【golang项目-GeeCache】动手写分布式缓存 day1 - 实现LRU算法
介绍 LRU 内存淘汰算法
LRU(Least Recently Used) 最近最少使用 算法 ,系统认为如果这个数据最近使用过那么它被再次使用的概率会高,所以系统会先淘汰最久没被使用的数据
基本逻辑
-----------------------------------------------------------------------出自极客兔兔
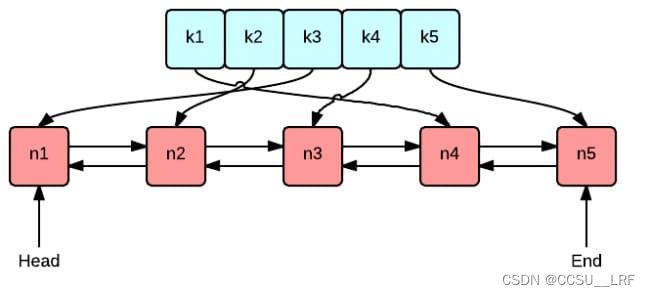
k(绿色)为map,即实际中的缓存,当我们读取数据时就是先从这个查询和获取,复杂度为log 级别,非常快
n(红色)为双向链表,用来记录哪个数据是最晚出现的,使用双向链表的原因是为了快速让数据放在队首/队尾,当我们访问一个数据时,我们把这个数据放在链表队首,当我们需要淘汰内存时我们删除队尾的数据,这个数据就是最晚出现的
具体实现
实现数据结构
- 实现Cache,包含允许的最大缓存,当前的缓存,双向链表,map,回调函数
type Cache struct {
maxBytes int64 // 允许的最大内存
nbytes int64 // 已使用的内存
ll *list.List //双向链表
cache map[string]*list.Element // map
OnEvicted func(key string, value Value) //是某条记录被移除时的回调函数
}
- 实现双向链表的数据类型,便于删除双向链表时根据key删除map的值
type entry struct { // 代表双向链表的数据类型
key string
value Value
}
- 为了存取数据的通用性,实现Len()获取元素个数
type Value interface {
Len() int
}
初始化缓存函数
func New(maxBytes int64, onEvicted func(string, Value)) *Cache { // 创建
return &Cache{
maxBytes: maxBytes,
ll: list.New(),
cache: make(map[string]*list.Element),
OnEvicted: onEvicted,
}
}
实现查找功能
这个函数首先在缓存(map)中查询是否存在,如果存在就返回这个值,并且把这个值放在双向链表的首部,也标记成最新出现
func (c *Cache) Get(key string) (value Value, ok bool) { // 查找
if ele, ok := c.cache[key]; ok {
c.ll.MoveToFront(ele) // 移动到队首
kv := ele.Value.(*entry) // 找到值
return kv.value, true
}
return
}
在这里写的时候 我对这段代码有疑惑
kv := ele.Value.(*entry) // 找到值
错误的认为ele.Value.(T) 是 Value中的一个成员变量,但实际又不是
实际上这是接口类型的类型转换 Value.(Type) 是吧接口类型Value转换成Type类型
补充知识 :Go语言接口和类型之间的转换
类型断言
类型断言用于将接口类型转换为指定类型,其语法为:
value.(type) 或者 value.(T)
类型转换
类型转换用于将一个接口类型的值转换为另一个接口类型,其语法为:
T(value)
实现内存淘汰功能 即删除
内存删除就是移除最近最少访问的节点,就是删除队尾,然后修改当前缓存大小,使用回调函数通知系统
func (c *Cache) RemoveOldest() { // 缓存淘汰
ele := c.ll.Back() // 取到队首节点,从链表中删除
if ele != nil { // 非空
c.ll.Remove(ele) // 移除最近最少访问
kv := ele.Value.(*entry)
delete(c.cache, kv.key)
c.nbytes -= int64(len(kv.key)) + int64(kv.value.Len())
if c.OnEvicted != nil {
c.OnEvicted(kv.key, kv.value) // 回调
}
}
}
实现添加/修改数据操作
添加/修改数据时查询缓存是否存在,否则在缓存中(map)中创建个新的键值对,最后把这个数据放在队首,表示最新出现
func (c *Cache) Add(key string, value Value) {
if ele, ok := c.cache[key]; ok {
c.ll.MoveToFront(ele)
kv := ele.Value.(*entry)
c.nbytes += int64(value.Len()) - int64(kv.value.Len())
kv.value = value
} else {
ele := c.ll.PushFront(&entry{key, value})
c.cache[key] = ele
c.nbytes += int64(len(key)) + int64(value.Len())
}
for c.maxBytes != 0 && c.maxBytes < c.nbytes {
c.RemoveOldest() //如果超过了设定的最大值 c.maxBytes,则移除最少访问的节点。
}
}
全部代码
实现代码
package lru
import "container/list"
type Cache struct {
maxBytes int64 // 允许的最大内存
nbytes int64 // 已使用的内存
ll *list.List //双向链表
cache map[string]*list.Element // map
OnEvicted func(key string, value Value) //是某条记录被移除时的回调函数
