集成定时器事件
一,定时器事件
1、概述
libevent提供了高性能定时器的功能,方便执行延迟回调逻辑。在添加事件监听的时候,可以不指定fd和监听的事件,指定超时的时间,实现定时器功能。定时器的实现主要依赖下面的数据结构,如下:
1)最小堆:按事件的超时时间构造,超时时间最早的在堆顶。
2)公共超时队列:这个可以个性化设置每个队列的超时时间,添加事件时时间相同的放到同一个队列里,在最小堆里只添加一个队列首部的事件到最小堆。能避免大量事件都放到最小堆,导致最小堆添加、删除时性能变差的问题。
2、实现原理
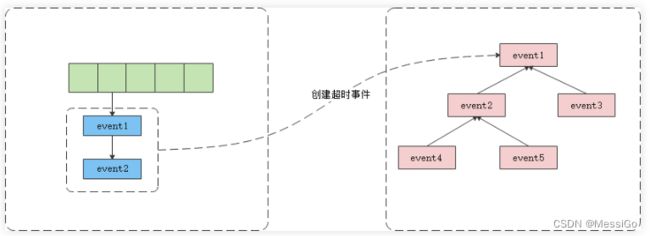
Libevent实现超时事件的原理是,多路IO复用函数都是有一个超时值。如果用户需要Libevent同时监听多个超时event,那么Libevent就把超时值最小的那个作为多路IO复用函数的超时值。自然,当时间一到,就会从多路IO复用函数返回,此时对超时event进行处理即可。当运行事件循环时,根据timer-heap中的事件最小超时时间,计算系统I/O demultiplexer的最大等待时间,下面是event_base_loop函数对应的代码段,如下:
3、超时事件管理
3.1、小根堆
Libevent内部使用小根堆来管理超时事件,堆的实现采用了典型的数组来维护,当数组元素满时扩容数组调整最小堆。堆中的元素是struct event,按照事件的ev_timeout字段对超时时间进行排序,如下:
注意:小根堆按照ev->ev_timeout值(绝对超时时间)进行排序
3.2、往min_heap中添加event
每一个event_base都对应一个min_heap数据结构,event_base中的所有设置了超时的event都会放在event_base的timeheap这一成员中,其定义如下:
struct event_base {
......
/** Priority queue of events with timeouts. */
struct min_heap timeheap;
......
};
event添加一个超时是通过event_add实现的,而在event_add内部实际上是event_add_internal函数,该函数共有三个传入参数,第一个参数是event指针,第二个参数是一个超时结构体timeval,第三个参数用于指明传入的超时结构体是否为绝对时间。如果传入的timeval非空,说明event是需要设置超时的,通过event_add_internal就可以将该event添加到min_heap中,如下所示:
static inline int
event_add_internal(struct event *ev, const struct timeval *tv,
int tv_is_absolute)
{
/* 处理超时事件 */
if (res != -1 && tv != NULL) {
......
common_timeout = is_common_timeout(tv, base);
if (tv_is_absolute) { //如果是绝对时间 就直接用ev_timeout存储
ev->ev_timeout = *tv;
} else if (common_timeout) {
......
} else {
evutil_timeradd(&now, tv, &ev->ev_timeout); //如果就只是一个普通的相对时间,就直接用系统时间加上超时时长作为超时时间
}
......
event_queue_insert(base, ev, EVLIST_TIMEOUT); //插入到超时队列中
......
