分布式事务二 Seata使用及其原理剖析
一 Seata 是什么
Seata 介绍
Seata 是一款开源的分布式事务解决方案,致力于提供高性能和简单易用的分布式事务服务。Seata 将为用户提供了 AT、TCC、SAGA 和 XA 事务模式,为用户打造一站式的分布式解决方案。AT模式是阿里首推的模式,阿里云上有商用版本的GTS(Global Transaction Service 全局事务服务)
官网:https://seata.io/zh-cn/index.html
源码: https://github.com/seata/seata
官方Demo: https://github.com/seata/seata-samples
seata版本:v1.4.0
1.1 Seata的三大角色
在 Seata 的架构中,一共有三个角色:
-
TC (Transaction Coordinator) - 事务协调者
维护全局和分支事务的状态,驱动全局事务提交或回滚。 -
TM (Transaction Manager) - 事务管理器
定义全局事务的范围:开始全局事务、提交或回滚全局事务。 -
RM (Resource Manager) - 资源管理器
管理分支事务处理的资源,与TC交谈以注册分支事务和报告分支事务的状态,并驱动分支事务提交或回滚。(分布式下的每一个服务对应的数据库就相当于一个个资源)
其中,TC 为单独部署的 Server 服务端(可以单独部署,也可以集群部署),TM 和 RM 为嵌入到应用中的 Client 客户端。
在 Seata 中,一个分布式事务的生命周期如下(下边有三个微服务):
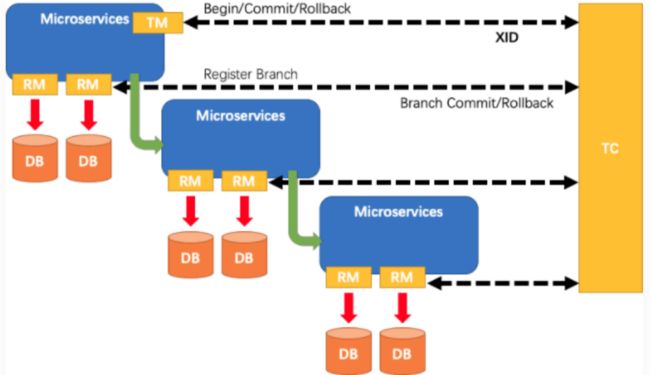
- TM 请求 TC 开启一个全局事务。TC 会生成一个 XID 作为该全局事务的编号(全局事物ID)。XID,会在微服务的调用链路中传播,保证将多个微服务的子事务关联在一起(不管是dubbo还是feign,都要把这个XID传递下去)。
- RM 请求 TC 将本地事务注册为全局事务的分支事务(因为有三个微服务,所以这里注册三个分支事物),通过全局事务的 XID 进行关联。
- TM 请求 TC 告诉 XID 对应的全局事务是进行提交还是回滚。
- TC 驱动 RM 们将 XID 对应的自己的本地事务进行提交还是回滚。
