Java进阶(下篇2)
Java进阶(下篇2)
- 一、IO流
-
- 01.File类的使用
-
- 1.1、File类的实例化
- 1.2、File类的常用方法1
- 1.3、File类的常用方法2
- 1.4、课后练习
- 02、IO流原理及流的分类
-
- 2.1、IO流原理
- 2.2、流的分类
- 2.3、IO 流体系 P586
- 03、节点流(或文件流)
-
- 3.1、FileReader读入数据的基本操作
- 3.2、FileReader中使用read(char[] cbuf)读入数据
- 3.3、FileWriter写出数据的操作
- 3.4、使用FileReader和FileWriter实现文本文件的复制
- 3.5、使用FileInputStream不能读取文本文件的测试
- 3.6、使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream读写非文本文件
- 3.7、使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream复制文件的方法测试
- 04、缓冲流
-
- 4.1、缓冲流(字节型)实现非文本文件的复制
- 4.2、缓冲流与节点流读写速度对比
- 4.3、缓冲流(字符型)实现文本文件的复制
- 5.4、缓冲流课后练习
- 05、转换流
-
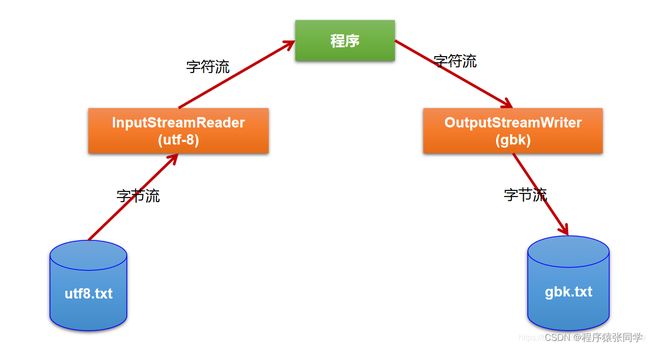
- 5.1、转换流概述与InputStreamReader的使用
- 5.2、转换流实现文件的读入和写出
- 5.3、多种字符编码集的说明
- 06、标准输入、输出流
- 07、打印流
- 08、数据流
- 09、对象流
-
- 9.1、对象序列化机制的理解
- 9.2、对象流序列化与反序列化字符串操作
- 9.3、自定义类实现序列化与反序列化操作
- 9.4、serialVersionUID的理解
- 9.5、自定义类可序列化的其它要求
- 10.随机存取文件流
-
- 10.1、RandomAccessFile实现数据的读写操作
- 10.2、RandomAccessFile实现数据的插入操作
- 11、NIO.2中Path、Paths、Files类的使用
- 二、网络编程
-
- 01、网络编程概述
- 02、网络通信要素概述
- 03、通信要素1:IP和端口号
-
- 3.1、IP的理解与InetAddress类的实例化
- 3.2、端口号的理解
- 04、通信要素2:网络协议
-
- 4.1、TCP和UDP网络通信协议的对比
- 05、TCP网络编程
- 06、UDP网络编程
-
- 7.2、URL网络编程实现Tomcat服务端数据下载
- 7.3、URI、URL和URN的区别
- 三、反射与动态代理
-
- 01、Java反射机制概述
-
- 1.1、使用反射,实现同上的操作
- 1.2、反射的强大:调用类的私有结构
- 02、理解Class类并获取Class实例
-
- 2.3、Class类的理解
一、IO流
01.File类的使用
1.1、File类的实例化
P585
- java.io.File类:文件和文件目录路径的抽象表示形式,与平台无关
- File 能新建、删除、重命名文件和目录,但File 不能访问文件内容本身。如果需要访问文件内容本身,则需要使用输入/输出流。
- 想要在Java程序中表示一个真实存在的文件或目录,那么必须有一个File对象,但是Java程序中的一个File对象,可能没有一个真实存在的文件或目录。
- File对象可以作为参数传递给流的构造器
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
/**
* File类的使用
*
* 1. File类的一个对象,代表一个文件或一个文件目录(俗称:文件夹)
* 2. File类声明在java.io包下
*
*/
public class FileTest {
/**
* 1.如何创建file类的实例
* File(String filePath):以filePath为路径创建File对象,可以是绝对路径或者相对路径
* File(String parentPath,String childPath):以parentPath为父路径,childPath为子路径创建File对象。
* File(File parentFile,String childPath):根据一个父File对象和子文件路径创建File对象
* 2.
* 相对路径:相较于某个路径下,指明的路径。
* 绝对路径:包含盘符在内的文件或文件目录的路径
*
* 3.路径分隔符
* windows:\\
* unix:/
* 4.Java程序支持跨平台运行,因此路径分隔符要慎用。
*
* 5.为了解决这个隐患,File类提供了一个常量:
* public static final String separator。
* 根据操作系统,动态的提供分隔符。
*
* File file1= new File("d:\\Work\\info.txt");
* File file2= new File("d:"+ File.separator+ "Work"+ File.separator+ "info.txt");
* File file3= new File("d:/Work");
*
*/
@Test
public void test(){
//构造器1:
File file1 = new File("hello.txt");//相对于当前module
File file2 = new File("F:\\java\\Work2\\JavaSenior\\day08\\num.txt");
System.out.println(file1);
System.out.println(file2);
//构造器2:
File file3 = new File("D:\\workspace_idea1","JavaSenior");
System.out.println(file3);
//构造器3:
File file4 = new File(file3,"hi.txt");
System.out.println(file4);
}
}
1.2、File类的常用方法1
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* File类的使用
*
* 1. File类的一个对象,代表一个文件或一个文件目录(俗称:文件夹)
* 2. File类声明在java.io包下
*/
public class FileTest {
/**
* public String getAbsolutePath():获取绝对路径
* public String getPath() :获取路径
* public String getName() :获取名称
* public String getParent():获取上层文件目录路径。若无,返回null
* public long length() :获取文件长度(即:字节数)。不能获取目录的长度。
* public long lastModified() :获取最后一次的修改时间,毫秒值
*
* 如下的两个方法适用于文件目录:
* public String[] list() :获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的名称数组
* public File[] listFiles() :获取指定目录下的所有文件或者文件目录的File数组
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
File file = new File("Hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("F:\\java\\Work2\\JavaSenior\\day08\\num.txt");
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(file.getPath());
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file.length());
System.out.println(new Date(file.lastModified()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println(file2.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(file2.getPath());
System.out.println(file2.getName());
System.out.println(file2.getParent());
System.out.println(file2.length());
System.out.println(file2.lastModified());
}
@Test
public void test3(){
//文件需存在!!!
File file = new File("F:\\java\\Work2\\JavaSenior");
String[] list = file.list();
for(String s : list){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println();
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for(File f : files){
System.out.println(f);
}
}
/**
* File类的重命名功能
*
* public boolean renameTo(File dest):把文件重命名为指定的文件路径
* 比如:file1.renameTo(file2)为例:
* 要想保证返回true,需要file1在硬盘中是存在的,且file2不能在硬盘中存在。
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
File file1 = new File("hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:\\book\\num.txt");
boolean renameTo = file2.renameTo(file1);
System.out.println(renameTo);
}
}
1.3、File类的常用方法2
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* File类的使用
*
* 1. File类的一个对象,代表一个文件或一个文件目录(俗称:文件夹)
* 2. File类声明在java.io包下
* 3. File类中涉及到关于文件或文件目录的创建、删除、重命名、修改时间、文件大小等方法,
* 并未涉及到写入或读取文件内容的操作。如果需要读取或写入文件内容,必须使用IO流来完成。
* 4. 后续File类的对象常会作为参数传递到流的构造器中,指明读取或写入的"终点".
