java NIO非阻塞式IO网络编程学习笔记(一)
使用Java的Socket API编写一个简单的TCP Echo Server。其阻塞式IO的处理方式虽然简单,但每个客户端都需要一个单独的Thread来处理,当服务器需要同时处理大量客户端时,这种做法不再可行。使用NIO API可以让一个或有限的几个Thread同时处理连接到服务器上的所有客户端。
NIO API允许一个线程通过Selector对象同时监控多个SelectableChannel来处理多路IO,NIO应用程序一般按下图所示工作:
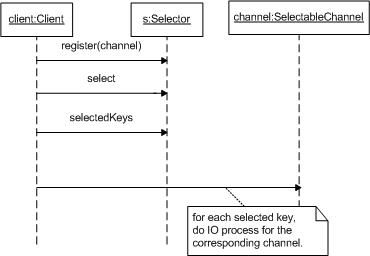
Figure 1
Figure 1 所示,Client一直在循环地进行select操作,每次select()返回以后,通过selectedKeys()可以得到需要处理的SelectableChannel并对其一一处理。 这样做虽然简单但也有个问题,当有不同类型的SelectableChannel需要做不同的IO处理时,在图中Client的代码就需要判断channel的类型然后再作相应的操作,这往往意味着一连串的if else。更糟糕的是,每增加一种新的channel,不但需要增加相应的处理代码,还需要对这一串if else进行维护。(在本文的这个例子中,我们有ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel这两种channel需要分别被处理。)
如果考虑将channel及其需要的IO处理进行封装,抽象出一个统一的接口,就可以解决这一问题。在Listing 1中的NioSession就是这个接口。
NioSession的channel()方法返回其封装的SelectableChannel对象,interestOps()返回用于这个channel注册的interestOps。registered()是当SelectableChannel被注册后调用的回调函数,通过这个回调函数,NioSession可以得到channel注册后的SelectionKey。process()函数则是NioSession接口的核心,这个方法抽象了封装的SelectableChannel所需的IO处理逻辑。
Listing 1:
public SelectableChannel channel();
public int interestOps();
public void registered(SelectionKey key);
public void process();
}
和NioSession一起工作的是NioWorker这个类(Listing 2),它是NioSession的调用者,封装了一个Selector对象和Figure 1中循环select操作的逻辑。理解这个类可以帮助我们了解该如何使用NioSession这个接口。 NioWorker实现了Runnable接口,循环select操作的逻辑就在run()方法中。在NioWorker – NioSession这个框架中,NioSession在channel注册的时候会被作为attachment送入register函数,这样,在每次select()操作的循环中,对于selectedKeys()中的每一个SelectionKey,我们都可以通过attachment拿到其相对应的NioSession然后调用其process()方法。 每次select()循环还有一个任务,就是将通过add()方法加入到这个NioWorker的NioSession注册到Selector上。在Listing 2的代码中可以看出,NioSession中的channel()被取出并注册在Selector上,注册所需的interestOps从NioSession中取出,NioSession本身则作为attachment送入register()函数。注册成功后,NioSession的registered()回调函数会被调用。 NioWorker的add()方法的作用是将一个NioSession加入到该NioWorker中,并wakeup当前的select操作,这样在下一次的select()调用之前,这个NioSession会被注册。stop()方法则是让一个正在run()的NioWorker停止。closeAllChannels()会关闭当前注册的所有channel,这个方法可在NioWorker不再使用时用来释放IO资源。 Listing 2:
public NioWorker(Selector sel) {
_sel = sel;
_added = new HashSet();
}
public void run() {
try {
try {
while (_run) {
_sel.select();
Set selected = _sel.selectedKeys();
for (Iterator itr = selected.iterator(); itr.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) itr.next();
NioSession s = (NioSession) key.attachment();
s.process();
itr.remove();
}
synchronized (_added) {
for (Iterator itr = _added.iterator(); itr.hasNext();) {
NioSession s = (NioSession) itr.next();
SelectionKey key = s.channel().register(_sel, s.interestOps(), s);
s.registered(key);
itr.remove();
}
}
}
} finally {
_sel.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
public void add(NioSession s) {
synchronized (_added) {
_added.add(s);
}
_sel.wakeup();
}
public synchronized void stop() {
_run = false ;
_sel.wakeup();
}
public void closeAllChannels() {
for (Iterator itr = _sel.keys().iterator(); itr.hasNext();) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) itr.next();
try {
key.channel().close();
} catch (IOException ex) {}
}
}
protected Selector _sel = null ;
