【go项目-geecache】动手写分布式缓存 - day3 - HTTP 服务端
收获总结:
- 了解go函数的可变参数的使用,还有切片展开的方式即…
- 了解了HTTP通信方式,hinder的使用
- 了解了go.mod ,import 和modoule的使用
分布式缓存需要实现点对点的通信,我们可以使用HTTP来实现节点之间的通信,如果说某个节点开始了HTTP服务,那么其他节点就可以进行通信
实现HTTP通信数据结构——HTTPPool
实现HTTPPool结构体
package geecache
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
const defaultBasePath = "/_geecache/"
type HTTPPool struct {
self string // 自己的地址
basePath string // 节点间通讯地址的前缀
}
- self 表示自己的地址
- basePath 表示通讯地址的前缀,默认是
/_geecache/
比如https://A.com/_geecache/就是一个请求
实现实例化函数
func NewHTTPPool(self string) *HTTPPool {
return &HTTPPool{
self: self,
basePath: defaultBasePath,
}
}
实现HTTPPool通信的接口 http.go
定义Log输出日志
func (p *HTTPPool) Log(format string, v ...interface{}) {
log.Printf("[Server %s] %s", p.self, fmt.Sprintf(format, v...))
}
这里的v …inerface{} 是什么意思 ?
在 Go 语言中,v …interface{} 是一种可变参数的语法,它表示一个包含任意个 interface{} 类型参数的切片。这种语法常常用于函数或方法的定义中,以支持不定数量的参数。比如v … int就表示若干个int类型参数的切片
这里的v… 意思?
…可以用于将切片展开为独立的参数。这种语法通常用于需要将一个切片中的元素传递给函数或方法的调用
实现 http.Handler接口的 ServeHTTP方法
实现ServeHTTP方法是干什么的?
当该 HTTP 服务接收到请求时,会调用 HTTPPool 的 ServeHTTP 方法来处理请求,该方法会解析请求路径中的参数,然后使用这些参数来获取缓存数据并将其写入 HTTP 响应。
具体实现
func (p *HTTPPool) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if !strings.HasPrefix(r.URL.Path, p.basePath) {
panic("HTTPPool serving unexpected path: " + r.URL.Path)
}
p.Log("%s %s", r.Method, r.URL.Path)
// /// required
parts := strings.SplitN(r.URL.Path[len(p.basePath):], "/", 2)
if len(parts) != 2 {
http.Error(w, "bad request", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
groupName := parts[0]
key := parts[1]
group := GetGroup(groupName)
if group == nil {
http.Error(w, "no such group: "+groupName, http.StatusNotFound)
return
}
view, err := group.Get(key)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream")
w.Write(view.ByteSlice())
}
我们规定访问的路径格式是 /。
func (p *HTTPPool) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request):定义了一个方法,接收两个参数w和r,分别表示 HTTP 响应的写入器和 HTTP 请求的内容和元数据。if !strings.HasPrefix(r.URL.Path, p.basePath) {...}:判断请求的路径是否以 HTTPPool 的 basePath 开头,如果不是,则抛出异常,终止请求处理。p.Log("%s %s", r.Method, r.URL.Path):记录日志,表示收到了一个 HTTP 请求。parts := strings.SplitN(r.URL.Path[len(p.basePath):], "/", 2):将请求路径从 basePath 开始的部分按照 “/” 分割成两个部分,并存储到parts变量中。例如,如果请求路径为 /basepath/groupname/key,则parts的值为 [“groupname”, “key”]。if len(parts) != 2 {...}:判断parts是否为两个元素,如果不是,则返回 HTTP 状态码 400 Bad Request。groupName := parts[0]:从parts中获取第一个元素,即缓存组名。key := parts[1]:从parts中获取第二个元素,即缓存键。group := GetGroup(groupName):根据组名获取缓存组。if group == nil {...}:如果缓存组不存在,则返回 HTTP 状态码 404 Not Found。view, err := group.Get(key):从缓存组中获取指定键的缓存数据。if err != nil {...}:如果获取缓存数据失败,则返回 HTTP 状态码 500 Internal Server Error。w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream"):设置 HTTP 响应头部的 Content-Type 字段为 “application/octet-stream”,表示响应数据的 MIME 类型为二进制流。w.Write(view.ByteSlice()):将缓存数据的字节数组写入 HTTP 响应的写入器中,从而将缓存数据返回给客户端。
测试文件
package main