XID是全局会话ID,BID是每个服务自己的ID,二者如何绑定——保存的时候一起保存;
1.2 设计思路
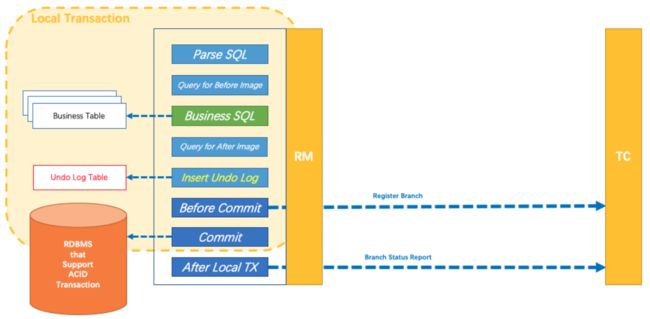
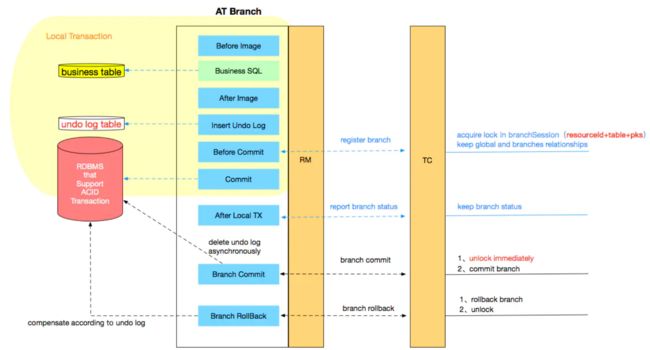
AT模式的核心是对业务无侵入,是一种改进后的两阶段提交,其设计思路如图
第一阶段
业务数据和回滚日志记录在同一个本地事务中提交,释放本地锁和连接资源。核心在于对业务sql进行解析,转换成undolog(每个服务都有一张undolog),并同时入库,这是怎么做的呢?先抛出一个概念DataSourceProxy代理数据源,通过名字大家大概也能基本猜到是什么个操作,后面做具体分析
参考官方文档: https://seata.io/zh-cn/docs/dev/mode/at-mode.html
第二阶段
分布式事务操作成功,则TC通知RM异步删除undolog

分布式事务操作失败,TM向TC发送回滚请求,RM 收到协调器TC发来的回滚请求,通过 XID 和 Branch ID 找到相应的回滚日志记录,通过回滚记录生成反向的更新 SQL 并执行,以完成分支的回滚。

整体执行流程
1.3 设计亮点
相比与其它分布式事务框架,Seata架构的亮点主要有几个:
- 应用层基于SQL解析实现了自动补偿,从而最大程度的降低业务侵入性;
- 将分布式事务中TC(事务协调者)独立部署,负责事务的注册、回滚;
- 通过全局锁实现了写隔离与读隔离。
1.4 存在的问题
性能损耗
一条Update的SQL,则需要全局事务xid获取(与TC通讯)、before image(解析SQL,查询一次数据库)、after image(查询一次数据库)、insert undo log(写一次数据库)、before commit(与TC通讯,判断锁冲突),这些操作都需要一次远程通讯RPC,而且是同步的。另外undo log写入时blob字段的插入性能也是不高的。每条写SQL都会增加这么多开销,粗略估计会增加5倍响应时间。
性价比
为了进行自动补偿,需要对所有交易生成前后镜像并持久化,可是在实际业务场景下,这个是成功率有多高,或者说分布式事务失败需要回滚的有多少比率?按照二八原则预估,为了20%的交易回滚,需要将80%的成功交易的响应时间增加5倍,这样的代价相比于让应用开发一个补偿交易是否是值得?
