SpringMVC
1. springMVC简介
1.1 什么是MVC
MVC是按照模型、视图、控制器来划分,
M:Model,模型层,指工程中的JavaBean,作用是处理数据
javaBean分为两类
- 一类称为实体类Bean:专门存储业务数据的,如 Student、User 等
- 一类称为业务处理 Bean:指 Service 或 Dao 对象,专门用于处理业务逻辑和数据访问。
V:View,视图层,指工程中的html或jsp等页面,作用是与用户进行交互,展示数据
C:Controller,控制层,指工程中的servlet,作用是接收请求和响应浏览器
MVC的工作流程: 用户通过视图层发送请求到服务器,在服务器中请求被Controller接收,Controller调用相应的Model层处理请求,处理完毕将结果返回到Controller,Controller再根据请求处理的结果找到相应的View视图,渲染数据后最终响应给浏览器
1.2 什么是SpringMVC
SpringMVC是Spring的一个后续产品,是Spring的一个子项目
SpringMVC 是 Spring 为表述层开发提供的一整套完备的解决方案。在表述层框架历经 Strust、WebWork、Strust2 等诸多产品的历代更迭之后,目前业界普遍选择了SpringMVC 作为 Java EE 项目表述层开发的首选方案。
1.3 SpringMC的特点
- Spring 家族原生产品,与 IOC 容器等基础设施无缝对接
- 基于原生的Servlet,通过了功能强大的前端控制器DispatcherServlet,对请求和响应进行统一处理
- 表述层各细分领域需要解决的问题全方位覆盖,提供全面解决方案
- 代码清新简洁,大幅度提升开发效率
- 内部组件化程度高,可插拔式组件即插即用,想要什么功能配置相应组件即可
- 性能卓著,尤其适合现代大型、超大型互联网项目要求
2. 入门案例
2.1 开发环境
IDE:idea 2019.2
构建工具:maven3.5.4
服务器:tomcat8.5
Spring版本:5.3.1
2.2 创建maven工程
- 添加web模块
- 打包方式为:war
- 引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>5.3.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logbackgroupId>
<artifactId>logback-classicartifactId>
<version>1.2.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleafgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.3 配置web.xml
注册SpringMVCD前端控制器
2.3.1 默认配置方式
此配置作用下,SpringMVC的配置文件默认位于WEB-INF下,默认名称为
servlet.xml,例如,以下配置所对应SpringMVC的配置文件位于WEB-INF下,文件名为springMVC-servlet.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservletclass>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
2.3.2 扩展配置方式
可通过init-param标签设置SpringMVC配置文件的位置和名称,通过load-on-startup标签设置SpringMVC前端控制器DispatcherServlet的初始化时间
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservletclass>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
标签中使用/和/*的区别:
/所匹配的请求可以是/login或.html或.js或.css方式的请求路径,但是/不能匹配.jsp请求路径的请求因此就可以避免在访问jsp页面时,该请求被DispatcherServlet处理,从而找不到相应的页面
/*则能够匹配所有请求,例如在使用过滤器时,若需要对所有请求进行过滤,就需要使用/*的写
法
2.4 创建请求控制器
由于前端控制器对浏览器发送的请求进行了统一的处理,但是具体的请求有不同的处理过程,因此需要创建处理具体请求的类,即请求控制器
请求控制器中每一个处理请求的方法成为控制器方法
因为SpringMVC的控制器由一个POJO(普通的Java类)担任,因此需要通过@Controller注解将其标识为一个控制层组件,交给Spring的IoC容器管理,此时SpringMVC才能够识别控制器的存在
@Controller
public class HelloController {
}
2.5 创建SpringMVC的配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.gdhd.Controller"/>
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="templateEngine">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine" >
<property name="templateResolver">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".html"/>
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
bean>
property>
bean>
property>
bean>
beans>
2.6 测试HelloWord
- 实现对首页的访问
在请求控制器中创建请求的方法
package com.gdhd.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
// @RequestMapping注解:处理请求和控制器方法之间的映射关系
// @RequestMapping注解的value属性可以通过请求地址匹配请求,/表示的当前工程的上下文路径
@RequestMapping("/")
public String Hello(){
//设置视图名称
return "index";
}
}
- 创建index.html视图
由于在SpringMVC.xml配置文件中设置了视图的前缀与后缀,则视图创建必须前后缀一致
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".html"/>
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>首页h1>
<a th:href="@{/hello}">HelloWorlda><br/>
body>
html>
处理请求的方法
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String HelloWorld() {
return "target";
}
2.7 总结
浏览器发送请求,若请求地址符合前端控制器的url-pattern,该请求就会被前端控制器
DispatcherServlet处理。前端控制器会读取SpringMVC的核心配置文件,通过扫描组件找到控制器,将请求地址和控制器中@RequestMapping注解的value属性值进行匹配,若匹配成功,该注解所标识的控制器方法就是处理请求的方法。处理请求的方法需要返回一个字符串类型的视图名称,该视图名称会被视图解析器解析,加上前缀和后缀组成视图的路径,通过Thymeleaf对视图进行渲染,最终转发到视图所对应页面