}
3.3、min_heap中event的激活
在event_base_loop函数中会调用timeout_process函数去处理定时器中超时的event,该函数定义如下:
static void
timeout_process(struct event_base *base)
{
/* Caller must hold lock. */
struct timeval now;
struct event *ev;
if (min_heap_empty_(&base->timeheap)) {
return;
}
gettime(base, &now);
while ((ev = min_heap_top_(&base->timeheap))) {
/* 比较定时器堆顶的event是否超时,如果没有超时说明定时器中没有event超时 */
if (evutil_timercmp(&ev->ev_timeout, &now, >))
break;
/* delete this event from the I/O queues */
event_del_nolock_(ev, EVENT_DEL_NOBLOCK);
event_debug(("timeout_process: event: %p, call %p",
ev, ev->ev_callback));
/* 按超时激活类型添加到激活队列中 */
event_active_nolock_(ev, EV_TIMEOUT, 1);
}
}
定时器min_heap中event的激活是通过timeout_process函数实现的,在该函数中会把已经超时的event从定时器中删除,并且把该event添加到激活队列中。接着只需要处理激活队列,就可以执行这些超时的event对应的回调函数。
4、公共超时事件
4.1、超时时间相关的概念
1)超时时间:是一个绝对超时时间,即从1970年1月1日到当前的某个时间点经过的时间
2)超时时长:是一个相对超时时间,例如:设置的超时时长是2秒,即在2秒后会超时
3)公共超时时间:带有COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC标志(Libevent定义的一个宏)的一个超时时间
4.2、common_timeout的作用
common_timeout把base中所有拥有共同点的event放在了一起,而这个所谓的“共同点”就是指超时时长相同,这些超时时长相同的event,他们的超时时间是不同的。 拥有相同超时时长的所有event构成一个链表events,并且让它们按照超时时间的先后按升序排列(即相同超时时长中最先超时的那个event放在最前面),而events中设置一个内部使用的timeout_event作为代表,把最先超时的那个event的超时时间添加到timeout_event中,然后把超时事件放到min_heap中,当放到min_heap中的timeout_event超时,就回到events中,从前往后把所有超时的event全部激活。如下:
4.3、common_timeout的结构定义
在event_base的结构体中,含有以下定义:
struct event_base
{
......
/** An array of common_timeout_list* for all of the common timeout
* values we know. */
struct common_timeout_list **common_timeout_queues; //common_timeout_list *数组,存放不同超时时长的common_timeout_list的指针
/** The number of entries used in common_timeout_queues */
int n_common_timeouts; //common_timeout_queues中实际的元素个数
/** The total size of common_timeout_queues. */
int n_common_timeouts_allocated; //common_timeout_queues的容量
......
}
在event_base中,common_timeout_queues是一个common_timeout_list *类型的指针数组,其中每个元素都指向一个common_timeout_list,common_timeout_list的定义如下:
//event-internal.h
struct common_timeout_list {
/* List of events currently waiting in the queue. */
struct event_list events; //event的双向链表
/* 'magic' timeval used to indicate the duration of events in this
* queue. */
struct timeval duration; //该common_timeout_list的超时时长,events双向链表中的所有event都是相同的超时时长
/* Event that triggers whenever one of the events in the queue is
* ready to activate */
struct event timeout_event; //“event代表”,最终只有这个event实际插到了min_heap中
/* The event_base that this timeout list is part of */
struct event_base *base; //该common_timeout_list所在的event_base
};
//event_struct.h
TAILQ_HEAD (event_list, event); //由event组成的双向链表
4.4、common_timeout与一般timeout的区分
对于一个timeval超时结构体来说,它有两个成员,一个数tv_sec用来指明超时时间中的秒数,一个就是tv_usec用来指明超时时间中的微秒数。由于微秒的数值范围只能是0~999999,而tv_usec的变量类型实际上是32位的,能表示的数值范围远远大于999999,因此用低20位足以来表示timeval中的tv_usec,这样一来,tv_usec的高12位就是没有使用的。而libevent中则是通过这高12位来区分一个timeval超时结构体是common_timeout还是普通的timeout。有如下定义:
//event-internal.h
#define COMMON_TIMEOUT_MICROSECONDS_MASK 0x000fffff //取低20位掩码
//event.c
#define MICROSECONDS_MASK COMMON_TIMEOUT_MICROSECONDS_MASK //取低20位,即微秒超时时长
#define COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_MASK 0x0ff00000 //20~27bit为该超时时长在common_timeout_queues中的位置
#define COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_SHIFT 20 //微秒最大为999999,因此用低20位存储即可,高12位中前4位标识是否为common_timeout
