全网最全瑞吉外卖项目笔记(含扩展功能)
写在最前
- 想获得最佳的阅读体验,请移步至我的个人博客查看此文:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/29/ReggieTakeOut/
- 项目地址(求star):https://github.com/Cyborg2077/Reggie_Takeout
- 源码网盘链接(防止有小伙伴还不会用git):https://pan.baidu.com/s/11X9aKxFb07AwhhQKjsbubQ?pwd=2077 提取码:2077
- 另一个实战项目:https://github.com/Cyborg2077/xuecheng-plus
- 我的其他文章
- Spring:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/08/29/Spring/
- SprinMVC:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/08/SpringMVC/
- SSM整合:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/10/SSMIntegration/
- Mavne高级:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/13/MavenSenior/
- SpringBoot:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/14/SpringBoot/
- MyBatisPlus:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/20/MyBatisPlus/
- Redis基础篇:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/10/21/RedisBasic/
- Redis实战篇:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/10/22/RedisPractice/
- Docker:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/12/21/Docker/
- MQ:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/12/22/MeassageQueue/
- ElasticSearch:https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/12/24/ElasticSearch/
- 更多文章请关注我的个人博客:https://cyborg2077.github.io/
准备工作
话不多说,先建表,然后创建一个SpringBoot的工程,勾选Spring Web,MySQL和MyBatis,然后在pom.xml中导入druid,lombok和MyBatisPlus的坐标
com.alibaba
druid
1.1.16
com.baomidou
mybatis-plus-boot-starter
3.4.1
org.projectlombok
lombok
导入前端资源,放在resources/static目录下,资源链接: https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/Drs29egDxnh (包含前端资源和数据库脚本)
如果直接放在resources目录下,则需要配置一下资源映射
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
log.info("开始进行静态资源映射...");
registry.addResourceHandler("/backend/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/backend/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/front/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/front/");
}
}
之后配置一下端口号和数据库连接四要素就能访问静态页面了
server:
port: 80
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/reggie?serverTimezone=Asia
username: root
password: PASSWORD
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
打开浏览器,访问 http://localhost/backend/page/login/login.html 可以看到登录页面,不过此时无法登录
关于数据库设计以及前端页面的编写,后期我也会专门抽时间学的,第一个项目就当了解一下整体的开发流程
后台系统登录功能分析
数据库的数据和简单的SQL语句都不用我们管,数据已经提供好了,简单的SQL语句用MyBatisPlus。
创建对应的实体类
这部分我们先来完成后台的登录功能,所以目前只要一个Employee类
@Data
public class Employee implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
private String username;
private String name;
private String password;
private String phone;
private String sex;
private String idNumber;
private Integer status;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//这两个先不用管,后面再说
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
}
创建对应的Mapper和Service
{% tabs 建对应的Mapper和Service %}
直接继承BaseMapper就行了,别忘了@Mapper注解
@Mapper
public interface EmployeeMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
继承IService
public interface EmployeeService extends IService {
}
继承ServiceImpl,实现EmployeeService接口,别忘了@Service注解
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
}
{% endtabs %}
统一结果封装
这个在之前的文章也讲过了,忘了可以回顾一下这篇文章,第二小节就是在讲解统一结果封装
{% link SSM整合, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/10/SSMIntegration/, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
编写一个Result类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Result {
private Integer code; // 编码:1成功。0和其他数字失败
private String errMsg; // 错误信息
private T data; // 数据
private Map map = new HashMap(); // 动态数据
public static Result success(T data) {
Result r = new Result<>();
r.code = 1; //成功状态码
r.data = data;
return r;
}
public static Result error(String errMsg) {
Result r = new Result<>();
r.errMsg = errMsg; //设置错误信息
r.code = 0; //默认失败状态码,后期我们可以根据自己的需求来设置其他状态码
return r;
}
public Result add(String msg, String value) {
this.map.put(msg, value);
return this;
}
}
编写Controller
给EmployeeController类添加一个login方法
@RequestBody主要用于接收前端传递给后端的json字符串(请求体中的数据)HttpServletRequest作用:如果登录成功,将员工对应的id存到session一份,这样想获取一份登录用户的信息就可以随时获取出来
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/employee")
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
/**
* 登入功能
* @param request
* @param employee
* @return
*/
//发送post请求
@PostMapping("/login")
public Result login(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody Employee employee) {
String password = employee.getPassword();
password = DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex(password.getBytes());
//这部分就是MP
LambdaQueryWrapper lqw = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
lqw.eq(Employee::getUsername, employee.getUsername());
Employee emp = employeeService.getOne(lqw);
if (emp == null) {
return Result.error("登陆失败");
}
if (!emp.getPassword().equals(password)) {
return Result.error("登录失败");
}
if (emp.getStatus() == 0) {
return Result.error("该用户已被禁用");
}
//存个Session,只存个id就行了
request.getSession().setAttribute("employee",emp.getId());
return Result.success(emp);
}
/**
* 登出功能
* @param request
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/logout")
public Result logout(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getSession().removeAttribute("employee");
return Result.success("退出成功");
}
}
如果你忘了Session怎么用,可以看一下这篇文章
{% link Cookie与Session, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/08/20/JavaWeb07/, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
如果你忘了MP怎么用,可以看一下这篇文章
{% link MyBatisPlus, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/20/MyBatisPlus/, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
登录测试
数据库中目前只有一条用户信息,username为admin,password为123456(已经经过MD5加密了)
现在我们访问 http://localhost/backend/page/login/login.html
输入正确的用户名和密码,正常登录,并跳转至http://localhost/backend/index.html
输入错误的用户名或密码,会显示登陆失败
对应的HTML代码如下
methods: {
async handleLogin() {
this.$refs.loginForm.validate(async (valid) => {
if (valid) {
this.loading = true
let res = await loginApi(this.loginForm)
if (String(res.code) === '1') {
localStorage.setItem('userInfo',JSON.stringify(res.data))
window.location.href= '/backend/index.html'
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg)
this.loading = false
}
}
})
}
}
对应的JS代码如下
function loginApi(data) {
return $axios({
'url': '/employee/login',
'method': 'post',
data
})
}
function logoutApi(){
return $axios({
'url': '/employee/logout',
'method': 'post',
})
}
完善登录功能
问题分析:
- 之前的登录功能,我们不登录,直接访问 http://localhost/backend/index.html 也可以正常访问,这显然是不合理的
- 我们希望看到的效果是,只有登录成功才能看到页面,未登录状态则跳转到登录页面
- 那么具体改如何实现呢?使用过滤器或拦截器,在过滤器或拦截器中判断用户是否登录,然后在选择是否跳转到对应页面
如果你忘了Filter的知识,可以先通过这篇文章简单了解一下
{% link Filter&Listener&AJAX, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/08/21/JavaWeb08/, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
测试Filter拦截路径
@Slf4j
@WebFilter(filterName = "loginCheckFilter", urlPatterns = "/*")
public class LoginCheckFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
//将拦截到的URI输出到日志,{}是占位符,将自动填充request.getRequestURI()的内容
log.info("拦截到的URI:{}", request.getRequestURI());
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
并在启动类上加入注解@ServletComponentScan
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan
public class ReggieApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ReggieApplication.class, args);
}
}
启动服务器,访问index页面,查看日志,现在可以拦截到URI了
2022-09-29 18:05:53.190 …… : 拦截到的URI:/backend/index.html
2022-09-29 18:06:01.174 …… : 拦截到的URI:/employee/page
编写Filter逻辑
上面我们已经能成功拦截到路径了,那现在我们来开发逻辑,主要分为以下几个步骤
- 获取本次请求的URI
//获取本次请求的URI
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
//定义不需要被拦截的请求
String[] urls = new String[]{
"/employee/login.html",
"/employee/logout.html",
"/backend/**",
"/front/**"
};
- 判断本次请求是否需要处理
使用Spring 概念模型 :PathMatcher路径匹配器
public static final AntPathMatcher PATH_MATCHER = new AntPathMatcher();
private boolean check(String[] urls, String uri) {
for (String url : urls) {
boolean match = PATH_MATCHER.match(url, uri);
if (match)
return true;
}
return false;
}
- 如果不需要处理,则直接放行
if (check) {
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
- 判断登录状态,如果已登录,则直接放行
//我们当初存的session是employee,所以这里就拿它判断
if (request.getSession().getAttribute("employee") != null) {
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
- 如果未登录则返回未登录结果
//未登录状态为什么要返回一个error呢?而且msg为NOTLOGIN
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(Result.error("NOTLOGIN")));
我们看一下JS代码就懂了,当符合未登录状态的条件时,会自动重定向到登录页面
// 响应拦截器
service.interceptors.response.use(res => {
if (res.data.code === 0 && res.data.msg === 'NOTLOGIN') {// 返回登录页面
console.log('---/backend/page/login/login.html---')
localStorage.removeItem('userInfo')
window.top.location.href = '/backend/page/login/login.html'
} else {
return res.data
}
}
注意这里需要导一下fastjson的坐标
com.alibaba
fastjson
1.2.62
- 完整代码
完整步骤就是上面的五步,在这里我们再使用日志来输出一些东西,方便我们来调试代码
@WebFilter(filterName = "loginCheckFilter",urlPatterns = "/*")
@Slf4j
public class LoginCheckFilter implements Filter {
//路径匹配
public static final AntPathMatcher PATH_MATCHER = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//强转
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
//1.获取本次请求的URI
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("拦截到请求:{}",requestURI);
//定义不需要处理的请求
String[] urls = new String[]{
"/employee/login",
"/employee/logout",
"/backend/**",
"/front/**"
};
//2.判断本次请求是否需要处理
boolean check = check(urls, requestURI);
//3.如果不需要处理,则直接放行
if (check) {
log.info("本次请求:{},不需要处理",requestURI);
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
//4.判断登录状态,如果已登录,则直接放行
if (request.getSession().getAttribute("employee") != null) {
log.info("用户已登录,id为{}",request.getSession().getAttribute("employee"));
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
//5.如果未登录则返回未登录结果,通过输出流方式向客户端页面响应数据
log.info("用户未登录");
log.info("用户id{}",request.getSession().getAttribute("employee"));
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(Result.error("NOTLOGIN")));
}
public boolean check(String[] urls, String requestURI){
for (String url : urls) {
boolean match = PATH_MATCHER.match(url, requestURI);
if (match) {
//匹配
return true;
}
}
//不匹配
return false;
}
}
测试登录
当我们直接访问 http://localhost/backend/index.html 时,日志输出如下
: 用户未登录
- 用户id为:null
随后将自动跳转至登录页面
: 拦截到请求:/employee/login
- 本次请求:/employee/login,不需要处理
成功登录后
: 拦截到请求:/employee/page
- 用户已登录,id为1
那么至此,登录功能就已经做好了
登出功能
登出功能的后端操作很简单,只要删除session就好了
/**
* 登出功能
* @param request
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/logout")
public Result logout(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getSession().removeAttribute("employee");
return Result.success("退出成功");
}
那这里来简单分析一下前端代码
登出的功能是在index页面的,右上角有一个按钮,点击就能登出
对应的函数如下,这里的logoutApi是用来发送post请求的
{% tabs 登出对应函数 %}
logout() {
logoutApi().then((res)=>{
if(res.code === 1){
localStorage.removeItem('userInfo')
window.location.href = '/backend/page/login/login.html'
}
})
}
function logoutApi(){
return $axios({
'url': '/employee/logout',
'method': 'post',
})
}
{% endtabs %}
添加员工
流程分析
实现功能之前,我们先梳理一下整个执行流程
- 页面发送ajax请求,将新增员工页面中输入的数据以json的形式提交到服务端
- 服务端Controller接收页面提交的数据并调用Service将数据进行保存
- Service调用Mapper操作数据库,保存数据
前端的内容我们简单了解一下就好了
{% tabs 添加员工前端代码 %}
数据模型绑定的是ruleForm
保存并添加的按钮绑定的函数是submitForm('ruleForm', true)
<el-form
ref="ruleForm"
:model="ruleForm"
:rules="rules"
:inline="false"
label-width="180px"
class="demo-ruleForm"
>
<el-form-item label="账号:" prop="username">
<el-input v-model="ruleForm.username" placeholder="请输入账号" maxlength="20"/>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item
label="员工姓名:"
prop="name"
>
<el-input
v-model="ruleForm.name"
placeholder="请输入员工姓名"
maxlength="20"
/>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item
label="手机号:"
prop="phone"
>
<el-input
v-model="ruleForm.phone"
placeholder="请输入手机号"
maxlength="20"
/>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item
label="性别:"
prop="sex"
>
<el-radio-group v-model="ruleForm.sex">
<el-radio label="男">el-radio>
<el-radio label="女">el-radio>
el-radio-group>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item
label="身份证号:"
prop="idNumber"
>
<el-input
v-model="ruleForm.idNumber"
placeholder="请输入身份证号"
maxlength="20"
/>
el-form-item>
<div class="subBox address">
<el-form-item>
<el-button @click="goBack()">
取消
el-button>
<el-button
type="primary"
@click="submitForm('ruleForm', false)"
>
保存
el-button>
<el-button
v-if="actionType == 'add'"
type="primary"
class="continue"
@click="submitForm('ruleForm', true)"
>
保存并继续添加
el-button>
el-form-item>
div>
el-form>
默认性别为男
ruleForm : {
'name': '',
'phone': '',
'sex': '男',
'idNumber': '',
username: ''
}
从第九行的addEmployee开始看就行
submitForm (formName, st) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
if (this.actionType === 'add') {
const params = {
...this.ruleForm,
sex: this.ruleForm.sex === '女' ? '0' : '1'
}
addEmployee(params).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('员工添加成功!')
if (!st) {
this.goBack()
} else {
this.ruleForm = {
username: '',
'name': '',
'phone': '',
// 'password': '',
// 'rePassword': '',/
'sex': '男',
'idNumber': ''
}
}
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
} else {
const params = {
...this.ruleForm,
sex: this.ruleForm.sex === '女' ? '0' : '1'
}
editEmployee(params).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('员工信息修改成功!')
this.goBack()
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
}
} else {
console.log('error submit!!')