*/
public class FileTest {
/**
* public boolean isDirectory():判断是否是文件目录
* public boolean isFile() :判断是否是文件
* public boolean exists() :判断是否存在
* public boolean canRead() :判断是否可读
* public boolean canWrite() :判断是否可写
* public boolean isHidden() :判断是否隐藏
*/
@Test
public void test5(){
File file1 = new File("hello.txt");
file1 = new File("hello1.txt");
System.out.println(file1.isDirectory());
System.out.println(file1.isFile());
System.out.println(file1.exists());
System.out.println(file1.canRead());
System.out.println(file1.canWrite());
System.out.println(file1.isHidden());
System.out.println();
File file2 = new File("D:\\book");
file2 = new File("D:\\book1");
System.out.println(file2.isDirectory());
System.out.println(file2.isFile());
System.out.println(file2.exists());
System.out.println(file2.canRead());
System.out.println(file2.canWrite());
System.out.println(file2.isHidden());
}
/**
* 创建硬盘中对应的文件或文件目录
* public boolean createNewFile() :创建文件。若文件存在,则不创建,返回false
* public boolean mkdir() :创建文件目录。如果此文件目录存在,就不创建了。如果此文件目录的上层目录不存在,也不创建。
* public boolean mkdirs() :创建文件目录。如果此文件目录存在,就不创建了。如果上层文件目录不存在,一并创建
*
* 删除磁盘中的文件或文件目录
* public boolean delete():删除文件或者文件夹
* 删除注意事项:Java中的删除不走回收站。
*/
@Test
public void test6() throws IOException {
File file1 = new File("hi.txt");
if(!file1.exists()){
//文件的创建
file1.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功");
}else{//文件存在
file1.delete();
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}
@Test
public void test7(){
//文件目录的创建
File file1 = new File("d:\\io\\io1\\io3");
boolean mkdir = file1.mkdir();
if(mkdir){
System.out.println("创建成功1");
}
File file2 = new File("d:\\io\\io1\\io4");
boolean mkdir1 = file2.mkdirs();
if(mkdir1){
System.out.println("创建成功2");
}
//要想删除成功,io4文件目录下不能有子目录或文件
File file3 = new File("D:\\io\\io1\\io4");
file3 = new File("D:\\io\\io1");
System.out.println(file3.delete());
}
}
1.4、课后练习
1、FileTest类
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 1. 利用File构造器,new一个文件目录file
* 1)在其中创建多个文件和目录
* 2)编写方法,实现删除file中指定文件的操作
*/
public class FileTest {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\\io\\io1\\hello.txt");
//创建一个与file同目录下的另外一个文件,文件名为:haha.txt
File destFile = new File(file.getParent(),"haha.txt");
boolean newFile = destFile.createNewFile();
if(newFile){
System.out.println("创建成功!");
}
}
}
2、FindJPGFileTest类
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
/**
* 2.判断指定目录下是否有后缀名为.jpg的文件,如果有,就输出该文件名称
*/
public class FindJPGFileTest {
@Test
public void test(){
File srcFile = new File("d:\\code");
String[] fileNames = srcFile.list();
for(String fileName : fileNames){
if(fileName.endsWith(".jpg")){
System.out.println(fileName);
}
}
}
@Test
public void test2(){
File srcFile = new File("d:\\code");
File[] listFiles = srcFile.listFiles();
for(File file : listFiles){
if(file.getName().endsWith(".jpg")){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
/**
* File类提供了两个文件过滤器方法
* public String[] list(FilenameFilter filter)
* public File[] listFiles(FileFilter filter)
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
File srcFile = new File("d:\\code");
File[] subFiles = srcFile.listFiles(new FilenameFilter() {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
return name.endsWith(".jpg");
}
});
for(File file : subFiles){
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
3、ListFilesTest类
import java.io.File;
/**
* 3. 遍历指定目录所有文件名称,包括子文件目录中的文件。
* 拓展1:并计算指定目录占用空间的大小
* 拓展2:删除指定文件目录及其下的所有文件
*/
public class ListFilesTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 递归:文件目录
/** 打印出指定目录所有文件名称,包括子文件目录中的文件 */
// 1.创建目录对象
File dir = new File("E:\\teach\\01_javaSE\\_尚硅谷Java编程语言\\3_软件");
// 2.打印目录的子文件
printSubFile(dir);
}
public static void printSubFile(File dir) {
// 打印目录的子文件
File[] subfiles = dir.listFiles();
for (File f : subfiles) {
if (f.isDirectory()) {// 文件目录
printSubFile(f);
} else {// 文件
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}
// 方式二:循环实现
// 列出file目录的下级内容,仅列出一级的话
// 使用File类的String[] list()比较简单
public void listSubFiles(File file) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
String[] all = file.list();
for (String s : all) {
System.out.println(s);
}
} else {
System.out.println(file + "是文件!");
}
}
// 列出file目录的下级,如果它的下级还是目录,接着列出下级的下级,依次类推
// 建议使用File类的File[] listFiles()
public void listAllSubFiles(File file) {
if (file.isFile()) {
System.out.println(file);
} else {
File[] all = file.listFiles();
// 如果all[i]是文件,直接打印
// 如果all[i]是目录,接着再获取它的下一级
for (File f : all) {
listAllSubFiles(f);// 递归调用:自己调用自己就叫递归
}
}
}
// 拓展1:求指定目录所在空间的大小
// 求任意一个目录的总大小
public long getDirectorySize(File file) {
// file是文件,那么直接返回file.length()
// file是目录,把它的下一级的所有大小加起来就是它的总大小
long size = 0;
if (file.isFile()) {
size += file.length();
} else {
File[] all = file.listFiles();// 获取file的下一级
// 累加all[i]的大小
for (File f : all) {
size += getDirectorySize(f);// f的大小;
}
}
return size;
}
// 拓展2:删除指定的目录
public void deleteDirectory(File file) {
// 如果file是文件,直接delete
// 如果file是目录,先把它的下一级干掉,然后删除自己
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] all = file.listFiles();
// 循环删除的是file的下一级
for (File f : all) {// f代表file的每一个下级
deleteDirectory(f);
}
}
// 删除自己
file.delete();
}
}
02、IO流原理及流的分类
2.1、IO流原理
- I/O是Input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理设备之间的数据传输。如读/写文件,网络通讯等。
- Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以“流(stream)”的方式进行。
- java.io包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过标准的方法输入或输出数据。
- 输入input:读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
- 输出output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中。

2.2、流的分类
- 按操作数据单位不同分为:字节流(8 bit),字符流(16 bit)
- 按数据流的流向不同分为:输入流,输出流
- 按流的角色的不同分为:节点流,处理流
抽象基类 字节流 字符流
输入流 InputStream Reader
输出流 OutputStream Writer

1.Java的IO流共涉及40多个类,实际上非常规则,都是从如下4个抽象基类派生的。
2.由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀。
2.3、IO 流体系 P586
03、节点流(或文件流)
3.1、FileReader读入数据的基本操作
1、读取文件【四个步骤】
1.建立一个流对象,将已存在的一个文件加载进流。
FileReaderfr= new FileReader(new File(“Test.txt”));
2.创建一个临时存放数据的数组。
char[] ch= new char[1024];
3.调用流对象的读取方法将流中的数据读入到数组中。
fr.read(ch);
4.关闭资源。
fr.close();
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 一、流的分类:
* 1.操作数据单位:字节流、字符流
* 2.数据的流向:输入流、输出流
* 3.流的角色:节点流、处理流
*
* 二、流的体系结构
* 抽象基类 节点流(或文件流) 缓冲流(处理流的一种)
* InputStream FileInputStream (read(byte[] buffer)) BufferedInputStream (read(byte[] buffer))
* OutputStream FileOutputStream (write(byte[] buffer,0,len) BufferedOutputStream (write(byte[] buffer,0,len) / flush()
* Reader FileReader (read(char[] cbuf)) BufferedReader (read(char[] cbuf) / readLine())
* Writer FileWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len) BufferedWriter (write(char[] cbuf,0,len) / flush()
*/
public class FileReaderWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("hello.txt");//相较于当前工程
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
File file1 = new File("day09\\hello.txt");
System.out.println(file1.getAbsolutePath());
}
/**
* 将day09下的hello.txt文件内容读入程序中,并输出到控制台
*
* 说明点:
* 1. read()的理解:返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1
* 2. 异常的处理:为了保证流资源一定可以执行关闭操作。需要使用try-catch-finally处理
* 3. 读入的文件一定要存在,否则就会报FileNotFoundException。
*
*/
@Test
public void test(){
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//实例化File对象,指明要操作的文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");//相较于当前的Module
//2.提供具体的流
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.数据的读入过程
//read():返回读入的一个字符。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1.