#define COMMON_TIMEOUT_MASK 0xf0000000 //取高四位掩码
#define COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC 0x50000000 //高四位标志是否为common timeout
1)timeval结构体中的tv_usec由32位表示,而实际上微秒的数值只需低20位即可表示,因此,tv_usec & MICROSECONDS_MASK 即可得到低20位的值,也就是实际的微秒数值。
2)对于高12位来说,tv_usec的高4位用来判断一个这个timeval是否是common_timeout,用 tv_usec & COMMON_TIMEOUT_MASK可以获取高4位的值,如果高4位是COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC(即0x5000000),说明这个timeval是一个common_timeout,否则就表示这个timeval只是一个普通的超时时间。
3)如果是common_timeout,那么这个event是放在base的common_timeout_queues某一项(如common_timeout_queues[i])所对应的common_timeout_list中的,而tv_usec剩下的20~27bit则用来表示这个common_timeout所在的common_timeout_list在common_timeout_queues数组中的索引。例如:如果tv_usec的20-27bit为00000101,则说明这个tv_usec对应的common_timeout_list放在common_timeout_queues[5]下面
4.5、获取common_timeout在common_timeout_queues中的下标
通过下面的宏可以获取common_timeout对应的下标,将tv_usec与COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_MASK按位与,屏蔽掉tv_usec除2027bit以外的其他位,得到的结果再右移20位得到的结果就是原来的tv_usec的2027bit的值,这个值就是common_timeout对应的common_timeout_list对应在common_timeout_queues中的下标。宏定义如下:
#define COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX(tv) \ //获取tv所在的common_timeout_list在common_timeout_queues中的位置
(((tv)->tv_usec & COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_MASK)>>COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_SHIFT)//20~27bit右移20位得到下标
4.6、判断一个timeval是否为common_timeout
调用下面的函数可以判断一个超时时间是否是一个common_timeout。 该函数先取出tv_usec的高四位来检查传入的timeval是否为common_timeout,在此基础上还要去判断tv_usec的20~27bit所对应的下标是否合法,因为有可能存在高四位表明为common_timeout,但是20-27bit是非法的情况。
static inline int
is_common_timeout(const struct timeval *tv,
const struct event_base *base)
{
int idx;
if ((tv->tv_usec & COMMON_TIMEOUT_MASK) != COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC)//取高4位,COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC说明它是一个common timeout,如果高四位不等于COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC,那么就不是commontimeout
return 0;
idx = COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX(tv);
return idx < base->n_common_timeouts; //下标必须小于 base中common_timeout_queues的实际元素个数
}
4.7、创建一个common_timeout
调用event_base_init_common_timeout接口可以创建一个common_timeout,下面是接口定义:
const struct timeval *
event_base_init_common_timeout(struct event_base *base,
const struct timeval *duration) //查看base中是否有duration相应的common_timeout_list,如果没有就分配一个,并且将新分配中的timeout_event进行设置回调函数。传入的duration既可以是带掩码的也可以是不带掩码的,返回的是相应的common_timeout_list的duration
{
int i;
struct timeval tv;
const struct timeval *result=NULL;
struct common_timeout_list *new_ctl;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
if (duration->tv_usec > 1000000) { //微秒最大值应该是999999,如果超过了1000000,要么它是一个common_timeout,就取出实际的超时时间,否则就把微秒进位到秒上去
memcpy(&tv, duration, sizeof(struct timeval));
if (is_common_timeout(duration, base))
tv.tv_usec &= MICROSECONDS_MASK;
tv.tv_sec += tv.tv_usec / 1000000;
tv.tv_usec %= 1000000;
duration = &tv; //更新duration的实际时长
}
for (i = 0; i < base->n_common_timeouts; ++i) { //遍历现在有的common_timeout_list,查看是否存在超时时长等于duration的list
const struct common_timeout_list *ctl =
base->common_timeout_queues[i];
if (duration->tv_sec == ctl->duration.tv_sec &&
duration->tv_usec ==
(ctl->duration.tv_usec & MICROSECONDS_MASK)) {