return false
}
})
}
不难看出,添加员工是使用的post请求,而且没有参数
// 新增---添加员工
function addEmployee (params) {
return $axios({
url: '/employee',
method: 'post',
data: { ...params }
})
}
{% endtabs %}
那么前端代码我们就简单了解了一下
我们主要做第二步和第三步
先测试一下是否能成功接收到员工信息,用日志输出看一下
@PostMapping
public Result save(@RequestBody Employee employee){
log.info("新增的员工信息:{}",employee.toString());
return null;
}
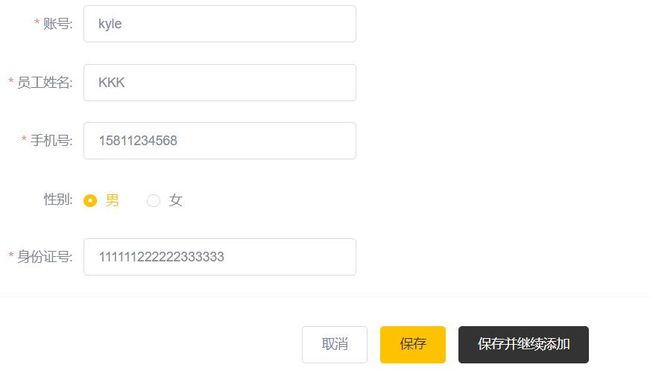
: 新增的员工信息:Employee(id=null, username=kyle, name=KKK, password=null, phone=15811234568, sex=1, idNumber=111111222222333333, status=null, createTime=null, updateTime=null, createUser=null, updateUser=null)
但此时的表单中只有部分数据,id,password,status,createTime等都还没有指定。
那么我们现在来逐一分析这几项该如何设置
id这个就用自动生成的就好了(雪花算法/自动递增)password当你注册某些教育网站的时候,一般都会给你默认指定一个密码(身份证后六位,123456等),所以我们这里的解决策略就直接指定一个123456了,但是这个密码不能直接在数据库中设为默认值,因为数据库设置的默认值无法加密status设定员工的状态,1表示启用,0表示禁用,这个就可以直接用默认值了,不需要加密,默认给个1即可createTime创建时间,这个就指定当前时间就好了updateTime作用同上createUser这个是创建人的ID,我们首先需要一个管理员账号登录到后台管理界面,然后才能添加员工信息,所以我们也需要对这个员工信息的创建人,进行设置,避免出现莫名的员工账号,依靠这个可以溯源updateUser作用同上
具体实现
综上所述,我们只需要设置密码,创建时间和更新时间,创建人ID和修改人ID
从前端代码来看,我们需要发送Post请求,且不需要参数
@PostMapping
public Result save(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody Employee employee) {
log.info("新增的员工信息:{}", employee.toString());
//设置默认密码为123456,并采用MD5加密
employee.setPassword(DigestUtils.md5DigestAsHex("123456".getBytes()));
//设置createTime和updateTime
employee.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
employee.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
//根据session来获取创建人的id
Long empId = (Long) request.getSession().getAttribute("employee");
//并设置
employee.setCreateUser(empId);
employee.setUpdateUser(empId);
//存入数据库
employeeService.save(employee);
return Result.success("添加员工成功");
}
那么至此添加员工的功能就开发完毕了,启动服务器,测试一下添加员工,添加完毕后,如果没有问题,会显示添加员工成功,之后去数据库查看,数据库中也有对应的数据,且密码也经过了加密,createTime和createUser等数据也都有
{% note info no-icon %}
值得注意的一点是,username不能重复,因为在建表的时候设定了unique,只能存在唯一的username,如果存入相同的username则会报错
控制台报错java.sql.SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException: Duplicate entry 'Kyle' for key 'employee.idx_username'
{% endnote %}
但是这个报错目前也不太人性化,咱也不知道具体为啥添加失败了,所以我们还得继续完善一下,那么具体该怎么完善呢?我们在之前使用过统一异常处理,如果你没啥印象了,可以看看这篇文章的第三小节
{% link SSM整合, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/10/SSMIntegration/, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
完善全局异常处理器并测试
在com.blog.common包下创建一个全局异常处理类GlobalExceptionHandler,并添加exceptionHandler方法用来捕获异常,并返回结果
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException.class)
public Result exceptionHandler(SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException exception) {
log.error(exception.getMessage());
return Result.error("未知错误");
}
}
先用日志输出一下看看能不能正常运行,这也是代码开发的一个好习惯
启动服务器,新增员工测试,输入数据库中已存在的username,这次会报错未知错误(如果你还没报未知错误,建议先调试好再往下进行)
控制台日志输出的错误信息为Duplicate entry 'Kyle' for key 'employee.idx_username'
然后我们再来开发具体的异常处理逻辑
我们希望给出的错误信息为该用户名已存在,所以我们就需要对错误信息来进行判断,如果错误信息中包含Duplicate entry,则说明有条目是重复的,在本案例中,只可能是username重复了,所以我们在用split()方法来对错误信息切片,取出重复的username,采用字符串拼接的方式,告知该用户已经存在了
@Slf4j
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException.class)
public Result exceptionHandler(SQLIntegrityConstraintViolationException exception) {
log.error(exception.getMessage());
//如果包含Duplicate entry,则说明有条目重复
if (exception.getMessage().contains("Duplicate entry")) {
//对字符串切片
String[] split = exception.getMessage().split(" ");
//字符串格式是固定的,所以这个位置必然是username
String username = split[2];
//拼串作为错误信息返回
return Result.error("用户名" + username + "已存在");
}
//如果是别的错误那我也没招儿了
return Result.error("未知错误");
}
}
接下来重启服务器,测试添加功能,输入已经存在的username,输出的错误信息符合我们的预期

员工信息分页查询
在开发代码之前,需要梳理一下整个程序的执行过程:
- 页面发送ajax请求,将分页查询参数(page、pageSize、name)提交到服务
- 服务端Controller接收页面提交的数据并调用Service查询数据
- Service调用Mapper操作数据库,查询分页数据
- Controller将查询到的分页数据响应给页面
- 页面接收到分页数据并通过ElementUI的Table组件展示到页面上
关于分页功能的实现,我们在之前的学习中也做过了,下面文章连接中的第七小节就是分页查询
{% link JavaWeb–综合案例, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/08/24/JavaWeb10, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
但是我们现在可以用MyBatisPlus来简化分页查询的代码实现,对应的官方文档链接:https://baomidou.com/pages/97710a/#paginationinnerinterceptor
关于插件的使用的官方文档链接:https://baomidou.com/pages/2976a3/#spring-boot ,暂时只需要看在SpringBoot中是如何配置的,剩下的可以等遇到需求的时候再来看
配置MyBatisPlus分页插件
新建com.blog.config包,并在其中新建MybatisPlusConfig类
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
mybatisPlusInterceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor());
return mybatisPlusInterceptor;
}
}
前端代码分析
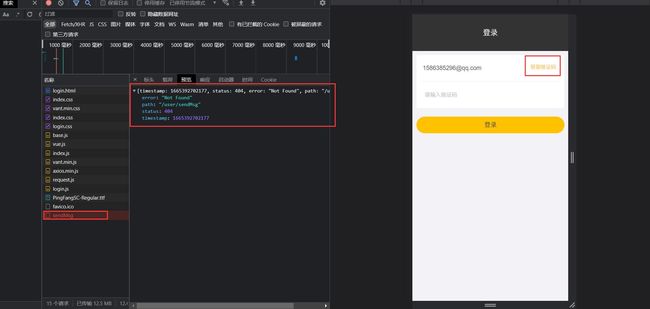
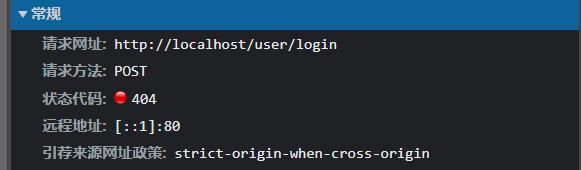
我们先来访问页面,打开开发者工具,点击员工管理,监测一下Network请求,会看到这么个东西
请求网址: http://localhost/employee/page?page=1&pageSize=10
请求方法: GET
使用GET发送的请求,请求参数在URL中
在搜索框中输入123,进行查询,发现name也出现在URL中了
请求网址: http://localhost/employee/page?page=1&pageSize=10&name=123
请求方法: GET
那现在我们来具体看一下前端的代码
{% tabs MP提供的Page类 %}
关于数据显示的功能,就是由这部分代码完成的
这个第9行和第10行的tableData和counts我们貌似没有提供,但是在之前的JavaWeb项目中,我们是自己写了一个PageBean来封装数据,但现在我们可以用MP给我们提供好的Page类来简化开发
async init () {
const params = {
page: this.page,
pageSize: this.pageSize,
name: this.input ? this.input : undefined
}
await getMemberList(params).then(res => {
if (String(res.code) === '1') {
this.tableData = res.data.records || []
this.counts = res.data.total
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
}S
这里的rows对应tableData,totalCount对应counts
//分页查询的JavaBean
public class PageBean<T> {
// 总记录数
private int totalCount;
// 当前页数据
private List<T> rows;
public int getTotalCount() {
return totalCount;
}
public void setTotalCount(int totalCount) {
this.totalCount = totalCount;
}
public List<T> getRows() {
return rows;
}
public void setRows(List<T> rows) {
this.rows = rows;
}
}
发送的是GET请求,请求路径为/employee/page,那么请求参数是从哪儿来的呢?继续往后看
function getMemberList (params) {
return $axios({
url: '/employee/page',
method: 'get',
params
})
}
前端代码配置了一个request拦截器,拦截get请求,并将请求参数使用拼串的方式拼接到URL上
// request拦截器
service.interceptors.request.use(config => {
// 是否需要设置 token
// const isToken = (config.headers || {}).isToken === false
// if (getToken() && !isToken) {
// config.headers['Authorization'] = 'Bearer ' + getToken() // 让每个请求携带自定义token 请根据实际情况自行修改
// }
// get请求映射params参数
if (config.method === 'get' && config.params) {
let url = config.url + '?';
for (const propName of Object.keys(config.params)) {
const value = config.params[propName];
var part = encodeURIComponent(propName) + "=";
if (value !== null && typeof(value) !== "undefined") {
if (typeof value === 'object') {
for (const key of Object.keys(value)) {
let params = propName + '[' + key + ']';
var subPart = encodeURIComponent(params) + "=";
url += subPart + encodeURIComponent(value[key]) + "&";
}
} else {
url += part + encodeURIComponent(value) + "&";
}
}
}
url = url.slice(0, -1);
config.params = {};
config.url = url;
}
return config
}, error => {
console.log(error)
Promise.reject(error)
})
{% endtabs %}
编写具体的业务逻辑
我们先来用日志输出一下,看看能不能正常接收到数据
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result page(int page, int pageSize, String name) {
log.info("page={},pageSize={},name={}", page, pageSize, name);
return null;
}
重新启动服务器,在搜索框输入123并搜索,查看日志输出,符合我们的预期
: page=1,pageSize=10,name=123
一切正常之后,我们继续完善业务逻辑
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result page(int page, int pageSize, String name) {
log.info("page={},pageSize={},name={}", page, pageSize, name);
//构造分页构造器
Page pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//构造条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加过滤条件(当我们没有输入name时,就相当于查询所有了)
wrapper.like(!(name == null || "".equals(name)), Employee::getName, name);
//并对查询的结果进行降序排序,根据更新时间
wrapper.orderByDesc(Employee::getUpdateTime);
//执行查询
employeeService.page(pageInfo, wrapper);
return Result.success(pageInfo);
}
重新启动服务器,测试员工信息分页查询功能,得到如下页面,当我们在搜索框输入K来进行查询,只会查询到Kyle这一条数据

补充说明
- 为什么后端传给页面的status数据为Integer类型,到页面展示效果的时候显示的是已禁用或者正常?
- 看一下源码就知道了
三目运算符+插值表达式
{{ String(scope.row.status) === '0' ? '已禁用' : '正常' }} - 看一下源码就知道了
启用/禁用员工账号
需求分析
- 在员工管理列表页面,可以对某个员工账号进行启用或者禁用操作。账号禁用的员工不能登录系统,启用后的员工可以正常登录。
- 需要注意,只有管理员(admin用户)可以对其他普通用户进行启用、禁用操作,所以普通用户登录系统后启用、禁用按钮不显示。
- 管理员admin登录系统可以对所有员工账号进行启用、禁用操作。
- 如果某个员工账号状态为正常,则按钮显示为“禁用”,如果员工账号状态为已禁用,则按钮显示为“启用”
动态按钮显示分析
怎么才能做到:只有当登录的是管理员账号时,才能看到启用/禁用按钮呢?
- 当我们加载完页面的时候,获取一下当前登录账号的用户名,也就是username
created() {
this.init()
this.user = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('userInfo')).username
}
- 随后判断一下这个用户名是不是
admin,如果是的话就显示启用/禁用,否则不显示
那么我们现在就来button里设置一下,使用v-if来判断
{{ scope.row.status == '1' ? '禁用' : '启用' }}
Ajax请求发送过程
- 页面发送ajax请求,将参数(id、status)提交到服务端
- 服务端Controller接收页面提交的数据并调用Service更新数据
- Service调用Mapper操作数据库
- 前端代码分析
{% tabs 禁用/启用前端代码分析 %}
从禁用/启用的按钮中,我们可以看到是绑定了一个名为statusHandle(scope.row)函数
<el-button
type="text"
size="small"
class="delBut non"
@click="statusHandle(scope.row)"
v-if="user === 'admin'"
>
{{ scope.row.status == '1' ? '禁用' : '启用' }}
el-button>
从代码中我们可以看到,此方法先获取了当前行的id值与status
随后弹出提示窗口,点击确定之后,会使用enableOrDisableEmployee调用PUT请求
对当前状态进行取反操作
'status': !this.status ? 1 : 0
如果this.status为1,则status为0
如果this.status为0,则status为1
这样我们就能切换禁用/启用状态了
最后根据返回的状态码来确定是否更改成功
//状态修改
statusHandle (row) {
this.id = row.id
this.status = row.status
this.$confirm('确认调整该账号的状态?', '提示', {
'confirmButtonText': '确定',
'cancelButtonText': '取消',
'type': 'warning'
}).then(() => {
enableOrDisableEmployee({ 'id': this.id, 'status': !this.status ? 1 : 0 }).then(res => {
console.log('enableOrDisableEmployee',res)
if (String(res.code) === '1') {
this.$message.success('账号状态更改成功!')
this.handleQuery()
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
})
}
可以看出这个修改状态的接口是使用的PUT请求,路径为/employee
// 修改---启用禁用接口
function enableOrDisableEmployee (params) {
return $axios({
url: '/employee',
method: 'put',
data: { ...params }
})
}
{% endtabs %}
- 后端代码分析
启用、禁用员工账号,本质上就是一个更新操作,也就是对status状态字段进行操作在Controller中创建update方法,此方法是一个通用的修改员工信息的方法
只不过现在我们的update只需要修改status,而后面我们还有修改员工其他信息的业务,根据传进来的employee
@PutMapping
public Result update(@RequestBody Employee employee) {
log.info(employee.toString());
return null;
}
按照惯例,我们先启动一下服务器,看看是否能接收到employee对象数据
点击禁用按钮,日志输出如下
: Employee(id=1575840690817011700, username=null, name=null, password=null, phone=null, sex=null, idNumber=null, status=0, createTime=null, updateTime=null, createUser=null, updateUser=null)
-
id和status均有值,符合我们的预期,那我们继续往下进行
-
完善update方法的代码逻辑
状态修改我们已经在前面完成了,这里来编写一下更新时间和更新用户
依旧是通过我们之前存的session来获取当前user的id
@PutMapping
public Result update(@RequestBody Employee employee, HttpServletRequest request) {
log.info(employee.toString());
Long id = (Long) request.getSession().getAttribute("employee");
employee.setUpdateUser(id);
employee.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
employeeService.updateById(employee);
return Result.success("员工信息修改成功");
}
查看数据库,我们发现status并没有被修改
通过查看日志,我们发现更新操作并没有完成,这是怎么回事呢?
==> Preparing: UPDATE employee SET status=?, update_time=?, update_user=? WHERE id=?
> Parameters: 0(Integer), 2022-10-04T09:37:21.459(LocalDateTime), 1(Long), 1575840690817011700(Long)
< Updates: 0
- 仔细观察这里的id值为
1575840690817011700,而实际的id值为1575840690817011713 - 问题的原因:
- JS对Long型数据进行处理时丢失精度,导致提交的id和数据库中的id不一致。
- 如何解决这个问题?
- 我们可以在服务端给页面响应json数据时进行处理,将Long型数据统一转为String字符串
配置状态转换器
配置对象映射器JacksonObjectMapper,继承ObjectMapper
直接Copy这份代码也行
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.module.SimpleModule;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.ToStringSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateTimeDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalTimeDeserializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateTimeSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalTimeSerializer;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import static com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES;
/**
* 对象映射器:基于jackson将Java对象转为json,或者将json转为Java对象
* 将JSON解析为Java对象的过程称为 [从JSON反序列化Java对象]
* 从Java对象生成JSON的过程称为 [序列化Java对象到JSON]
*/
public class JacksonObjectMapper extends ObjectMapper {
public static final String DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd";
public static final String DEFAULT_DATE_TIME_FORMAT = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
public static final String DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT = "HH:mm:ss";
public JacksonObjectMapper() {
super();
//收到未知属性时不报异常
this.configure(FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
//反序列化时,属性不存在的兼容处理
this.getDeserializationConfig().withoutFeatures(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES);
SimpleModule simpleModule = new SimpleModule()
.addDeserializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_TIME_FORMAT)))
.addDeserializer(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT)))
.addDeserializer(LocalTime.class, new LocalTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT)))
.addSerializer(BigInteger.class, ToStringSerializer.instance)
.addSerializer(Long.class, ToStringSerializer.instance)
.addSerializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_TIME_FORMAT)))
.addSerializer(LocalDate.class, new LocalDateSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_DATE_FORMAT)))
.addSerializer(LocalTime.class, new LocalTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(DEFAULT_TIME_FORMAT)));
//注册功能模块 例如,可以添加自定义序列化器和反序列化器
this.registerModule(simpleModule);
}
}
扩展Mvc框架的消息转换器
@Configuration
@Slf4j
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/backend/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/backend/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/front/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/front/");
}
@Override
protected void extendMessageConverters(List> converters) {
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter messageConverter = new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter();
//设置对象转化器,底层使用jackson将java对象转为json
messageConverter.setObjectMapper(new JacksonObjectMapper());
//将上面的消息转换器对象追加到mvc框架的转换器集合当中(index设置为0,表示设置在第一个位置,避免被其它转换器接收,从而达不到想要的功能)
converters.add(0, messageConverter);
}
}
再次测试
启动服务器,尝试禁用按钮
数据库中的status字段数据发生了改变,且页面上也显示已禁用,再次点击启用,也能正常操作

编辑员工信息
流程分析
在开发代码之前,我们先来梳理一下整个操作流程与对应程序的执行顺序
- 点击编辑按钮时,页面将跳转到
add.html,并在url中携带参数员工id - 在
add.html页面中获取url中的参数员工id - 发送
ajax请求,请求服务端,同时提交员工id参数 - 服务端接受请求,并根据
员工id查询员工信息,并将员工信息以json形式响应给页面 - 页面接收服务端响应的
json数据,并通过Vue的双向绑定进行员工信息回显 - 点击保存按钮,发送ajax请求,将页面中的员工信息以json形式提交给服务端
- 服务端接受员工信息,并进行处理,完成后给页面响应
- 页面接收到服务端响应信息后进行相应处理
具体实现
- 点击编辑按钮时,页面将跳转到
add.html,并在url中携带参数员工id
编辑按钮绑定的点击事件为addMemberHandle(scope.row.id)
<el-button
type="text"
size="small"
class="blueBug"
@click="addMemberHandle(scope.row.id)"
:class="{notAdmin:user !== 'admin'}"
>
编辑
el-button>
- 在
add.html页面中获取url中的参数员工id
addMemberHandle (st) {
if (st === 'add'){
window.parent.menuHandle({
id: '2',
url: '/backend/page/member/add.html',
name: '添加员工'
},true)
} else {
window.parent.menuHandle({
id: '2',
url: '/backend/page/member/add.html?id='+st,
name: '修改员工'
},true)
}
}
- 发送
ajax请求,请求服务端,同时提交员工id参数
{% tabs 修改员工信息第三步 %}
add.html加载完毕之后,调用钩子函数,主要看其中requestUrlParam函数
created() {
this.id = requestUrlParam('id')
this.actionType = this.id ? 'edit' : 'add'
if (this.id) {
this.init()
}
}
//获取url地址上面的参数
function requestUrlParam(argname){
//获取本次请求id
var url = location.href
//按照从?后面开始以&进行切片,这样就能获取到id=1577442478456389634,如果有其他参数,也会一并获取,根据&切片的
var arrStr = url.substring(url.indexOf("?")+1).split("&")
for(var i =0;i<arrStr.length;i++)
{
var loc = arrStr[i].indexOf(argname+"=")
if(loc!=-1){
return arrStr[i].replace(argname+"=","").replace("?","")
}
}
return ""
}
{% endtabs %}
- 服务端接受请求,并根据
员工id查询员工信息,并将员工信息以json形式响应给页面
{% tabs 修改员工信息第四步 %}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Result getById(@PathVariable Long id){
log.info("根据id查询员工信息..");
Employee employee = employeeService.getById(id);
return Result.success(employee);
}
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Result getById(@PathVariable Long id) {
log.info("根据id查询员工信息..");
Employee employee = employeeService.getById(id);
if (employee != null) {
return Result.success(employee);
}
return Result.error("未查询到该员工信息");
}
{% endtabs %}
5. 页面接收服务端响应的json数据,并通过Vue的双向绑定进行员工信息回显
在created钩子函数中还调用了init函数
该函数接收到服务端响应的json数据之后,先判断一下状态码,如果是1,则说明是操作成功
随后将获取到的数据赋给表单,从而达到回显数据的效果
async init () {
queryEmployeeById(this.id).then(res => {
console.log(res)
if (String(res.code) === '1') {
console.log(res.data)
this.ruleForm = res.data
this.ruleForm.sex = res.data.sex === '0' ? '女' : '男'
// this.ruleForm.password = ''
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
})
}
- 点击保存按钮,发送ajax请求,将页面中的员工信息以json形式提交给服务端
{% tabs 修改员工信息第六步 %}
保存
从代码中我们不难看出,添加和修改的保存按钮,都是用的同一个表单提交事件
submitForm (formName, st) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
if (this.actionType === 'add') {
const params = {
...this.ruleForm,
sex: this.ruleForm.sex === '女' ? '0' : '1'
}
addEmployee(params).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('员工添加成功!')
if (!st) {
this.goBack()
} else {
this.ruleForm = {
username: '',
'name': '',
'phone': '',
// 'password': '',
// 'rePassword': '',/
'sex': '男',
'idNumber': ''
}
}
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
} else {
const params = {
...this.ruleForm,
sex: this.ruleForm.sex === '女' ? '0' : '1'
}
editEmployee(params).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('员工信息修改成功!')
this.goBack()
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
}
} else {
console.log('error submit!!')
