Spring中Bean初始化和销毁的多种方式
Spring中Bean初始化和销毁的多种方式
- 一、Bean的多种初始化方式
-
- 1.PostConstruct注解
- 2.实现InitializingBean接口
- 3.声明init-method方法
- 二、Bean的多种销毁方式
-
- 1.PreDestroy注解
- 2.实现DisposableBean接口
- 3.声明destroy-method方法
- 三、总结
Spring中支持在Bean的加载时声明初始化方法,该方法会在Bean对象完成初始化之前进行执行,可以为对象指定一些特定的行为,同样的Bean销毁时,也是支持这个动作的。其中因为对象的作用域不同,销毁的表现形式略有区别。初始化都没有区别,无论是单例、原型、request、session、global session等他们的创建时初始化都没啥区别,但是销毁会略有区别,单例模式默认不会销毁,只有在Spring容器被销毁时才会执行Bean的销毁,从而执行他的销毁方法。session、request等他们是作用范围到了就会被销毁,并不会长期存在,所以他们的销毁方法是在作用范围执行之后来调用的。
一、Bean的多种初始化方式
Spring中总共支持了三种方式对Bean进行初始化,依次是在方法上使用PostConstruct注解、实现InitializtingBean接口重写对应方法、声明init-method方法来实现,且他们三个支持并行。也就是说我们可以三个都是用,当三个都是用时就是按照下面的顺序执行的,即限制性PostConstruct注解的方法,再执行InitializingBean的方法,最终执行init-method的方法。
1.PostConstruct注解
如下所示,这里使用配置类的方式进行注入,因为一会延时init-method必须使用配置类才可以实现,启动容器当加载TestA这个Bean时,他的初始化方法就会被执行。
@Configuration
public class TestInitmestond {
@Bean
public TestA getBeanA(){
return new TestA();
}
}
class TestA{
@PostConstruct
public void postConstructor(){
System.out.println("这是使用了PostConstruct注解的初始化方法");
}
}
2.实现InitializingBean接口
下面是结合了第一种和第二种的初始化方式:
@Configuration
public class TestInitmestond {
@Bean
public TestA getBeanA(){
return new TestA();
}
}
class TestA implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是实现InitializingBean的初始化方法");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstructor(){
System.out.println("这是使用了PostConstruct注解的初始化方法");
}
}
3.声明init-method方法
init-method方法必须使用配置类进行加载Bean才可以配置,因为该属性是Bean标签的属性,在注解中也就是Bean注解的属性,所以我们使用Component等其他IOC注解时是无法指定的。
@Configuration
public class TestInitmestond {
@Bean(initMethod = "initMethod")
public TestA getBeanA(){
return new TestA();
}
}
class TestA implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是实现InitializingBean的初始化方法");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstructor(){
System.out.println("这是使用了PostConstruct注解的初始化方法");
}
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("这是使用了init-method声明的初始化方法");
}
}
下面启动下容器展示下他们的执行顺序,如下:

可以看到他们的顺序是固定的即:PostConstruct—>initializingBean—>init-method.
二、Bean的多种销毁方式
同样的Spring也支持了三种销毁的方式,且这三种销毁方式与三种创建方式是完全对应的。同时与初始化方法一样Spring也是支持三种销毁方法的并行的。且他们并行时顺序是固定的:执行PreDestroy–>DisposableBean–>destroy-method.
1.PreDestroy注解
这里容器采用手动启动的方式进行创建,然后为容器设置一个销毁的钩子,这样当容器销毁时我们就可以去执行销毁方法了,对于单例模式的销毁方法只能通过这种测试了,若是我们直接停止IDEA的服务是不会执行销毁方法的。不过对于scope不是singleton的Bean来说,比如request在正常服务里是可以体现销毁动作的。
public class TestDestroyMethod {
//手动启动容器,模拟关闭
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfig.class);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.start();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
@Configuration
class TestConfig{
@Bean
public TestB getBean(){
return new TestB();
}
}
class TestB{
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("这是使用PreDestroy注解的销毁方法");
}
}
2.实现DisposableBean接口
这种就是直接实现接口重写destroy方法即可
public class TestDestroyMethod {
//手动启动容器,模拟关闭
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfig.class);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.start();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
@Configuration
class TestConfig{
@Bean
public TestB getBean(){
return new TestB();
}
}
class TestB implements DisposableBean {
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("这是使用PreDestroy注解的销毁方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是实现DisposableBean的方法");
}
}
3.声明destroy-method方法
下面是结合了三种销毁方法的代码
public class TestDestroyMethod {
//手动启动容器,模拟关闭
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(TestConfig.class);
annotationConfigApplicationContext.start();
annotationConfigApplicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
@Configuration
class TestConfig{
@Bean(destroyMethod = "destroyMethod")
public TestB getBean(){
return new TestB();
}
}
class TestB implements DisposableBean {
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("这是使用PreDestroy注解的销毁方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("这是实现DisposableBean的方法");
}
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("这是制定了destroy-method的销毁方法");
}
}
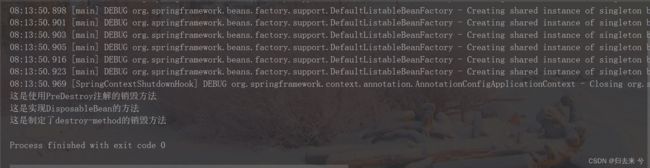
下面是执行的截图,可以看到三种销毁方式与初始化方式一样都是有固定顺序的,事实上初始化方式与销毁方式他们是有对应关系的。
PostConstruct与PreDestroy是一组,InitializingBean与DisposableBean是一组,init-method与destroy-method是一组。