//方式一:
// int data = fr.read();
// while(data != -1){
// System.out.print((char) data);
// data = fr.read();
// }
//方式二:语法上针对于方式一的修改
int data;
while((data = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//4.流的关闭操作
// try {
// if(fr != null)
// fr.close();
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//或
if(fr != null){
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3.2、FileReader中使用read(char[] cbuf)读入数据
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileReaderWriterTest {
//对read()操作升级:使用read的重载方法
@Test
public void test2(){
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//1.File类的实例化
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.FileReader流的实例化
fr = new FileReader(file);
//3.读入的操作
//read(char[] cbuf):返回每次读入cbuf数组中的字符的个数。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
int len;
fr.read(cbuf);
while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){
//方式一:
//错误的写法
// for(int i = 0;i < cbuf.length;i++){
// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);
// }
//正确的写法
// for(int i = 0;i < len;i++){
// System.out.print(cbuf[i]);
// }
//方式二:
//错误的写法,对应着方式一的错误的写法
// String str = new String(cbuf);
// System.out.print(str);
//正确的写法
String str = new String(cbuf,0,len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fr != null){
//4.资源的关闭
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3.3、FileWriter写出数据的操作
1、写入文件
1.创建流对象,建立数据存放文件
FileWriterfw= new FileWriter(new File(“Test.txt”));
2.调用流对象的写入方法,将数据写入流
fw.write(“atguigu-songhongkang”);
3.关闭流资源,并将流中的数据清空到文件中。
fw.close();
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class FileReaderWriterTest {
/**
* 从内存中写出数据到硬盘的文件里。
*
* 说明:
* 1.输出操作,对应的File可以不存在的。并不会报异常
* 2.
* File对应的硬盘中的文件如果不存在,在输出的过程中,会自动创建此文件。
* File对应的硬盘中的文件如果存在:
* 如果流使用的构造器是:FileWriter(file,false) / FileWriter(file):对原有文件的覆盖
* 如果流使用的构造器是:FileWriter(file,true):不会对原有文件覆盖,而是在原有文件基础上追加内容
*/
@Test
public void test3(){
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//1.提供File类的对象,指明写出到的文件
File file = new File("hello1.txt");
//2.提供FileWriter的对象,用于数据的写出
fw = new FileWriter(file,false);
//3.写出的操作
fw.write("I have a dream!\n");
fw.write("you need to have a dream!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.流资源的关闭
if(fw != null){
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3.4、使用FileReader和FileWriter实现文本文件的复制
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class FileReaderWriterTest {
@Test
public void test4() {
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
//1.创建File类的对象,指明读入和写出的文件
File srcFile = new File("hello1.txt");
File srcFile2 = new File("hello2..txt");
//不能使用字符流来处理图片等字节数据
// File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg");
// File srcFile2 = new File("爱情与友情1.jpg");
//2.创建输入流和输出流的对象
fr = new FileReader(srcFile);
fw = new FileWriter(srcFile2);
//3.数据的读入和写出操作
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
int len;//记录每次读入到cbuf数组中的字符的个数
while((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1){
//每次写出len个字符
fw.write(cbuf,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.关闭流资源
//方式一:
// try {
// if(fw != null)
// fw.close();
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }finally{
// try {
// if(fr != null)
// fr.close();
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
//方式二:
try {
if(fw != null)
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(fr != null)
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.5、使用FileInputStream不能读取文本文件的测试
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 测试FileInputStream和FileOutputStream的使用
*
* 结论:
* 1. 对于文本文件(.txt,.java,.c,.cpp),使用字符流处理
* 2. 对于非文本文件(.jpg,.mp3,.mp4,.avi,.doc,.ppt,...),使用字节流处理
*/
public class FileIOPutTest {
//使用字节流FileInputStream处理文本文件,可能出现乱码。
@Test
public void testFileInputStream(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File file = new File("hello.txt");
//2.造流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
//3.读数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len;//记录每次读取的字节的个数
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
String str = new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fis != null) {
//4.关闭资源
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3.6、使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream读写非文本文件
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileIOPutTest {
/**
* 实现对图片的复制操作
*/
@Test
public void testFileInputOutputStream() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg");
File destFile = new File("爱情与友情2.jpg");
//2.造流
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//3.复制的过程
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len;
//4.读数据
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("复制成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fos != null){
//5.关闭资源
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3.7、使用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream复制文件的方法测试
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileIOPutTest {
//指定路径下文件的复制
public void copyFile(String srcPath,String destPath){
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
//
File srcFile = new File(srcPath);
File destFile = new File(destPath);
//
fis = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//复制的过程
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fos != null){
//
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void testCopyFile(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\29433\\Desktop\\164.jpg";
// String destPath = "C:\\Users\\29433\\Desktop\\164.jpg";
String srcPath = "hello.txt";
String destPath = "hello3.txt";
copyFile(srcPath,destPath);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//1
}
}
04、缓冲流
- 为了提高数据读写的速度,Java
API提供了带缓冲功能的流类,在使用这些流类时,会创建一个内部缓冲区数组,缺省使用8192个字节(8Kb)的缓冲区。

- 缓冲流要“套接”在相应的节点流之上,根据数据操作单位可以把缓冲流分为:
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter - 当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直接访问缓冲区
- 当使用BufferedInputStream读取字节文件时,BufferedInputStream会一次性从文件中读取8192个(8Kb),存在缓冲区中,直到缓冲区装满了,才重新从文件中读取下一个8192个字节数组。
- 向流中写入字节时,不会直接写到文件,先写到缓冲区中直到缓冲区写满,BufferedOutputStream才会把缓冲区中的数据一次性写到文件里。使用方法flush()可以强制将缓冲区的内容全部写入输出流
- 关闭流的顺序和打开流的顺序相反。只要关闭最外层流即可,关闭最外层流也会相应关闭内层节点流
- flush()方法的使用:手动将buffer中内容写入文件
- 如果是带缓冲区的流对象的close()方法,不但会关闭流,还会在关闭流之前刷新缓冲区,关闭后不能再写出。

4.1、缓冲流(字节型)实现非文本文件的复制
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 处理流之一:缓冲流的使用
*
* 1.缓冲流:
* BufferedInputStream
* BufferedOutputStream
* BufferedReader
* BufferedWriter
*/
public class BufferedTest {
/**
* 实现非文本文件的复制
*/
@Test
public void BufferedStreamTest(){
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File srcFile = new File("爱情与友情.jpg");
File destFile = new File("爱情与友情3.jpg");
//2.造流
//2.1 造节点流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile));
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//2.2 造缓冲流
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3.复制的细节:读取、写入
byte[] buffer = new byte[10];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
bos.write(buffer,0,len);
// bos.flush();//刷新缓冲区
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.资源关闭
//要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(bis != null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略.