import (
"fmt"
"geecache"
"log"
"net/http"
)
var db = map[string]string{
"Tom": "630",
"Jack": "589",
"Sam": "567",
}
func main() {
geecache.NewGroup("scores", 2<<10, geecache.GetterFunc(
func(key string) ([]byte, error) {
log.Println("[SlowDB] search key", key)
if v, ok := db[key]; ok {
return []byte(v), nil
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s not exist", key)
}))
addr := "localhost:9999"
peers := geecache.NewHTTPPool(addr)
log.Println("geecache is running at", addr)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(addr, peers))
}
我们的main文件使用了geecache,但我们开启的go modules,不支持相对路径,所有在go.mod 应声明
require geecache v0.0.0
replace geecache => ./geecache
最后的go.mod文件是
module day3
go 1.20
require geecache v0.0.0
replace geecache => ./geecache
go.mod 到底是干什么的?
简而言之,go.mod就是管理项目依赖、版本控制和构建过程
测试
接下来,运行 main 函数,使用 curl 做一些简单测试:
$ curl http://localhost:9999/_geecache/scores/Tom
630
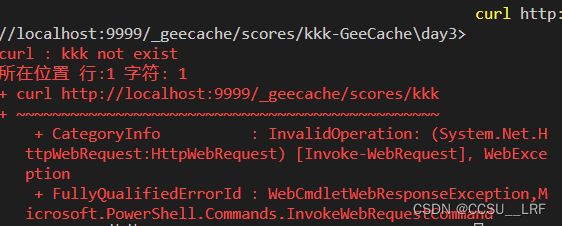
$ curl http://localhost:9999/_geecache/scores/kkk
kkk not exist
成功截图
- 在对应目录下运行 go run main(这里我运行过一次,所以已经存在了)
然后curl http://localhost:9999/_geecache/scores/Tom
实现代码和测试代码
http.go
package geecache
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
const defaultBasePath = "/_geecache/"
type HTTPPool struct {
self string
basePath string
}
func NewHTTPPool(self string) *HTTPPool {
return &HTTPPool{
self: self,
basePath: defaultBasePath,
}
}
func (p *HTTPPool) Log(format string, v ...interface{}) {
log.Printf("[Server %s] %s", p.self, fmt.Sprintf(format, v...))
}
func (p *HTTPPool) ServeHTTP(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if !strings.HasPrefix(r.URL.Path, p.basePath) {
panic("HTTPPool serving unexpected path: " + r.URL.Path)
}
p.Log("%s %s", r.Method, r.URL.Path)
// /// required
parts := strings.SplitN(r.URL.Path[len(p.basePath):], "/", 2)
if len(parts) != 2 {
http.Error(w, "bad request", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
groupName := parts[0]
key := parts[1]
group := GetGroup(groupName)
if group == nil {
http.Error(w, "no such group: "+groupName, http.StatusNotFound)
return
}
view, err := group.Get(key)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream")
w.Write(view.ByteSlice())
}
main.go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"geecache"
"log"
"net/http"
)
var db = map[string]string{
"Tom": "630",
"Jack": "589",
"Sam": "567",
}
func main() {
geecache.NewGroup("scores", 2<<10, geecache.GetterFunc(
func(key string) ([]byte, error) {
log.Println("[SlowDB] search key", key)
if v, ok := db[key]; ok {
return []byte(v), nil
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("%s not exist", key)
}))
addr := "localhost:9999"
peers := geecache.NewHTTPPool(addr)
log.Println("geecache is running at", addr)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(addr, peers))
}
go.mod
module day3
go 1.20
require geecache v0.0.0
replace geecache => ./geecache