Spring Boot 监听器详解
Spring Boot 3.x系列文章
- Spring Boot 2.7.8 中文参考指南(一)
- Spring Boot 2.7.8 中文参考指南(二)-Web
- Spring Boot 源码阅读初始化环境搭建
- Spring Boot 框架整体启动流程详解
- Spring Boot 系统初始化器详解
- Spring Boot 监听器详解
监听器的介绍
通过前面的几篇文章,我们都能看到SpringApplicationRunListener,SpringApplicationRunListener 是SpringApplication 的运行监听器,提供Spring Boot启动时各个运行状态的监听,可以在应用程序启动的时候执行一些自定义操作或记录一些信息。SpringApplicationRunListener 在run中加载SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);。
ApplicationListener是Spring 提供的上下文监听器,可用于监听指定感兴趣的事件。
监听器的使用
SpringApplicationRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListener 的使用比较简单,实现该接口,并在META-INF/spring.factories中定义该实现
MyApplicationRunListener.java
public class MyApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener {
@Override
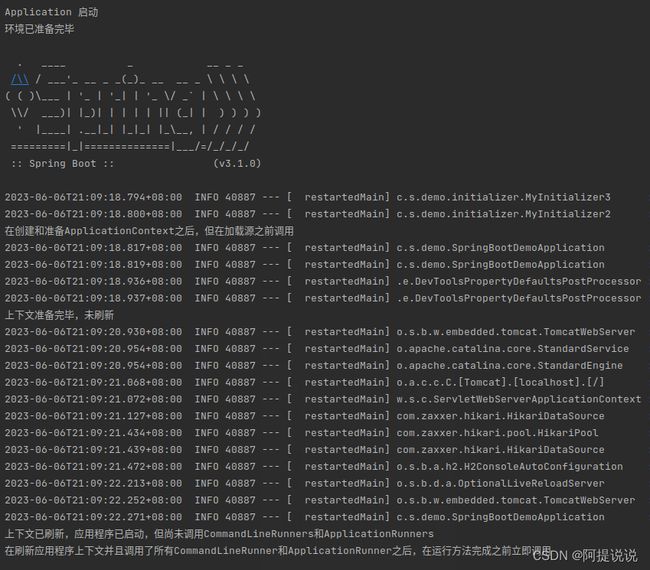
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
System.out.println("Application 启动");
}
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
System.out.println("环境已准备完毕");
}
@Override
public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("在创建和准备ApplicationContext之后,但在加载源之前调用");
}
@Override
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
System.out.println("上下文准备完毕,未刷新");
}
@Override
public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
System.out.println("上下文已刷新,应用程序已启动,但尚未调用CommandLineRunners和ApplicationRunners");
}
@Override
public void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) {
System.out.println("在刷新应用程序上下文并且调用了所有CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner之后,在运行方法完成之前立即调用");
}
@Override
public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
System.out.println("当运行应用程序时发生故障时调用");
}
}
META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=com.springboot.demo.listeners.MyApplicationRunListener
ApplicationListener
1、实现ApplicationListener接口
MyApplicationListener.java
@Slf4j
public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
log.info("应用启动完成");
}
}
META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=com.springboot.demo.listeners.MyApplicationListener
2、addListener
在springApplication 中添加,同样达到效果
SpringApplication springApplication = new SpringApplication(SpringBootDemoApplication.class);
springApplication.addListeners(new MyApplicationListener());
3、context.istener.classes
在配置文件中添加该配置,value为MyApplicationListener的全路径限定名
context:
listener:
classes: com.springboot.demo.listeners.MyApplicationListener
4、@EventListener
该注解是spring 提供的方式,支持同时监听多种事件,支持SpEL表达式
@Component
@Slf4j
public class MyApplicationListener2 {
//监听单个事件
@EventListener
public void listenerApplicationStarted(ApplicationStartedEvent event) {
log.info("应用启动完成");
}
@EventListener({ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent.class})
public void listenerApplicationEnv() {
//实际测试,没有监听到,后面说明原理
log.info("监听到了环境准备完成事件");
}
//监听多个事件
@EventListener({ApplicationReadyEvent.class, ApplicationStartedEvent.class})
public void listenerApplication() {