protected Collection _added = null ;
protected volatile boolean _run = true ;
}
在Echo Server这个例子中,我们需要一个ServerSocketChannel来接受新的TCP连接,对于每个TCP连接,我们还需要一个SocketChannel来处理这个TCP连接上的IO操作。把这两种channel和上面的NioWorker – NioSession结构整合在一起,可以得到NioServerSession和NioEchoSession这两个类,它们分别封装了ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel及其对应的IO操作。下面这个UML类图描述了这4个类的关系:

Figure 2
可以看到NioWorker和NioSession对新加入的两个类没有任何依赖性,NioServerSession和NioEchoSession通过实现NioSession这个接口为系统加入了新的功能。这样的一个体系架构符合了Open-Close原则,新的功能可以通过实现NioSession被加入而无需对原有的模块进行修改,这体现了面向对象设计的强大威力。 NioServerSession的实现(Listing 3)相对比较简单,其封装了一个ServerSocketChannel以及从这个channel上接受新的TCP连接的逻辑。NioServerSession还需要一个NioWorker的引用,这样每接受一个新的TCP连接,NioServerSession就为其创建一个NioEchoSession的对象,并将这个对象加入到NioWorker中。 Listing 3:
public NioServerSession(ServerSocketChannel channel, NioWorker worker) {
_channel = channel;
_worker = worker;
}
public void registered(SelectionKey key) {}
public void process() {
try {
SocketChannel c = _channel.accept();
if (c != null ) {
c.configureBlocking( false );
NioEchoSession s = new NioEchoSession(c);
_worker.add(s);
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
public SelectableChannel channel() {
return _channel;
}
public int interestOps(){
return SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT;
}
protected ServerSocketChannel _channel;
protected NioWorker _worker;
}
NioEchoSession的行为要复杂一些,NioEchoSession会先从TCP连接中读取数据,再将这些数据用同一个连接写回去,并重复这个步骤直到客户端把连接关闭为止。我们可以把“Reading”和“Writing”看作NioEchoSession的两个状态,这样可以用一个有限状态机来描述它的行为,如下图所示:

Figure 3
接下来的工作就是如何实现这个有限状态机了。在这个例子中,我们使用State模式来实现它。下面这张UML类图描述了NioEchoSession的设计细节。
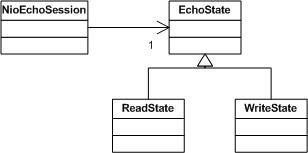
Figure 4
NioEchoSession所处的状态由EchoState这个抽象类来表现,其两个子类分别对应了“Reading”和“Writing”这两个状态。NioEchoSession会将process()和interestOps()这两个方法delegate给EchoState来处理,这样,当NioEchoSession处于不同的状态时,就会有不同的行为。 Listing 4是EchoState的实现。EchoState定义了process()和interestOps()这两个抽象的方法来让子类实现。NioEchoSession中的process()方法会被delegate到其当前EchoState的process()方法,NioEchoSession本身也会作为一个描述context的参数被送入EchoState的process()方法中。EchoState定义的interestOps()方法则会在NioEchoSession注册和转变State的时候被用到。
EchoState还定义了两个静态的方法来返回预先创建好的ReadState和WriteState,这样做的好处是可以避免在NioEchoSession转换state的时候创建一些不必要的对象从而影响性能。然而,这样做要求state类必须是无状态的,状态需要保存在context类,也就是NioEchoSession中。
Listing 4:
public abstract void process(NioEchoSession s) throws IOException;
public abstract int interestOps();
public static EchoState readState() {
return _read;
}
public static EchoState writeState() {
return _write;
}
protected static EchoState _read = new ReadState();
protected static EchoState _write = new WriteState();
}
Listing 5是NioEchoSession的实现。NioEchoSession包含有一个SocketChannel,这个channel注册后得到的SelectionKey,一个用于存放数据的ByteBuffer和一个记录当前state的EchoState对象。在初始化时,EchoState被初始化为一个ReadState。NioEchoSession把process()方法和interestOps()方法都delegate到当前的EchoState中。其setState()方法用于切换当前state,在切换state后,NioEchoSession会通过SelectionKey更新注册的interestOps。close()方法用于关闭这个NioEchoSession对象。
Listing 5:
public NioEchoSession(SocketChannel c) {
