Qt C++ 调用Python
目录
-
- 环境
- 在Qt Creator配置Python环境
-
- 1. 修改Path变量
- 2. 添加编译选项中的includepath和链接libs
- 3. 在代码里#include
- 调用Python
-
- 初始化
- 调用方程
- Python类的实例化 / 调用类函数
- 结束调用Python
- Anaconda 虚拟环境下的 Python
- 参考资料
环境
- Windows 11
- Qt 5.15.2
- Qt Creator 7.0.2 (MSVS 2019, 64 bit)
- Python 3.8
在Qt Creator配置Python环境
1. 修改Path变量
点击Qt Creator最左侧的“项目”选项,找到Build Encironment里的环境变量Path,将自己主机里的Python路径添加到Path里(也可以是虚拟环境的Python路径)。

选中Path,点击“Edit”,添加自己的Python路径。也有可能在Python下载后就已经自动写入了。比如我下载的Python路径为:C:\Users\chxi\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38\
2. 添加编译选项中的includepath和链接libs
在pro文件中添加:
INCLUDEPATH += \
-I C:\Users\chxi\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38\include
LIBS += \
-LC:\Users\chxi\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python38\libs -lpython38
可能出现的报错:
error: LNK1104: 无法打开文件“python38_d.lib”
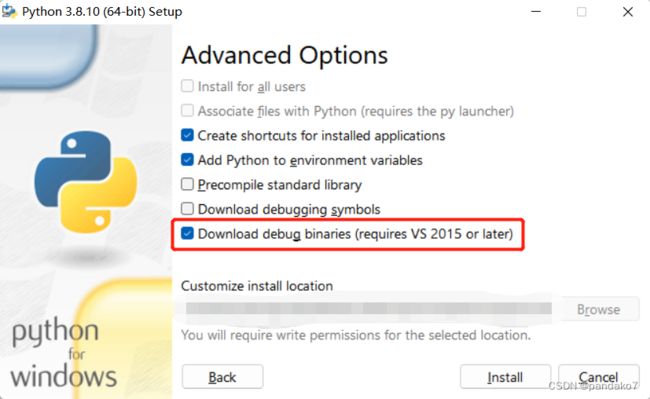
解决办法:在Windows下,Python下载时需要打勾“Download debug binaries”!(在Linux下,需要下载python-dev!)
打开Python的安装文件 python-3.8.10-amd64.exe,点击“Modify”。

在Optional Features下点击“Next”,在Advanced Options下勾选上,再下载即可。
3. 在代码里#include
在使用时,可能会出现slots关键词冲突,可以这样include:
#pragma push_macro("slots")
#undef slots
#include 然后就可以调用Python的方程了。
调用Python
我的测试Python文件是 PythonClass.py
def test_func(a, b, c):
return a + b + c
class PythonClass:
def __init__(self, a=0, b=0):
self.a = a
self.b = b
self.i = 0
def test(self, c):
self.i += 1
return self.a + self.b + c + self.i
在C++代码中,这样调用:
初始化
// 1. 类似于先连接上Python
Py_Initialize();
if (!Py_IsInitialized()) {
qDebug() << "Fail to init Python.";
}
// 2. 加入python文件的路径
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
std::string path = "sys.path.append('C:/Users/chxi/Desktop/qt/myTestProject')";
PyRun_SimpleString(&path[0]);
// 3. 找到要用的python文件
PyObject * pModule = PyImport_ImportModule("PythonClass");
if (pModule == NULL) {
qDebug() <<"Fail to load Python module (PythonClass.py)";
}
可能出现的报错:
File "", line 1 SyntaxError: (unicode error) 'unicodeescape' codec can't decode bytes in position 2-3: truncated \UXXXXXXXX escape
解决办法:把path里路径的\\符号改为Linux里的/。
调用方程
// 1. 找到要调用的方程
PyObject * pFunc = PyObject_GetAttrString(pModule, "test_func");
if(!pFunc) {
qDebug() << "Cant find function test_func().\n";
}
// 2. 构建参数,调用
PyObject * args = Py_BuildValue("iii", 1, 2, 3);
PyObject * pRet = PyEval_CallObject(pFunc, args);
// 3. 得到返回值
int test_ret;
PyArg_Parse(pRet, "i", &test_ret);
qDebug() << test_ret;
构建参数Py_BuildValue的格式:
| Python | C++ | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| s | str or None | const char * | |
| s# | str or None | const char *, int or Py_ssize_t | |
| y | bytes | const char * | |
| y# | bytes | const char * | |
| i | int | int | |
| b | int | char | |
| h | int | short int | |
| l | int | long int | |
| B | int | unsigned char | |
| H | int | unsigned short int | |
| I | int | unsigned int | |
| n | int | Py_ssize_t | |
| d | float | double | |
| f | float | float | |