log.info("监听到了多个事件");
}
//自己发布了一个Person事件,Person并没有继承ApplicationEvent
@EventListener
public void myCustomListener(Person person) {
log.info("监听到自己发布的事件,{}", person);
}
//只有Person事件中name属性值为csdn时才接收到
@EventListener(condition = "#person.name == 'csdn'")
public void myCustomListener2(Person person) {
log.info("SpEL表达式监听到自己发布的事件,{}", person);
}
}
原理解析
SpringApplicationRunListener 的原理在之前的文章都有体现,可以查看《Spring Boot 框架整体启动流程详解》,我们只需要关注ApplicationListener。
Spring Boot 中不同的使用方式有不同的加载,我们一个个来分析。
1、从spring.factories中加载
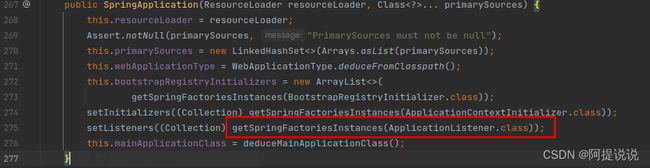
首先Spring Boot 会在SpringApplication初始化的时候从META-INF/spring.factories中加载ApplicationListener的实现,并保存在private List中,待后续使用。
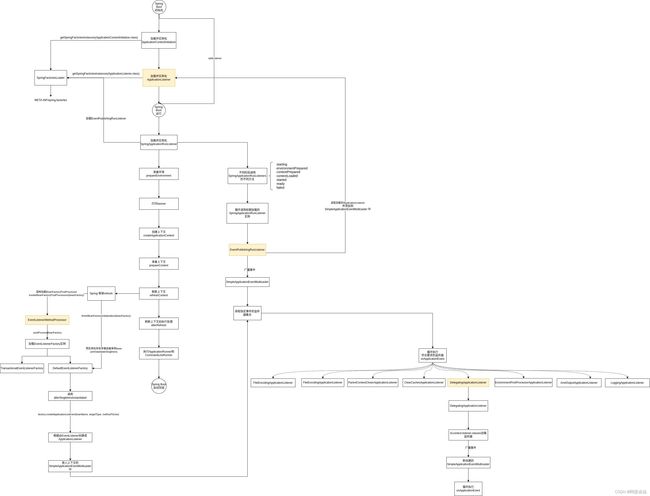
第二个关键是EventPublishingRunListener,在run方法中通过SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);加载,getRunListeners 从 spring.factories加载SpringApplicationRunListener的实现保存在SpringApplicationRunListeners内部,其相当于是代理器,Spring Boot 内部只定义了一个EventPublishingRunListener实现。

在Spring Boot 中在不同的阶段调用不同的SpringApplicationRunListeners方法,如图只是部分
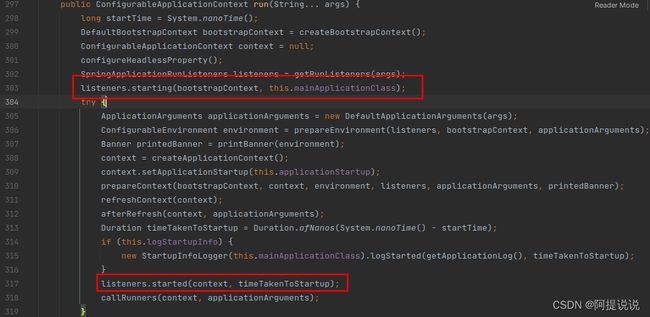
以starting为例,会在SpringApplicationRunListeners内部通过循环前期加载的SpringApplicationRunListener实现,此处只需要关注EventPublishingRunListener
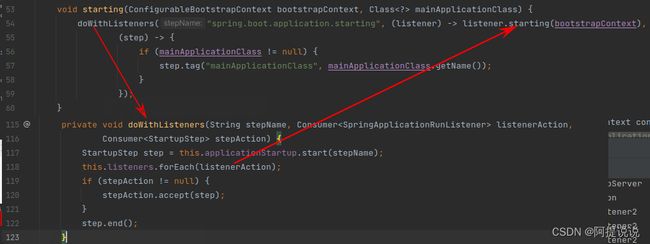
进入EventPublishingRunListener的starting方法中,starting调用同类的multicastInitialEvent,事件定义为ApplicationStartingEvent
private void multicastInitialEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
refreshApplicationListeners();
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
refreshApplicationListeners 会从SpringApplication保存的listeners中读取初始化时加载的ApplicationListener实现,并添加到SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster的内部类DefaultListenerRetriever中,待后续使用。
private void refreshApplicationListeners() {
this.application.getListeners().forEach(this.initialMulticaster::addApplicationListener);
}
第三个关键是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event) 调用到了SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster中,multicastEvent又调用了一个同名方法。
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, null);
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
//获取事件类的类型信息
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : ResolvableType.forInstance(event));
// 获取执行事件的线程池,如果设置了,可以异步执行
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
//获取指定事件类型的监听器集合
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
//如果定义了执行线程池,则用线程池调用
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
//同步调用监听器
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
//获取失败处理器
ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler();
if (errorHandler != null) {
try {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
errorHandler.handleError(err);
}
}
else {
doInvokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
try {
//此处执行事件监听器的onApplicationEvent方法
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}
catch (ClassCastException ex) {
String msg = ex.getMessage();
