模型泛化(一)图像增广及其在CIFAR10数据集上的应用
模型泛化(一)图像增广及其在CIFAR10数据集上的应用
import numpy as np
import torch
import torchvision
from PIL import Image
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.utils import data
from torchvision import transforms
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
1、图像增广__反转和裁剪
def set_figsize(figsize=(3.5, 2.5)):
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = figsize
def show_images(imgs, num_rows, num_cols, titles=None, scale=1.5):
figsize = (num_cols * scale, num_rows * scale)
_, axes = plt.subplots(num_rows, num_cols, figsize=figsize)
axes = axes.flatten()
for i, (ax, img) in enumerate(zip(axes, imgs)):
if torch.is_tensor(img):
# Tensor Image
ax.imshow(img.numpy())
else:
# PIL Image
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
if titles:
ax.set_title(titles[i])
return axes
'''
定义辅助函数apply。
此函数在输⼊图像img上多次运⾏图像增⼴⽅法aug并显⽰所有结果。
'''
def apply(img, aug, num_rows=2, num_cols=4, scale=1.5):
Y = [aug(img) for _ in range(num_rows * num_cols)]
show_images(Y, num_rows, num_cols, scale=scale)
set_figsize(figsize=(3.5, 4.5))
img = Image.open('./img.png')
plt.imshow(img)
'''
1、水平反转
使⽤transforms模块来创建RandomFlipLeftRight实例,这样就各有50%的⼏率使图像向左或向右翻转。
'''
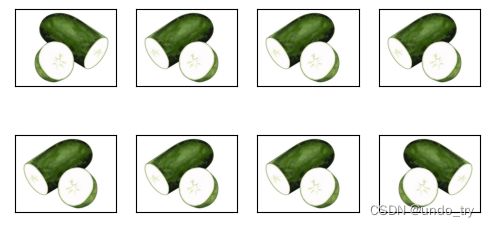
apply(img,torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip())
'''
2、上下翻转
上下翻转图像不如左右图像翻转那样常⽤。
创建⼀个RandomFlipTopBottom实例,使图像各有50%的⼏率向上或向下翻转
'''
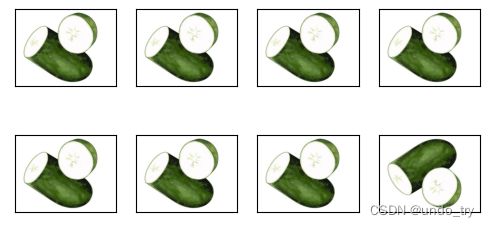
apply(img,torchvision.transforms.RandomVerticalFlip())
'''
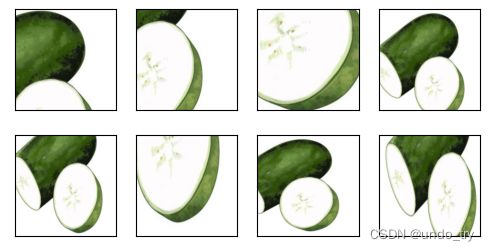
3、随机裁剪
池化层可以降低卷积层对于位置的敏感性。
通过对图像进行随机裁剪,可以让物体以不同比例出现在不同的位置上,也可以降低模型对于位置的敏感性。
随机裁剪⼀个⾯积为原始⾯积10%到100%的区域,该区域的宽⾼⽐从0.5到2之间随机取值。
然后,区域的宽度和⾼度都被缩放到200像素。
'''
shape_aug = torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(
(200,200),scale=(0.1,1),ratio=(0.5,2)
)
apply(img,shape_aug)
2、图像增广_颜色(亮度、对比度、饱和度、色调)
'''
1、亮度
随机更改图像的亮度,随机值为原始图像的50%(1 − 0.5)到150%(1 + 0.5)之间
'''
apply(
img,
torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0)
)
'''
2、色调
'''
apply(img, torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0.5))
'''
3、同时随机更改图像的亮度(brightness)、对⽐度(contrast)、饱和度(saturation)和⾊调(hue)。
'''
color_aug = torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, contrast=0.5, saturation=0.5, hue=0.5)
apply(img, color_aug)
'''
4、结合多种图像增⼴⽅法
通过使⽤⼀个Compose实例来综合上⾯定义的不同的图像增⼴⽅法,并将它们应⽤到每个图像
'''
augs = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),# 水平翻转
torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop(
(200,200),scale=(0.1,1),ratio=(0.5,2)
), # 随机裁剪
torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter(
brightness=0.5,contrast=0.5,saturation=0.5,hue=0.5
) # 改变颜色
]
)
apply(img,augs)
3、图像增广_应用到CIFAR10数据集
'''
1、加载CIFAR-10数据集
Fashion-MNIST数据集中对象的位置和⼤⼩已被规范化,⽽CIFAR-10数据集中对象的颜⾊和⼤⼩差异更明显。
'''
all_images = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(
root='/root/autodl-fs/data/cifar10data',train=True,download=False
)
show_images(
[all_images[i][0] for i in range(32)],num_rows=4, num_cols=8, scale=0.8
)
'''
通常对训练样本只进⾏图像增⼴,且在预测过程中不使⽤随机操作的图像增⼴。
我们使⽤最简单的随机左右翻转。此外,我们使⽤ToTensor实例将⼀批图像转换为深度学习框架所要求的格式,
即形状为(批量⼤⼩,通道数,⾼度,宽度)的32位浮点数,取值范围为0到1。
'''
train_augs = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[
torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 训练样本进行随机水平反转的图像增广
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
]
)
test_augs = torchvision.transforms.Compose(
[
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor() # 预测过程不使用随机操作的图像增广
]
)
'''
将加载数据集,封装为函数
'''
def get_dataloader_workers():
"""使⽤4个进程来读取数据"""
return 4
def get_cifar10_data(is_train, augs, batch_size):
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='/root/autodl-fs/data/cifar10data',train=is_train,transform=augs,download=False)
dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,shuffle=True,num_workers=get_dataloader_workers()
)
return dataloader
'''
2、多GPU小批量训练
'''
from AnimatorClass import Animator
from TimerClass import Timer
from AccumulatorClass import Accumulator
def try_all_gpus():
devices = [torch.device(f'cuda:{i}')