全局锁
热点数据
相比XA,Seata 虽然在一阶段成功后会释放数据库锁,但一阶段在commit前全局锁的判定也拉长了对数据锁的占有时间,这个开销比XA的prepare低多少需要根据实际业务场景进行测试。全局锁的引入实现了隔离性,但带来的问题就是阻塞,降低并发性,尤其是热点数据,这个问题会更加严重。
回滚锁释放时间
Seata在回滚时,需要先删除各节点的undo log,然后才能释放TC内存中的锁,所以如果第二阶段是回滚,释放锁的时间会更长。
死锁问题
Seata的引入全局锁会额外增加死锁的风险,但如果出现死锁,会不断进行重试,最后靠等待全局锁超时,这种方式并不优雅,也延长了对数据库锁的占有时间。
二 Seata快速开始
2.1 Seata Server(TC)环境搭建
https://seata.io/zh-cn/docs/ops/deploy-guide-beginner.html
Server端存储模式(store.mode)支持三种:
- file:单机模式,全局事务会话信息内存中读写并持久化本地文件root.data,性能较高
- db:高可用模式,全局事务会话信息通过db共享,相应性能差些
- redis:Seata-Server 1.3及以上版本支持,性能较高,存在事务信息丢失风险,请提前配置适合当前场景的redis持久化配置
资源目录:https://github.com/seata/seata/tree/1.4.0/script
- client
存放client端sql脚本,参数配置 - config-center
各个配置中心参数导入脚本,config.txt(包含server和client,原名nacos-config.txt)为通用参数文件 - server
server端数据库脚本及各个容器配置
db存储模式+Nacos(注册&配置中心)部署
步骤一:下载安装包
https://github.com/seata/seata/releases
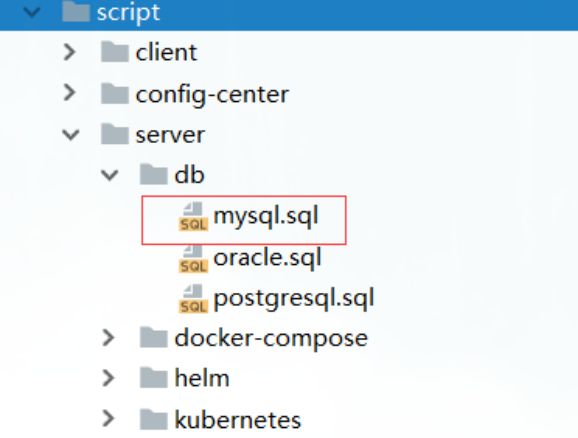
步骤二:建表(仅db模式)
全局事务会话信息由3块内容构成,全局事务表–>分支事务表–>全局锁表,对应表global_table、branch_table、lock_table
创建数据库seata,执行sql脚本,文件在script/server/db/mysql.sql(seata源码)中(下载地址:https://github.com/seata/seata/tree/1.4.0/script)
步骤三:修改store.mode
启动包: seata–>conf–>file.conf,修改store.mode=“db”
源码: 根目录–>seata-server–>resources–>file.conf,修改store.mode=“db”

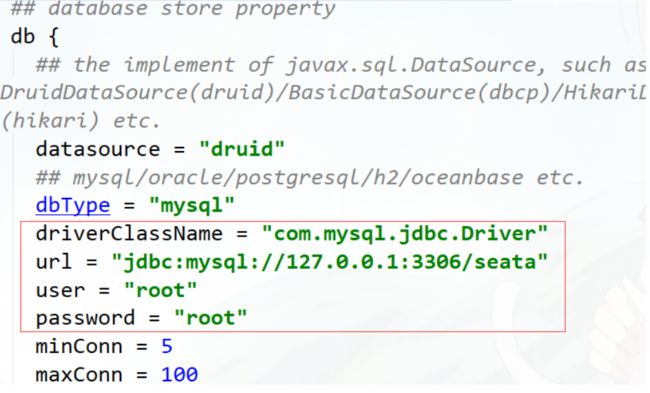
步骤四:修改数据库连接
启动包: seata–>conf–>file.conf,修改store.db相关属性。
源码: 根目录–>seata-server–>resources–>file.conf,修改store.db相关属性。
此时可以调到步骤七:直接启动Seata Server,注册中心和配置中心都是file
步骤五:配置Nacos注册中心
将Seata Server注册到Nacos,修改conf目录下的registry.conf配置

然后启动注册中心Nacos Server
#进入Nacos安装目录,linux单机启动
bin/startup.sh -m standalone
# windows单机启动
bin/startup.bat
步骤六:配置Nacos配置中心

注意:如果配置了seata server使用nacos作为配置中心,则配置信息会从nacos读取,file.conf可以不用配置。 客户端配置registry.conf使用nacos时也要注意group要和seata server中的group一致,默认group是"DEFAULT_GROUP"
获取/seata/script/config-center/config.txt,修改配置信息

配置事务分组, 要与客户端配置的事务分组一致
(客户端properties配置:spring.cloud.alibaba.seata.tx‐service‐group=my_test_tx_group)

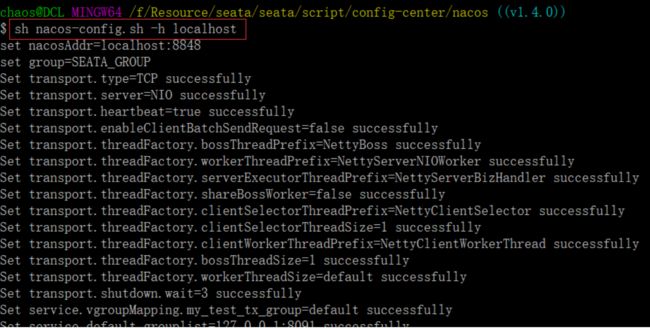
配置参数同步到Nacos
shell:
sh ${SEATAPATH}/script/config-center/nacos/nacos-config.sh -h localhost -p 8848 -g SEATA_GROUP -t 5a3c7d6c-f497-4d68-a71a-2e5e3340b3ca
参数说明:
-h: host,默认值 localhost
-p: port,默认值 8848
-g: 配置分组,默认值为 ‘SEATA_GROUP’
-t: 租户信息,对应 Nacos 的命名空间ID字段, 默认值为空 ‘’
service.vgroupMapping.my_test_tx_group=default
service.default.grouplist=127.0.0.1:8091
service.enableDegrade=false
service.disableGlobalTransaction=false
store.mode=db
store.db.datasource=druid
store.db.dbType=mysql
store.db.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
store.db.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/seata?useUnicode=true
store.db.user=root
store.db.password=root
store.db.minConn=5
store.db.maxConn=30
store.db.globalTable=global_table
store.db.branchTable=branch_table
store.db.queryLimit=100
store.db.lockTable=lock_table
store.db.maxWait=5000
步骤七:启动Seata Server
- 源码启动: 执行server模块下io.seata.server.Server.java的main方法
- 命令启动: bin/seata-server.sh -h 127.0.0.1 -p 8091 -m db -n 1 -e test
#单机启动
bin/seata-server.sh
#集群启动
bin/seata-server.sh -p 8091 -n 1
bin/seata-server.sh -p 8092 -n 2
。。。。。。。。。。
启动成功,默认端口8091

在注册中心中可以查看到seata-server注册成功

2.2 Seata Client快速开始
2.2.1 编程式事务实现(GlobalTransaction API)
Demo:seata-samples/api
客户端环境配置
- 修改jdbc.properties配置
- registry.conf中指定registry.type=“file” , config.type=“file”
基于GlobalTransaction API的实现