3. @RequestMapping注解
3.1 @RequestMapping注解的功能
从注解名称上我们可以看到,@RequestMapping注解的作用就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系。
SpringMVC 接收到指定的请求,就会来找到在映射关系中对应的控制器方法来处理这个请求。
3.2、@RequestMapping注解的位置
@RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息
@RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/test")
public class RequestMappingController {
//此时请求映射所映射的请求的请求路径为:/test/testRequestMapping
@RequestMapping("/testRequestMapping")
public String testRequestMapping(){
return "success";
}
}
3.3 @RequestMapping注解的value属性
@RequestMapping注解的value属性通过请求的请求地址匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的value属性是一个字符串类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求
@RequestMapping注解的value属性必须设置,至少通过请求地址匹配请求映射
<a th:href="@{/demo1}">第一个a>
<a th:href="@{/demo2}">第二个a>
@RequestMapping(value = {"demo1","demo2"})
public String hello(){
return "success";
}
3.4 @RequestMapping注解的method属性
@RequestMapping注解的method属性通过请求的请求方式(get或post)匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的method属性是一个RequestMethod类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多种请求方式的请求
若当前请求的请求地址满足请求映射的value属性,但是请求方式不满足method属性,则浏览器报错
405:Request method ‘POST’ not supported
<a th:href="@{/test}">测试@RequestMapping的value属性-->/testa><br>
<form th:action="@{/test}" method="post">
<input type="submit">
form>
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/test"},
method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST}
)
public String testRequestMapping(){
return "success";
}
注:
1、对于处理指定请求方式的控制器方法,SpringMVC中提供了@RequestMapping的派生注解
处理get请求的映射–>@GetMapping
处理post请求的映射–>@PostMapping
处理put请求的映射–>@PutMapping
处理delete请求的映射–>@DeleteMapping
2、常用的请求方式有get,post,put,delete
但是目前浏览器只支持get和post,若在form表单提交时,为method设置了其他请求方式的字符
串(put或delete),则按照默认的请求方式get处理
若要发送put和delete请求,则需要通过spring提供的过滤器HiddenHttpMethodFilter,在
RESTful部分会讲到
3.5 @RequestMapping注解的params属性(了解)
@RequestMapping注解的params属性通过请求的请求参数匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的params属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求参数和请求映射的匹配关系
“param”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数
“!param”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带param请求参数
“param=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数且param=value
“param!=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数但是param!=value
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/testRequestMapping", "/test"}
,method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST}
,params = {"username","password!=123456"}
)
public String testRequestMapping(){
return "success";
}
注
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足params属性,此时
页面回报错400:Parameter conditions “username, password!=123456” not met for actual
request parameters: username={admin}, password={123456}
3.6 @RequestMapping注解的headers属性(了解)
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求映射
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求头信息和请求映射的匹配关系
“header”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息
“!header”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息
“header=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value
“header!=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header!=value
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到
3.7 SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径
- ?:表示任意的单个字符(不包括?)