// fos.close();
// fis.close();
}
}
}
4.2、缓冲流与节点流读写速度对比
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 处理流之一:缓冲流的使用
*
* 1.缓冲流:
* BufferedInputStream
* BufferedOutputStream
* BufferedReader
* BufferedWriter
*
* 2.作用:提供流的读取、写入的速度
* 提高读写速度的原因:内部提供了一个缓冲区
*
* 3. 处理流,就是“套接”在已有的流的基础上。
*
*/
public class BufferedTest {
//实现文件复制的方法
public void copyFileWithBuffered(String srcPath,String destPath){
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//1.造文件
File srcFile = new File(srcPath);
File destFile = new File(destPath);
//2.造流
//2.1 造节点流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream((srcFile));
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//2.2 造缓冲流
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//3.复制的细节:读取、写入
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
bos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.资源关闭
//要求:先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(bis != null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层流也会自动的进行关闭。关于内层流的关闭,我们可以省略.
// fos.close();
// fis.close();
}
}
@Test
public void testCopyFileWithBuffered(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String srcPath = "C:\\Users\\29433\\Desktop\\book.flv";
String destPath = "C:\\Users\\29433\\Desktop\\book1.flv";
copyFileWithBuffered(srcPath,destPath);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("复制操作花费的时间为:" + (end - start));//1
}
}
4.3、缓冲流(字符型)实现文本文件的复制
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedTest {
/**
* 使用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter实现文本文件的复制
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
//创建文件和相应的流
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File("dbcp.txt")));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(new File("dbcp1.txt")));
//读写操作
//方式一:使用char[]数组
// char[] cbuf = new char[1024];
// int len;
// while((len = br.read(cbuf)) != -1){
// bw.write(cbuf,0,len);
// // bw.flush();
// }
//方式二:使用String
String data;
while((data = br.readLine()) != null){
//方法一:
// bw.write(data + "\n");//data中不包含换行符
//方法二:
bw.write(data);//data中不包含换行符
bw.newLine();//提供换行的操作
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
if(bw != null){
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(br != null){
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
5.4、缓冲流课后练习
1、练习2
package git;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class PicTest {
//图片的加密
@Test
public void test() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("爱情与友情.jpg");
fos = new FileOutputStream("爱情与友情secret.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[20];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
//字节数组进行修改
//错误的
// for(byte b : buffer){
// b = (byte) (b ^ 5);
// }
//正确的
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
buffer[i] = (byte) (buffer[i] ^ 5);
}
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//图片的解密
@Test
public void test2() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream("爱情与友情secret.jpg");
fos = new FileOutputStream("爱情与友情4.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[20];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
//字节数组进行修改
//错误的
// for(byte b : buffer){
// b = (byte) (b ^ 5);
// }
//正确的
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
buffer[i] = (byte) (buffer[i] ^ 5);
}
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
2、练习3
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* 练习3:获取文本上字符出现的次数,把数据写入文件
*
* 思路:
* 1.遍历文本每一个字符
* 2.字符出现的次数存在Map中
*
* Map map = new HashMap();
* map.put('a',18);
* map.put('你',2);
*
* 3.把map中的数据写入文件
*/
public class WordCount {
/**
* 说明:如果使用单元测试,文件相对路径为当前module
* 如果使用main()测试,文件相对路径为当前工程
*/
@Test
public void testWordCount() {
FileReader fr = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
//1.创建Map集合
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
//2.遍历每一个字符,每一个字符出现的次数放到map中
fr = new FileReader("dbcp.txt");
int c = 0;
while ((c = fr.read()) != -1) {
//int 还原 char
char ch = (char) c;
// 判断char是否在map中第一次出现
if (map.get(ch) == null) {
map.put(ch, 1);
} else {
map.put(ch, map.get(ch) + 1);
}
}
//3.把map中数据存在文件count.txt
//3.1 创建Writer
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("wordcount.txt"));
//3.2 遍历map,再写入数据
Set<Map.Entry<Character, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Character, Integer> entry : entrySet) {
switch (entry.getKey()) {
case ' ':
bw.write("空格=" + entry.getValue());
break;
case '\t'://\t表示tab 键字符
bw.write("tab键=" + entry.getValue());
break;
case '\r'://
bw.write("回车=" + entry.getValue());
break;
case '\n'://
bw.write("换行=" + entry.getValue());
break;
default:
bw.write(entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue());
break;
}
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.关流
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (bw != null) {
try {
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
05、转换流
5.1、转换流概述与InputStreamReader的使用
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* 处理流之二:转换流的使用
* 1.转换流:属于字符流
* InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
* OutputStreamWriter:将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
*
* 2.作用:提供字节流与字符流之间的转换
*
* 3.解码:字节、字节数组 --->字符数组、字符串
* 编码:字符数组、字符串 ---> 字节、字节数组
*
* 4.字符集
*/
public class InputStreamReaderTest {
/**
* 此时处理异常的话,仍然应该使用try-catch-finally
* InputStreamReader的使用,实现字节的输入流到字符的输入流的转换
*/
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("dbcp.txt");
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);//使用系统默认的字符集
//参数2指明了字符集,具体使用哪个字符集,取决于文件dbcp.txt保存时使用的字符集
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"UTF-8");//使用系统默认的字符集
char[] cbuf = new char[20];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){
String str = new String(cbuf,0,len);
System.out.print(str);
}
isr.close();
}
}
5.2、转换流实现文件的读入和写出
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 处理流之二:转换流的使用
* 1.转换流:属于字符流
* InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
* OutputStreamWriter:将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
*
* 2.作用:提供字节流与字符流之间的转换
*
* 3.解码:字节、字节数组 --->字符数组、字符串
* 编码:字符数组、字符串 ---> 字节、字节数组
*
* 4.字符集
*/
public class InputStreamReaderTest {
/**
* 此时处理异常的话,仍然应该使用try-catch-finally
* 综合使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
//1.造文件、造流
File file1 = new File("dbcp.txt");
File file2 = new File("dbcp_gbk.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
//2.读写过程
char[] cbuf = new char[20];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(cbuf)) != -1){
osw.write(cbuf,0,len);
}
//3.关闭资源
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
}
5.3、多种字符编码集的说明
1、编码表的由来
计算机只能识别二进制数据,早期由来是电信号。为了方便应用计算机,让它可以识别各个国家的文字。就将各个国家的文字用数字来表示,并一一对应,形成一张表。这就是编码表。
2、常见的编码表
/**
* 4.字符集
* ASCII:美国标准信息交换码。
* 用一个字节的7位可以表示。
* ISO8859-1:拉丁码表。欧洲码表
* 用一个字节的8位表示。
* GB2312:中国的中文编码表。最多两个字节编码所有字符
* GBK:中国的中文编码表升级,融合了更多的中文文字符号。最多两个字节编码
* Unicode:国际标准码,融合了目前人类使用的所有字符。为每个字符分配唯一的字符码。所有的文字都用两个字节来表示。
* UTF-8:变长的编码方式,可用1-4个字节来表示一个字符。
*/
说明:
- Unicode不完美,这里就有三个问题, 一个是,我们已经知道,英文字母只用一个字节表示就够了,
第二个问题是如何才能区别Unicode和ASCII?计算机怎么知道两个字节表示一个符号,而不是分别表 示两个符号呢?