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException, TransactionException, InterruptedException {
String userId = "U100001";
String commodityCode = "C00321";
int commodityCount = 100;
int money = 999;
AccountService accountService = new AccountServiceImpl();
StorageService storageService = new StorageServiceImpl();
OrderService orderService = new OrderServiceImpl();
orderService.setAccountService(accountService);
//reset data 重置数据
accountService.reset(userId, String.valueOf(money));
storageService.reset(commodityCode, String.valueOf(commodityCount));
orderService.reset(null, null);
//init seata; only once
String applicationId = "api";
String txServiceGroup = "my_test_tx_group";
TMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
RMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
//trx 开启全局事务
GlobalTransaction tx = GlobalTransactionContext.getCurrentOrCreate();
try {
tx.begin(60000, "testBiz");
System.out.println("begin trx, xid is " + tx.getXid());
//biz operate 3 dataSources
//set >=5 will be rollback(200*5>999) else will be commit
int opCount = 5;
// 扣减库存
storageService.deduct(commodityCode, opCount);
// 创建订单 ,扣款 money = opCount * 200
orderService.create(userId, commodityCode, opCount);
//check data if negative
boolean needCommit = ((StorageServiceImpl)storageService).validNegativeCheck("count", commodityCode)
&& ((AccountServiceImpl)accountService).validNegativeCheck("money", userId);
//if data negative rollback else commit
if (needCommit) {
tx.commit();
} else {
System.out.println("rollback trx, cause: data negative, xid is " + tx.getXid());
tx.rollback();
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
System.out.println("rollback trx, cause: " + exx.getMessage() + " , xid is " + tx.getXid());
tx.rollback();
throw exx;
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
}
2.2.2 声明式事务实现(@GlobalTransactional)
业务场景:
用户下单,整个业务逻辑由三个服务构成:
- 启动seata server服务,指定registry.type=“file” , config.type=“file”
- 客户端应用接入seata配置
1)配置多数据源
客户端支持多数据源,yml中添加多数据源jdbc配置
# Order
spring.datasource.order.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata_order?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.order.username=root
spring.datasource.order.password=root
spring.datasource.order.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# Storage
spring.datasource.storage.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata_storage?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.storage.username=root
spring.datasource.storage.password=root
spring.datasource.storage.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# Account
spring.datasource.account.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata_account?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.account.username=root
spring.datasource.account.password=root
spring.datasource.account.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
2)配置多数据源代理,并支持动态切换数据源
@Configuration
@MapperScan("com.tuling.mutiple.datasource.mapper")
public class DataSourceProxyConfig {
@Bean("originOrder")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.order")
public DataSource dataSourceMaster() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean("originStorage")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.storage")
public DataSource dataSourceStorage() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean("originAccount")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.account")