return false
}
})
}
其中修改员工信息使用的PUT请求,将数据以json形式提交给服务端
// 修改---添加员工
function editEmployee (params) {
return $axios({
url: '/employee',
method: 'put',
data: { ...params }
})
}
{% endtabs %}
7. 服务端接受员工信息,并进行处理,完成后给页面响应
由于修改员工信息也是发送的PUT请求,与之前启用/禁用员工账号是一致的,而且前面我们已经写过了PUT请求的Controller层
所以当我们点击保存按钮时,调用submitForm函数,而在submitForm函数中我们又调用了editEmployee函数,发送PUT请求,实现修改功能
@PutMapping
public Result update(@RequestBody Employee employee, HttpServletRequest request) {
log.info(employee.toString());
Long id = (Long) request.getSession().getAttribute("employee");
employee.setUpdateUser(id);
employee.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
employeeService.updateById(employee);
return Result.success("员工信息修改成功");
}
- 页面接收到服务端响应信息后进行相应处理
员工信息修改成功之后,调用了goBack函数,跳转至员工管理页面
goBack(){
window.parent.menuHandle({
id: '2',
url: '/backend/page/member/list.html',
name: '员工管理'
},false)
}
那么至此,编辑员工信息的功能就完成了
公共字段自动填充
问题分析
- 前面我们已经完成了对员工数据的添加与修改,在添加/修改员工数据的时候,都需要指定一下创建人、创建时间、修改人、修改时间等字段,而这些字段又属于公共字段,不仅员工表有这些字段,在菜品表、分类表等其他表中,也拥有这些字段。
- 那我们有没有办法让这些字段在一个地方统一管理呢?这样可以简化我们的开发
- 答案就是使用
MybatisPlus给我们提供的公共字段自动填充功能
- 答案就是使用
代码实现
- 实现步骤
- 在实体类的属性上方加入
@TableFiled注解,指定自动填充的策略
{% tabs 公共字段自动填充代码实现01 %}
这是个枚举类@Data public class Employee implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Long id; private String username; private String name; private String password; private String phone; private String sex; private String idNumber;//身份证号码 private Integer status; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) private LocalDateTime createTime; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE) private LocalDateTime updateTime; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT) private Long createUser; @TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE) private Long updateUser; }
DEFAULT为默认值,表示不填充
INSERT表示插入时填充
UPDATE表示修改时填充
INSERT_UPDATE表示插入和修改时填充
{% endtabs %}public enum FieldFill { DEFAULT, INSERT, UPDATE, INSERT_UPDATE; private FieldFill() { } }
2. 按照框架要求编写元数据对象处理器,在此类中统一对公共字段赋值,此类需要实现MetaObjectHandler接口
实现接口之后,重写两个方法,一个是插入时填充,一个是修改时填充
关于字段填充方式,使用metaObject的setValue来实现
关于id的获取,我们之前是存到session里的,但在MyMetaObjectHandler类中不能获得HttpSession对象,所以我们需要用其他方式来获取登录用户Id@Component @Slf4j public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler { @Override public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) { log.info("公共字段自动填充(insert)..."); log.info(metaObject.toString()); metaObject.setValue("createTime", LocalDateTime.now()); metaObject.setValue("updateTime", LocalDateTime.now()); } @Override public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) { log.info("公共字段自动填充(update)..."); log.info(metaObject.toString()); metaObject.setValue("updateTime", LocalDateTime.now()); } } - 在实体类的属性上方加入
功能完善
-
现在存在一个问题,如何获取当前登录用户的id值
- 我们可以使用
ThreadLocal来解决这个问题
- 我们可以使用
-
在学习ThreadLocal之前,我们需要先确认一个事情,就是客户端发送的每次http请求,对应的在服务端都会分配一个新的线程来处理,在处理过程中涉及到下面类中的方法都属于相同的一个线程:
LocalCheekFilter中的doFilter方法EmployeeController中的update方法MyMetaObjectHandler中的updateFill方法
现在我们在这三个方法中添加日志输出测试
doFilter
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
//强转
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
//1.获取本次请求的URI
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.info("拦截到请求:{}", requestURI);
//定义不需要处理的请求
String[] urls = new String[]{
"/employee/login",
"/employee/logout",
"/backend/**",
"/front/**"
};
//2.判断本次请求是否需要处理
boolean check = check(urls, requestURI);
//3.如果不需要处理,则直接放行
if (check) {
log.info("本次请求:{},不需要处理", requestURI);
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
//4.判断登录状态,如果已登录,则直接放行
if (request.getSession().getAttribute("employee") != null) {
log.info("用户已登录,id为{}", request.getSession().getAttribute("employee"));
//在这里获取一下线程id
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
log.info("doFilter的线程id为:{}", id);
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
//5.如果未登录则返回未登录结果,通过输出流方式向客户端页面响应数据
log.info("用户未登录");
log.info("用户id{}", request.getSession().getAttribute("employee"));
response.getWriter().write(JSON.toJSONString(Result.error("NOTLOGIN")));
}
update
@PutMapping
public Result<String> update(@RequestBody Employee employee, HttpServletRequest request) {
log.info(employee.toString());
//获取线程id
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
log.info("update的线程id为:{}", id);
employeeService.updateById(employee);
return Result.success("员工信息修改成功");
}
updateFill
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("公共字段自动填充(update)...");
log.info(metaObject.toString());
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
log.info("updateFill的线程id为:{}", id);
metaObject.setValue("createTime", LocalDateTime.now());
metaObject.setValue("updateTime", LocalDateTime.now());
metaObject.setValue("updateUser", new Long(1));
metaObject.setValue("createUser", new Long(1));
}
重新启动服务器,登录页面并编辑员工信息(什么都不需要动),随后点击保存,随后查看日志输出信息
com.blog.filter.LoginCheckFilter : doFilter的线程id为:34
com.blog.controller.EmployeeController : update的线程id为:34
com.blog.common.MyMetaObjectHandler : updateFill的线程id为:34
发现这三者确实是在同一个线程中
那么什么是ThreadLocal?
- ThreadLocal并不是一个Thread,而是Thread的局部变量
- 当使用ThreadLocal维护变量时,ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本
- 所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本
- ThreadLocal为每个线程提供单独一份存储空间,具有线程隔离的效果,只有在线程内才能获取到对应的值,线程外则不能访问。
ThreadLocal常用方法:
public void set(T value)设置当前线程的线程局部变量的值public T get()返回当前线程所对应的线程局部变量的值
那么我们如何用ThreadLocal来解决我们上述的问题呢?
- 我们可以在
LoginCheckFilter的doFilter方法中获取当前登录用户id,并调用ThreadLocal的set方法来设置当前线程的线程局部变量的值(用户id),然后在MyMetaObjectHandler的updateFill方法中调用ThreadLocal的get方法来获得当前线程所对应的线程局部变量的值(用户id)。
具体实现
- 在com.blog.common包下新建BaseContext类
- 作用:基于ThreadLocal的封装工具类,用于保护和获取当前用户id
public class BaseContext {
private static ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
public static void setCurrentId(Long id) {
threadLocal.set(id);
}
public static Long getCurrentId() {
return threadLocal.get();
}
}
- 随后在LoginCheckFilter类中添加代码
使用request.getSession来获取当前登录用户的id值
//4.判断登录状态,如果已登录,则直接放行
if (request.getSession().getAttribute("employee") != null) {
log.info("用户已登录,id为{}", request.getSession().getAttribute("employee"));
//在这里获取一下线程id
long id = Thread.currentThread().getId();
log.info("doFilter的线程id为:{}", id);
//根据session来获取之前我们存的id值
Long empId = (Long) request.getSession().getAttribute("employee");
//使用BaseContext封装id
BaseContext.setCurrentId(empId);
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
- 在MyMetaObjectHandler类中,添加设置id的代码
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyMetaObjectHandler implements MetaObjectHandler {
@Override
public void insertFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("公共字段填充(create)...");
metaObject.setValue("createTime", LocalDateTime.now());
metaObject.setValue("updateTime", LocalDateTime.now());
//设置创建人id
metaObject.setValue("createUser", BaseContext.getCurrentId());
metaObject.setValue("updateUser", BaseContext.getCurrentId());
}
@Override
public void updateFill(MetaObject metaObject) {
log.info("公共字段填充(insert)...");
metaObject.setValue("updateTime", LocalDateTime.now());
//设置更新人id
metaObject.setValue("updateUser", BaseContext.getCurrentId());
}
}
- 重新启动服务器,并登录一个非管理员账户,然后进行添加用户操作,观察数据库中的
updateUser是否符合预期
例如我这里登录的账号是Kyle,添加了Tony,Tony的create_user的id是Kyle的
| id | name | username | password | phone | sex | id_number | status | create_time | update_time | create_user | update_user |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1575840690817011713 | KKK | Kyle | e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e | 15811233075 | 1 | 111222333444555666 | 1 | 2022-10-05 17:02:53 | 2022-10-05 17:02:53 | 1 | 1 |
| 1577590825519423490 | 史塔克 | Tony | e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e | 15732165478 | 1 | 111333222444666555 | 1 | 2022-10-05 17:25:38 | 2022-10-05 17:25:38 | 1575840690817011713 | 1575840690817011713 |
- 那么至此,公共字段填充功能,我们就完成了
新增菜品分类
需求分析
- 后台系统中可以管理分类信息,分类包括两种类型,分别是菜品分类和套餐分类
- 当我们在后台系统中添加菜品时,需要选择一个菜品分类
- 当我们在后台系统中天啊及一个套餐时,需要选择一个套餐分类
- 在移动端也会按照菜品分类和套餐分类来战士对应的菜品和套餐
可以在后台系统的分类管理页面分别添加菜品分类和套餐分类,如下
数据模型
简单浏览一下category表中的数据
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| type | int | (NULL) | YES | 类型 1 菜品分类 2 套餐分类 | ||
| name | varchar(64) | utf8_bin | NO | UNI | (NULL) | 分类名称 |
| sort | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 顺序 | |
| create_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建时间 | |
| update_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 更新时间 | |
| create_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建人 | |
| update_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 修改人 |
id是主键,name分类名称是unique唯一的,type为1表示菜品分类,type为2表示套餐分类
准备工作
在开发业务之前,先将需要用到的类和接口的基本结构先创建好
- 实体类Category,对应上表来创建
菜品分类也有createUser和createTime等字段,也可以用上面的公共字段自动填充
@Data
public class Category implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//类型 1 菜品分类 2 套餐分类
private Integer type;
//分类名称
private String name;
//顺序
private Integer sort;
//创建时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private LocalDateTime createTime;
//更新时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//创建人
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
//修改人
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
}
- Mapper接口CategoryMapper
跟之前的EmployeeMapper没有本质上的区别
@Mapper
public interface CategoryMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
- 业务层接口CategoryService
public interface CategoryService extends IService {
}
- 业务层实现类CatrgoryServiceImpl
@Service
public class CategoryServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements CategoryService {
}
- 控制层CategoryController
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/category")
public class CategoryController {
@Autowired
private CategoryService categoryService;
}
流程分析
在编写代码之前,我们还是先来分析一下整个流程
- 页面发送ajax请求,将新增分类窗口输入的数据以json形式提交给服务端
- 服务端Controller接收页面提交的数据并调用Service将数据存储到数据库
- Service调用Mapper操作数据库,保存数据
我们先尝试监测一下前端给我们提供的是什么请求,以及会提交什么数据,打开开发者工具,监测NetWork,点击新增菜品分类表单的确定按钮
- 请求方式
请求网址: http://localhost/category
请求方法: POST
- json数据
{name: “川菜”, type: “1”, sort: “10”}
点击新增套餐分类表单的确定按钮
- 请求方式
请求网址: http://localhost/category
请求方法: POST
- json数据
{name: “好吃的套餐”, type: “2”, sort: “10”}
新增菜品分类和新增套餐分类请求的服务端地址和提交的json数据结构相同,所以服务端只需要提供一个方法统一处理即可
代码实现
服务端只需要将接收到的json数据添加到数据库中,并响应一个成功的提示信息
@PostMapping
public Result save(@RequestBody Category category) {
log.info("category:{}", category);
categoryService.save(category);
return Result.success("新增分类成功");
}
- 但通过查看前端代码,发现显示的信息在前端写死了,只要最后的状态码是成功状态码,则均显示
分类添加成功!
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('分类添加成功!')
- 如果我们想要添加菜品和添加套餐显示不同的响应结果,可以按照如下方式修改代码
{% tabs 不同相应结果651 %}
响应结果直接改为res.data,这样就能获取到后端返回的success中的内容
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success(res.data)
返回结果根据type来决定,type为1,则添加的是菜品分类,否则添加的是套餐分类
return Result.success(category.getType() == 1 ? "添加菜品分类成功!" : "添加套餐分类成功!");
{% endtabs%}
- 值得注意的一点是:当初建表的时候
name是unique唯一的,如果我们尝试存入相同的菜品名称,则会报错,提示信息大概就是有字段名重复了,跟我们前面写过的全局异常处理器要处理的操作一样,所以会帮我们处理这个异常
分类信息分页查询
与之前的员工信息分页查询类似
流程分析
按照惯例,我们还是先来分析一下流程
- 页面发送Ajax请求,将分页查询的参数(page、pageSize)提交到服务端
- 服务端Controller接受到页面提交的数据之后,调用Service进行查询
- Service调用Mapper操作数据库,查询分页数据
- Controller将查询到的分页数据响应给页面
- 页面接收分页数据,并通过ElementUI的Table组件战士到页面上
代码实现
在CategorYController类中编写page方法
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result page(int page, int pageSize) {
//分页构造器
Page pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//条件查询器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加排序条件
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Category::getSort);
//分页查询
categoryService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper);
return Result.success(pageInfo);
}
前端代码分析
其实跟之前的也大差不差,这里还是再来分析一遍吧
{% tabs 菜品分类前端代码分析 %}
页面加载完毕之后调用created钩子函数
钩子函数内又调用的是init进行初始化
created() {
this.init()
}
async init () {
await getCategoryPage({'page': this.page, 'pageSize': this.pageSize}).then(res => {
if (String(res.code) === '1') {
//将服务端查询到的数据赋给tableData,然后就能看到了
this.tableData = res.data.records
this.counts = Number(res.data.total)
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
}
发送的请求是get请求,请求参数值为this.page和this.pageSize,默认值分别为1和10
// 查询列表接口
const getCategoryPage = (params) => {
return $axios({
url: '/category/page',
method: 'get',
params
})
}
{% endtabs %}
删除分类
需求分析
- 在分类管理列表页面,可以对某个分类进行删除操作
- 需要注意的是:当分类关联了菜品或者套餐时,此分类将不允许被删除
流程分析
按照惯例,继续分析一遍流程
- 页面发送ajax请求,将参数(id)提交给服务端
- 服务端Controller接收页面提交的数据,并调用Service删除数据
- Service调用Mapper操作数据库
代码实现
在CategoryController类上添加delete方法
@DeleteMapping
private Result delete(Long id) {
log.info("将被删除的id:{}", id);
categoryService.removeById(id);
return Result.success("分类信息删除成功");
}
前端代码分析
{% tabs 删除按钮前端代码 %}
删除按钮绑定了deleteHandle函数
删除
先给一个提示信息防止误操作
然后使用deleCategory函数发送delete请求
若服务端返回的状态为success,则状态码为1,删除成功
否则删除失败
deleteHandle(id) {
this.$confirm('此操作将永久删除该文件, 是否继续?', '提示', {
'confirmButtonText': '确定',
'cancelButtonText': '取消',
'type': 'warning'
}).then(() => {
deleCategory(id).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('删除成功!')
this.handleQuery()
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
})
}
参数映射也配置好了,就是没用restFul风格
黑马给的前端资料中这里其实是ids,我们需要将它改为id,然后清除浏览器缓存在进一步测试功能
// 删除当前列的接口
const deleCategory = (id) => {
return $axios({
url: '/category',
method: 'delete',
params: {id}
})
}
{% endtabs %}
功能测试
现在我们重启服务器,删除一条分类信息试试
功能完善
当菜品分类或套餐分类关联了其他菜品或套餐时,该分类将不允许被删除
- 那么我们如何实现这个功能呢?
- 其实也很简单,我们只需要在删除的时候,拿着当前分类的id值,去对应的菜品/套餐表中进行查询,如果能查询到数据,则说明该分类关联了菜品,不允许被删除,否则则可以删除
那么明确了思路之后,我们就来写代码
- 首先我们需要根据数据表创建菜品和套餐对应的模型类
{% tabs 菜品分类删除功能完善模型类 %}
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.FieldFill;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
菜品
*/
@Data
public class Dish implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//菜品名称
private String name;
//菜品分类id
private Long categoryId;
//菜品价格
private BigDecimal price;
//商品码
private String code;
//图片
private String image;
//描述信息
private String description;
//0 停售 1 起售
private Integer status;
//顺序
private Integer sort;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
}
/**
* 套餐
*/
@Data
public class Setmeal implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//分类id
private Long categoryId;
//套餐名称
private String name;
//套餐价格
private BigDecimal price;
//状态 0:停用 1:启用
private Integer status;
//编码
private String code;
//描述信息
private String description;
//图片
private String image;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
}
{% endtabs %}
- 随后编写对应的Mapper接口
{% tabs 删除分类的模型类的Mapper接口 %}
@Mapper
public interface DishMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
@Mapper
public interface SetmealMapper extends BaseMapper<Setmeal> {
}
{% endtabs %}
- 编写对应的Service接口及Impl实现类
{% tabs 6513!@#ERGE %}
public interface SetmealService extends IService {
}
@Service
public class SetmealServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements SetmealService {
}
public interface DishService extends IService {
}
@Service
public class DishServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements DishService {
}
{% endtabs %}
- 在common包下新增
CustomException类
该类用于封装我们的自定义异常
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException{
public CustomException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
- 在我们的全局异常处理器类中,使用
exceptionHandler处理CustomerException异常
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
public Result exceptionHandler(CustomException exception) {
log.error(exception.getMessage());
return Result.error(exception.getMessage());
}
- 在CategoryService接口中自己写一个
remove方法
public interface CategoryService extends IService {
void remove(Long id);
}
- 在CategoryServiceImpl中来写具体业务逻辑
我们需要在删除数据之前,根据id值,去Dish表和Setmeal表中查询是否关联了数据
如果存在关联数据,则不能删除,并抛一个异常
如果不存在关联数据(也就是查询到的数据条数为0),正常删除即可
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CategoryServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements CategoryService {
@Autowired
DishService dishService;
@Autowired
SetmealService setmealService;
/**
* 根据id删除分类,删除之前需要进行判断
* @param id
*/
@Override
public void remove(Long id) {
LambdaQueryWrapper dishLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加dish查询条件,根据分类id进行查询
dishLambdaQueryWrapper.eq(Dish::getCategoryId, id);
//方便Debug用的
int count1 = dishService.count(dishLambdaQueryWrapper);
log.info("dish查询条件,查询到的条目数为:{}",count1);
//查看当前分类是否关联了菜品,如果已经关联,则抛出异常
if (count1 > 0){
//已关联菜品,抛出一个业务异常
throw new CustomException("当前分类下关联了菜品,不能删除");
}
LambdaQueryWrapper setmealLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加dish查询条件,根据分类id进行查询
setmealLambdaQueryWrapper.eq(Setmeal::getCategoryId,id);
int count2 = setmealService.count(setmealLambdaQueryWrapper);
//方便Debug用的
log.info("setmeal查询条件,查询到的条目数为:{}",count2);
//查看当前分类是否关联了套餐,如果已经关联,则抛出异常
if (count2 > 0){
//已关联套餐,抛出一个业务异常
throw new CustomException("当前分类下关联了套餐,不能删除");
}
//正常删除
super.removeById(id);
}
}
- 最后记得在controller中调用我们新写的remove方法
@DeleteMapping
public Result delete(Long id){
log.info("将要删除的分类id:{}",id);
categoryService.remove(id);
return Result.success("分类信息删除成功");
}
{% note warning no-icon %}
遇到的问题:
我刚刚在测试删除的时候,一直都能删除成功。我一开始以为是写的有问题,所以拿日志输出一下查询到的count是几,结果运行程序,根本找不到这条日志啊,随后恍然大悟,我的Controller层好像还没改方法,还是用的原生的removeById,也算是增强了一下自己的Debug能力吧{% psw (仔细看上图,分类就被我删的只剩俩了)%}
附上正常输出的日志
: dish查询条件,查询到的条目数为:1
- 当前分类下关联了菜品,不能删除
{% endnote %}
修改分类
需求分析
在分类管理列表页面点击修改按钮,弹出修改窗口,在修改窗口回显分类信息并进行修改,最后点击确定按钮完成修改操作

回显效果
这个回显效果完全就是由前端来完成的了,我们直接看代码
{% tabs 编辑分类数据回显分析 %}
修改按钮绑定了一个editHandle函数,并传入了当前行数据
修改
那我们再来看看这个editHandle函数做了什么
将当前行的数据赋给了classData下的name和sort属性
editHandle(dat) {
this.classData.title = '修改分类'
this.action = 'edit'
this.classData.name = dat.name
this.classData.sort = dat.sort
this.classData.id = dat.id
this.classData.dialogVisible = true
}
classData: {
'title': '添加菜品分类',
'dialogVisible': false,
'categoryId': '',
'name': '',
sort: ''
}
表单中又使用v-model实现双向绑定,这样就实现了数据回显
<el-form
class="demo-form-inline"
label-width="100px"
>
<el-form-item label="分类名称:">
<el-input
v-model="classData.name"
placeholder="请输入分类名称"
maxlength="14"
/>
el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="排序:">
<el-input v-model="classData.sort" type="number" placeholder="请输入排序" />
el-form-item>
el-form>
{% endtabs %}
代码开发
- 数据提交是采用的一个通用的
submitForm函数,由于我们是修改操作,所以直接从else开始往后看就行了
{% tabs 修改分类代码开发 %}
//数据提交
submitForm(st) {
const classData = this.classData
const valid = (classData.name === 0 ||classData.name) && (classData.sort === 0 || classData.sort)
if (this.action === 'add') {
if (valid) {
const reg = /^\d+$/
if (reg.test(classData.sort)) {
addCategory({'name': classData.name,'type':this.type, sort: classData.sort}).then(res => {
console.log(res)
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('分类添加成功!')