第三个,如果和GBK等双字节编码方式一样,用最高位是1或0表示两个字节和一个字节,就少了很多值无法用于表示字符,不够表示所有字符。Unicode在很长一段时间内无法推广,直到互联网的出现。- 面向传输的众多UTF(UCS Transfer
Format)标准出现了,顾名思义,**UTF-8就是每次8个位传输数据,而UTF-16就是每次16个位。**这是为传输而设计的编码,并使编码无国界,这样就可以显示全世界上所有文化的字符了。- Unicode只是定义了一个庞大的、全球通用的字符集,并为每个字符规定了唯一确定的编号,具体存储成什么样的字节流,取决于字符编码方案。推荐的Unicode编码是UTF-8和UTF-16。
06、标准输入、输出流
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
/**
* 其他流的使用
* 1.标准的输入、输出流
* 2.打印流
* 3.数据流
*/
public class OtherStreamTest {
/**
* 1.标准的输入、输出流
* 1.1
* System.in:标准的输入流,默认从键盘输入
* System.out:标准的输出流,默认从控制台输出
* 1.2
* System类的setIn(InputStream is) / setOut(PrintStream ps)方式重新指定输入和输出的流。
*
* 1.3练习:
* 从键盘输入字符串,要求将读取到的整行字符串转成大写输出。然后继续进行输入操作,
* 直至当输入“e”或者“exit”时,退出程序。
*
* 方法一:使用Scanner实现,调用next()返回一个字符串
* 方法二:使用System.in实现。System.in ---> 转换流 ---> BufferedReader的readLine()
*/
@Test
public void test(){
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
br = new BufferedReader(isr);
while (true) {
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
String data = br.readLine();
if ("e".equalsIgnoreCase(data) || "exit".equalsIgnoreCase(data)) {
System.out.println("程序结束");
break;
}
String upperCase = data.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(upperCase);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (br != null) {
try {
br.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
07、打印流
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class OtherStreamTest {
/**
* 2. 打印流:PrintStream 和PrintWriter
* 2.1 提供了一系列重载的print() 和 println()
* 2.2 练习:
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
PrintStream ps = null;
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\IO\\text.txt"));
// 创建打印输出流,设置为自动刷新模式(写入换行符或字节 '\n' 时都会刷新输出缓冲区)
ps = new PrintStream(fos, true);
if (ps != null) {// 把标准输出流(控制台输出)改成文件
System.setOut(ps);
}
for (int i = 0; i <= 255; i++) { // 输出ASCII字符
System.out.print((char) i);
if (i % 50 == 0) { // 每50个数据一行
System.out.println(); // 换行
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
}
}
}
08、数据流
boolean readBoolean() byte readByte()
char readChar() float readFloat()
double readDouble() short readShort()
long readLong() int readInt()
String readUTF() void readFully(byte[s] b)
- DataOutputStream中的方法
将上述的方法的read改为相应的write即可。
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class OtherStreamTest {
/**
* 3.数据流
* 3.1 DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream
* 3.2 作用:用于读取或写出基本数据类型的变量或字符串
*
* 练习:将内存中的字符串、基本数据类型的变量写出到文件中。
*
* 注意:处理异常的话,仍然应该使用try-catch-finally.
*/
@Test
public void test3() throws IOException {
//1.
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("data.txt"));
//2.
dos.writeUTF("刘刚");
dos.flush();//刷新操作,将内存中的数据写入文件
dos.writeInt(23);
dos.flush();
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.flush();
//3.
dos.close();
}
/**
* 将文件中存储的基本数据类型变量和字符串读取到内存中,保存在变量中。
*
* 注意点:读取不同类型的数据的顺序要与当初写入文件时,保存的数据的顺序一致!
*/
@Test
public void test4() throws IOException {
//1.
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data.txt"));
//2.
String name = dis.readUTF();
int age = dis.readInt();
boolean isMale = dis.readBoolean();
System.out.println("name = " + name);
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("isMale = " + isMale);
//3.
dis.close();
}
}
09、对象流
9.1、对象序列化机制的理解
9.2、对象流序列化与反序列化字符串操作
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 对象流的使用
* 1.ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream
* 2.作用:用于存储和读取基本数据类型数据或对象的处理流。它的强大之处就是可以把Java中的对象写入到数据源中,也能把对象从数据源中还原回来。
*/
public class ObjectTest {
/**
* 序列化过程:将内存中的java对象保存到磁盘中或通过网络传输出去
* 使用ObjectOutputStream实现
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
//创造流
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.dat"));
//制造对象
oos.writeObject(new String("秦始皇陵欢迎你"));
//刷新操作
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(oos != null){
//3.关闭流
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 反序列化:将磁盘文件中的对象还原为内存中的一个java对象
* 使用ObjectInputStream来实现
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.dat"));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
String str = (String) obj;
System.out.println(str);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
9.3、自定义类实现序列化与反序列化操作
1、Person类
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Person需要满足如下的要求,方可序列化
* 1.需要实现接口:Serializable
*/
public class Person implements Serializable {
public static final long serialVersionUID = 475463534532L;
private String name;
private int age;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
2、测试类
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 对象流的使用
* 1.ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream
* 2.作用:用于存储和读取基本数据类型数据或对象的处理流。它的强大之处就是可以把Java中的对象写入到数据源中,也能把对象从数据源中还原回来。
*
* 3.要想一个java对象是可序列化的,需要满足相应的要求。见Person.java
*
* 4.序列化机制:
* 对象序列化机制允许把内存中的Java对象转换成平台无关的二进制流,从而允许把这种
* 二进制流持久地保存在磁盘上,或通过网络将这种二进制流传输到另一个网络节点。
* 当其它程序获取了这种二进制流,就可以恢复成原来的Java对象。
*
*/
public class ObjectTest {
/**
* 序列化过程:将内存中的java对象保存到磁盘中或通过网络传输出去
* 使用ObjectOutputStream实现
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
//创造流
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.dat"));
//制造对象
oos.writeObject(new String("秦始皇陵欢迎你"));
//刷新操作
oos.flush();
oos.writeObject(new Person("李时珍",65));
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(oos != null){
//3.关闭流
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 反序列化:将磁盘文件中的对象还原为内存中的一个java对象
* 使用ObjectInputStream来实现
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.dat"));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
String str = (String) obj;
Person p = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(p);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
9.4、serialVersionUID的理解
1、Person类
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Person需要满足如下的要求,方可序列化
* 1.需要实现接口:Serializable
* 2.当前类提供一个全局常量:serialVersionUID
* 3.除了当前Person类需要实现Serializable接口之外,还必须保证其内部所有属性
* 也必须是可序列化的。(默认情况下,基本数据类型可序列化)
*
*
* 补充:ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream不能序列化static和transient修饰的成员变量
*/
public class Person implements Serializable {
public static final long serialVersionUID = 475463534532L;
private String name;
private int age;
private int id;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
2、测试类
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 对象流的使用
* 1.ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream
* 2.作用:用于存储和读取基本数据类型数据或对象的处理流。它的强大之处就是可以把Java中的对象写入到数据源中,也能把对象从数据源中还原回来。
*
* 3.要想一个java对象是可序列化的,需要满足相应的要求。见Person.java
*