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_common_timeout(&ctl->duration, base));
result = &ctl->duration; //如果存在duration等于传入的参数的common_timeout_list,那么就把这个common_timeout_list的duration存到result中返回即可。
goto done;
}
}
if (base->n_common_timeouts == MAX_COMMON_TIMEOUTS) {
event_warnx("%s: Too many common timeouts already in use; "
"we only support %d per event_base", __func__,
MAX_COMMON_TIMEOUTS);
goto done;
}
if (base->n_common_timeouts_allocated == base->n_common_timeouts) { //如果base中的common_timeout_list分配满了
int n = base->n_common_timeouts < 16 ? 16 : //如果少于16则分配16的容量,否则容量加倍
base->n_common_timeouts*2;
struct common_timeout_list **newqueues =
mm_realloc(base->common_timeout_queues,
n*sizeof(struct common_timeout_queue *));//重新分配common_timeout_queues的空间大小
if (!newqueues) {
event_warn("%s: realloc",__func__);
goto done;
}
base->n_common_timeouts_allocated = n; //更新common_timeout_queues地址及其容量
base->common_timeout_queues = newqueues;
}
//执行到这里说明没有common_timeout_list的duration等于传入的参数duration
new_ctl = mm_calloc(1, sizeof(struct common_timeout_list)); //新分配一个common_timeout_list
if (!new_ctl) {
event_warn("%s: calloc",__func__);
goto done;
}
TAILQ_INIT(&new_ctl->events); //初始化该duration对应的events链表为空
new_ctl->duration.tv_sec = duration->tv_sec;
new_ctl->duration.tv_usec =
duration->tv_usec | COMMON_TIMEOUT_MAGIC |
(base->n_common_timeouts << COMMON_TIMEOUT_IDX_SHIFT); //把微秒转换为为带掩码、并且添上下标位
evtimer_assign(&new_ctl->timeout_event, base,
common_timeout_callback, new_ctl); //给新分配的common_timeout_list中的timeout_event注册信息,回调函数为common_timeout_callback
new_ctl->timeout_event.ev_flags |= EVLIST_INTERNAL; //标志为内部使用的event
event_priority_set(&new_ctl->timeout_event, 0); //设置timeout_event的优先级为0
new_ctl->base = base;
base->common_timeout_queues[base->n_common_timeouts++] = new_ctl; //在common_timeout_queues现有元素的最后加上新创建的common_timeout_list
result = &new_ctl->duration; //result保存common_timeout_list的duration
done:
if (result)
EVUTIL_ASSERT(is_common_timeout(result, base));
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
return result; //返回的result是已经设置过相应标志位的common_timeout,也就是指定了超时时长为duration的common_timeout,之后就可以用result作为参数调用event_add,就可以把event添加到相应的common_timeout_list中
}
4.8、激活common_timeout对应的event
被插入到heap中的timeout_event设置的回调函数是common_timeout_callback,当min_heap中的timeout_event发生超时而激活后,就会直接去调用common_timeout_callback,该函数定义如下:
static void
common_timeout_callback(evutil_socket_t fd, short what, void *arg)
{
struct timeval now;
struct common_timeout_list *ctl = arg; //传入的参数是event所在的那个common_timeout_list
struct event_base *base = ctl->base;
struct event *ev = NULL;
EVBASE_ACQUIRE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
gettime(base, &now); //获取系统时间
while (1) {
ev = TAILQ_FIRST(&ctl->events); //遍历这个common_timeout_list中的所有event,如果有超时的就添加到激活队列中
if (!ev || ev->ev_timeout.tv_sec > now.tv_sec ||
(ev->ev_timeout.tv_sec == now.tv_sec &&
(ev->ev_timeout.tv_usec&MICROSECONDS_MASK) > now.tv_usec))
break;
event_del_internal(ev);
event_active_nolock(ev, EV_TIMEOUT, 1);
}
if (ev) //此时的ev如果不为空,那么它就是未来最先超时的那个event
common_timeout_schedule(ctl, &now, ev); //重新将这个event的超时时间加上common_timeout_callback添加到min_heap中
EVBASE_RELEASE_LOCK(base, th_base_lock);
}
common_timeout_callback函数的作用就是遍历common_timeout_list中的event,激活所有超时的event,并且根据未来最先超时的那个event重新设置一个新的“代表”timeout_event插入到min_heap中。