if (!st) {
this.classData.dialogVisible = false
} else {
this.classData.name = ''
this.classData.sort = ''
}
this.handleQuery()
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
} else {
this.$message.error('排序只能输入数字类型')
}
} else {
this.$message.error('请输入分类名称或排序')
}
} else if (valid) {
const reg = /^\d+$/
if (reg.test(this.classData.sort)) {
editCategory({'id':this.classData.id,'name': this.classData.name, sort: this.classData.sort}).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('分类修改成功!')
this.classData.dialogVisible = false
this.handleQuery()
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
} else {
this.$message.error('排序只能输入数字类型')
}
} else {
this.$message.error('请输入分类名称或排序')
}
}
修改操作是发送PUT请求
// 修改接口
const editCategory = (params) => {
return $axios({
url: '/category',
method: 'put',
data: { ...params }
})
}
{% endtabs %}
- 后端代码开发
@PutMapping
public Result update(@RequestBody Category category) {
log.info("修改分类信息为:{}", category);
categoryService.updateById(category);
return Result.success("修改分类信息成功");
}
{% note info no-icon %}
前端分析那么老半天,后端代码就五行…
{% endnote %}
文件上传与下载
文件上传简介
-
文件上传,也叫upload,是指将本地图片、视频、音频等文件上传到服务器中,可以供其他用户浏览或下载的过程
-
文件上传时,对页面的form表单有如下要求:
method="post",采用post方式提交数据enctype="multipart/form-data",采用multipart格式上传文件type="file",使用input的file控件上传
-
举例
头像:
头像:
- 目前一些前端组件库也提供了相应的上传组件,但是底层原理还是基于form表单的文件上传,这里我们就用提供好的组件就行了
我们把这段代码放在backend/demo目录下,命名为upload.html
文件上传
![]()
- 服务端要接收客户端页面上传的文件,通常都会使用Apache的两个组件:
commons-fileuploadcommons-io
- Spring框架在spring-web包中对文件上传进行了封装,大大简化了服务端代码,我们只需要在Controller的方法中声明一个MultipartFile类型的参数即可接收上传的文件,例如
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/common")
@Slf4j
public class CommonController {
@PostMapping("/upload")
public Result upload(MultipartFile file) {
log.info("获取文件:{}", file.toString());
return null;
}
}
- 启动服务器,登陆之后访问 http://localhost/backend/page/demo/upload.html ,看看日志信息会不会输出获取文件:……
com.blog.controller.CommonController : 获取文件:org.springframework.web.multipart.support.StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest$StandardMultipartFile@57ad9cc9
文件下载简介
- 文件下载,也成为了download,是指将文件从服务器传输到本地计算机的过程
- 通过浏览器进行文件下载,通常有两种表现形式
- 以附件形式下载,弹出保存对话框,将文件保存到指定磁盘目录
- 直接在浏览器中打开
- 通过浏览器进行文件下载,本质上就是服务端将文件以流的形式写回浏览器的过程
文件上传代码实现
- 在编写代码之前,我们先来设置一下拦截路径
//定义不需要处理的请求
String[] urls = new String[]{
"/employee/login",
"/employee/logout",
"/backend/**",
"/front/**",
"/common/**"
};
- 随后将我们上传的临时文件转存到指定位置
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/common")
@Slf4j
public class CommonController {
@PostMapping("/upload")
//file是个临时文件,我们在断点调试的时候可以看到,但是执行完整个方法之后就消失了
public Result upload(MultipartFile file) {
log.info("获取文件:{}", file.toString());
//方法会抛异常,我们这里用try/catch处理一下
try {
//我们将其转存为E盘下的test.jpg
file.transferTo(new File("E:\\test.jpg"));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return null;
}
}
- 那么我们现在再来试试上传一张图片,然后到E盘看看有没有,如果没有,说明你代码有问题,继续检查奥
- 文件转存的位置改为动态可配置的,通过配置文件的方式指定,我们在application.yml文件中加入以下内容
reggie:
path: E:\\reggie\\img\\
- 使用 @Value(“${reggie.path}”)读取到配置文件中的动态转存位置
- 使用uuid方式重新生成文件名,避免文件名重复造成文件覆盖
- 通过获取原文件名来截取文件后缀
- 注意事项:我们需要先判断一下文件目录是否存在,如果不存在则先创建
- 最后的返回值是将我们生成的新文件名返回给前端
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/common")
@Slf4j
public class CommonController {
@Value("${reggie.path}")
private String basepath;
@PostMapping("/upload")
//file是个临时文件,我们在断点调试的时候可以看到,但是执行完整个方法之后就消失了
public Result upload(MultipartFile file) {
log.info("获取文件:{}", file.toString());
//判断一下当前目录是否存在,不存在则创建
File dir = new File(basepath);
if (!dir.exists()) {
dir.mkdirs();
}
//获取一下传入的原文件名
String originalFilename = file.getOriginalFilename();
//我们只需要获取一下格式后缀,取子串,起始点为最后一个.
String suffix = originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));
//为了防止出现重复的文件名,我们需要使用UUID
String fileName = UUID.randomUUID() + suffix;
try {
//我们将其转存到我们的指定目录下
file.transferTo(new File(basepath + fileName));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
//将文件名返回给前端,便于后期的开发
return Result.success(fileName);
}
}
- 重启服务器,随便上传一张图片,然后去对应的目录下看看是否有上传的图片
- 如果一切顺利的话,目录不存在则会自动创建,而且上传的图片也在文件夹内,如果没有这种效果请先检查前面代码是否有误
文件下载代码实现
前端处理
- 前端页面的ElementUI的upload组件会在上传完图片后,触发img组件发送请求,服务端以流的方式(输出流)将文件写回给浏览器,在浏览器中展示图片
![]()
- 定义前端发送回显图片请求的地址
通过这个url我们可以看出,请求路径为/common/download,且发送的是GET请求
handleAvatarSuccess (response, file, fileList) {
this.imageUrl = `/common/download?name=${response.data}`
}
后端处理
- 在
CommonController类中添加download方法- 通过输入流读取文件内容
- 通过输出流将文件写回浏览器,在浏览器展示图片
- 关闭输入输出流,释放资源
{% tabs 后端处理核心/完整代码 %}
核心代码没多少,但是加上try/catch/finally,篇幅就挺大的了
@GetMapping("/download")
public void download(String name, HttpServletResponse response) {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(basePath + name);
ServletOutputStream os = response.getOutputStream();
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1)
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
fis.close();
os.close();
}
@GetMapping("/download")
public void download(String name, HttpServletResponse response) {
FileInputStream fis = null;
ServletOutputStream os = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(basePath + name);
os = response.getOutputStream();
response.setContentType("image/jpeg");
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1)
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (os != null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
{% endtabs %}
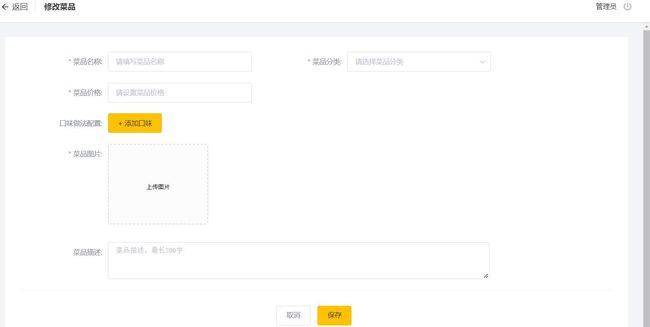
新增菜品
需求分析
- 后台系统中可以管理菜品信息,通过新增功能来添加一个新的菜品
- 在添加菜品时需要选择当前菜品所属的菜品分类,并且需要上传当前的菜品图片
- 在移动端会按照菜品分类来展示对应的菜品信息(前端的活儿,跟咱没啥太大关系)
数据模型
dish表,最后一条字段is_deleted是逻辑删除,在之前的MyBatisPlus文章中讲过,忘了的可以回顾一下
{% link MyBatisPlus, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/09/20/MyBatisPlus/, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| name | varchar(64) | utf8_bin | NO | UNI | (NULL) | 菜品名称 |
| category_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 菜品分类id | |
| price | decimal(10,2) | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 菜品价格 | |
| code | varchar(64) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 商品码 | |
| image | varchar(200) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 图片 | |
| description | varchar(400) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 描述信息 | |
| status | int | (NULL) | NO | 1 | 0 停售 1 起售 | |
| sort | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 顺序 | |
| create_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建时间 | |
| update_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 更新时间 | |
| create_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建人 | |
| update_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 修改人 | |
| is_deleted | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 是否删除 |
dish_flavor表
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| dish_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 菜品 | |
| name | varchar(64) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 口味名称 | |
| value | varchar(500) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 口味数据list | |
| create_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建时间 | |
| update_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 更新时间 | |
| create_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建人 | |
| update_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 修改人 | |
| is_deleted | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 是否删除 |
代码开发
准备工作
- 我们先来创建对应的实体类,Mapper接口,Service接口及其对应的实现类
{% tabs dishflavor的准备工作 %}
/**
* 菜品口味
*/
@Data
public class DishFlavor implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//菜品id
private Long dishId;
//口味名称
private String name;
//口味数据list
private String value;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
//是否删除
private Integer isDeleted;
}
@Mapper
public interface DishFlavorMapper extends BaseMapper<DishFlavor> {
}
public interface DishFlavorService extends IService<DishFlavor> {
}
@Service
public class DishFlavorServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<DishFlavorMapper, DishFlavor> implements DishFlavorService {
}
{% endtabs %}
- 编写Controller层
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/dish")
@Slf4j
public class DishController {
@Autowired
private DishService dishService;
@Autowired
private DishFlavorService dishFlavorService;
}
梳理交互过程
按照惯例,在开发代码之前,我们先来梳理一下整个流程
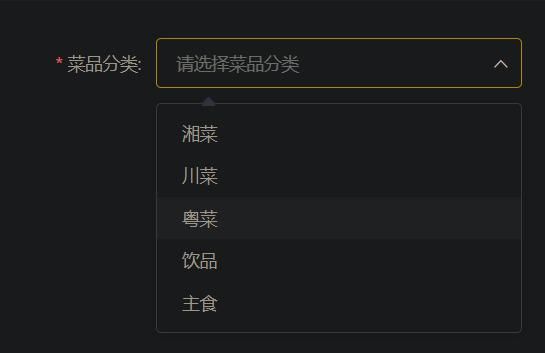
- 页面(backend/page/food/add.html)发送ajax请求,请求服务端获取菜品分类数据并展示到下拉框中
- 页面发送请求进行图片上传,请求服务端将图片保存到服务器
- 页面发送请求进行图片下载,并回显上传的图片
- 点击保存按钮,发送ajax请求,将菜品相关数据以json形式提交到服务端
所以开发新增菜品功能,其实就是在服务端编写代码去处理前端发送的这4次请求即可
查询分类数据
- 前端分析
{% tabs 查询分类数据前端分析 %}
当页面加载完成之后,调用如下几个方法
created() {
this.getDishList()
// 口味临时数据
this.getFlavorListHand()
this.id = requestUrlParam('id')
this.actionType = this.id ? 'edit' : 'add'
if (this.id) {
this.init()
}
}
根据响应状态码来判断操作是否成功,成功则将返回的数据赋给dishList,将获取到的菜品分类数据展示到下拉框中
getDishList () {
getCategoryList({ 'type': 1 }).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.dishList = res.data
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
})
}
发送get请求,路径为/category/list
// 获取菜品分类列表
const getCategoryList = (params) => {
return $axios({
url: '/category/list',
method: 'get',
params
})
}
使用v-for遍历获取到的dishList
{% endtabs %}
- 在
CategoryController类中,添加list方法
我们只需要发送get请求,将数据返回给前端即可,操作很简单
@GetMapping("/list")
public Result> list(Category category) {
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加条件,这里只需要判断是否为菜品(type为1是菜品,type为2是套餐)
queryWrapper.eq(category.getType() != null,Category::getType,category.getType());
//添加排序条件
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Category::getSort).orderByDesc(Category::getUpdateTime);
//查询数据
List list = categoryService.list(queryWrapper);
//返回数据
return Result.success(list);
}
接收与回显图片
这个功能再刚刚我们已经实现了,到现在可以直接用
提交数据到服务端
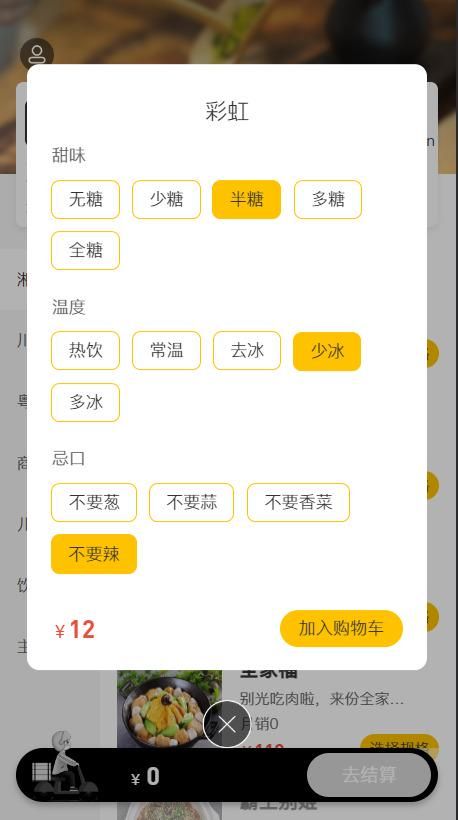
{name: "啊", price: 32100, code: "", image: "1eefc77c-12b6-4cd0-8e6e-347d8f92ae84.jpg",…}
categoryId:"1397844263642378242"
code:""
description:"好吃的彩虹"
flavors:[{name: "甜味", value: "["无糖","少糖","半糖","多糖","全糖"]", showOption: false},…]
0:{name: "甜味", value: "["无糖","少糖","半糖","多糖","全糖"]", showOption: false}
1:{name: "温度", value: "["热饮","常温","去冰","少冰","多冰"]", showOption: false}
image:"1eefc77c-12b6-4cd0-8e6e-347d8f92ae84.jpg"
name:"啊"
price:32100
status:1
{% note warning no-icon %}
- 价格在前端已被处理,在点击提交按钮后,先执行前端的submitForm方法,并将price做相应的处理(在页面中单位为元,在数据库中存储的单位为分,处理的时候将原有价格乘上了100),再通过ajax请求向后端提供相应的json数据。
submitForm(formName, st) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
let params = {...this.ruleForm}
// params.flavors = this.dishFlavors
params.status = this.ruleForm ? 1 : 0
params.price *= 100
params.categoryId = this.ruleForm.categoryId
params.flavors = this.dishFlavors.map(obj => ({ ...obj, value: JSON.stringify(obj.value) }))
delete params.dishFlavors
if(!this.imageUrl){
this.$message.error('请上传菜品图片')
return
}
if (this.actionType == 'add') {
delete params.id
addDish(params).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('菜品添加成功!')
if (!st) {
this.goBack()
} else {
this.dishFlavors = []
// this.dishFlavorsData = []
this.imageUrl = ''
this.ruleForm = {
'name': '',
'id': '',
'price': '',
'code': '',
'image': '',
'description': '',
'dishFlavors': [],
'status': true,
categoryId: ''
}
}
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
} else {
delete params.updateTime
editDish(params).then(res => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('菜品修改成功!')
this.goBack()
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
}).catch(err => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
}
} else {
return false
}
})
}
- 因为Dish实体类不满足接收flavor参数,即需要导入DishDto,用于封装页面提交的数据
- DTO,全称为
Data Transfer Object,即数据传输对象,一般用于展示层与服务层之间的数据传输。
@Data
public class DishDto extends Dish {
private List flavors = new ArrayList<>();
//后面这两条属性暂时没用,这里只需要用第一条属性
private String categoryName;
private Integer copies;
}
{% endnote %}
- 在
DishController类中添加save方法,重启服务器,断点调试一下看看是否封装好了数据
@PostMapping
public Result save(@RequestBody DishDto dishDto) {
log.info("接收到的数据为:{}",dishDto);
return null;
}

从图中我们可以看出,DishFlavor中的dishId为null
但是我们需要对DishFlavor中的dishId进行赋值
所以我们要取出dishDto的dishId,然后对每一组flavor的dishId赋值
-
这里进行一下小结,我们需要做的有以下几点
- 将菜品数据保存到
dish表 - 将菜品口味数据保存到
dish_flavor表- 但是
dish_flavor表中需要一个dishId字段值,这个字段值需要我们从dishDto中获取 - 获取方式为:取出
dishDto的dishId,对每一组flavor的dishId赋值
- 但是
- 将菜品数据保存到
-
梳理完毕之后,那么我们就在
DishFlavorService中编写一个saveWithFlavor方法
public interface DishService extends IService {
void saveWithFlavor(DishDto dishDto);
}
- 同时在
DishFlavorServiceImpl中重写方法
@Service
public class DishServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements DishService {
@Autowired
private DishFlavorService dishFlavorService;
@Override
public void saveWithFlavor(DishDto dishDto) {
//将菜品数据保存到dish表
this.save(dishDto);
//获取dishId
Long dishId = dishDto.getId();
//将获取到的dishId赋值给dishFlavor的dishId属性
List flavors = dishDto.getFlavors();
for (DishFlavor dishFlavor : flavors) {
dishFlavor.setDishId(dishId);
}
//同时将菜品口味数据保存到dish_flavor表
dishFlavorService.saveBatch(flavors);
}
}
功能测试
重启服务器,登录,测试新增菜品功能
菜品信息分页查询
需求分析
- 系统中的菜品数据很多的时候,如果在一个页面中全部展示出来会显得比较乱,不便于查看
- 所以一般的系统中都会以分页的方式来展示列表数据。
- 其中图片列和菜品分类列比较特殊
- 图片列:会用到文件的下载功能
- 菜品分类列:由于我们的菜品表只保存了category_id,所以我们需要查询category_id对应的菜品分类名称,从而回显数据
梳理交互过程
按照惯例,我们还是先来梳理一遍流程
- 页面(backend/page/food/list.html)发送ajax请求,将分页查询参数(
page、pageSize、name),提交到服务端,获取分页数据 - 页面发送请求,请求服务端进行图片下载,用于页面图片展示
那么开发菜品信息分页查询功能,其实就是在服务端编写代码去处理前端页面发送的这2次请求即可
代码开发
- 在
DishController下添加page方法,进行分页查询
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result page(int page, int pageSize, String name) {
//构造分页构造器对象
Page pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加条件
queryWrapper.like(name != null, Dish::getName, name);
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//执行分页查询
dishService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper);
return Result.success(pageInfo);
}
- 重启服务器,效果如下,但是现在没有菜品分类数据,部分图片也没有加载
- 那么为什么没有菜品分类数据呢?