_channel = c;
_buf = ByteBuffer.allocate( 128 );
_state = EchoState.readState();
}
public void registered(SelectionKey key) {
_key = key;
}
public void process() {
try {
_state.process( this );
} catch (IOException ex) {
close();
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
public SelectableChannel channel() {
return _channel;
}
public int interestOps() {
return _state.interestOps();
}
public void setState(EchoState state) {
_state = state;
_key.interestOps(interestOps());
}
public void close() {
try {
_channel.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
protected SocketChannel _channel = null ;
protected SelectionKey _key;
protected ByteBuffer _buf = null ;
protected EchoState _state = null ;
}
Listing 6和Listing 7分别是ReadState和WriteState的实现。ReadState在process()中会先从NioEchoSession的channel中读取数据,如果未能读到数据,NioEchoSession会继续留在ReadState;如果读取出错,NioEchoSession会被关闭;如果读取成功,NioEchoSession会被切换到WriteState。WriteState则负责将NioEchoSession中已经读取的数据写回到channel中,全部写完后,NioEchoSession会被切换回ReadState。
Listing 6:
| public class ReadState extends EchoState {
public void process(NioEchoSession s)
throws IOException
{
SocketChannel channel = s._channel;
ByteBuffer buf = s._buf;
int count = channel.read(buf);
if (count == 0) {
return;
}
if (count == -1) {
s.close();
return;
}
buf.flip();
s.setState(EchoState.writeState());
}
public int interestOps() {
return SelectionKey.OP_READ;
}
}
|
Listing 7:
| public class WriteState extends EchoState {
public void process(NioEchoSession s)
throws IOException
{
SocketChannel channel = s._channel;
ByteBuffer buf = s._buf;
channel.write(buf);
if (buf.remaining() == 0) {
buf.clear();
s.setState(EchoState.readState());
}
}
public int interestOps() {
return SelectionKey.OP_WRITE;
}
}
|
NioEchoServer(Listing 8)被用来启动和关闭一个TCP Echo Server,这个类实现了Runnable接口,调用其run()方法就启动了Echo Server。其shutdown()方法被用来关闭这个Echo Server,注意shutdown()和run()的finally block中的同步代码确保了只有当Echo Server被关闭后,shutdown()方法才会返回。
Listing 8:
| public class NioEchoServer implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
ServerSocketChannel serv = ServerSocketChannel.open();
try {
serv.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(7));
serv.configureBlocking(false);
_worker = new NioWorker(Selector.open());
NioServerSession s = new NioServerSession(serv, _worker);
_worker.add(s);
_worker.run();
} finally {
_worker.closeAllChannels();
synchronized (this) {
notify();
}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
public synchronized void shutdown() {
_worker.stop();
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
throw new Error(ex);
}
}
protected NioWorker _worker = null;
}
|
最后,通过一个简单的main()函数(Listing 9),我们就可以运行这个Echo Server了。
Listing 9:
| public static void main(String [] args) {
new NioEchoServer().run();
}
|
我们可以通过telnet程序来检验这个程序的运行状况:
1. 打开一个命令行,输入 telnet localhost 7 来运行一个telnet程序并连接到Echo Server上。
2. 在telnet程序中输入字符,可以看到输入的字符被显示在屏幕上。(这是因为Echo Server将收到的字符写回到客户端)
3. 多打开几个telnet程序进行测试,可以看到Echo Server能通过NIO API用一个Thread服务多个客户端。