public DataSource dataSourceAccount() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean(name = "order")
public DataSourceProxy masterDataSourceProxy(@Qualifier("originOrder") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "storage")
public DataSourceProxy storageDataSourceProxy(@Qualifier("originStorage") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "account")
public DataSourceProxy payDataSourceProxy(@Qualifier("originAccount") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(dataSource);
}
@Bean("dynamicDataSource")
public DataSource dynamicDataSource(@Qualifier("order") DataSource dataSourceOrder,
@Qualifier("storage") DataSource dataSourceStorage,
@Qualifier("account") DataSource dataSourcePay) {
DynamicRoutingDataSource dynamicRoutingDataSource = new DynamicRoutingDataSource();
// 数据源的集合
Map<Object, Object> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>(3);
dataSourceMap.put(DataSourceKey.ORDER.name(), dataSourceOrder);
dataSourceMap.put(DataSourceKey.STORAGE.name(), dataSourceStorage);
dataSourceMap.put(DataSourceKey.ACCOUNT.name(), dataSourcePay);
dynamicRoutingDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dataSourceOrder);
dynamicRoutingDataSource.setTargetDataSources(dataSourceMap);
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKeys().addAll(dataSourceMap.keySet());
return dynamicRoutingDataSource;
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis")
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(@Qualifier("dynamicDataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
}
@Slf4j
public class DynamicRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
log.info("当前数据源 [{}]", DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey());
return DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceKey();
}
}
public class DynamicDataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal<String> CONTEXT_HOLDER = ThreadLocal.withInitial(DataSourceKey.ORDER::name);
private static List<Object> dataSourceKeys = new ArrayList<>();
public static void setDataSourceKey(DataSourceKey key) {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.set(key.name());
}
public static String getDataSourceKey() {
return CONTEXT_HOLDER.get();
}
public static void clearDataSourceKey() {
CONTEXT_HOLDER.remove();
}
public static List<Object> getDataSourceKeys() {
return dataSourceKeys;
}
}
3)接入seata配置
registry.conf中指定registry.type=“file” , config.type=“file” ,对应seata-server的registry.conf配置相同
registry {
# file 、nacos 、eureka、redis、zk、consul、etcd3、sofa
type = "file"
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}
config {
# file、nacos 、apollo、zk、consul、etcd3、springCloudConfig
type = "file"
file {
name = "file.conf"
}
}
4)指定seata事务分组,用于获取seata server服务实例
# Seata事务分组 从file.conf获取service.vgroupMapping.my_test_tx_group的集群名称default,用于确定seata server的服务实例
spring.cloud.alibaba.seata.tx-service-group=my_test_tx_group
5)OrderServiceImpl作为发起者配置@GlobalTransactional注解
@Override
//@Transactional
@GlobalTransactional(name="createOrder")
public Order saveOrder(OrderVo orderVo){
log.info("=============用户下单=================");
//切换数据源
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceKey(DataSourceKey.ORDER);
log.info("当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 保存订单