- 我们传递的是一个Dish对象,dish对象没有菜品分类名称属性,但是有菜品分类id
- 那我们就可以根据这个菜品分类id,去菜品分类表中查询对应的菜品分类名称
- 所以我们之前的DishDto类中的另外一个属性就派上用场了,我们返回一个DishDto对象就有菜品分类名称数据了
@Data
public class DishDto extends Dish {
//菜品口味
private List flavors = new ArrayList<>();
//菜品分类名称
private String categoryName;
private Integer copies;
}
- 那么我们现在就可以把DishDto看做是Dish类的基础上,增加了一个categoryName属性,到时候返回DishDto
具体实现思路就是,将查询出来的dish数据,赋给dishDto,然后在根据dish数据中的category_id,去菜品分类表中查询到category_name,将其赋给dishDto
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result page(int page, int pageSize, String name) {
//构造分页构造器对象
Page pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//这个就是我们到时候返回的结果
Page dishDtoPage = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加条件
queryWrapper.like(name != null, Dish::getName, name);
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//执行分页查询
dishService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper);
//对象拷贝,这里只需要拷贝一下查询到的条目数
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pageInfo, dishDtoPage, "records");
//获取原records数据
List records = pageInfo.getRecords();
//遍历每一条records数据
List list = records.stream().map((item) -> {
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
//将数据赋给dishDto对象
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, dishDto);
//然后获取一下dish对象的category_id属性
Long categoryId = item.getCategoryId(); //分类id
//根据这个属性,获取到Category对象(这里需要用@Autowired注入一个CategoryService对象)
Category category = categoryService.getById(categoryId);
//随后获取Category对象的name属性,也就是菜品分类名称
String categoryName = category.getName();
//最后将菜品分类名称赋给dishDto对象就好了
dishDto.setCategoryName(categoryName);
//结果返回一个dishDto对象
return dishDto;
//并将dishDto对象封装成一个集合,作为我们的最终结果
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
dishDtoPage.setRecords(list);
return Result.success(dishDtoPage);
}
{% note warning no-icon %}
上面的代码中用到了Java8中新特性的stream流操作,后面我会专门写篇文章讲解的,{% del 这里先挖个坑 %}
{% endnote %}
- 填坑,见下文
{% link Java8 新特性, https://cyborg2077.github.io/2022/11/05/NewFeaturesOfJava8/, https://pic1.imgdb.cn/item/6335135c16f2c2beb100182d.jpg %}
修改菜品
梳理交互过程
按照惯例,还是先来梳理一下整个流程
- 页面发送ajax请求,请求服务器获取分类数据,用于菜品分类下拉框的数据回显(之前我们已经实现过了)
- 页面发送ajax请求,请求服务端,根据id查询当前菜品信息,用于菜品信息回显
- 页面发送请求,请求服务端进行图片下载,用于页面图片回显(之前我们已经实现过了)
- 点击保存按钮,页面发送ajax请求,将修改后的菜品相关数据以json形式提交到服务端
开发修改菜品功能,其实就是在服务端写代码去处理以上四次请求
查询菜品信息
- 菜品信息回显功能,需要我们先根据id来查询到对应的菜品信息才能回显
- 但修改表单中有一个菜品口味属性,普通的Dish类没有这个属性,所以还是要用到DishDto
- 那我们这里先编写一个
getByIdWithFlavor方法 - 菜品口味需要根据
dish_id去dish_flavor表中查询,将查询到的菜品口味数据赋给我们的DishDto对象即可
@Override
public DishDto getByIdWithFlavor(Long id) {
//先根据id查询到对应的dish对象
Dish dish = this.getById(id);
//创建一个dishDao对象
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
//拷贝对象
BeanUtils.copyProperties(dish, dishDto);
//条件构造器,对DishFlavor表查询
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//根据dish_id来查询对应的菜品口味数据
queryWrapper.eq(DishFlavor::getDishId, id);
//获取查询的结果
List flavors = dishFlavorService.list(queryWrapper);
//并将其赋给dishDto
dishDto.setFlavors(flavors);
//作为结果返回给前端
return dishDto;
}
- 在
DishController中添加get方法,实现添加在DishServicelmpl中的逻辑代码,返回查询到的数据信息
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public Result getByIdWithFlavor(@PathVariable Long id) {
DishDto dishDto = dishService.getByIdWithFlavor(id);
log.info("查询到的数据为:{}", dishDto);
return Result.success(dishDto);
}
- 然后我们去访问一下修改菜品页面,看看是否有效果,如果没效果,打个断点或者看看日志
修改菜品信息
由于Dish表中没有Flavor这个属性,所以修改的时候,我们也是需要修改两张表
{% tabs 修改菜品信息前端代码分析 %}
修改按钮绑定过的是addFoodtype方法
修改
该方法也是一个新增/修改通用的方法,修改的时候多一个id属性
// 添加
addFoodtype (st) {
if (st === 'add'){
window.parent.menuHandle({
id: '4',
url: '/backend/page/food/add.html',
name: '添加菜品'
},true)
} else {
window.parent.menuHandle({
id: '4',
url: '/backend/page/food/add.html?id='+st,
name: '修改菜品'
},true)
}
从这我们能看出请求路径与方式,所以后端代码我们需要提交PUT请求
// 修改接口
const editDish = (params) => {
return $axios({
url: '/dish',
method: 'put',
data: { ...params }
})
}
{% endtabs %}
- 前端代码就分析到这里,我们开始编写后端逻辑
{% tabs 修改菜品后端代码分析 %}
主要框架就这点东西,重点是编写updateWithFlavor方法
首先去DishService中创建updateWithFlavor方法,然后在DishServiceImpl中重写方法
@PutMapping
public Result update(@RequestBody DishDto dishDto) {
log.info("接收到的数据为:{}", dishDto);
dishService.updateWithFlavor(dishDto);
return Result.success("修改菜品成功");
}
- 根据
id修改菜品的基本信息 - 通过
dish_id,删除菜品的flavor - 获取前端提交的
flavor数据 - 为条
flavor的dishId属性赋值 - 将数据批量保存到
dish_flavor数据库
@Override
public void updateWithFlavor(DishDto dishDto) {
//更新当前菜品数据(dish表)
this.updateById(dishDto);
//下面是更新当前菜品的口味数据
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//条件是当前菜品id
queryWrapper.eq(DishFlavor::getDishId, dishDto.getId());
//将其删除掉
dishFlavorService.remove(queryWrapper);
//获取传入的新的口味数据
List flavors = dishDto.getFlavors();
//这些口味数据还是没有dish_id,所以需要赋予其dishId
flavors = flavors.stream().map((item) -> {
item.setDishId(dishDto.getId());
return item;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//再重新加入到表中
dishFlavorService.saveBatch(flavors);
}
{% endtabs %}
- 那么至此,我们的修改菜品功能就完成了,重启服务器,测试一下
{% note warning no-icon %}
注意要在DishServiceImpl上添加@Transactional注解,同时也要在主启动类上加上@EnableTransactionManagement注解
{% endnote %}
新增套餐
需求分析
- 套餐就是菜品的集合
- 后台系统中可以管理套餐信息,通过新增套餐来添加一个新的套餐
- 在添加套餐时需要选择当前套餐所属的套餐分类和包含的菜品,并且需要上传套餐对应的图片
数据模型
-
新增套餐,其实就是将新增页面录入的套餐信息插入到setmeal表中,而且还要向setmeal_dish表中插入套餐和菜品关联数据
-
所以在新增套餐时,需要对两张表进行操作
- setmeal表 --> 套餐表
- setmeal_dish表 --> 套餐菜品关系表
-
setmeal表
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| category_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 菜品分类id | |
| name | varchar(64) | utf8_bin | NO | UNI | (NULL) | 套餐名称 |
| price | decimal(10,2) | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 套餐价格 | |
| status | int | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 状态 0:停用 1:启用 | |
| code | varchar(32) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 编码 | |
| description | varchar(512) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 描述信息 | |
| image | varchar(255) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 图片 | |
| create_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建时间 | |
| update_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 更新时间 | |
| create_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建人 | |
| update_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 修改人 | |
| is_deleted | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 是否删除 |
- setmeal_dish表
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| setmeal_id | varchar(32) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 套餐id | |
| dish_id | varchar(32) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 菜品id | |
| name | varchar(32) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 菜品名称 (冗余字段) | |
| price | decimal(10,2) | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 菜品原价(冗余字段) | |
| copies | int | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 份数 | |
| sort | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 排序 | |
| create_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建时间 | |
| update_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 更新时间 | |
| create_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建人 | |
| update_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 修改人 | |
| is_deleted | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 是否删除 |
准备工作
在开发业务功能前,先将需要用到的类和接口基本结构创建好:
- 实体类SetmealDish
/**
* 套餐菜品关系
*/
@Data
public class SetmealDish implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//套餐id
private Long setmealId;
//菜品id
private Long dishId;
//菜品名称 (冗余字段)
private String name;
//菜品原价
private BigDecimal price;
//份数
private Integer copies;
//排序
private Integer sort;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private LocalDateTime createTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
//是否删除
private Integer isDeleted;
}
- DTO SetmealDto
普通的SetmealDish类肯定是不够我们用的,这里还需要加上套餐内的具体菜品和套餐分类名称
@Data
public class SetmealDto extends Setmeal {
private List setmealDishes;
private String categoryName;
}
- Mapper接口SetmealDishMapper
@Mapper
public interface SetmealDishMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
- 业务层接口SetmealDishService
public interface SetmealDishService extends IService {
}
- 业务层实现类SetmealDishservicelmpl
@Service
public class SetmealDishServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements SetmealDishService {
}
- 控制层SetmealController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/setmeal")
@Slf4j
public class SetmealController {
@Autowired
private SetmealService setmealService;
@Autowired
private SetmealDishService setmealDishService;
}
梳理交互过程
在开发代码之前,我们先来梳理一下新增套餐时前端页面与服务端的交互过程
- 页面发送ajax请求,请求服务端,获取套餐分类数据并展示到下拉框中(这个之前做过)
- 页面发送ajax请求,请求服务端,获取菜品分类数据并展示到添加菜品窗口中
- 页面发送ajax请求,请求服务端,根据菜品分类查询对应的菜品数据并展示到添加菜品窗口中
- 页面发送请求进行图片上传,请求服务端将图片保存到服务器(已完成)
- 页面发送请求进行图片下载,将上传的图片进行回显(已完成)
- 点击保存按钮,发送ajax请求,将套餐相关数据以json形式提交到服务端
开发新增套餐功能,其实就是在服务端编写代码去处理前端页面发送的这6次请求
代码开发
新增套餐页面,现在的套餐分类下拉框中已经能显示套餐分类了,这个功能在之前我们已经实现过了

@GetMapping("/list")
public Result> get(Dish dish) {
//条件查询器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//根据传进来的categoryId查询
queryWrapper.eq(dish.getCategoryId() != null, Dish::getCategoryId, dish.getCategoryId());
//只查询状态为1的菜品(启售菜品)
queryWrapper.eq(Dish::getStatus, 1);
//简单排下序,其实也没啥太大作用
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Dish::getSort).orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//获取查询到的结果作为返回值
List list = dishService.list(queryWrapper);
return Result.success(list);
}
- 前端代码分析
{% tabs 新增套餐前端代码分析 %}
<el-button type="primary" @click="submitForm('ruleForm', false)"> 保存 el-button>
表单提交也是一个通用的代码,分为新增/修改
submitForm(formName, st) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
let prams = { ...this.ruleForm }
prams.price *= 100
prams.setmealDishes = this.dishTable.map((obj) => ({
copies: obj.copies,
dishId: obj.dishId,
name: obj.name,
price: obj.price,
}))
prams.status = this.ruleForm ? 1 : 0
prams.categoryId = this.ruleForm.idType
if(prams.setmealDishes.length < 1){
this.$message.error('请选择菜品!')
return
}
if(!this.imageUrl){
this.$message.error('请上传套餐图片')
return
}
// delete prams.dishList
if (this.actionType == 'add') {
delete prams.id
addSetmeal(prams)
.then((res) => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('套餐添加成功!')
if (!st) {
this.goBack()
} else {
this.$refs.ruleForm.resetFields()
this.dishList = []
this.dishTable = []
this.ruleForm = {
name: '',
categoryId: '',
price: '',
code: '',
image: '',
description: '',
dishList: [],
status: true,
id: '',
idType: '',
}
this.imageUrl = ''
}
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
})
.catch((err) => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
} else {
delete prams.updateTime
editSetmeal(prams)
.then((res) => {
if (res.code === 1) {
this.$message.success('套餐修改成功!')
