Java异常处理
异常是程序中的一些错误,但并不是所有的错误都是异常,并且错误有时候是可以避免的。
比如说,你的代码少了一个分号,那么运行出来结果是提示是错误 java.lang.Error;如果你System.out.println(11/0),那么你是因为你用0做了除数,会抛出 java.lang.ArithmeticException 的异常。
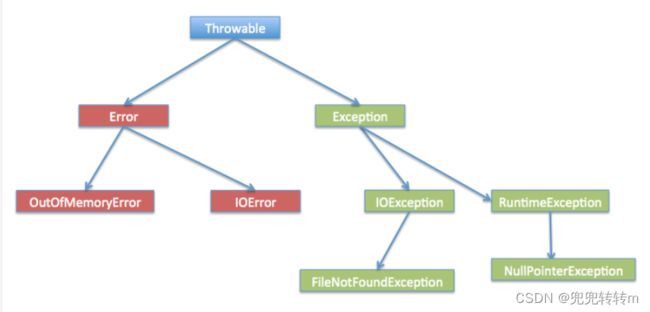
要理解Java异常处理是如何工作的,你需要掌握以下三种类型的异常:
1、检查性异常:这类异常是程序员无法预见的,例如打开一个不存在的文件等。
2、运行时异常:运行时异常可以被编译时忽略。
3、错误:错误在代码中通常被忽略。例如,当栈溢出时,一个错误就发生了,它们在编译也检查不到的。
检查性异常:IOException,SQLException
运行时异常:NullPointer
错误:OutOfMemoryError,IOError
异常处理方法
当我们使用try--catch捕获到异常后,可以得到一个异常对象,它有以下这些常用方法。
try{
// 程序代码
}catch(ExceptionName e1){
//Catch 块
}Catch 语句包含要捕获异常类型的声明。当保护代码块中发生一个异常时,try 后面的 catch 块就会被检查。如果发生的异常包含在 catch 块中,异常会被传递到该 catch 块,这和传递一个参数到方法是一样。
| 序号 | 方法说明 |
| 1 | String getMessage() 返回关于发生的异常的详细信息。(最常用) |
| 2 | Throwable getCause() 返回一个 Throwable 对象代表异常原因。 |
| 3 | String toString() 返回此 Throwable 的简短描述 |
| 4 | void printStackTrace() 将此 Throwable 及其回溯打印到标准错误流。 |
实例:
下面的例子中声明有两个元素的一个数组,当代码试图访问数组的第四个元素的时候就会抛出一个异常。
public class Main3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
int a[] = new int[2];
System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("Exception thrown: " + e);
}
System.out.println("Out of the block");
}
}throws 与 throw 关键字
在Java中, throw 和 throws 关键字是用于处理异常的。
throw 关键字用于在代码中抛出异常。
public void checkNumber(int num) {
if (num < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Number must be positive");
}
}throws 关键字用于在方法声明中指定可能会抛出的异常类型。
public void readFile(String filePath) throws IOException {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
String line = reader.readLine();
while (line != null) {
System.out.println(line);
line = reader.readLine();
}
reader.close();
}finally关键字
finally 关键字用来创建在 try 代码块后面执行的代码块。无论是否发生异常,finally 代码块中的代码总会被执行。
try{
// 程序代码
}catch(异常类型1 异常的变量名1){
// 程序代码
}finally{
// 程序代码
}public class ExcepTest{
public static void main(String args[]){
int a[] = new int[2];
try{
System.out.println("Access element three :" + a[3]);
}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
}
finally{
a[0] = 6;
System.out.println("First element value: " +a[0]);
System.out.println("The finally statement is executed");
}
}
}以上实例运行结果如下: Exception thrown :java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3 First element value: 6 The finally statement is executed
自定义异常
在 Java 中你可以自定义异常。编写自己的异常类时需要记住下面的几点。
- 所有异常都必须是 Throwable 的子类。
- 如果希望写一个检查性异常类,则需要继承 Exception 类。
- 如果你想写一个运行时异常类,那么需要继承 RuntimeException 类。
可以像下面这样定义自己的异常类:
class MyException extends Exception{
}一般在项目中基本使用的就是自定义异常。