Oracle中的instr()函数 详解及应用
总结
1.下面代码是一个模糊查询 ,myName可以理解为输入框里面输入的内容
e.name是数据库里面的内容
简单来说就是 用输入框里面的myName 到数据库里面 查找e.name和 myName匹配的内容 进行模糊查询
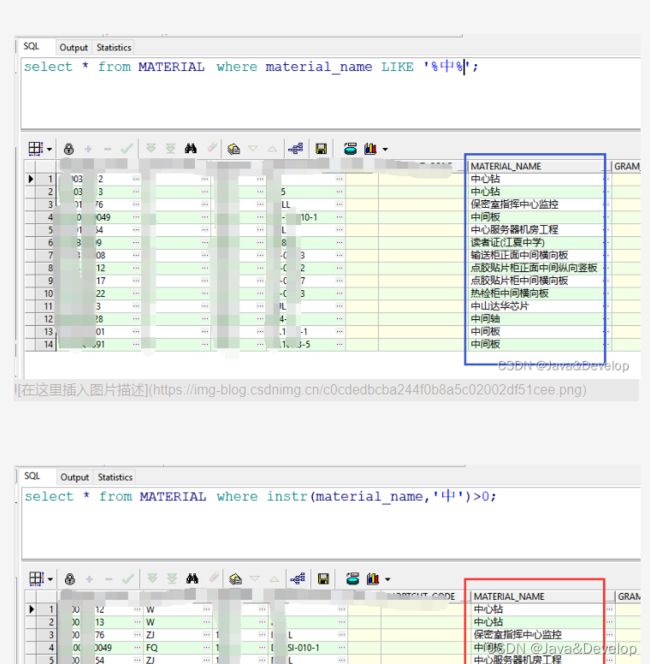
2.注:MySQL中的模糊查询 like 和 Oracle中的 instr() 函数有同样的查询效果; 如下所示:
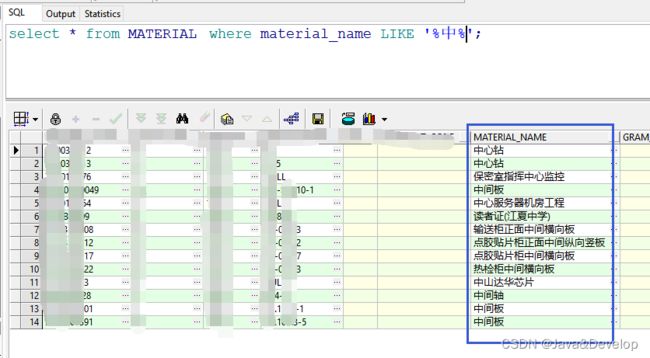
MySQL: select * from tableName where name like ‘%helloworld%’;
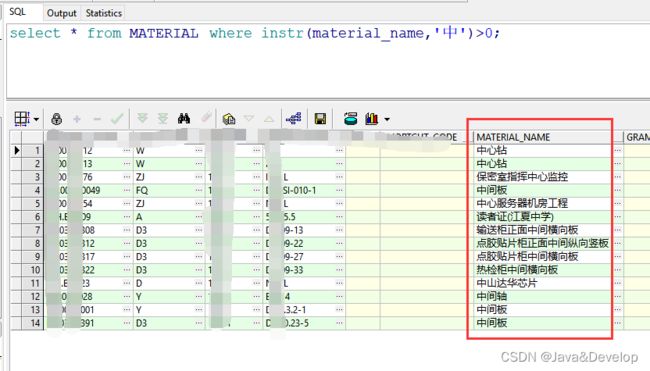
Oracle:select * from tableName where instr(name,‘helloworld’)>0; --这两条语句的效果是一样的
1、instr()函数的格式 (俗称:字符查找函数)
格式一:instr( string1, string2 ) / instr(源字符串, 目标字符串)
格式二:instr( string1, string2 [, start_position [, nth_appearance ] ] ) / instr(源字符串, 目标字符串, 起始位置, 匹配序号)
解析:string2 的值要在string1中查找,是从start_position给出的数值(即:位置)开始在string1检索,检索第nth_appearance(几)次出现string2。
注:在Oracle/PLSQL中,instr函数返回要截取的字符串在源字符串中的位置。只检索一次,也就是说从字符的开始到字符的结尾就结束。
2、实例
格式一
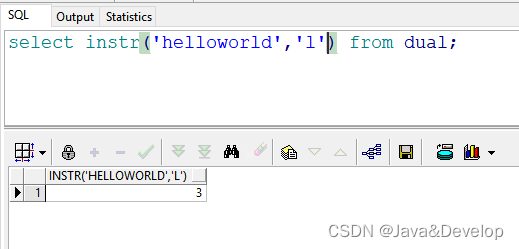
1 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’) from dual; --返回结果:3 默认第一次出现“l”的位置
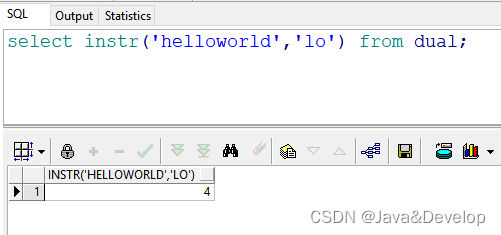
2 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘lo’) from dual; --返回结果:4 即:在“lo”中,“l”开始出现的位置
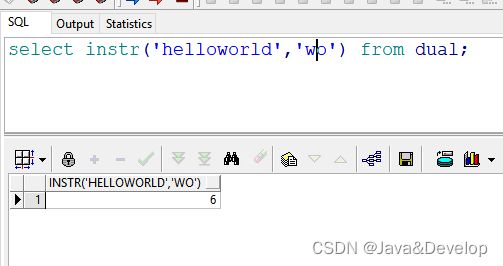
3 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘wo’) from dual; --返回结果:6 即“w”开始出现的位置
格式二
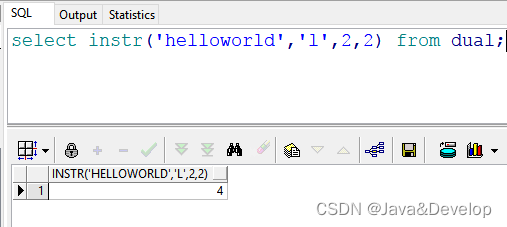