for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())]
return devices if devices else [torch.device('cpu')]
def accuracy(y_hat, y):
"""计算预测正确的数量"""
if len(y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1:
y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y
return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())
def evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, data_iter, device=None):
"""使⽤GPU计算模型在数据集上的精度"""
if isinstance(net, nn.Module):
net.eval() # 设置为评估模式
if not device:
device = next(iter(net.parameters())).device
# 正确预测的数量,总预测的数量
metric = Accumulator(2)
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(X, list):
# BERT微调所需的
X = [x.to(device) for x in X]
else:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
metric.add(accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]
def train_ch(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, devices = try_all_gpus()):
"""⽤GPU训练模型"""
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)
net = nn.DataParallel(net,device_ids=devices).to(devices[0]) # 多GPU数据并行
print('training on', devices)
# optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
animator = Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
timer, num_batches = Timer(), len(train_iter)
num_batches = len(train_iter)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 训练损失之和,训练准确率之和,实例数,特点数
metric = Accumulator(4)
net.train()
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(devices[0]), y.to(devices[0])
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
metric.add(l * X.shape[0], accuracy(y_hat, y), y.shape[0], y.numel())
timer.stop()
train_l = metric[0] / metric[2]
train_acc = metric[1] / metric[3]
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,(train_l, train_acc, None))
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
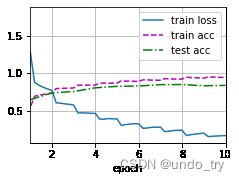
print(f'loss {train_l:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, test acc {test_acc:.3f}')
print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec on {str(devices)}')
'''
4、定义resnet模型
'''
class Residual(nn.Module):
"""The Residual block of ResNet."""
def __init__(self, input_channels, num_channels,use_1x1conv=False, strides=1):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=strides)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=3, padding=1)
if use_1x1conv:
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(input_channels, num_channels,
kernel_size=1, stride=strides)
else:
self.conv3 = None
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels)
def forward(self, X):
Y = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(X)))
Y = self.bn2(self.conv2(Y))
if self.conv3:
X = self.conv3(X)
Y += X
return F.relu(Y)
def resnet18(num_classes, in_channels=1):
def resnet_block(in_channels, out_channels, num_residuals,
first_block=False):
blk = []
for i in range(num_residuals):
if i == 0 and not first_block:
blk.append(Residual(in_channels, out_channels,
use_1x1conv=True, strides=2))
else:
blk.append(Residual(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*blk)
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU())
net.add_module("resnet_block1", resnet_block(64, 64, 2, first_block=True))
net.add_module("resnet_block2", resnet_block(64, 128, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block3", resnet_block(128, 256, 2))
net.add_module("resnet_block4", resnet_block(256, 512, 2))
net.add_module("global_avg_pool", nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1)))
net.add_module("fc", nn.Sequential(nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(512, num_classes)))
return net
'''
4、训练模型
'''
batch_size = 128
lr = 0.001
epochs = 10
# 创建resnet18模型
net = resnet18(10, 3)
train_iter = get_cifar10_data(True, train_augs, batch_size)
test_iter = get_cifar10_data(False, test_augs, batch_size)
train_ch(net, train_iter, test_iter,num_epochs=epochs,lr=lr)
loss 0.166, train acc 0.941, test acc 0.835
2219.4 examples/sec on [device(type='cuda', index=0)]