- *:表示任意的0个或多个字符(不包括?与/)
- ** 表示任意层数的任意目录
注意:在使用 ** 时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式
3.8 SpringMVC支持路径中的占位符(重点)
原始方式:/deleteUser?id=1
rest方式:/user/delete/1
SpringMVC路径中的占位符常用于RESTful风格中,当请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符{xxx}表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参
<a th:href="@{/testRest/1/admin}">测试路径中的占位符-->/testResta><br>
@RequestMapping("/testRest/{id}/{username}")
public String testRest(@PathVariable("id") String id, @PathVariable("username")
String username){
System.out.println("id:"+id+",username:"+username);
return "success";
}
//最终输出的内容为-->id:1,username:admin
4 SpringMVC获取请求参数、
4.1 通过ServletAPI获取
将HttpServletRequest作为控制器方法的形参,此时HttpServletRequest类型的参数表示封装了当前请求的请求报文的对象
@RequestMapping("/testParam")
public String testParam(HttpServletRequest request){
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username:"+username+",password:"+password);
return "success";
}
4.2 通过控制器方法的形参获取请求参数
在控制器方法的形参位置,设置和请求参数同名的形参,当浏览器发送请求,匹配到请求映射时,在DispatcherServlet中就会将请求参数赋值给相应的形参
<a th:href="@{/testParam(username='admin',password=123456)}">测试获取请求参数--
>/testParama><br>
@RequestMapping("/testParam")
public String testParam(String username, String password){
System.out.println("username:"+username+",password:"+password);
return "success";
}
4.3 @RequestParam
@RequestParam是将请求参数和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@RequestParam注解一共有三个属性:
- value:指定为形参赋值的请求参数的参数名
- required:设置是否必须传输此请求参数,默认值为true,若设置为true时,则当前请求必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输该请求参数,且没有设置defaultValue属性,则页面报错400:Required String parameter ‘xxx’ is not present;若设置为false,则当前请求不是必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输,则注解所标识的形参的值为null
- defaultValue:不管required属性值为true或false,当value所指定的请求参数没有传输或传输的值
为""时,则使用默认值为形参赋值
<a th:href="@{/param}">测试a>
@RequestMapping("/param")
public String param(@RequestParam(required = false,defaultValue = "hello")String name){
System.out.println(name);
return "success";
}
4.4 @RequestHeader
@RequestHeader是将请求头信息和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@RequestHeader注解一共有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,用法同@RequestParam
4.5 @CookieValue
@CookieValue是将cookie数据和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
@CookieValue注解一共有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,用法同@RequestParam
4.6 通过POJO获取请求参数
可以在控制器方法的形参位置设置一个实体类类型的形参,此时若浏览器传输的请求参数的参数名和实体类中的属性名一致,那么请求参数就会为此属性赋值
<form th:action="@{/testpojo}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
性别:<input type="radio" name="sex" value="男">男<input type="radio"
name="sex" value="女">女<br>
年龄:<input type="text" name="age"><br>
邮箱:<input type="text" name="email"><br>
<input type="submit">
form>
@RequestMapping("/testpojo")
public String testPOJO(User user){
System.out.println(user);
return "success";
}
//最终结果-->User{id=null, username='张三', password='123', age=23, sex='男',
email='123@qq.com'}
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(Integer id, String username, String password) {
this.id = id;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
4.7 解决获取请求参数的乱码问题
解决解决获取请求参数的乱码问题,可以使用SpringMVC提供的编码过滤器CharacterEncodingFilter,但是必须在web.xml中进行注册
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encodingparam-name>
<param-value>UTF-8param-value>
init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncodingparam-name>
<param-value>trueparam-value>
init-param>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
filter-mapping>
SpringMVC中处理编码的过滤器一定要配置到其他过滤器之前,否则无效
5. 域对象共享数据
5.1 使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testServletAPI")
public String testServletAPI(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("testScope", "hello,servletAPI");