}
type entry struct { // 代表双向链表的数据类型
key string
value Value
}
type Value interface {
Len() int
}
func New(maxBytes int64, onEvicted func(string, Value)) *Cache { // 创建
return &Cache{
maxBytes: maxBytes,
ll: list.New(),
cache: make(map[string]*list.Element),
OnEvicted: onEvicted,
}
}
func (c *Cache) Get(key string) (value Value, ok bool) { // 查找
if ele, ok := c.cache[key]; ok {
c.ll.MoveToFront(ele) // 移动到队尾
kv := ele.Value.(*entry) // 找到值
return kv.value, true
}
return
}
func (c *Cache) RemoveOldest() { // 缓存淘汰
ele := c.ll.Back() // 取到队首节点,从链表中删除
if ele != nil { // 非空
c.ll.Remove(ele) // 移除最近最少访问
kv := ele.Value.(*entry)
delete(c.cache, kv.key)
c.nbytes -= int64(len(kv.key)) + int64(kv.value.Len())
if c.OnEvicted != nil {
c.OnEvicted(kv.key, kv.value) // 回调
}
}
}
func (c *Cache) Add(key string, value Value) {
if ele, ok := c.cache[key]; ok {
c.ll.MoveToFront(ele)
kv := ele.Value.(*entry)
c.nbytes += int64(value.Len()) - int64(kv.value.Len())
kv.value = value
} else {
ele := c.ll.PushFront(&entry{key, value})
c.cache[key] = ele
c.nbytes += int64(len(key)) + int64(value.Len())
}
for c.maxBytes != 0 && c.maxBytes < c.nbytes {
c.RemoveOldest() //如果超过了设定的最大值 c.maxBytes,则移除最少访问的节点。
}
}
func (c *Cache) Len() int {
return c.ll.Len()
}
测试代码
在这里也可以学会testing库的使用
package lru
import (
"reflect"
"testing"
)
type String string
func (d String) Len() int {
return len(d)
}
func TestGet(t *testing.T) {
lru := New(int64(0), nil)
lru.Add("key1", String("1234"))
if v, ok := lru.Get("key1"); !ok || string(v.(String)) != "1234" {
t.Fatalf("cache hit key1=1234 failed")
}
if _, ok := lru.Get("key2"); ok {
t.Fatalf("cache miss key2 failed")
}
}
func TestRemoveoldest(t *testing.T) {
k1, k2, k3 := "key1", "key2", "k3"
v1, v2, v3 := "value1", "value2", "v3"
cap := len(k1 + k2 + v1 + v2)
lru := New(int64(cap), nil)
lru.Add(k1, String(v1))
lru.Add(k2, String(v2))
lru.Add(k3, String(v3))
if _, ok := lru.Get("key1"); ok || lru.Len() != 2 {
t.Fatalf("Removeoldest key1 failed")
}
}
func TestOnEvicted(t *testing.T) {
keys := make([]string, 0)
callback := func(key string, value Value) {
keys = append(keys, key)
}
lru := New(int64(10), callback)
lru.Add("key1", String("123456"))
lru.Add("k2", String("k2"))
lru.Add("k3", String("k3"))
lru.Add("k4", String("k4"))
expect := []string{"key1", "k2"}
if !reflect.DeepEqual(expect, keys) {
t.Fatalf("Call OnEvicted failed, expect keys equals to %s", expect)
}
}
func TestAdd(t *testing.T) {
lru := New(int64(0), nil)
lru.Add("key", String("1"))
lru.Add("key", String("111"))
if lru.nbytes != int64(len("key")+len("111")) {
t.Fatal("expected 6 but got", lru.nbytes)
}
}