this.goBack()
} else {
this.$message.error(res.msg || '操作失败')
}
})
.catch((err) => {
this.$message.error('请求出错了:' + err)
})
}
} else {
return false
}
})
}
新增套餐的保存按钮是发送的post请求,请求路径为/setmeal
// 新增数据接口
const addSetmeal = (params) => {
return $axios({
url: '/setmeal',
method: 'post',
data: { ...params }
})
}
{% endtabs %}
- 编写save方法
我们先打个断点,看看提交的数据是啥样的
@PostMapping
public Result<String> save(@RequestBody SetmealDto setmealDto) {
log.info("套餐信息:{}", setmealDto);
return Result.success("套餐添加成功");
}

需要注意的是这个setmealId为null,我们具体的代码中,要从setmealDao中获取并赋值
- 具体业务逻辑如下
{% tabs 新增套餐具体后端业务 %}
这里依旧是需要我们自己在SetmealService中编写一个setWithDish方法,并在SetmealServiceImpl中实现
@PostMapping
public Result save(@RequestBody SetmealDto setmealDto) {
log.info("套餐信息:{}", setmealDto);
setmealService.saveWithDish(setmealDto);
return Result.success("套餐添加成功");
}
public interface SetmealService extends IService {
void saveWithDish(SetmealDto setmealDto);
}
注意这里需要注入一下SetmealDishService
@Service
public class SetmealServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<SetmealMapper, Setmeal> implements SetmealService {
@Autowired
protected SetmealDishService setmealDishService;
@Override
public void saveWithDish(SetmealDto setmealDto) {
this.save(setmealDto);
List<SetmealDish> setmealDishes = setmealDto.getSetmealDishes();
setmealDishes = setmealDishes.stream().map((item) -> {
item.setSetmealId(setmealDto.getId());
return item;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
setmealDishService.saveBatch(setmealDishes);
}
}
{% endtabs %}
- 那么至此,新增套餐的功能就实现了,重启服务器测试一下,不过现在看不到页面效果,因为还没做分页查询,所以只能暂时去数据库查看
套餐信息分页查询
需求分析
- 系统中的套餐数据很多的时候,如果在一个页面中全部展示出来会显得比较乱,不便于查看
- 一般的系统中都会以分页的方式来展示列表数据
梳理交互过程
- 页面发送ajax请求,将分页查询参数(page,pageSize,name)提交到服务端,获取分页数据
- 页面发送请求,请求服务端进行图片下载,用于页面图片展示(已完成)
前端分析
点击套餐管理,在搜索框输入1,获取请求url与请求方式
- 请求网址: http://localhost/setmeal/page?page=1&pageSize=10&name=1
- 请求方法: GET
代码开发
- SetmealController类中,添加list方法
其实跟前面的菜品信息分页查询代码几乎一模一样,这遍就当review了
{% tabs 984651EFWERR %}
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result page(int page, int pageSize, String name) {
Page pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
Page dtoPage = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like(name != null, Setmeal::getName, name);
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Setmeal::getUpdateTime);
setmealService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pageInfo, dtoPage, "records");
List records = pageInfo.getRecords();
List list = records.stream().map((item) -> {
SetmealDto setmealDto = new SetmealDto();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, setmealDto);
Long categoryId = item.getCategoryId();
Category category = categoryService.getById(categoryId);
if (category != null) {
setmealDto.setCategoryName(category.getName());
}
return setmealDto;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
dtoPage.setRecords(list);
return Result.success(dtoPage);
}
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result page(int page, int pageSize, String name) {
//构造分页构造器对象
Page pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//这个就是我们到时候返回的结果
Page dishDtoPage = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加条件
queryWrapper.like(name != null, Dish::getName, name);
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//执行分页查询
dishService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper);
//对象拷贝,这里只需要拷贝一下查询到的条目数
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pageInfo, dishDtoPage, "records");
//获取原records数据
List records = pageInfo.getRecords();
//遍历每一条records数据
List list = records.stream().map((item) -> {
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
//将数据赋给dishDto对象
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, dishDto);
//然后获取一下dish对象的category_id属性
Long categoryId = item.getCategoryId(); //分类id
//根据这个属性,获取到Category对象(这里需要用@Autowired注入一个CategoryService对象)
Category category = categoryService.getById(categoryId);
//随后获取Category对象的name属性,也就是菜品分类名称
String categoryName = category.getName();
//最后将菜品分类名称赋给dishDto对象就好了
dishDto.setCategoryName(categoryName);
//结果返回一个dishDto对象
return dishDto;
//并将dishDto对象封装成一个集合,作为我们的最终结果
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
dishDtoPage.setRecords(list);
return Result.success(dishDtoPage);
}
{% endtabs %}
删除套餐
需求分析
- 在套餐管理列表页面点击删除按钮,可以删除对应的套餐信息
- 也可以通过复选框选择多个套餐,选择批量删除一次性删除多个套餐
{% note warning no-icon %}
注意:对于在售中的套餐不能删除,需要先停售,然后才能删除
{% endnote %}
梳理交互过程
- 删除单个套餐时,页面发送ajax请求,根据套餐id删除对应套餐
- 删除多个套餐时,页面发送ajax请求,根据提交的多个套餐id删除对应套餐开发删除套餐功能
- 请求网址: http://localhost/setmeal?ids=1579044544635232258,1415580119015145474
- 请求方法: DELETE
- 删除单个套餐和批量删除这两种请求的地址和请求方式都是相同的
- 不同的则是传递的id个数,所以在服务端可以提供一个方法来统一处理。
代码开发
- 在SetmealController中添加delete方法
@DeleteMapping
public Result deleteByIds(@RequestParam List ids) {
log.info("要删除的套餐id为:{}",ids);
setmealService.removeWithDish(ids);
return Result.success("删除成功");
}
- 在
SetmealService中创建removeWithDish方法
void removeWithDish(List ids);
- 在
SetmealServiceImpl中重写方法
@Override
public void removeWithDish(List ids) {
//先判断一下能不能删,如果status为1,则套餐在售,不能删
//select * from setmeal where id in (ids) and status = 1
LambdaQueryWrapper setmealLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
setmealLambdaQueryWrapper.in(Setmeal::getId, ids);
setmealLambdaQueryWrapper.eq(Setmeal::getStatus, 1);
int count = this.count(setmealLambdaQueryWrapper);
//下面两行是我debug输出的日志,没啥用
List list = this.list(setmealLambdaQueryWrapper);
log.info("查询到的数据为:{}",list);
if (count > 0) {
throw new CustomException("套餐正在售卖中,请先停售再进行删除");
}
//如果没有在售套餐,则直接删除
this.removeByIds(ids);
//继续删除
LambdaQueryWrapper setmealDishLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
setmealDishLambdaQueryWrapper.in(SetmealDish::getSetmealId, ids);
setmealDishService.remove(setmealDishLambdaQueryWrapper);
}
- 重启服务器,并测试
{% note warning no-icon %}
由于我们这里暂时没有编写更改销售状态的代码,所以我们需要去数据库中手动修改status字段,从而正常删除
我加的那个日志输出是debug用的,因为我改完status字段忘保存了,一直删不掉…
注意需要在SetmealServiceImpl类上方增加@Transactional注解
{% endnote %}
邮件发送(替换手机验证)
其实黑马这里用的是短信业务,但咱也没那条件,所以我只能自己换成QQ邮箱验证码了,这个简单,具体操作我们也只需要开启POP3/STMP服务,获取一个16位的授权码
需求分析
-
为了方便用户登录,移动端通常都会提供通过手机验证码登录的功能(咱平替成邮箱验证码)
-
手机(邮箱)验证码登录的优点:
- 方便快捷,无需注册,直接登录
- 使用短信验证码作为登录凭证,无需记忆密码
- 安全
-
登录流程:
- 输入手机号(邮箱) > 获取验证码 > 输入验证码 > 点击登录 > 登录成功
{% note warning no-icon %}
注意:通过手机(邮箱)验证码登录,手机号是区分不同用户的标识
{% endnote %}
数据模型
这里的手机号也是varchar类型,所以我们就不用动它了,咱就用它存咱自己邮箱号就行(动手能力强的自己改一下也无所谓,大不了改出BUG再自己修)
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| name | varchar(50) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 姓名 | |
| phone | varchar(100) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 手机号 | |
| sex | varchar(2) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 性别 | |
| id_number | varchar(18) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 身份证号 | |
| avatar | varchar(500) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 头像 | |
| status | int | (NULL) | YES | 0 | 状态 0:禁用,1:正常 |
{% note warning no-icon %}
- 手机号(邮箱)是区分不同用户的标识,在用户登录的时候判断所输入的手机号(邮箱)是否存储在表中
- 如果不在表中,说明该用户为一个新的用户,将该用户自动保在user表中
{% endnote %}
准备工作
在开发业务功能之前,我们先将要用到的类和接口的基本结构都创建好
- 实体类User
/**
* 用户信息
*/
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//姓名
private String name;
//手机号
private String phone;
//性别 0 女 1 男
private String sex;
//身份证号
private String idNumber;
//头像
private String avatar;
//状态 0:禁用,1:正常
private Integer status;
}
- Mapper接口UserMapper
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
- 业务层接口UserService
public interface UserService extends IService {
}
- 业务层实现类UserServiceImpl
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements UserService {
}
- 控制层UserController
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
}
- 工具类(我们自己造自己的邮箱工具类)
- 首先导入坐标
javax.activation activation 1.1.1 javax.mail mail 1.4.7 org.apache.commons commons-email 1.4 - 然后编写一个工具类,用于发送邮件验证码
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.Properties; import javax.mail.Authenticator; import javax.mail.MessagingException; import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication; import javax.mail.Session; import javax.mail.Transport; import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress; import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage; import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage.RecipientType; public class MailUtils { public static void main(String[] args) throws MessagingException { //可以在这里直接测试方法,填自己的邮箱即可 sendTestMail("[email protected]", new MailUtils().achieveCode()); } public static void sendTestMail(String email, String code) throws MessagingException { // 创建Properties 类用于记录邮箱的一些属性 Properties props = new Properties(); // 表示SMTP发送邮件,必须进行身份验证 props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); //此处填写SMTP服务器 props.put("mail.smtp.host", "smtp.qq.com"); //端口号,QQ邮箱端口587 props.put("mail.smtp.port", "587"); // 此处填写,写信人的账号 props.put("mail.user", "[email protected]"); // 此处填写16位STMP口令 props.put("mail.password", "tnpXXXXXXXXjb"); // 构建授权信息,用于进行SMTP进行身份验证 Authenticator authenticator = new Authenticator() { protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() { // 用户名、密码 String userName = props.getProperty("mail.user"); String password = props.getProperty("mail.password"); return new PasswordAuthentication(userName, password); } }; // 使用环境属性和授权信息,创建邮件会话 Session mailSession = Session.getInstance(props, authenticator); // 创建邮件消息 MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(mailSession); // 设置发件人 InternetAddress form = new InternetAddress(props.getProperty("mail.user")); message.setFrom(form); // 设置收件人的邮箱 InternetAddress to = new InternetAddress(email); message.setRecipient(RecipientType.TO, to); // 设置邮件标题 message.setSubject("Kyle's Blog 邮件测试"); // 设置邮件的内容体 message.setContent("尊敬的用户:你好!\n注册验证码为:" + code + "(有效期为一分钟,请勿告知他人)", "text/html;charset=UTF-8"); // 最后当然就是发送邮件啦 Transport.send(message); } public static String achieveCode() { //由于数字 1 、 0 和字母 O 、l 有时分不清楚,所以,没有数字 1 、 0 String[] beforeShuffle = new String[]{"2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H", "I", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "O", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X", "Y", "Z", "a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f", "g", "h", "i", "j", "k", "l", "m", "n", "o", "p", "q", "r", "s", "t", "u", "v", "w", "x", "y", "z"}; Listlist = Arrays.asList(beforeShuffle);//将数组转换为集合 Collections.shuffle(list); //打乱集合顺序 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (String s : list) { sb.append(s); //将集合转化为字符串 } return sb.substring(3, 8); } }
修改拦截器
- 对用户登录操作放行
//定义不需要处理的请求
String[] urls = new String[]{
"/employee/login",
"/employee/logout",
"/backend/**",
"/front/**",
"/common/**",
//对用户登陆操作放行
"/user/login",
"/user/sendMsg"
};
- 判断用户是否登录
//判断用户是否登录
if(request.getSession().getAttribute("user") != null){
log.info("用户已登录,用户id为:{}",request.getSession().getAttribute("user"));
Long userId = (Long)request.getSession().getAttribute("user");
BaseContext.setCurrentId(userId);
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
return;
}
发送验证码
{% note warning no-icon %}
这里需要我们重新导入一下前端资料,将day06中的front资源再导入一遍,因为部分代码进行了修改
注意将login.html中判断手机号的正则表达式换成判断邮箱的正则表达式
直接copy这个就行了 ^\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*$
{% endnote %}
-
从上图中我们可以看到,发送验证码的请求方式是POST,路径为
/user/sendMsg -
那么我们在UserController控制层中,添加sendMsg方法
这个是真滴能发送的奥,邮箱里可以收到的,待会儿我就写校验功能了
@PostMapping("/sendMsg")
public Result sendMsg(@RequestBody User user, HttpSession session) throws MessagingException {
String phone = user.getPhone();
if (!phone.isEmpty()) {
//随机生成一个验证码
String code = MailUtils.achieveCode();
log.info(code);
//这里的phone其实就是邮箱,code是我们生成的验证码
MailUtils.sendTestMail(phone, code);
//验证码存session,方便后面拿出来比对
session.setAttribute(phone, code);
return Result.success("验证码发送成功");
}
return Result.error("验证码发送失败");
}
- 在UserController控制层中,添加
login方法
先用日志输出一下,看看是否能接受到数据
@PostMapping("/login")
public Result<String> login(@RequestBody Map map,HttpSession session){
log.info(map.toString());
return null;
}
com.blog.controller.UserController : {[email protected], code=bxQCK}
- 看样子是可以获取到数据的,那么我们继续完善login方法
@PostMapping("/login")
public Result login(@RequestBody Map map, HttpSession session) {
log.info(map.toString());
//获取邮箱
String phone = map.get("phone").toString();
//获取验证码
String code = map.get("code").toString();
//从session中获取验证码
String codeInSession = session.getAttribute(phone).toString();
//比较这用户输入的验证码和session中存的验证码是否一致
if (code != null && code.equals(codeInSession)) {
//如果输入正确,判断一下当前用户是否存在
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//判断依据是从数据库中查询是否有其邮箱
queryWrapper.eq(User::getPhone, phone);
User user = userService.getOne(queryWrapper);
//如果不存在,则创建一个,存入数据库
if (user == null) {
user = new User();
user.setPhone(phone);
userService.save(user);
user.setName("用户" + codeInSession);
}
//存个session,表示登录状态
session.setAttribute("user",user.getId());
//并将其作为结果返回
return Result.success(user);
}
return Result.error("登录失败");
}
{% note warning no-icon %}
可能遇到的问题:
javax.mail.AuthenticationFailedException: 535 Login Fail.- 遇到这个问题请重新获取一下授权码并更新授权码
- 如果在从session中取code验证码的时候报
java.lang.NullPointerException- 请清除浏览器缓存之后再次测试
{% endnote %}
- 请清除浏览器缓存之后再次测试
地址簿
需求分析
- 地址簿,指的是移动端消费者用户的地址信息(外卖快递的收货地址)
- 用户登录成功后可以维护自己的地址信息(自己修改删除新增等)
- 同一个用户可以有多个地址信息,但是只能有一个默认地址。(有默认地址的话会很方便)
数据模型
{% note warning no-icon %}
注意这里的phone类型为varchar(11),这显然不够我们邮箱用的,所以我们自己改一下这里,改大一点,不然做到新增地址的时候,会报错
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.MysqlDataTruncation: Data truncation: Data too long for column 'phone' at row 1
{% endnote %}
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| user_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 用户id | |
| consignee | varchar(50) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 收货人 | |
| sex | tinyint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 性别 0 女 1 男 | |
| phone | varchar(11) | utf8_bin | NO | (NULL) | 手机号 | |
| province_code | varchar(12) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 省级区划编号 | |
| province_name | varchar(32) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 省级名称 | |
| city_code | varchar(12) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 市级区划编号 | |
| city_name | varchar(32) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 市级名称 | |
| district_code | varchar(12) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 区级区划编号 | |
| district_name | varchar(32) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 区级名称 | |
| detail | varchar(200) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 详细地址 | |
| label | varchar(100) | utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci | YES | (NULL) | 标签 | |
| is_default | tinyint(1) | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 默认 0 否 1是 | |
| create_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建时间 | |
| update_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 更新时间 | |
| create_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 创建人 | |
| update_user | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 修改人 | |
| is_deleted | int | (NULL) | NO | 0 | 是否删除 |
准备工作
- 创建对应的实体类
AddressBook
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.FieldFill;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableField;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 地址簿
*/
@Data
public class AddressBook implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//用户id
private Long userId;
//收货人
private String consignee;
//手机号
private String phone;
//性别 0 女 1 男
private String sex;
//省级区划编号
private String provinceCode;
//省级名称
private String provinceName;
//市级区划编号
private String cityCode;
//市级名称
private String cityName;
//区级区划编号
private String districtCode;
//区级名称
private String districtName;
//详细地址
private String detail;
//标签
private String label;
//是否默认 0否 1是
private Integer isDefault;
//创建时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private LocalDateTime createTime;
//更新时间
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
//创建人
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT)
private Long createUser;
//修改人
@TableField(fill = FieldFill.INSERT_UPDATE)
private Long updateUser;
//是否删除
private Integer isDeleted;
}
Mapper接口AddressBookMapper
@Mapper
public interface AddressBookMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
- 业务层接口
AddressBookService
public interface AddreddBookService extends IService {
}
- 业务层实现类
AddressBookServicelmpl
@Service
public class AddressBookServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements AddressBookService {
}
- 控制层
AddressBookController
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/addreddBook")
public class AddressBookController {
@Autowired
private AddressBookService addressBookService;
}
完善地址管理页面
请求网址: http://localhost/addressBook/list
请求方法: GET
- 请求路径为
/addressBook/list,请求方式为GET,那么我们现在来AddressBookController中编写对应的方法
@GetMapping("/list")
public Result> list(AddressBook addressBook) {
addressBook.setUserId(BaseContext.getCurrentId());
log.info("addressBook={}", addressBook);
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(addressBook.getUserId() != null, AddressBook::getUserId, addressBook.getUserId());
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(AddressBook::getUpdateTime);
List addressBooks = addressBookService.list(queryWrapper);
return Result.success(addressBooks);
}
- 不过写完了暂时还是不能看到效果的,数据库中并没有添加对应账号的数据,所以我们继续来做新增收货地址功能
新增收货地址
- 修改前端代码
这段代码是新增地址的前端代码,我们将其中的手机号全部替换成邮箱,判断手机号的正则也换成判断邮箱的正则,懒人就直接Copy我这段代码就好了
菩提阁
{{title}}
联系人:
- 填写表单,点击保存,发送请求
请求网址: http://localhost/addressBook
请求方法: POST
- 请求路径Wie
/addressBook,请求方式为POST,那么我们在AddressBookController中编写对应的方法
@PostMapping
public Result addAddress(@RequestBody AddressBook addressBook) {
addressBook.setUserId(BaseContext.getCurrentId());
log.info("addressBook:{}", addressBook);
addressBookService.save(addressBook);
return Result.success(addressBook);
}
设置默认地址
- 先来想想怎么设置默认地址
- 默认地址,按理说数据库中,有且仅有一条数据为默认地址,也就是
is_default字段为1 - 如何保证整个表中的
is_default字段只有一条为1- 每次设置默认地址的时候,将当前用户所有地址的
is_default字段设为0,随后将当前地址的is_default字段设为1
- 每次设置默认地址的时候,将当前用户所有地址的
- 默认地址,按理说数据库中,有且仅有一条数据为默认地址,也就是
- 当我们点击上图的设为默认按钮的时候,会发送请求
请求网址: http://localhost/addressBook/default
请求方法: PUT
- 请求路径为
/addressBook/default,请求方式为PUT,那么我们现在就在AddressBookController中编写对应的方法
@PutMapping("/default")