| O | object | PyObject * | Pass a Python object untouched (except for its reference count, which is incremented by one). If the object passed in is a NULL pointer, it is assumed that this was caused because the call producing the argument found an error and set an exception. Therefore, Py_BuildValue() will return NULL but won’t raise an exception. If no exception has been raised yet, SystemError is set. |
| O& | object | [converter, anything] | |
| (items) | (tuple) | [matching-items] | Convert a sequence of C values to a Python tuple with the same number of items. |
| [items] | (list) | [matching-items] | Convert a sequence of C values to a Python list with the same number of items. |
| {items} | (dict) | [matching-items] | Convert a sequence of C values to a Python dictionary. Each pair of consecutive C values adds one item to the dictionary, serving as key and value, respectively. |
- 在使用
d(double)的时候,带入的参数要写为1.0,而不是1。- 如果参数代入有错误,或Python程序内部出错,可能会打印出一些错误的随机数字、内存错误或未知错误。假如看到的结果不对,并且没有看到正常的C++报错,那么可以多看看Python方程写的对不对,参数代入是否准确,数据类型是否正确。
Python类的实例化 / 调用类函数
// 1. 找到Python的类
PyObject* pDict = PyModule_GetDict(pModule);
if(!pDict) {
qDebug() << "Cant find dictionary.";
}
PyObject* pClassCalc = PyDict_GetItemString(pDict, "PythonClass");
if (!pClassCalc) {
qDebug() << "Cant find PythonClass class.";
}
// 2. 初始化对象
PyObject* pConstruct = PyInstanceMethod_New(pClassCalc);
if (!pConstruct) {
qDebug() << "Cant find PythonClass constructor.";
}
PyObject* cons_args = PyTuple_New(2);
PyTuple_SetItem(cons_args, 0, Py_BuildValue("d", 1.0));
PyTuple_SetItem(cons_args, 1, Py_BuildValue("d", 2.0));
pInstance = PyObject_CallObject(pConstruct, cons_args);
if (!pInstance) {
qDebug() << "Cant construct instance.";
}
// 3. 调用类函数
pRet = PyObject_CallMethod(pInstance,"test","d", 3.0);
double ret = PyFloat_AsDouble(pRet);
qDebug() << "first: " << ret;
pRet = PyObject_CallMethod(pInstance,"test","d", 3.0);
ret = PyFloat_AsDouble(pRet);
qDebug() << "second: " << ret;
- 实例化Python对象时,
__init__需要单独调用!- 如果报出的错误不是C++的错误,耐心debug Python部分!
结束调用Python
Py_XDECREF(pRet);
Py_XDECREF(pFunc);
Py_XDECREF(pModule);
Py_XDECREF(pInstance);
Py_XDECREF(args);
Py_XDECREF(pDict);
Py_XDECREF(pClassCalc);
Py_XDECREF(pConstruct);
Py_XDECREF(cons_args);
Py_Finalize();
Anaconda 虚拟环境下的 Python
配置方式大体相同,比如PATH变量、includepath和libs只是改成相应路径下的Python即可。
python38_d.lib可能用conda不好下载,可以用正常下载Python的方式得到这个文件,复制进虚拟环境下Python的路径里。- 在
Py_Initialize()之前,需要加一句Py_SetPythonHome(L"C:\\Users\\username\\anaconda3\\envs\\py38");来指定使用哪个环境的Python(假设我的虚拟环境叫py38)。 - 以防一些下载好的包报错,可以把
C:\Users\username\anaconda3\envs\py38\Library\bin放入环境变量的PATH中。我遇到过的报错:
# import numpy 之后
...
ImportError: DLL load failed while importing _multiarray_umath: 找不到指定的模块。
- 如果都找到的
.py文件,路径也都对,但无法成功PyImport_ImportModule,那可能就是python文件内部报错,可以先分别尝试import不同的包/部分代码来debug。
参考资料
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43788499/article/details/84933210
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq1512165940/article/details/103617894
- https://docs.python.org/3.8/c-api/arg.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/u011728480/article/details/103903612