* 4.序列化机制:
* 对象序列化机制允许把内存中的Java对象转换成平台无关的二进制流,从而允许把这种
* 二进制流持久地保存在磁盘上,或通过网络将这种二进制流传输到另一个网络节点。
* 当其它程序获取了这种二进制流,就可以恢复成原来的Java对象。
*
*/
public class ObjectTest {
/**
* 序列化过程:将内存中的java对象保存到磁盘中或通过网络传输出去
* 使用ObjectOutputStream实现
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
//创造流
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.dat"));
//制造对象
oos.writeObject(new String("秦始皇陵欢迎你"));
//刷新操作
oos.flush();
oos.writeObject(new Person("李时珍",65,0));
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(oos != null){
//3.关闭流
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 反序列化:将磁盘文件中的对象还原为内存中的一个java对象
* 使用ObjectInputStream来实现
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.dat"));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
String str = (String) obj;
Person p = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(p);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
9.5、自定义类可序列化的其它要求
1、Person类
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Person需要满足如下的要求,方可序列化
* 1.需要实现接口:Serializable
* 2.当前类提供一个全局常量:serialVersionUID
* 3.除了当前Person类需要实现Serializable接口之外,还必须保证其内部所有属性
* 也必须是可序列化的。(默认情况下,基本数据类型可序列化)
*
*
* 补充:ObjectOutputStream和ObjectInputStream不能序列化static和transient修饰的成员变量
*
*/
public class Person implements Serializable{
public static final long serialVersionUID = 475463534532L;
private String name;
private int age;
private int id;
private Account acct;
public Person(String name, int age, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
}
public Person(String name, int age, int id, Account acct) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
this.acct = acct;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", id=" + id +
", acct=" + acct +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
}
}
class Account implements Serializable{
public static final long serialVersionUID = 4754534532L;
private double balance;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public Account(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
2、测试类
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 对象流的使用
* 1.ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream
* 2.作用:用于存储和读取基本数据类型数据或对象的处理流。它的强大之处就是可以把Java中的对象写入到数据源中,也能把对象从数据源中还原回来。
*
* 3.要想一个java对象是可序列化的,需要满足相应的要求。见Person.java
*
* 4.序列化机制:
* 对象序列化机制允许把内存中的Java对象转换成平台无关的二进制流,从而允许把这种
* 二进制流持久地保存在磁盘上,或通过网络将这种二进制流传输到另一个网络节点。
* 当其它程序获取了这种二进制流,就可以恢复成原来的Java对象。
*/
public class ObjectTest {
/**
* 序列化过程:将内存中的java对象保存到磁盘中或通过网络传输出去
* 使用ObjectOutputStream实现
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
//创造流
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("object.dat"));
//制造对象
oos.writeObject(new String("秦始皇陵欢迎你"));
//刷新操作
oos.flush();
oos.writeObject(new Person("李时珍",65));
oos.flush();
oos.writeObject(new Person("张学良",23,1001,new Account(5000)));
oos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(oos != null){
//3.关闭流
try {
oos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 反序列化:将磁盘文件中的对象还原为内存中的一个java对象
* 使用ObjectInputStream来实现
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("object.dat"));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
String str = (String) obj;
Person p = (Person) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(p);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(ois != null){
try {
ois.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
10.随机存取文件流
10.1、RandomAccessFile实现数据的读写操作
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
/**
* RandomAccessFile的使用
* 1.RandomAccessFile直接继承于java.lang.Object类,实现了DataInput和DataOutput接口
* 2.RandomAccessFile既可以作为一个输入流,又可以作为一个输出流
* 3.如果RandomAccessFile作为输出流时,写出到的文件如果不存在,则在执行过程中自动创建。
* 如果写出到的文件存在,则会对原有文件内容进行覆盖。(默认情况下,从头覆盖)
*/
public class RandomAccessFileTest {
@Test
public void test(){
RandomAccessFile raf1 = null;
RandomAccessFile raf2 = null;
try {
raf1 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("爱情与友情.jpg"),"r");
raf2 = new RandomAccessFile(new File("爱情与友情1.jpg"),"rw");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = raf1.read(buffer)) != -1){
raf2.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(raf1 != null){
try {
raf1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(raf2 != null){
try {
raf2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile raf1 = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt","rw");
raf1.write("xyz".getBytes());
raf1.close();
}
}
10.2、RandomAccessFile实现数据的插入操作
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
/**
* RandomAccessFile的使用
* 1.RandomAccessFile直接继承于java.lang.Object类,实现了DataInput和DataOutput接口
* 2.RandomAccessFile既可以作为一个输入流,又可以作为一个输出流
* 3.如果RandomAccessFile作为输出流时,写出到的文件如果不存在,则在执行过程中自动创建。
* 如果写出到的文件存在,则会对原有文件内容进行覆盖。(默认情况下,从头覆盖)
*
* 4.可以通过相关的操作,实现RandomAccessFile“插入”数据的效果
*/
public class RandomAccessFileTest {
/**
* 使用RandomAccessFile实现数据的插入效果
*/
@Test
public void test3() throws IOException {
RandomAccessFile raf1 = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt","rw");
raf1.seek(3);//将指针调到角标为3的位置
//保存指针3后面的所有数据到StringBuilder中
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder((int) new File("hello.txt").length());
byte[] buffer = new byte[20];
int len;
while((len = raf1.read(buffer)) != -1){
builder.append(new String(buffer,0,len)) ;
}
//调回指针,写入“xyz”
raf1.seek(3);
raf1.write("xyz".getBytes());
//将StringBuilder中的数据写入到文件中
raf1.write(builder.toString().getBytes());
raf1.close();
//思考:将StringBuilder替换为ByteArrayOutputStream
}
}
11、NIO.2中Path、Paths、Files类的使用
import java.io.File;
File file = new File(“index.html”);
但在Java7 中,我们可以这样写:
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
Path path = Paths.get(“index.html”);
二、网络编程
01、网络编程概述
- Java是Internet 上的语言,它从语言级上提供了对网络应用程序的支持,程序员能够很容易开发常见的网络应用程序。
- Java提供的网络类库,可以实现无痛的网络连接,联网的底层细节被隐藏在Java 的本机安装系统里,由JVM 进行控制。并且Java
实现了一个跨平台的网络库,程序员面对的是一个统一的网络编程环境。 - 计算机网络:
把分布在不同地理区域的计算机与专门的外部设备用通信线路互连成一个规模大、功能强的网络系统,从而使众多的计算机可以方便地互相传递信息、共享硬件、软件、数据信息等资源。 - 网络编程的目的:
直接或间接地通过网络协议与其它计算机实现数据交换,进行通讯。 - 网络编程中有两个主要的问题:
①如何准确地定位网络上一台或多台主机;定位主机上的特定的应用 。
②找到主机后如何可靠高效地进行数据传输。
02、网络通信要素概述
- 通信双方地址
IP
端口号 - 一定的规则(即:网络通信协议。有两套参考模型)
OSI参考模型:模型过于理想化,未能在因特网上进行广泛推广
TCP/IP参考模型(或TCP/IP协议):事实上的国际标准。 - 网络通信协议


/**
* 一、网络编程中有两个主要的问题:
* 1.如何准确地定位网络上一台或多台主机;定位主机上的特定的应用
* 2.找到主机后如何可靠高效地进行数据传输
*
* 二、网络编程中的两个要素:
* 1.对应问题一:IP和端口号
* 2.对应问题二:提供网络通信协议:TCP/IP参考模型(应用层、传输层、网络层、物理+数据链路层)
*/
03、通信要素1:IP和端口号
3.1、IP的理解与InetAddress类的实例化
- IP 地址:InetAddress
唯一的标识Internet 上的计算机(通信实体) 本地回环地址(hostAddress):127.0.0.1