public Result setDefaultAddress(@RequestBody AddressBook addressBook) {
//获取当前用户id
addressBook.setUserId(BaseContext.getCurrentId());
//条件构造器
LambdaUpdateWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>();
//条件:当前用户的地址
queryWrapper.eq(addressBook.getUserId() != null, AddressBook::getUserId, addressBook.getUserId());
//将当前用户地址的is_default字段全部设为0
queryWrapper.set(AddressBook::getIsDefault, 0);
//执行更新操作
addressBookService.update(queryWrapper);
//随后再将当前地址的is_default字段设为1
addressBook.setIsDefault(1);
//再次执行更新操作
addressBookService.updateById(addressBook);
return Result.success(addressBook);
}
{% note warning no-icon %}
注意这里的条件构造器是LambdaUpdateWrapper,而不是我们前面经常用的LambdaQueryWrapper
{% endnote %}
菜品展示
需求分析
- 用户登陆成功之后,跳转到菜品页面,根据菜品分类来展示菜品和套餐
- 如果菜品设置了口味信息,则需要展示选择规格按钮,否则只展示+按钮(这部分是前端实现的)
梳理交互过程
- 页面(front/index.html)发送ajax请求,获取分类数据(菜品分类和套餐分类)
- 页面发送ajax请求,根据具体的菜品/套餐分类,展示对应分类中的具体菜品
前端分析
- 启动服务器,登录账号,监测Network选项卡,发现登录到首页会发送两个请求
- 分类
请求网址: http://localhost/category/list
请求方法: GET- 购物车
请求网址: http://localhost/shoppingCart/list
请求方法: GET - 其中分类请求我们之前写过了,但是当我们访问页面的时候,并没有加载出来,原因我们来看看前端代码
{% tabs fglkj!@#fdg %}
Promise.all在处理多个异步请求时,需要等待绑定的每个ajax请求返回数据以后才能正常显示
虽然categoryListApi可以正常返回数据,但是cartListApi不能,看一下代码的请求路径就知道,我们还没开始写
//初始化数据
initData(){
Promise.all([categoryListApi(),cartListApi({})]).then(res=>{
//获取分类数据
if(res[0].code === 1){
this.categoryList = res[0].data
if(Array.isArray(res[0].data) && res[0].data.length > 0){
this.categoryId = res[0].data[0].id
if(res[0].data[0].type === 1){
this.getDishList()
}else{
this.getSetmealData()
}
}
}else{
this.$notify({ type:'warning', message:res[0].msg});
}
//获取菜品数据
if(res[1].code === 1){
this.cartData = res[1].data
}else{
this.$notify({ type:'warning', message:res[1].msg});
}
})
}
这个请求路径我们写过了,而且可以正常返回数据
//获取所有的菜品分类
function categoryListApi() {
return $axios({
'url': '/category/list',
'method': 'get',
})
}
@GetMapping("/list")
public Result> get(Dish dish) {
//条件查询器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//根据传进来的categoryId查询
queryWrapper.eq(dish.getCategoryId() != null, Dish::getCategoryId, dish.getCategoryId());
//只查询状态为1的菜品(在售菜品)
queryWrapper.eq(Dish::getStatus, 1);
//简单排下序
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Dish::getSort).orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//获取查询到的结果作为返回值
List list = dishService.list(queryWrapper);
return Result.success(list);
}
购物车相关功能还没写,所以这里我们用一个写死了的json数据骗骗它
将url换成我们注释掉的那个就好了
//获取购物车内商品的集合
function cartListApi(data) {
return $axios({
'url': '/shoppingCart/list',
//'url': '/front/cartData.json',
'method': 'get',
params: {...data}
})
}
{"code":1,"msg":null,"data":[],"map":{}}
{% endtabs %}
- 那我们再次重启服务器,看看首页是否能显示分类数据
- 但是现在还存在一个问题,我们的菜品是有口味数据的,那么这里的按钮不该是一个
+,而应该是选择规格
选择规格
通过代码我们可以看出,选择规格按钮,是根据服务端返回数据中是否有flavors字段来决定的,但我们返回的是一个List,其中并没有flavors属性,所以我们需要修改前面的方法返回值为DishDto,DishDto继承了Dish,且新增了flavors属性
选择规格
- 前面我们已经分析了该怎么做,那么现在我们直接来修改原本的list方法
具体代码如下,其实跟前面的部分代码也是类似的,如果还是不清楚具体的代码执行流程,可以打个断点自己看看
@GetMapping("/list")
public Result> get(Dish dish) {
//条件查询器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//根据传进来的categoryId查询
queryWrapper.eq(dish.getCategoryId() != null, Dish::getCategoryId, dish.getCategoryId());
//只查询状态为1的菜品(在售菜品)
queryWrapper.eq(Dish::getStatus, 1);
//简单排下序,其实也没啥太大作用
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Dish::getSort).orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
//获取查询到的结果作为返回值
List list = dishService.list(queryWrapper);
log.info("查询到的菜品信息list:{}",list);
//item就是list中的每一条数据,相当于遍历了
List dishDtoList = list.stream().map((item) -> {
//创建一个dishDto对象
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
//将item的属性全都copy到dishDto里
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, dishDto);
//由于dish表中没有categoryName属性,只存了categoryId
Long categoryId = item.getCategoryId();
//所以我们要根据categoryId查询对应的category
Category category = categoryService.getById(categoryId);
if (category != null) {
//然后取出categoryName,赋值给dishDto
dishDto.setCategoryName(category.getName());
}
//然后获取一下菜品id,根据菜品id去dishFlavor表中查询对应的口味,并赋值给dishDto
Long itemId = item.getId();
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper lambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//条件就是菜品id
lambdaQueryWrapper.eq(itemId != null, DishFlavor::getDishId, itemId);
//根据菜品id,查询到菜品口味
List flavors = dishFlavorService.list(lambdaQueryWrapper);
//赋给dishDto的对应属性
dishDto.setFlavors(flavors);
//并将dishDto作为结果返回
return dishDto;
//将所有返回结果收集起来,封装成List
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return Result.success(dishDtoList);
}
- 那么至此,菜品展示功能就做好了
套餐展示
- 关于菜品的展示我们就完成了,但是套餐和菜品用的并不是同一个controller,所以我们还需要来完善套餐展示
请求网址: http://localhost/setmeal/list?categoryId=1413342269393674242&status=1
请求方法: GET
- 那么我们现在就在
SetmealController中编写对应的方法
由于套餐没有口味数据,所以开发起来还是比较简单的
@GetMapping("/list")
public Result> list(Setmeal setmeal) {
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//添加条件
queryWrapper.eq(setmeal.getCategoryId() != null, Setmeal::getCategoryId, setmeal.getCategoryId());
queryWrapper.eq(setmeal.getStatus() != null, Setmeal::getStatus, 1);
//排序
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Setmeal::getUpdateTime);
List setmealList = setmealService.list(queryWrapper);
return Result.success(setmealList);
}
购物车
需求分析
- 移动端用户可以将菜品/套餐添加到购物车
- 对于菜品来说,如果设置了口味信息,则需要选择规格后才能加入购物车(前端实现)
- 对于套餐来说,可以直接点击当前套餐加入购物车
- 在购物车中可以修改菜品/套餐的数量,也可以清空购物车
数据模型
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| name | varchar(50) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 名称 | |
| image | varchar(100) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 图片 | |
| user_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 主键 | |
| dish_id | bigint | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 菜品id | |
| setmeal_id | bigint | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 套餐id | |
| dish_flavor | varchar(50) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 口味 | |
| number | int | (NULL) | NO | 1 | 数量 | |
| amount | decimal(10,2) | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 金额 | |
| create_time | datetime | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 创建时间 |
梳理交互过程
- 点击加入购物车按钮,页面发送ajax请求,请求服务端,将菜品/套餐添加到购物车
- 点击购物车图标,页面发送ajax请求,请求服务端,查询购物车中的菜品和套餐
- 点击清空购物车按钮,页面发送ajax请求,请求服务端来执行清空购物车操作
准备工作
在开发业务功能之前,先将需要用到的类和接口的基本结构都创建好
- 实体类
ShoppingCart
/**
* 购物车
*/
@Data
public class ShoppingCart implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//名称
private String name;
//用户id
private Long userId;
//菜品id
private Long dishId;
//套餐id
private Long setmealId;
//口味
private String dishFlavor;
//数量
private Integer number;
//金额
private BigDecimal amount;
//图片
private String image;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
}
Mapper接口ShoppingCartMapper
@Mapper
public interface ShoppingCartMapper extends BaseMapper {
}
- 业务层接口
ShoppingCartService
public interface ShoppingCartService extends IService {
}
- 业务层实现类
ShoppingCartServiceImpl
@Service
public class ShoppingCartServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements ShoppingCartService {
}
- 控制层
ShoppingCartController
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/shoppingCart")
public class ShoppingCartController {
@Autowired
private ShoppingCartService shoppingCartService;
}
代码开发
加入购物车
- 点击
加入购物车,页面发送请求,请求路径/shoppingCart/add,请求方式POST
请求网址: http://localhost/shoppingCart/add
请求方法: POST
- 页面将数据以json也是发送给服务端
{amount: 521, dishId: "1578917585305587714", name: "好吃的彩虹啊",…}
amount: 521
dishId: "1578917585305587714"
image: "c0713287-977f-4004-8a23-d5e1d89cb4c9.jpg"
name: "好吃的彩虹啊"
- 那么我们在
ShoppingCartController添加对应的方法
@PostMapping("/add")
public Result add(@RequestBody ShoppingCart shoppingCart){
log.info("购物车添加信息:{}",shoppingCart);
return null;
}
先打个断点试试能不能接收到数据
- 完善逻辑
@PostMapping("/add")
public Result add(@RequestBody ShoppingCart shoppingCart) {
log.info("shoppingCart={}", shoppingCart);
//获取当前用户id
Long currentId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
//设置当前用户id
shoppingCart.setUserId(currentId);
//获取当前菜品id
Long dishId = shoppingCart.getDishId();
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//判断添加的是菜品还是套餐
if (dishId != null) {
queryWrapper.eq(ShoppingCart::getDishId, dishId);
} else {
queryWrapper.eq(ShoppingCart::getSetmealId, shoppingCart.getSetmealId());
}
//查询当前菜品或者套餐是否在购物车中
ShoppingCart cartServiceOne = shoppingCartService.getOne(queryWrapper);
if (cartServiceOne != null) {
//如果已存在就在当前的数量上加1
Integer number = cartServiceOne.getNumber();
cartServiceOne.setNumber(number + 1);
shoppingCartService.updateById(cartServiceOne);
} else {
//如果不存在,则还需设置一下创建时间
shoppingCart.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
//如果不存在,则添加到购物车,数量默认为1
shoppingCartService.save(shoppingCart);
//这里是为了统一结果,最后都返回cartServiceOne会比较方便
cartServiceOne = shoppingCart;
}
return Result.success(cartServiceOne);
}
- 功能测试
重启服务器,尝试添加购物车,随后去数据库中查询是否有对应数据
查看购物车
- 之前为了不报错,我们将查看购物车的地址换成了一个死数据
那现在我们要做的就是换成真数据
//获取购物车内商品的集合
function cartListApi(data) {
return $axios({
// 'url': '/shoppingCart/list',
'url': '/front/cartData.json',
'method': 'get',
params: {...data}
})
}
- 请求路径为
/shoppingCart/list,请求方式为GET
直接来ShoppingCartController中添加对应的方法
@GetMapping("/list")
public Result> list() {
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
Long userId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
queryWrapper.eq(ShoppingCart::getUserId, userId);
List shoppingCarts = shoppingCartService.list(queryWrapper);
return Result.success(shoppingCarts);
}
- 如果一切顺利的话,现在就可以看到数据了,不过减号的功能我们还没有开发(我后面会补上)
清空购物车
- 我们点击上图中的清空按钮,请求路径为
/shoppingCart/clean,请求方式为DELETE
请求网址: http://localhost/shoppingCart/clean
请求方法: DELETE
- 清空购物车的逻辑倒是比较简单,获取用户id,然后去
shopping__cart表中删除对应id的数据即可
那么我们现在就来ShoppingCartController中编写对应的方法
@DeleteMapping("/clean")
public Result clean() {
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//获取当前用户id
Long userId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
queryWrapper.eq(userId != null, ShoppingCart::getUserId, userId);
//删除当前用户id的所有购物车数据
shoppingCartService.remove(queryWrapper);
return Result.success("成功清空购物车");
}
用户下单
需求分析
- 移动端用户将菜品或者套餐加入购物车后,可以点击购物车中的去结算按钮,页面跳转到订单确认页面,点击去支付按钮,完成下单操作
数据模型
户下单业务对应的数据表为orders表和order_detail表
orders表
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| number | varchar(50) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 订单号 | |
| status | int | (NULL) | NO | 1 | 订单状态 1待付款,2待派送,3已派送,4已完成,5已取消 | |
| user_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 下单用户 | |
| address_book_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 地址id | |
| order_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 下单时间 | |
| checkout_time | datetime | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 结账时间 | |
| pay_method | int | (NULL) | NO | 1 | 支付方式 1微信,2支付宝 | |
| amount | decimal(10,2) | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 实收金额 | |
| remark | varchar(100) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 备注 | |
| phone | varchar(255) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 手机号 | |
| address | varchar(255) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 地址 | |
| user_name | varchar(255) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 用户名 | |
| consignee | varchar(255) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 收货人 |
order_detail表
| Field | Type | Collation | Null | Key | Default | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | PRI | (NULL) | 主键 |
| name | varchar(50) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 名字 | |
| image | varchar(100) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 图片 | |
| order_id | bigint | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 订单id | |
| dish_id | bigint | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 菜品id | |
| setmeal_id | bigint | (NULL) | YES | (NULL) | 套餐id | |
| dish_flavor | varchar(50) | utf8_bin | YES | (NULL) | 口味 | |
| number | int | (NULL) | NO | 1 | 数量 | |
| amount | decimal(10,2) | (NULL) | NO | (NULL) | 金额 |
梳理交互过程
- 在购物车中点击去结算按钮,页面跳转到订单确认页面
- 在订单确认页面中,发送ajax请求,请求服务端,获取当前登录用户的默认地址
- 在订单确认页面,发送ajax请求,请求服务端,获取当前登录用户的购物车数据
- 在订单确认页面点击去支付按钮,发送ajax请求,请求服务端,完成下单操作
准备工作
- 实体类
Orders和OrderDetail
{% tabs 用户下单实体类模型 %}
/**
* 订单
*/
@Data
public class Orders implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//订单号
private String number;
//订单状态 1待付款,2待派送,3已派送,4已完成,5已取消
private Integer status;
//下单用户id
private Long userId;
//地址id
private Long addressBookId;
//下单时间
private LocalDateTime orderTime;
//结账时间
private LocalDateTime checkoutTime;
//支付方式 1微信,2支付宝
private Integer payMethod;
//实收金额
private BigDecimal amount;
//备注
private String remark;
//用户名
private String userName;
//手机号
private String phone;
//地址
private String address;
//收货人
private String consignee;
}
/**
* 订单明细
*/
@Data
public class OrderDetail implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Long id;
//名称
private String name;
//订单id
private Long orderId;
//菜品id
private Long dishId;
//套餐id
private Long setmealId;
//口味
private String dishFlavor;
//数量
private Integer number;
//金额
private BigDecimal amount;
//图片
private String image;
}
{% endtabs %}
2. Mapper接口OrderMapper、OrderDetailMapper
{% tabs 用户下单的两个Mapper接口 %}
@Mapper
public interface OrderMpper extends BaseMapper<Orders> {
}
@Mapper
public interface OrderDetailMapper extends BaseMapper<OrderDetail> {
}
{% endtabs %}
3. 业务层接口OrderService、OrderDetailService
{% tabs 用户下单的两个业务层接口 %}
public interface OrderService extends IService<Orders> {
}
public interface OrderDetailService extends IService<OrderDetail> {
}
{% endtabs %}
4. 业务层接口实现类OrderServiceImpl、OrderDetailServiceImpl
{% tabs 用户下单的两个业务层接口实现类 %}
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<OrderMapper, Orders> implements OrderService {
}
@Service
public class OrderDetailServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<OrderDetailMapper, OrderDetail> implements OrderDetailService {
}
{% endtabs %}
5. 控制层OrderController、OrderDetailController
{% tabs 用户下单的两个控制层 %}
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/order")
public class OrderController {
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
}
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/orderDetail")
public class OrderDetailController {
@Autowired
private OrderDetailService orderDetailService;
}
{% endtabs %}
前端分析
请求网址: http://localhost/addressBook/default
请求方法: GET
- 页面跳转到确认订单页面,发送ajax请求,用于获取用户的默认地址,但是请求失败,服务端没有对应的映射
- 那么我们根据请求路径
/addressBook/default,请求方式GET自己来编写方法,进入到AddressBookController编写
@GetMapping("/default")
public Result defaultAddress() {
//获取当前用户id
Long userId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//当前用户
queryWrapper.eq(userId != null, AddressBook::getUserId, userId);
//默认地址
queryWrapper.eq(AddressBook::getIsDefault, 1);
AddressBook addressBook = addressBookService.getOne(queryWrapper);
return Result.success(addressBook);
}
结算
- 点击上图中的去结算按钮,查看发送的请求url与请求方式
请求网址: http://localhost/order/submit
请求方法: POST
- 提交给服务端的数据格式为JSON
addressBookId: "1579828298672885762",
payMethod: 1,
remark: ""
- 请求路径
/order/submit,请求方式POST,那么我们现在就去OrderController中开发对应的功能
具体的submit方法我们放在OrderService写,OrderController调用写好的submit方法就好了
{% tabs 用户下单的submit方法 %}
public interface OrderService extends IService<Orders> {
void submit(Orders orders);
}
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<OrderMapper, Orders> implements OrderService {
@Override
public void submit(Orders orders) {
}
}
@PostMapping("/submit")
public Result<String> submit(@RequestBody Orders orders) {
log.info("orders:{}", orders);
orderService.submit(orders);
return Result.success("用户下单成功");
}
{% endtabs %}
- 编写具体的submit方法的逻辑代码,我们先来分析一下下单功能,都需要做什么事情
- 获取当前用户id
- 根据用户id查询其购物车数据
- 根据查询到的购物车数据,对订单表插入数据(1条)
- 根据查询到的购物车数据,对订单明细表插入数据(多条)
- 清空购物车数据
@Service
public class OrderServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Autowired
private ShoppingCartService shoppingCartService;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private AddressBookService addressBookService;
@Autowired
private OrderDetailService orderDetailService;
@Override
public void submit(Orders orders) {
//获取当前用户id
Long userId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper shoppingCartLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//根据当前用户id查询其购物车数据
shoppingCartLambdaQueryWrapper.eq(userId != null, ShoppingCart::getUserId, userId);
List shoppingCarts = shoppingCartService.list(shoppingCartLambdaQueryWrapper);
//判断一下购物车是否为空
if (shoppingCarts == null) {
throw new CustomException("购物车数据为空,不能下单");
}
//判断一下地址是否有误
Long addressBookId = orders.getAddressBookId();
AddressBook addressBook = addressBookService.getById(addressBookId);
if (addressBookId == null) {
throw new CustomException("地址信息有误,不能下单");
}
//获取用户信息,为了后面赋值
User user = userService.getById(userId);
long orderId = IdWorker.getId();
AtomicInteger amount = new AtomicInteger(0);
//向订单细节表设置属性
List orderDetailList= shoppingCarts.stream().map((item) -> {
OrderDetail orderDetail = new OrderDetail();
orderDetail.setOrderId(orderId);
orderDetail.setName(item.getName());
orderDetail.setImage(item.getImage());
orderDetail.setDishId(item.getDishId());
orderDetail.setSetmealId(item.getSetmealId());
orderDetail.setDishFlavor(item.getDishFlavor());
orderDetail.setNumber(item.getNumber());
orderDetail.setAmount(item.getAmount());
amount.addAndGet(item.getAmount().multiply(new BigDecimal(item.getNumber())).intValue());
return orderDetail;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//向订单表设置属性
orders.setId(orderId);
orders.setNumber(String.valueOf(orderId));
orders.setStatus(2);
orders.setUserId(userId);
orders.setAddressBookId(addressBookId);
orders.setOrderTime(LocalDateTime.now());
orders.setCheckoutTime(LocalDateTime.now());
orders.setAmount(new BigDecimal(amount.get()));
orders.setPhone(addressBook.getPhone());
orders.setUserName(user.getName());
orders.setConsignee(addressBook.getConsignee());
orders.setAddress(
(addressBook.getProvinceName() == null ? "":addressBook.getProvinceName())+
(addressBook.getCityName() == null ? "":addressBook.getCityName())+
(addressBook.getDistrictName() == null ? "":addressBook.getDistrictName())+
(addressBook.getDetail() == null ? "":addressBook.getDetail())
);
//根据查询到的购物车数据,对订单表插入数据(1条)
super.save(orders);
//根据查询到的购物车数据,对订单明细表插入数据(多条)
orderDetailService.saveBatch(orderDetailList);
//清空购物车数据