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(orderVo.getUserId());
order.setCommodityCode(orderVo.getCommodityCode());
order.setCount(orderVo.getCount());
order.setMoney(orderVo.getMoney());
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.INIT.getValue());
Integer saveOrderRecord = orderMapper.insert(order);
log.info("保存订单{}", saveOrderRecord > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
//扣减库存
storageService.deduct(orderVo.getCommodityCode(),orderVo.getCount());
//扣减余额
accountService.debit(orderVo.getUserId(),orderVo.getMoney());
log.info("=============更新订单状态=================");
//切换数据源
DynamicDataSourceContextHolder.setDataSourceKey(DataSourceKey.ORDER);
//更新订单
Integer updateOrderRecord = orderMapper.updateOrderStatus(order.getId(),OrderStatus.SUCCESS.getValue());
log.info("更新订单id:{} {}", order.getId(), updateOrderRecord > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
return order;
}
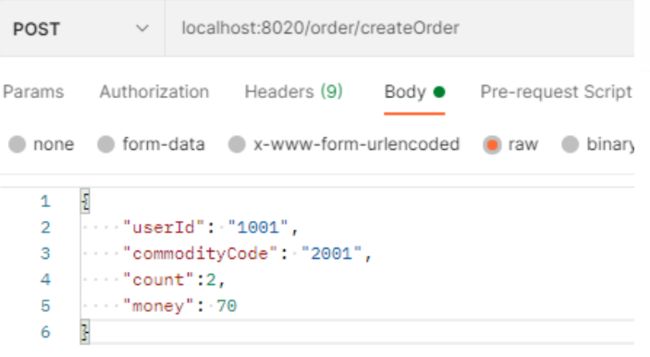
测试成功场景
调用 /order/createOrder 接口,将 money 设置为 10,此时余额为 20,可以下单成功

测试失败场景
设置 money 为 100,此时余额不足,会下单失败,account-service会抛出异常,事务会回滚

接入微服务应用
业务场景:
- 用户下单,整个业务逻辑由三个微服务构成:
- 仓储服务:对给定的商品扣除库存数量。
- 订单服务:根据采购需求创建订单。
- 帐户服务:从用户帐户中扣除余额。

1)启动Seata server端,Seata server使用nacos作为配置中心和注册中心
2)配置微服务整合seata
第一步:添加pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-seataartifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.seatagroupId>
<artifactId>seata-allartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seatagroupId>
<artifactId>seata-allartifactId>
<version>1.4.0version>
dependency>
第二步: 微服务对应数据库中添加undo_log表
CREATE TABLE `undo_log` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`branch_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`xid` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`context` varchar(128) NOT NULL,
`rollback_info` longblob NOT NULL,
`log_status` int(11) NOT NULL,
`log_created` datetime NOT NULL,
`log_modified` datetime NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `ux_undo_log` (`xid`,`branch_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
第三步:添加代理数据源配置,配置DataSourceProxy
/**
* @author Fox
*
* 需要用到分布式事务的微服务都需要使用seata DataSourceProxy代理自己的数据源
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan("com.tuling.datasource.mapper")
public class MybatisConfig {
/**
* 从配置文件获取属性构造datasource,注意前缀,这里用的是druid,根据自己情况配置,
* 原生datasource前缀取"spring.datasource"
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid")
public DataSource druidDataSource() {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
return druidDataSource;
}
/**
* 构造datasource代理对象,替换原来的datasource
* @param druidDataSource
* @return
*/
@Primary
@Bean("dataSource")
public DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy(DataSource druidDataSource) {
return new DataSourceProxy(druidDataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSourceProxy dataSourceProxy) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
//设置代理数据源
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSourceProxy);
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
factoryBean.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources("classpath*:mybatis/**/*-mapper.xml"));
org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration configuration=new org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration();
//使用jdbc的getGeneratedKeys获取数据库自增主键值