主机名(hostName):localhost IP地址分类方式1:IPV4和IPV6IPV4:4个字节组成,4个0-255。大概42亿,30亿都在北美,亚洲4亿。2011年初已经用尽。以点分十进制表示,如192.168.0.1
IPV6:128位(16个字节),写成8个无符号整数,每个整数用四个十六进制位表示,数之间用冒号 (:)分开,如:3ffe:3201:1401:1280:c8ff:fe4d:db39:1984
IP地址分类方式2:公网地址(万维网使用)和私有地址(局域网使用)。192.168.开头的就是私有地址,范围即为192.168.0.0–192.168.255.255,专门为组织机构内部使用
特点:不易记忆
- Internet上的主机有两种方式表示地址:
域名(hostName):www.atguigu.com
IP地址(hostAddress):202.108.35.210 - InetAddress类主要表示IP地址,两个子类:Inet4Address、Inet6Address。
- InetAddress类对象含有一个Internet主机地址的域名和IP地址:www.atguigu.com和202.108.35.210。
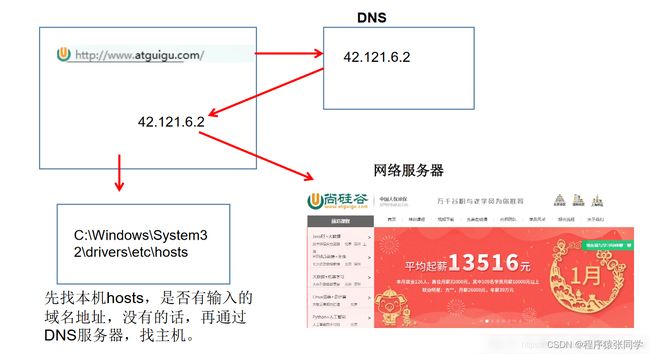
- 域名容易记忆,当在连接网络时输入一个主机的域名后,域名服务器(DNS)负责将域名转化成IP地址,这样才能和主机建立连接。-------域名解析
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
/**
* 一、网络编程中有两个主要的问题:
* 1.如何准确地定位网络上一台或多台主机;定位主机上的特定的应用
* 2.找到主机后如何可靠高效地进行数据传输
*
* 二、网络编程中的两个要素:
* 1.对应问题一:IP和端口号
* 2.对应问题二:提供网络通信协议:TCP/IP参考模型(应用层、传输层、网络层、物理+数据链路层)
*
*
* 三、通信要素一:IP和端口号
*
* 1. IP:唯一的标识 Internet 上的计算机(通信实体)
* 2. 在Java中使用InetAddress类代表IP
* 3. IP分类:IPv4 和 IPv6 ; 万维网 和 局域网
* 4. 域名: www.baidu.com www.mi.com www.sina.com www.jd.com
* www.vip.com
* 5. 本地回路地址:127.0.0.1 对应着:localhost
*
* 6. 如何实例化InetAddress:两个方法:getByName(String host) 、 getLocalHost()
* 两个常用方法:getHostName() / getHostAddress()
*
* 7. 端口号:正在计算机上运行的进程。
* 要求:不同的进程有不同的端口号
* 范围:被规定为一个 16 位的整数 0~65535。
*
* 8. 端口号与IP地址的组合得出一个网络套接字:Socket
*/
public class InetAddressTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//File file = new File("hello.txt");
InetAddress inet1 = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.10.14");
System.out.println(inet1);
InetAddress inet2 = InetAddress.getByName("www.atguigu.com");
System.out.println(inet2);
InetAddress inet3 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
System.out.println(inet3);
//获取本地ip
InetAddress inet4 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
System.out.println(inet4);
//getHostName()
System.out.println(inet2.getHostName());
//getHostAddress()
System.out.println(inet2.getHostAddress());
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.2、端口号的理解
04、通信要素2:网络协议
- 网络通信协议
计算机网络中实现通信必须有一些约定,即通信协议,对速率、传输代码、代码结构、传输控制步骤、出错控制等制定标准。 - 问题:网络协议太复杂
计算机网络通信涉及内容很多,比如指定源地址和目标地址,加密解密,压缩解压缩,差错控制,流量控制,路由控制,如何实现如此复杂的网络协议呢? - 通信协议分层的思想
在制定协议时,把复杂成份分解成一些简单的成份,再将它们复合起来。最常用的复合方式是层次方式,即同层间可以通信、上一层可以调用下一层,而与再下一层不发生关系。各层互不影响,利于系统的开发和扩展。
4.1、TCP和UDP网络通信协议的对比
- 传输层协议中有两个非常重要的协议:
传输控制协议TCP(Transmission Control Protocol)
用户数据报协议UDP(User Datagram Protocol)。 - TCP/IP
以其两个主要协议:传输控制协议(TCP)和网络互联协议(IP)而得名,实际上是一组协议,包括多个具有不同功能且互为关联的协议。 - IP(Internet Protocol)协议是网络层的主要协议,支持网间互连的数据通信。
- TCP/IP协议模型从更实用的角度出发,形成了高效的四层体系结构,即物理链路层、IP层、传输层和应用层。
- TCP协议:
使用TCP协议前,须先建立TCP连接,形成传输数据通道
传输前,采用“三次握手”方式,点对点通信,是可靠的
TCP协议进行通信的两个应用进程:客户端、服务端。
在连接中可进行大数据量的传输传输完毕,需释放已建立的连接,效率低 - UDP协议:
将数据、源、目的封装成数据包,不需要建立连接
每个数据报的大小限制在64K内
发送不管对方是否准备好,接收方收到也不确认,故是不可靠的
可以广播发送
发送数据结束时无需释放资源,开销小,速度快


05、TCP网络编程
1、例题1
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* 实现TCP的网络编程
* 例子1:客户端发送信息给服务端,服务端将数据显示在控制台上
*/
public class TCPTest {
//客户端
@Test
public void client() {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
//1.创建Socket对象,指明服务器端的ip和端口号
InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getByName("192.168.14.100");
socket = new Socket(inet,8899);
//2.获取一个输出流,用于输出数据
os = socket.getOutputStream();
//3.写出数据的操作
os.write("你好,我是客户端HH".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//4.资源的关闭
if(os != null){
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() {
ServerSocket ss = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
try {
//1.创建服务器端的ServerSocket,指明自己的端口号
ss = new ServerSocket(8899);
//2.调用accept()表示接收来自于客户端的socket
socket = ss.accept();
//3.获取输入流
is = socket.getInputStream();
//不建议这样写,可能会有乱码
// byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
// int len;
// while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
// String str = new String(buffer,0,len);
// System.out.print(str);
// }
//4.读取输入流中的数据
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[5];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
System.out.println("收到了来自于:" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress() + "的数据");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(baos != null){
//5.关闭资源
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket != null){
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(ss != null){
try {
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
2、例题2
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* 实现TCP的网络编程
* 例题2:客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端将文件保存在本地。
*
* @author subei
* @create 2020-05-16 17:05
*/
public class TCPTest2 {
/**
* 这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),9090);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("164.jpg"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
fis.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
}
/**
* 这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9090);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("1641.jpg"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
3、例题3
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
/**
* 实现TCP的网络编程
* 例题3:从客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端保存到本地。并返回“发送成功”给客户端。
* 并关闭相应的连接。
*
*/
public class TCPTest3 {
/**
* 这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),9090);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("164.jpg"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
//关闭数据的输出
socket.shutdownOutput();
//5.接收来自于服务器端的数据,并显示到控制台上
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bufferr = new byte[20];
int len1;
while((len1 = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len1);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
fis.close();
os.close();
socket.close();
baos.close();
}
/**
* 这里涉及到的异常,应该使用try-catch-finally处理
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9090);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("1642.jpg"));
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("图片传输完成");
//6.服务器端给予客户端反馈
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好,照片我已收到,风景不错!".getBytes());
fos.close();
is.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
os.close();
}
}
06、UDP网络编程
- 类DatagramSocket和DatagramPacket实现了基于UDP 协议网络程序。
- UDP数据报通过数据报套接字DatagramSocket发送和接收,系统不保证UDP数据报一定能够安全送到目的地,也不能确定什么时候可以抵达。
- DatagramPacket 对象封装了UDP数据报,在数据报中包含了发送端的IP地址和端口号以及接收端的IP地址和端口号。
- UDP协议中每个数据报都给出了完整的地址信息,因此无须建立发送方和接收方的连接。如同发快递包裹一样。
- 流程:
DatagramSocket与DatagramPacket
