:1px solid silver;">canvas>
body>
html>
多物体碰撞
总结规律,可得到下方代码:
balls.forEach(function(ballA,i){
for(var j = i + 1;balls.length;j++){
var ballB = balls[j];
if(tools.checkCircle(ballA,ballB)){
……
}
}
});
DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>title>
<script src="js/tools.js">script>
<script src="js/ball.js">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
function $$(id) {
return document.getElementById(id);
}
window.onload = function() {
var cnv = $$("canvas");
var cxt = cnv.getContext("2d");
var n = 8;
var balls = [];
//生成n个小球,小球的x、y、color、vx、vy属性取的都是随机值
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ball = new Ball();
ball.x = Math.random() * cnv.width;
ball.y = Math.random() * cnv.height;
ball.radius = 10;
ball.color = tools.getRandomColor();
ball.vx = Math.random() * 6 - 3;
ball.vy = Math.random() * 6 - 3;
//添加到数组balls中
balls.push(ball);
}
//碰撞检测(小球与小球)
function checkCollision(ballA, i) {
for (var j = i + 1; j < balls.length; j++) {
var ballB = balls[j];
//如果两个小球碰撞,则碰撞后vx、vy都取相反值
if (tools.checkCircle(ballB, ballA)) {
ballA.vx = -ballA.vx;
ballA.vy = -ballA.vy;
ballB.vx = -ballB.vx;
ballB.vy = -ballB.vy;
//每次碰撞,小球的x、y都加入偏移量,避免相互重叠
if (ballA.vx > 0) {
ballA.x += 5;
} else {
ballA.x -= 5;
}
if (ballA.vy > 0) {
ballA.y += 5;
} else {
ballA.y -= 5;
}
if (ballB.vx > 0) {
ballB.x += 5;
} else {
ballB.x -= 5;
}
if (ballB.vy > 0) {
ballB.y += 5;
} else {
ballB.y -= 5;
}
}
}
}
//边界检测(小球与边界)
function checkBorder(ball) {
//碰到左边界
if (ball.x < ball.radius) {
ball.x = ball.radius;
ball.vx = -ball.vx;
//碰到右边界
} else if (ball.x > canvas.width - ball.radius) {
ball.x = canvas.width - ball.radius;
ball.vx = -ball.vx;
}
//碰到上边界
if (ball.y < ball.radius) {
ball.y = ball.radius;
ball.vy = -ball.vy;
//碰到下边界
} else if (ball.y > canvas.height - ball.radius) {
ball.y = canvas.height - ball.radius;
ball.vy = -ball.vy;
}
}
//绘制小球
function drawBall(ball) {
ball.fill(cxt);
ball.x += ball.vx;
ball.y += ball.vy;
}
(function frame() {
window.requestAnimationFrame(frame);
cxt.clearRect(0, 0, cnv.width, cnv.height);
//碰撞检测
balls.forEach(checkCollision);
//边界检测
balls.forEach(checkBorder);
//绘制小球
balls.forEach(drawBall);
})();
};
script>
head>
<body>
<canvas
id="canvas"
width="200"
height="150"
style="border:1px solid silver;"
>canvas>
body>
html>
小球与小球相互重叠的bug还是可能出现,不过使用偏移量已经大大减少了重叠出现的概率。想要彻底修复这个bug,还需要先学习后面的知识。
这种碰撞实现方法比较勉强。如果想要创建更加真实的碰撞效果,还需要用到更加高级的动画技术,例如坐标旋转。
小结——常用开发技巧
- Math.random() * 2 - 1表示随机生成-1到1之间的任意数,有正有负,刚好符合小球有正方向也有反方向的特点。
- 多物体运动,一般情况下都是采取以下三个步骤进行处理:
(1)定义一个数组来存放多个物体。
(2)使用for循环生成单个物体,然后添加(push())到数组中。
(3)在动画循环中,使用forEach()方法遍历数组,从而处理单个物体。