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(true);
//使用列别名替换列名
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(true);
//自动使用驼峰命名属性映射字段,如userId ---> user_id
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true);
factoryBean.setConfiguration(configuration);
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
}
第四步:启动类上剔除DataSourceAutoConfiguration,用于解决数据源的循环依赖问题
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.tuling",exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableFeignClients
public class OrderServiceApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderServiceApplication.class, args);
}
}
第五步:修改register.conf,配置nacos作为registry.type&config.type,对应seata server也使用nacos
注意:需要指定group = “SEATA_GROUP”,因为Seata Server端指定了group = “SEATA_GROUP” ,必须保证一致
registry {
# file 、nacos 、eureka、redis、zk、consul、etcd3、sofa
type = "nacos"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost"
namespace = ""
cluster = "default"
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
}
}
config {
# file、nacos 、apollo、zk、consul、etcd3、springCloudConfig
type = "nacos"
nacos {
serverAddr = "localhost"
namespace = ""
group = "SEATA_GROUP"
}
}
如果出现这种问题:
![]()
一般大多数情况下都是因为配置不匹配导致的:
- 检查现在使用的seata服务和项目maven中seata的版本是否一致
- 检查tx-service-group,nacos.cluster,nacos.group参数是否和Seata Server中的配置一致
跟踪源码:seata/discover包下实现了RegistryService#lookup,用来获取服务列表
NacosRegistryServiceImpl#lookup
》String clusterName = getServiceGroup(key); #获取seata server集群名称
》List<Instance> firstAllInstances = getNamingInstance().getAllInstances(getServiceName(), getServiceGroup(), clusters)
第六步:修改application.yml配置
配置seata 服务事务分组,要与服务端nacos配置中心中service.vgroup_mapping的后缀对应
server:
port: 8020
spring:
application:
name: order-service
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
alibaba:
seata:
tx-service-group:
my_test_tx_group # seata 服务事务分组
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/seata_order?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root
initial-size: 10
max-active: 100
min-idle: 10
max-wait: 60000
pool-prepared-statements: true
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000
test-while-idle: true
test-on-borrow: false
test-on-return: false
stat-view-servlet:
enabled: true
url-pattern: /druid/*
filter:
stat:
log-slow-sql: true
slow-sql-millis: 1000
merge-sql: false
wall:
config:
multi-statement-allow: true
第七步:微服务发起者(TM 方)需要添加@GlobalTransactional注解
@Override
//@Transactional
@GlobalTransactional(name="createOrder")
public Order saveOrder(OrderVo orderVo){
log.info("=============用户下单=================");
log.info("当前 XID: {}", RootContext.getXID());
// 保存订单
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(orderVo.getUserId());
order.setCommodityCode(orderVo.getCommodityCode());
order.setCount(orderVo.getCount());
order.setMoney(orderVo.getMoney());
order.setStatus(OrderStatus.INIT.getValue());
Integer saveOrderRecord = orderMapper.insert(order);
log.info("保存订单{}", saveOrderRecord > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
//扣减库存
storageFeignService.deduct(orderVo.getCommodityCode(),orderVo.getCount());
//扣减余额
accountFeignService.debit(orderVo.getUserId(),orderVo.getMoney());
//更新订单
Integer updateOrderRecord = orderMapper.updateOrderStatus(order.getId(),OrderStatus.SUCCESS.getValue());
log.info("更新订单id:{} {}", order.getId(), updateOrderRecord > 0 ? "成功" : "失败");
return order;
}