shoppingCartService.remove(shoppingCartLambdaQueryWrapper);
}
}
-
虽然代码量很多,但是大部分都是赋值操作,由于购物车数据与订单数据和订单详情的重复字段不是很多,所以这里就没采用
BeanUtils.copyProperties()来复制属性了,而是自己一个一个set的
移动端补充功能
历史订单功能
- 当我们访问个人中心/历史订单的时候,都会发送请求
请求网址: http://localhost/order/userPage?page=1&pageSize=1
请求方法: GET
- 看样子是个分页的请求,我们之前把订单数据存进了order表中,那么该功能,大概率就是从表中查出数据然后返回给前端
- 那么我们直接来
OrderController中编写对应的方法- 在此之前,我们还是需要一个OrderDto
@Data public class OrdersDto extends Orders { private String userName; private String phone; private String address; private String consignee; private ListorderDetails; } - 其实这个分页的代码跟之前的也没啥区别,都是很类似的,多敲几遍就会了
@GetMapping("/userPage") public Resultpage(int page, int pageSize) { //获取当前id Long userId = BaseContext.getCurrentId(); Page pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize); Page ordersDtoPage = new Page<>(page, pageSize); //条件构造器 LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); //查询当前用户id订单数据 queryWrapper.eq(userId != null, Orders::getUserId, userId); //按时间降序排序 queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Orders::getOrderTime); orderService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper); List list = pageInfo.getRecords().stream().map((item) -> { OrdersDto ordersDto = new OrdersDto(); //获取orderId,然后根据这个id,去orderDetail表中查数据 Long orderId = item.getId(); LambdaQueryWrapper wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); wrapper.eq(OrderDetail::getOrderId, orderId); List details = orderDetailService.list(wrapper); BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, ordersDto); //之后set一下属性 ordersDto.setOrderDetails(details); return ordersDto; }).collect(Collectors.toList()); BeanUtils.copyProperties(pageInfo, ordersDtoPage, "records"); ordersDtoPage.setRecords(list); //日志输出看一下 log.info("list:{}", list); return Result.success(ordersDtoPage); } - 效果图
登出功能
- 这个应该算简单的了吧,点击退出登录,请求如下
请求网址: http://localhost/user/loginout
请求方法: POST
- 请求路径
/user/loginout,请求方式POST
所以我们应该去UserController中编写对应的方法
@PostMapping("/loginout")
public Result logout(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.getSession().removeAttribute("user");
return Result.success("退出成功");
}
{% note warning no-icon %}
前提是你login方法的是写的setAttribute("user", user.getId());,字段名要对上
{% endnote %}
修改/删除地址
-
数据回显- 点击地址选项卡的
铅笔图案,跳转到修改地址页面,发送请求
请求网址: http://localhost/addressBook/1579828298672885762
请求方法: GET- 第一感觉像是restFul的url,那么请求路径大概率为
/addressBook/{id}请求方式是GET,而且此次操作是数据回显 - 那么我们直接来
AddressBookController中编写对应的方法
@GetMapping("/{id}") public ResultgetById(@PathVariable Long id) { AddressBook addressBook = addressBookService.getById(id); if (addressBook == null){ throw new CustomException("地址信息不存在"); } return Result.success(addressBook); } - 点击地址选项卡的
-
修改地址
- 点击上图中的
保存地址按钮,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/addressBook
请求方法: PUT- 请求方式
PUT,我们直接来AddressBookController中编写对应的方法
@PutMapping public ResultupdateAdd(@RequestBody AddressBook addressBook) { if (addressBook == null) { throw new CustomException("地址信息不存在,请刷新重试"); } addressBookService.updateById(addressBook); return Result.success("地址修改成功"); } - 点击上图中的
-
删除地址
- 点击上图中的
删除地址按钮,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/addressBook?ids=1579828298672885762
请求方法: DELETE- 我们直接来
AddressBookController中编写对应的方法
@DeleteMapping() public ResultdeleteAdd(@RequestParam("ids") Long id) { if (id == null) { throw new CustomException("地址信息不存在,请刷新重试"); } AddressBook addressBook = addressBookService.getById(id); if (addressBook == null) { throw new CustomException("地址信息不存在,请刷新重试"); } addressBookService.removeById(id); return Result.success("地址删除成功"); } - 点击上图中的
{% note success no-icon %}
至此,地址修改的相关功能我们就完成了,现在自己测试一下,没啥问题的话就继续往下做别的功能
{% endnote %}
再来一单
- 这个功能其实比较隐晦,因为当订单状态为
已完成时才会出现这个按钮(修改orders表中的status字段为4),我也是看前端代码才发现有这个功能的
{% tabs 984651!@#B %}
点击事件调用addOrderAgain方法
<div class="btn" v-if="order.status === 4">
<div class="btnAgain" @click="addOrderAgain(order)">再来一单div>
div>
该方法会跳转至index页面,也就是下单结算那个界面
async addOrderAgain(order){
const res = await orderAgainApi({id:order.id})
if(res.code === 1){
window.requestAnimationFrame(()=>{
window.location.href= '/front/index.html'
})
}else{
this.$notify({ type:'warning', message:res.msg});
}
}
{% endtabs %}
请求网址: http://localhost/order/again
请求方法: POST
- 请求路径为
/order/again,请求方式为POST,数据只携带了一个json格式的id数据,根据常识,这个id只能是orders表中的订单id,即order_id
{id: "1580121916188971009"}
-
我们手里现在能用的数据只有一个order_id,我们要根据它去查询对应的下单信息
-
接下来我们分析一下这个
再来一单具体都会做什么操作 -
具体实现思路(参考一下当初我们怎么添加购物车的)
- 之前是我们手动选择数据(菜品/套餐)添加到购物车,现在相当于我们手里有个发票,想办法看看上一单都买了啥,然后复刻一遍
-
分析完毕之后,我们来
OrderController编写对应的方法
@PostMapping("/again")
public Result again(@RequestBody Map map){
//获取order_id
Long orderId = Long.valueOf(map.get("id"));
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//查询订单的口味细节数据
queryWrapper.eq(OrderDetail::getOrderId,orderId);
List details = orderDetailService.list(queryWrapper);
//获取用户id,待会需要set操作
Long userId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
List shoppingCarts = details.stream().map((item) ->{
ShoppingCart shoppingCart = new ShoppingCart();
//Copy对应属性值
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item,shoppingCart);
//设置一下userId
shoppingCart.setUserId(userId);
//设置一下创建时间为当前时间
shoppingCart.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
return shoppingCart;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
//加入购物车
shoppingCartService.saveBatch(shoppingCarts);
return Result.success("喜欢吃就再来一单吖~");
}
{% note info no-icon %}
这里我就直接用了BeanUtils.copyProperties直接复制了,然后在set俩属性,好像就完事儿了,不过我看数据库的时候,备注没有copy过来,地址是选择当前默认地址(如果你改了默认地址,那么不是之前的地址,好像也挺合理的)
{% endnote %}
减号按钮
- 之前下单的时候,只有加号按钮能用,减号按钮还没配置,我们点击
减号看看啥请求
请求网址: http://localhost/shoppingCart/sub
请求方法: POST
- 请求路径
/shoppingCart/sub,请求方式POST - 返回的json数据如下,只有
dishId和setmealId
{ dishId: null,
setmealId: "1579044544635232258"
}
- 思路分析
- 根据这两个id,来对不同的菜品/套餐的number属性修改(对应的数量-1),如果number等于0,则删除
- 那么我们现在就来
ShoppingCartController中开发对应的方法
@PostMapping("/sub")
public Result sub(@RequestBody ShoppingCart shoppingCart) {
Long dishId = shoppingCart.getDishId();
Long setmealId = shoppingCart.getSetmealId();
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//只查询当前用户ID的购物车
queryWrapper.eq(ShoppingCart::getUserId, BaseContext.getCurrentId());
//代表数量减少的是菜品数量
if (dishId != null) {
//通过dishId查出购物车菜品数据
queryWrapper.eq(ShoppingCart::getDishId, dishId);
ShoppingCart dishCart = shoppingCartService.getOne(queryWrapper);
//将查出来的数据的数量-1
dishCart.setNumber(dishCart.getNumber() - 1);
Integer currentNum = dishCart.getNumber();
//然后判断
if (currentNum > 0) {
//大于0则更新
shoppingCartService.updateById(dishCart);
} else if (currentNum == 0) {
//小于0则删除
shoppingCartService.removeById(dishCart.getId());
}
return Result.success(dishCart);
}
if (setmealId != null) {
//通过setmealId查询购物车套餐数据
queryWrapper.eq(ShoppingCart::getSetmealId, setmealId);
ShoppingCart setmealCart = shoppingCartService.getOne(queryWrapper);
//将查出来的数据的数量-1
setmealCart.setNumber(setmealCart.getNumber() - 1);
Integer currentNum = setmealCart.getNumber();
//然后判断
if (currentNum > 0) {
//大于0则更新
shoppingCartService.updateById(setmealCart);
} else if (currentNum == 0) {
//等于0则删除
shoppingCartService.removeById(setmealCart.getId());
}
return Result.success(setmealCart);
}
return Result.error("系统繁忙,请稍后再试");
}
点击图片查看套餐详情
- 常用的几个外卖App都有这个功能的,点击图片,查看套餐,这里随便点一个套餐图片,查看请求
请求网址: http://localhost/setmeal/dish/1579044544635232258
请求方法: GET
-
看样子是restFul风格,请求路径为
/setmeal/dish/{id},请求方式为GET -
前端代码分析
{% tabs 984651!@#blkjf %}
主要看第一行就好了,点击图片会触发dishDetails方法

{{item.name}}
{{item.description}}
{{'月销' + (item.saleNum ? item.saleNum : 0) }}
¥{{item.price/100}}
 {{item.number}}
选择规格
{{item.number}}
选择规格

async dishDetails(item) {
//先清除对象数据,如果不行的话dialog使用v-if
this.detailsDialog.item = {}
this.setMealDialog.item = {}
if (Array.isArray(item.flavors)) {
this.detailsDialog.item = item
this.detailsDialog.show = true
} else {
//显示套餐的数据
const res = await setMealDishDetailsApi(item.id)
if (res.code === 1) {
this.setMealDialog.item = {...item, list: res.data}
this.setMealDialog.show = true
} else {
this.$notify({type: 'warning', message: res.msg});
}
}
}
//获取套餐的全部菜品
function setMealDishDetailsApi(id) {
return $axios({
'url': `/setmeal/dish/${id}`,
'method': 'get',
})
}
{% endtabs %}
- 分析完之后,我们来
SetmealController中编写对应的方法
@GetMapping("/dish/{id}")
public Result> showSetmealDish(@PathVariable Long id) {
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper dishLambdaQueryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//手里的数据只有setmealId
dishLambdaQueryWrapper.eq(SetmealDish::getSetmealId, id);
//查询数据
List records = setmealDishService.list(dishLambdaQueryWrapper);
List dtoList = records.stream().map((item) -> {
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
//copy数据
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item,dishDto);
//查询对应菜品id
Long dishId = item.getDishId();
//根据菜品id获取具体菜品数据,这里要自动装配 dishService
Dish dish = dishService.getById(dishId);
//其实主要数据是要那个图片,不过我们这里多copy一点也没事
BeanUtils.copyProperties(dish,dishDto);
return dishDto;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
return Result.success(dtoList);
}
{% note success no-icon %}
那么到此为止,移动端的功能应该都实现了
{% endnote %}
后台系统补充功能
菜品启售/停售
- 点击停售按钮,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/dish/status/0?ids=1578942037036703745
请求方法: POST
- 当前商品为启售状态,其status为1,但点击停售按钮时,发送的status为0,前端是直接对这个status取反了,我们直接用发送的这个status来更新我们的商品状态就好了,不用在后端再次进行判断
- 那我们直接来
DishController中编写对应的方法
@PostMapping("/status/{status}")
public Result status(@PathVariable Integer status, Long ids) {
log.info("status:{},ids:{}", status, ids);
Dish dish = dishService.getById(ids);
if (dish != null) {
//直接用它传进来的这个status改就行
dish.setStatus(status);
dishService.updateById(dish);
return Result.success("售卖状态修改成功");
}
return Result.error("系统繁忙,请稍后再试");
}
菜品批量启售/停售
- 这个其实就是传进来了一个ids的数组,我们在上面的方法上稍作修改就好了,但我想到了一个更简单的方式,直接用
LambdaUpdateWrapper更方便
@PostMapping("/status/{status}")
public Result status(@PathVariable Integer status, @RequestParam List ids) {
log.info("status:{},ids:{}", status, ids);
LambdaUpdateWrapper updateWrapper = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.in(ids != null, Dish::getId, ids);
updateWrapper.set(Dish::getStatus, status);
dishService.update(updateWrapper);
return Result.success("批量操作成功");
}
菜品批量删除
- 删除跟批量删除应该也是同一个操作,点击删除按钮,查看请求
请求网址: http://localhost/dish?ids=1578674689490825217
请求方法: DELETE
- 但是按理说,这里应该是逻辑删除,表中有一个字段为
is_delete - 但是要按逻辑删除的话,还得改前面的
list和page代码,因为查询的时候,没涉及到逻辑删除,模型类中也没有isDelete属性 - 那我这里还是草率一点,直接删除掉吧,但如果是逻辑删除,执行的是update,将逻辑删除字段设为1表示逻辑删除,查询的时候只查询逻辑删除字段为0的数据,表示未删除的数据
- 需要注意的是,如果选中的删除列表中,存在启售状态商品,则不允许删除
- 直接来
DishController中编写对应的方法,方式一是我自己写的,效率低,方式二是之前删除套餐的代码,我做了些修改
{% tabs asd!@#dfgf %}
@DeleteMapping
public Result delete(@RequestParam List ids) {
log.info("删除的ids:{}", ids);
LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.in(Dish::getId, ids);
List dishes = dishService.list(queryWrapper);
for (Dish dish : dishes) {
if (dish.getStatus() == 1) {
throw new CustomException("删除列表中存在启售状态商品,无法删除");
}
}
dishService.remove(queryWrapper);
return Result.success("删除成功");
}
@DeleteMapping
public Result<String> delete(@RequestParam List<Long> ids) {
log.info("删除的ids:{}", ids);
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dish> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.in(Dish::getId, ids);
queryWrapper.eq(Dish::getStatus, 1);
int count = dishService.count(queryWrapper);
if (count > 0) {
throw new CustomException("删除列表中存在启售状态商品,无法删除");
}
dishService.removeByIds(ids);
return Result.success("删除成功");
}
{% endtabs %}
{% note success no-icon %}
那么至此,关于菜品的操作功能,我们都完善了
{% endnote %}
套餐批量启售/停售
- 点击批量启售,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/setmeal/status/1?ids=1580361600576114689
请求方法: POST
- 跟之前的菜品批量启售/停售没有太大区别
@PostMapping("/status/{status}")
public Result status(@PathVariable String status, @RequestParam List ids) {
LambdaUpdateWrapper updateWrapper = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.in(Setmeal::getId, ids);
updateWrapper.set(Setmeal::getStatus, status);
setmealService.update(updateWrapper);
return Result.success("批量操作成功");
}
套餐修改
数据回显- 点击修改按钮,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/setmeal/1580361496716759041
请求方法: GET- 这个请求大概率是用于处理数据回显的,请求路径
/setmeal/{setmealId},请求方式GET - 普通的
Setmeal实体类肯定是不够用的,还是要用到SetmealDto - 那么我们直接来
SetmealController中编写对应的方法
@GetMapping("/{id}") public ResultgetById(@PathVariable Long id) { Setmeal setmeal = setmealService.getById(id); SetmealDto setmealDto = new SetmealDto(); //拷贝数据 BeanUtils.copyProperties(setmeal, setmealDto); //条件构造器 LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); //根据setmealId查询具体的setmealDish queryWrapper.eq(SetmealDish::getSetmealId, id); List setmealDishes = setmealDishService.list(queryWrapper); //然后再设置属性 setmealDto.setSetmealDishes(setmealDishes); //作为结果返回 return Result.success(setmealDto); } 套餐修改- 点击保存按钮,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/setmeal
请求方法: PUT- 携带的数据如下
{ categoryId: "1580360438284144642" categoryName: null code: "" createTime: "2022-10-13 08:55:17" createUser: "1" description: "程序员的浪漫" id: "1580361496716759041" idType: "1580360438284144642" image: "2b195730-c6cf-4edb-91d3-89d23c88e69a.jpg" name: "彩虹大礼包" price: 102400 { 0: {copies: 2, dishId: "1578942037036703745", name: "难吃的彩虹", price: 94200} 1: {copies: 2, dishId: "1578917585305587714", name: "好吃的彩虹啊", price: 52100} 2: {copies: 2, dishId: "1578675342967574529", name: "好吃的彩虹", price: 32100} } status: 1 updateUser: "1" }- 请求路径
/setmeal,请求方式PUT - 那么我们直接来
SetmealController中编写对应的方法
@PutMapping public ResultupdateWithDish(@RequestBody SetmealDto setmealDto) { List setmealDishes = setmealDto.getSetmealDishes(); Long setmealId = setmealDto.getId(); //先根据id把setmealDish表中对应套餐的数据删了 LambdaQueryWrapper queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq(SetmealDish::getSetmealId,setmealId); setmealDishService.remove(queryWrapper); //然后在重新添加 setmealDishes = setmealDishes.stream().map((item) ->{ //这属性没有,需要我们手动设置一下 item.setSetmealId(setmealId); return item; }).collect(Collectors.toList()); //更新套餐数据 setmealService.updateById(setmealDto); //更新套餐对应菜品数据 setmealDishService.saveBatch(setmealDishes); return Result.success(setmealDto); }
订单明细
- 点击订单明细,输入查询条件,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/order/page?page=1&pageSize=10&number=1580166484741677057&beginTime=2022-10-19%2000%3A00%3A00&endTime=2022-11-16%2023%3A59%3A59
请求方法: GET
- 在前面,我们写过一个移动端的历史订单功能,其实跟这个差不多,我们直接把代码搬过来,然后改改就好了
{% tabs 移动端历史订单功能 %}
我们对比着看一下就好了,主要就是删除了按当前userId查询,新增了按订单号和时间段查询
@GetMapping("/userPage")
public Result<Page> userPage(int page, int pageSize) {
//获取当前id
Long userId = BaseContext.getCurrentId();
Page<Orders> pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
Page<OrdersDto> ordersDtoPage = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper<Orders> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//查询当前用户id订单数据
queryWrapper.eq(userId != null, Orders::getUserId, userId);
//按时间降序排序
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Orders::getOrderTime);
orderService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper);
List<OrdersDto> list = pageInfo.getRecords().stream().map((item) -> {
OrdersDto ordersDto = new OrdersDto();
//获取orderId,然后根据这个id,去orderDetail表中查数据
Long orderId = item.getId();
LambdaQueryWrapper<OrderDetail> wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(OrderDetail::getOrderId, orderId);
List<OrderDetail> details = orderDetailService.list(wrapper);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, ordersDto);
//之后set一下属性
ordersDto.setOrderDetails(details);
return ordersDto;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pageInfo, ordersDtoPage, "records");
ordersDtoPage.setRecords(list);
//日志输出看一下
log.info("list:{}", list);
return Result.success(ordersDtoPage);
}
历史订单是只查询指定用户的数据,那我们后台这里,查询所有的用户数据就行,也就不用指定userId
但是需要判断输入的订单号和时间段,这个要写动态SQL,不过我们可以用MP来帮我们完成
@GetMapping("/page")
public Result<Page> page(int page, int pageSize, Long number, String beginTime, String endTime) {
//获取当前id
Page<Orders> pageInfo = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
Page<OrdersDto> ordersDtoPage = new Page<>(page, pageSize);
//条件构造器
LambdaQueryWrapper<Orders> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
//按时间降序排序
queryWrapper.orderByDesc(Orders::getOrderTime);
//订单号
queryWrapper.eq(number != null, Orders::getId, number);
//时间段,大于开始,小于结束
queryWrapper.gt(!StringUtils.isEmpty(beginTime), Orders::getOrderTime, beginTime)
.lt(!StringUtils.isEmpty(endTime), Orders::getOrderTime, endTime);
orderService.page(pageInfo, queryWrapper);
List<OrdersDto> list = pageInfo.getRecords().stream().map((item) -> {
OrdersDto ordersDto = new OrdersDto();
//获取orderId,然后根据这个id,去orderDetail表中查数据
Long orderId = item.getId();
LambdaQueryWrapper<OrderDetail> wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(OrderDetail::getOrderId, orderId);
List<OrderDetail> details = orderDetailService.list(wrapper);
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item, ordersDto);
//之后set一下属性
ordersDto.setOrderDetails(details);
return ordersDto;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
BeanUtils.copyProperties(pageInfo, ordersDtoPage, "records");
ordersDtoPage.setRecords(list);
//日志输出看一下
log.info("list:{}", list);
return Result.success(ordersDtoPage);
}
{% endtabs %}
-
关于用户名字段为null,我们去修改前端代码
/backend/order/list.html,找到用户,将userName改成consignee就好了,如果还不显示,清除浏览器缓存再刷新重试
修改订单状态
- 点击上图中的
派送按钮,查看发送的请求
请求网址: http://localhost/order
请求方法: PUT
- 携带的json数据
{
status: 3,
id: "1580166484741677057"
}
- 携带的status为3,那该按钮的作用应该是将订单状态设置为传入的status
switch(row.status){
case 1:
str = '待付款'
break;
case 2:
str = '正在派送'
break;
case 3:
str = '已派送'
break;
case 4:
str = '已完成'
break;
case 5:
str = '已取消'
break;
}
- 那么我们直接来
OrderController中编写对应的方法
@PutMapping
public Result changeStatus(@RequestBody Map map) {
int status = Integer.parseInt(map.get("status"));
Long orderId = Long.valueOf(map.get("id"));
log.info("修改订单状态:status={status},id={id}", status, orderId);
LambdaUpdateWrapper updateWrapper = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.eq(Orders::getId, orderId);
updateWrapper.set(Orders::getStatus, status);
orderService.update(updateWrapper);
return Result.success("订单状态修改成功");
}
{% note success no-icon %}
那么至此,应该是把页面里的所有功能都实现了
{% endnote %}