1 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’,2,2) from dual; --返回结果:4 也就是说:在"helloworld"的第2(e)号位置开始,查找第二次出现的“l”的位置
2 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’,3,2) from dual; --返回结果:4 也就是说:在"helloworld"的第3(l)号位置开始,查找第二次出现的“l”的位置
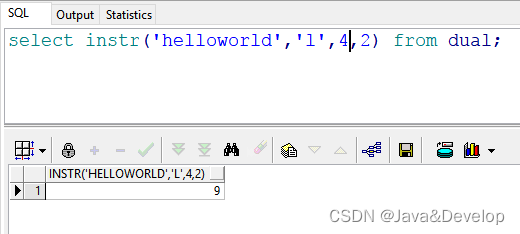
3 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’,4,2) from dual; --返回结果:9 也就是说:在"helloworld"的第4(l)号位置开始,查找第二次出现的“l”的位置
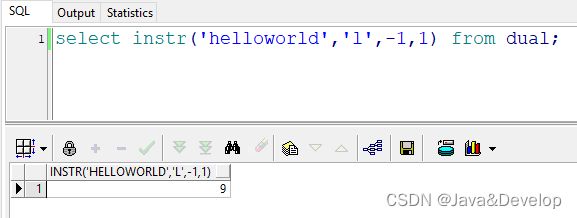
4 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’,-1,1) from dual; --返回结果:9 也就是说:在"helloworld"的倒数第1(d)号位置开始,往回查找第一次出现的“l”的位置
5 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’,-2,2) from dual; --返回结果:4 也就是说:在"helloworld"的倒数第1(d)号位置开始,往回查找第二次出现的“l”的位置
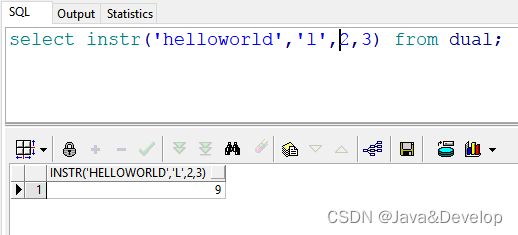
6 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’,2,3) from dual; --返回结果:9 也就是说:在"helloworld"的第2(e)号位置开始,查找第三次出现的“l”的位置
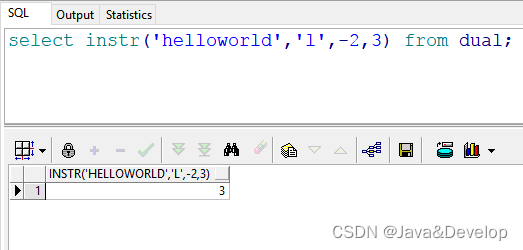
7 select instr(‘helloworld’,‘l’,-2,3) from dual; --返回结果:3 也就是说:在"helloworld"的倒数第2(l)号位置开始,往回查找第三次出现的“l”的位置
注:MySQL中的模糊查询 like 和 Oracle中的 instr() 函数有同样的查询效果; 如下所示:
MySQL: select * from tableName where name like ‘%helloworld%’;
Oracle:select * from tableName where instr(name,‘helloworld’)>0; --这两条语句的效果是一样的
3、
5、
6、
9、
原创作者:DSHORE
作者主页:http://www.cnblogs.com/dshore123/
原文出自:http://www.cnblogs.com/dshore123/p/7813230.html
欢迎转载,转载务必说明出处。