return "success";
}
5.2 使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testModel/demo1")
public ModelAndView demo1(){
/**
* ModelAndView有Model和View的功能
* Model主要用于向请求域共享数据
* View主要用于设置视图,实现页面跳转
*/
ModelAndView mvc = new ModelAndView();
//向请求域共享数据
mvc.addObject("name", "leixiaodao");
//设置视图,实现页面跳转
mvc.setViewName("success");
return mvc;
}
5.3 使用Model向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testModel/demo2")
public String demo2(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","hello,Model");
return "success";
}
5.4 使用map向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/testModel/demo3")
public String demo3(Map map){
map.put("name","hello,Map");
return "success";
}
5.5 使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/ttestModel/demo4")
public String testModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){
modelMap.addAttribute("testScope", "hello,ModelMap");
return "success";
}
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>首页h1>
<a th:href="@{/testModel/demo1}">使用ModelAndView域a>
<a th:href="@{/testModel/demo2}">使用Model域a>
<a th:href="@{/testModel/demo3}">使用mapa>
<a th:href="@{/testModel/demo4}">使用ModelMapa>
body>
html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="${name}"></p>
</body>
</html>
5.6 Model、ModelMap、Map的关系
Model、ModelMap、Map类型的参数其实本质上都是 BindingAwareModelMap 类型的
public interface Model{}
public class ModelMap extends LinkedHashMap<String, Object> {}
public class ExtendedModelMap extends ModelMap implements Model {}
public class BindingAwareModelMap extends ExtendedModelMap {}
5.7 向session域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/test/session")
public String testSession(HttpSession session){
session.setAttribute("name","Hello Session");
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${session.name}">p>
5.8 向application域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/test/application")
public String testApplication(HttpSession session){
ServletContext application = session.getServletContext();
application.setAttribute("name","Hello Application");
return "success";
}
<p th:text="${application.name}">p>
6. SpringMVC的视图
- SpringMVC中的视图是View接口,视图的作用渲染数据,将模型Model中的数据展示给用户
- SpringMVC视图的种类很多,默认有转发视图和重定向视图
- 当工程引入jstl的依赖,转发视图会自动转换为JstlView
- 若使用的视图技术为Thymeleaf,在SpringMVC的配置文件中配置了Thymeleaf的视图解析器,由此视图解析器解析之后所得到的是ThymeleafView
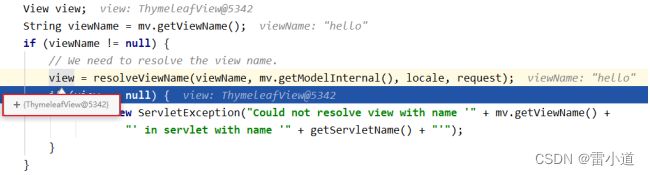
6.1 ThymeleafView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,视图名称拼接视图前缀和视图
后缀所得到的最终路径,会通过转发的方式实现跳转
@RequestMapping("/testHello")
public String testHello(){
return "hello";
}
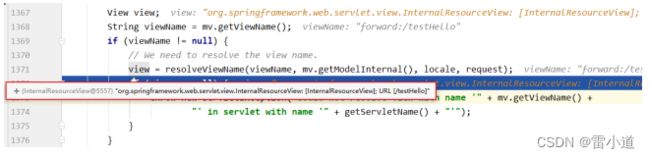
6.2 转发视图
SpringMVC中默认的转发视图是InternalResourceView
SpringMVC中创建转发视图的情况:
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"forward:"为前缀时,创建InternalResourceView视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"forward:"去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过转发的方式实现跳转
@RequestMapping("/testForward")
public String testForward(){
return "forward:/testHello";
}
6.3 重定向视图
SpringMVC中默认的重定向视图是RedirectView
当控制器方法中所设置的视图名称以"redirect:"为前缀时,创建RedirectView视图,此时的视图名称不会被SpringMVC配置文件中所配置的视图解析器解析,而是会将前缀"redirect:“去掉,剩余部分作为最终路径通过重定向的方式实现跳转
例如"redirect:/”,“redirect:/employee”
@RequestMapping("/testRedirect")
public String testRedirect(){
return "redirect:/testHello";
}
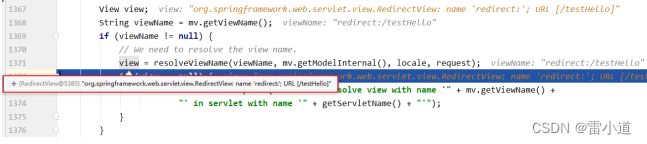
注:重定向视图在解析时,会先将redirect:前缀去掉,然后会判断剩余部分是否以/开头,若是则会自动拼接上下文路径
6.4、视图控制器
当控制器方法中,仅仅用来实现页面跳转,即只需要设置视图名称时,可以将处理器方法使用view-controller标签进行表示
<mvc:view-controller path="/testView" view-name="success">mvc:view-controller>
注
当SpringMVC中设置任何一个view-controller时,其他控制器中的请求映射将全部失效,此时需要在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中设置开启mvc注解驱动的标签:
7. RESTful
7.1 RESTful简介
REST:Representational State Transfer,表现层资源状态转移。
- 资源:资源是一种看待服务器的方式,即,将服务器看作是由很多离散的资源组成。每个资源是服务器上一个可命名的抽象概念。因为资源是一个抽象的概念,所以它不仅仅能代表服务器文件系统中的一个文件、数据库中的一张表等等具体的东西,可以将资源设计的要多抽象有多抽象,只要想象力允许而且客户端应用开发者能够理解。与面向对象设计类似,资源是以名词为核心来组织的,首先关注的是名词。一个资源可以由一个或多个URI来标识。URI既是资源的名称,也是资源在Web上的地址。对某个资源感兴趣的客户端应用,可以通过资源的URI与其进行交互。
- 资源的表述:资源的表述是一段对于资源在某个特定时刻的状态的描述。可以在客户端-服务器端之间转移(交换)。资源的表述可以有多种格式,例如HTML/XML/JSON/纯文本/图片/视频/音频等等。资源的表述格式可以通过协商机制来确定。请求-响应方向的表述通常使用不同的格式。
- 状态转移:状态转移说的是:在客户端和服务器端之间转移(transfer)代表资源状态的表述。通过转移和操作资源的表述,来间接实现操作资源的目的
7.2 RESTful的实现
- 具体说,就是 HTTP 协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。
- 它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE用来删除资源。
- REST 风格提倡 URL 地址使用统一的风格设计,从前到后各个单词使用斜杠分开,不使用问号键值对方式携带请求参数,而是将要发送给服务器的数据作为 URL 地址的一部分,以保证整体风格的一致性。
| 操作 | 传统方式 | REST风格 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询操作 | getUserById?id=1 | user/1–>get请求方式 |
| 保存操作 | saveUser | user–>post请求方式 |
| 删除操作 | deleteUser?id=1 | user/1–>delete请求方式 |
| 更新操作 | updateUser | user–>put请求方式 |
7.3 HiddenHttpMethodFilter
由于浏览器只支持发送get和post方式的请求,那么该如何发送put和delete请求呢?
SpringMVC 提供了 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 帮助我们将 POST 请求转换为 DELETE 或 PUT 请求
HiddenHttpMethodFilter 处理put和delete请求的条件:
- 当前请求的请求方式必须为post
- 当前请求必须传输请求参数_method
- 满足以上条件,HiddenHttpMethodFilter 过滤器就会将当前请求的请求方式转换为请求参数_method的值,因此请求参数_method的值才是最终的请求方式
在web.xml中注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-class>
filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilterfilter-name>
<url-pattern>/*url-pattern>
package com.gdhd.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
//@RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/user")
public String getAllUser(){
System.out.println("查询所有的用户信息-->/user-->get");
return "success";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public String getUserById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
System.out.println("根据id查询用户信息-->/user/"+id+"-->get");
return "success";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping("/user")
public String insertUser(){
System.out.println("添加用户信息-->/user-->post");
return "success";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/user", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping("/user")
public String updateUser(){
System.out.println("修改用户信息-->/user-->put");
return "success";
}
//@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/user/{id}")
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable("id") Integer id){
System.out.println("删除用户信息-->/user/"+id+"-->delete");
return "success";
}
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>首页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>index.htmlh1>
<a th:href="@{/user}">查询所有的用户信息a><br>
<a th:href="@{/user/1}">查询id为1的用户信息a><br>
<form th:action="@{/user}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="添加用户信息">
form>
<form th:action="@{/user}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put">
<input type="submit" value="修改用户信息">
form>
<form th:action="@{/user/5}" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
<input type="submit" value="删除用户信息">
form>
<hr>
<a th:href="@{/employee}">查询所有的员工信息a>
body>
html>
注意:
目前为止,SpringMVC中提供了两个过滤器:CharacterEncodingFilter和
HiddenHttpMethodFilter
在web.xml中注册时,必须先注册CharacterEncodingFilter,再注册HiddenHttpMethodFilter
原因:
- 在 CharacterEncodingFilter 中通过 request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法设置字符集的,request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding) 方法要求前面不能有任何获取请求参数的操作
而 HiddenHttpMethodFilter 恰恰有一个获取请求方式的操作:
8. SpringMV处理ajax请求
8.1 @RequestBody
@RequestBody可以获取请求体信息,使用@RequestBody注解标识控制器方法的形参,当前请求的请求体就会为当前注解所标识的形参赋值