建立发送端,接收端
建立数据包
调用Socket的发送、接收方法
关闭Socket
1、发送端与接收端是两个独立的运行程序
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
/**
* UDPd协议的网络编程
*/
public class UDPTest {
//发送端
@Test
public void sender() throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket();
String str = "我是UDP发送端";
byte[] data = str.getBytes();
InetAddress inet = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data,0,data.length,inet,9090);
```java
在这里插入代码片
socket.send(packet);
socket.close();
}
//接收端
@Test
public void receiver() throws IOException {
DatagramSocket socket = new DatagramSocket(9090);
byte[] buffer = new byte[100];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer,0,buffer.length);
socket.receive(packet);
System.out.println(new String(packet.getData(),0,packet.getLength()));
socket.close();
}
}
## 07、URL编程
### 7.1、URL的理解与实例化
```java
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
/**
* URL网络编程
* 1.URL:统一资源定位符,对应着互联网的某一资源地址
* 2.格式:
* http://127.0.0.1:8080/work/164.jpg?username=subei
* 协议 主机名 端口号 资源地址 参数列表
*/
public class URLTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
URL url = new URL("http://127.0.0.1:8080/work/164.jpg?username=subei");
// public String getProtocol( ) 获取该URL的协议名
System.out.println(url.getProtocol());
// public String getHost( ) 获取该URL的主机名
System.out.println(url.getHost());
// public String getPort( ) 获取该URL的端口号
System.out.println(url.getPort());
// public String getPath( ) 获取该URL的文件路径
System.out.println(url.getPath());
// public String getFile( ) 获取该URL的文件名
System.out.println(url.getFile());
// public String getQuery( ) 获取该URL的查询名
System.out.println(url.getQuery());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
7.2、URL网络编程实现Tomcat服务端数据下载
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class URLTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = null;
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
URL url = new URL("http://127.0.0.1:8080/work/164.jpg");
urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
urlConnection.connect();
is = urlConnection.getInputStream();
fos = new FileOutputStream("day10\\1643.jpg");
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("下载完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭资源
if(is != null){
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos != null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(urlConnection != null){
urlConnection.disconnect();
}
}
}
}
7.3、URI、URL和URN的区别
- URI,是uniform resource identifier,统一资源标识符,用来唯一的标识一个资源。而URL是uniform
resource
locator,统一资源定位符,它是一种具体的URI,即URL可以用来标识一个资源,而且还指明了如何locate这个资源。而URN,uniform
resource
name,统一资源命名,是通过名字来标识资源,比如mailto:[email protected]。也就是说,URI是以一种抽象的,高层次概念定义统一资源标识,而URL和URN则是具体的资源标识的方式。URL和URN都是一种URI。 - 在Java的URI中,一个URI实例可以代表绝对的,也可以是相对的,只要它符合URI的语法规则。而URL类则不仅符合语义,还包含了定位该资源的信息,因此它不能是相对的。

三、反射与动态代理
01、Java反射机制概述
- Reflection(反射)是被视为动态语言的关键,反射机制允许程序在执行期借助于Reflection
API取得任何类的内部信息,并能直接操作任意对象的内部属性及方法。 - 加载完类之后,在堆内存的方法区中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息。我们可以通过这个对象看到类的结构。这个对象就像一面镜子,透过这个镜子看到类的结构,所以,我们形象的称之为:反射。

1、动态语言
是一类在运行时可以改变其结构的语言:例如新的函数、对象、甚至代码可以被引进,已有的函数可以被删除或是其他结构上的变化。通俗点说就是在运行时代码可以根据某些条件改变自身结构。主要动态语言:Object-C、C#、JavaScript、PHP、Python、Erlang。
2、静态语言
与动态语言相对应的,运行时结构不可变的语言就是静态语言。如Java、C、C++。
- Java不是动态语言,但Java可以称之为“准动态语言”。即Java有一定的动态性,我们可以利用反射机制、字节码操作获得类似动态语言的特性。Java的动态性让编程的时候更加灵活!
- Java反射机制提供的功能
在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
在运行时获取泛型信息
在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
在运行时处理注解
生成动态代理
- 反射相关的主要API
java.lang.Class:代表一个类
java.lang.reflect.Method:代表类的方法
java.lang.reflect.Field:代表类的成员变量
java.lang.reflect.Constructor:代表类的构造器
测试类
import org.junit.Test;
public class ReflectionTest {
//反射之前,对于Person的操作
@Test
public void test(){
//1.创建类的对象
Person p1 = new Person("jay",21);
//2.调用对象,调用其内部的属性和方法
p1.age = 15;
System.out.println(p1.toString());
p1.show();
//在Person类的外部,不可以通过Person类的对象调用其内部私有的结构。
//比如:name、showNation以及私有的构造器。
}
}
Person类
package github;
public class Person {
private String name;
public int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("你好,我是");
}
private String showNation(String nation){
System.out.println("喷子实在太多了!!!" + nation);
return nation;
}
}
1.1、使用反射,实现同上的操作
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReflectionTest {
//反射之后 ,堆与Person的操作
@Test
public void test2() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class clazz = Person.class;
//1.通过反射,创建Person类的对象
Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);
Object obj = cons.newInstance("Jon",18);
Person p = (Person) obj;
System.out.println(p.toString());
//2.通过反射,调用对象指定的属性和方法
//调用属性
Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
age.set(p,10);
System.out.println(p.toString());
//调用方法
Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");
show.invoke(p);
}
}
1.2、反射的强大:调用类的私有结构
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class ReflectionTest {
//反射之后 ,堆与Person的操作
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
Class clazz = Person.class;
//1.通过反射,创建Person类的对象
Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);
Object obj = cons.newInstance("Jon",18);
Person p = (Person) obj;
System.out.println(p.toString());
//2.通过反射,调用对象指定的属性和方法
//调用属性
Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
age.set(p,10);
System.out.println(p.toString());
//调用方法
Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");
show.invoke(p);
System.out.println("+++++++++++++++++++++++++");
//通过反射,是可以调用Person类的私有结构的。比如:私有的构造器、方法、属性
//调用私有的构造器
Constructor cons2 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
cons2.setAccessible(true);
Person p1 = (Person) cons2.newInstance("kalo");
System.out.println(p1);
//调用私有的属性
Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(p1,"Taoyao");
System.out.println(p1);
//调用私有的方法
Method showNation = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("LiNin", String.class);
showNation.setAccessible(true);
String nation = (String) showNation.invoke(p1,"FaceBook");
//相当于String nation = p1.showNation("FaceBook")
System.out.println(nation);
}
/**
* 疑问1:通过直接new的方式或反射的方式都可以调用公共的结构,开发中到底用那个?
* 建议:直接new的方式。
* 什么时候会使用:反射的方式。 反射的特征:动态性
* 疑问2:反射机制与面向对象中的封装性是不是矛盾的?如何看待两个技术?
* 不矛盾。
*/
}
02、理解Class类并获取Class实例
2.3、Class类的理解
/**
* 关于java.lang.Class类的理解
* 1.类的加载过程:
* 程序经过Javac.exe命令后,会生成一个或多个字节码文件(.class结尾)。
* 接着我们使用java.exe命令对某个字节码文件进行解释运行。相当于将某个字节码文件
* 加载到内存中。此过程就称为类的加载。加载到内存中的类,我们就称为运行时类,此
* 运行时类,就作为Class的一个实例。
*
* 2.换句话说,Class的实例就对应着一个运行时类。
*/