<form th:action="@{/test/RequestBody}" method="post">
用户名:<input type="text" name="username"><br>
密码:<input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="submit">
form>
@RequestMapping("/test/ajax")
public void testAjax(Integer id, @RequestBody String requestBody, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
System.out.println("requestBody:"+requestBody);
System.out.println("id:"+id);
response.getWriter().write("hello,axios");
}
8.2. @RequestBody获取json格式的请求参数
在使用了axios发送ajax请求之后,浏览器发送到服务器的请求参数有两种格式:
- name=value&name=value…,此时的请求参数可以通过request.getParameter()获取,对应SpringMVC中,可以直接通过控制器方法的形参获取此类请求参数
- {key:value,key:value,…},此时无法通过request.getParameter()获取,之前我们使用操作json的相关jar包gson或jackson处理此类请求参数,可以将其转换为指定的实体类对象或map集合。在SpringMVC中,直接使用@RequestBody注解标识控制器方法的形参即可将此类请求参数转换为java对象
- 导入jackson的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
<version>2.12.1version>
dependency>
- SpringMVC的配置文件中设置开启mvc的注解驱动
<mvc:annotation-driven />
- 在控制器方法的形参位置,设置json格式的请求参数要转换成的java类型(实体类或map)的参数,并使用@RequestBody注解标识
<input type="button" value="使用@RequestBody注解处理json格式的请求参数" @click="testRequestBody()"><br>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/js/vue.js}">script>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/js/axios.min.js}">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
/**
* axios({
url:"",//请求路径
method:"",//请求方式
//以name=value&name=value的方式发送的请求参数
//不管使用的请求方式是get或post,请求参数都会被拼接到请求地址后
//此种方式的请求参数可以通过request.getParameter()获取
params:{},
//以json格式发送的请求参数
//请求参数会被保存到请求报文的请求体传输到服务器
//此种方式的请求参数不可以通过request.getParameter()获取
data:{}
}).then(response=>{
console.log(response.data);
});
*/
var vue = new Vue({
el:"#app",
methods:{
testRequestBody(){
axios.post(
"/SpringMVC/test/RequestBody/json",
{username:"admin",password:"123456",age:23,gender:"男"}
).then(response=>{
console.log(response.data);
});
}
}
});
script>
//将json格式的数据转换为map集合
@RequestMapping("/test/RequestBody/json")
public void testRequestBody(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> map, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
System.out.println(map);
response.getWriter().write("hello,RequestBody");
}
//将json格式的数据转换为实体类对象
public void testRequestBody(@RequestBody User user, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
System.out.println(user);
response.getWriter().write("hello,RequestBody");
}
8.3 @ResponseBody
@ResponseBody用于标识一个控制器方法,可以将该方法的返回值直接作为响应报文的响应体响应到浏览器
@RequestMapping("/testResponseBody")
public String testResponseBody(){
//此时会跳转到逻辑视图success所对应的页面
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping("/testResponseBody")
@ResponseBody
public String testResponseBody(){
//此时响应浏览器数据success
return "success";
}
8.4 @ResponseBody响应浏览器json数据
服务器处理ajax请求之后,大多数情况都需要向浏览器响应一个java对象,此时必须将java对象转换为json字符串才可以响应到浏览器,之前我们使用操作json数据的jar包gson或jackson将java对象转换为json字符串。在SpringMVC中,我们可以直接使@ResponseBody注解实现此功能
@ResponseBody响应浏览器json数据的条件:
- 导入jackson的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
<version>2.12.1version>
dependency>
- SpringMVC的配置文件中设置开启mvc的注解驱动
<mvc:annotation-driven />
- 使用@ResponseBody注解标识控制器方法,在方法中,将需要转换为json字符串并响应到浏览器的java对象作为控制器方法的返回值,此时SpringMVC就可以将此对象直接转换为json字符串并响应到浏览器
<input type="button" value="测试@ResponseBody响应浏览器json格式的数据"
@click="testResponseBody()"><br>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/js/vue.js}">script>
<script type="text/javascript" th:src="@{/js/axios.min.js}">script>
<script type="text/javascript">
var vue = new Vue({
el:"#app",
methods:{
testResponseBody(){
axios.post("/SpringMVC/test/ResponseBody/json").then(response=>{
console.log(response.data);
});
}
}
});
script>
//响应浏览器list集合@RequestMapping("/test/ResponseBody/json")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> testResponseBodyJson(){
User user1 = new User(1001, "admin1", "123456", 20, "男");
User user2 = new User(1002, "admin2", "123456", 20, "男");
User user3 = new User(1003, "admin3", "123456", 20, "男");
List<User> list = Arrays.asList(user1, user2, user3);
return list;
}
//响应浏览器map集合
public Map<String, Object> testResponseBodyJson(){
User user1 = new User(1001, "admin1", "123456", 20, "男");
User user2 = new User(1002, "admin2", "123456", 20, "男");
User user3 = new User(1003, "admin3", "123456", 20, "男");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("1001", user1);
map.put("1002", user2);
map.put("1003", user3);
return map;
}
//响应浏览器实体类对象
public User testResponseBodyJson(){
User user = new User(1001, "admin", "123456", 20, "男");
return user;
}*/
8.5 @RestController注解
@RestController注解是springMVC提供的一个复合注解,标识在控制器的类上,就相当于为类添加了@Controller注解,并且为其中的每个方法添加了@ResponseBody注解在这里插入代码片
9. 文件上传和下载
9.1 文件下载
ResponseEntily用于用于控制器方法的返回值类型,该控制器方法的返回值就是响应到浏览器的响应报文
@RequestMapping("/down")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> down(HttpSession session) throws IOException {
//获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
//获取服务器中文件的真实路径
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("/static/img/1.jpg");
//创建输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//根据输入流的长度创建字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[is.available()];
//将流读到字节数组中
is.read(bytes);
//创建HttpHeaders对象设置响应头信息
MultiValueMap<String, String> headers = new HttpHeaders();
//设置要下载方式以及下载文件的名字
headers.add("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=1.jpg");
//设置响应状态码
HttpStatus statusCode = HttpStatus.OK;
//创建ResponseEntity对象
ResponseEntity<byte[]> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity<>(bytes, headers,
statusCode);
//关闭输入流
is.close();
return responseEntity;
}
9.2 文件上传
文件上传要求form表单的请求方式必须为post,并且添加属性enctype=“multipart/form-data”
SpringMVC中将上传的文件封装到MultipartFile对象中,通过此对象可以获取文件相关信息
上传步骤:
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileuploadgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileuploadartifactId>
<version>1.3.1version>
dependency>
- 在springMVC的配置文件中配置
<bean id="multipartResolver"
class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
bean>
- 控制器方法:
@RequestMapping("/testUp")
public String testUp(MultipartFile photo, HttpSession session) throws
IOException {
//获取上传的文件的文件名
String fileName = photo.getOriginalFilename();
//处理文件重名问题
String hzName = fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + hzName;
//获取服务器中photo目录的路径
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
String photoPath = servletContext.getRealPath("photo");
File file = new File(photoPath);
if(!file.exists()){
file.mkdir();
}
String finalPath = photoPath + File.separator + fileName;
//实现上传功能
photo.transferTo(new File(finalPath));
return "success";
}
10 拦截器
10.1 拦截器的配置
SpringMVC中的拦截器用于拦截控制器方法的执行
SpringMVC中的拦截器需要实现HandlerInterceptor
SpringMVC的拦截器必须在SpringMVC的配置文件中进行配置:
<bean class="com.lxd.interceptor.FirstInterceptor">bean>
<ref bean="firstInterceptor">ref>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/testRequestEntity"/>
<ref bean="firstInterceptor">ref>
mvc:interceptor>
10.2 拦截器的三个抽象方法
SpringMVC中的拦截器有三个抽象方法:
- preHandle:控制器方法执行之前执行preHandle(),其boolean类型的返回值表示是否拦截或放行,返回true为放行,即调用控制器方法;返回false表示拦截,即不调用控制器方法
- postHandle:控制器方法执行之后执行postHandle()
- afterCompletion:处理完视图和模型数据,渲染视图完毕之后执行afterCompletion()
10.3 多个拦截器的执行顺序
①若每个拦截器的preHandle()都返回true
此时多个拦截器的执行顺序和拦截器在SpringMVC的配置文件的配置顺序有关:
preHandle()会按照配置的顺序执行,而postHandle()和afterCompletion()会按照配置的反序执行
②若某个拦截器的preHandle()返回了false
preHandle()返回false和它之前的拦截器的preHandle()都会执行,postHandle()都不执行,返回false的拦截器之前的拦截器的afterCompletion()会执行