if (msg == null || matchesClassCastMessage(msg, event.getClass()) ||
(event instanceof PayloadApplicationEvent payloadEvent &&
matchesClassCastMessage(msg, payloadEvent.getPayload().getClass()))) {
// Possibly a lambda-defined listener which we could not resolve the generic event type for
// -> let's suppress the exception.
Log loggerToUse = this.lazyLogger;
if (loggerToUse == null) {
loggerToUse = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
this.lazyLogger = loggerToUse;
}
if (loggerToUse.isTraceEnabled()) {
loggerToUse.trace("Non-matching event type for listener: " + listener, ex);
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
}
实际上到这里流程已经走完了,最后listener.onApplicationEvent(event);调用到自定义的MyApplicationListener中。
对于如何获取指定事件类型的监听器集合,getApplicationListeners(event, type),代码比较复杂,可看也可不看。
getApplicationListeners 方法在SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster 的父类AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster中,传入传播的事件类bean和事件的类型信息。
protected Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> getApplicationListeners(
ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
//获取事件发生的对象
Object source = event.getSource();
Class<?> sourceType = (source != null ? source.getClass() : null);
//根据事件的类型信息和源对象组成一个监听器的缓存key
ListenerCacheKey cacheKey = new ListenerCacheKey(eventType, sourceType);
// 创建一个新的监听器检索缓存
CachedListenerRetriever newRetriever = null;
// 根据key从检索缓存中获取缓存的监听器封装类
CachedListenerRetriever existingRetriever = this.retrieverCache.get(cacheKey);
//如果不存在
if (existingRetriever == null) {
//判断事件类型和源对象能否用指定的classLoader加载
// 创建并缓存一个新的ListenerRetriever
if (this.beanClassLoader == null ||
(ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(event.getClass(), this.beanClassLoader) &&
(sourceType == null || ClassUtils.isCacheSafe(sourceType, this.beanClassLoader)))) {
newRetriever = new CachedListenerRetriever();
//如果指定键没有关联值,则存入新值,返回null,有关联值返回关联值
existingRetriever = this.retrieverCache.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, newRetriever);
//有关联值,就不填充新值,将创建的对象取消关联
if (existingRetriever != null) {
newRetriever = null;
}
}
}
//缓存检索器中有值,就返回缓存的事件监听器列表
if (existingRetriever != null) {
Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> result = existingRetriever.getApplicationListeners();
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
//缓存检索器中没有值的话,继续检索
return retrieveApplicationListeners(eventType, sourceType, newRetriever);
}
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(
ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable CachedListenerRetriever retriever) {
List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>();
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> filteredListeners = (retriever != null ? new LinkedHashSet<>() : null);
Set<String> filteredListenerBeans = (retriever != null ? new LinkedHashSet<>() : null);
Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;
Set<String> listenerBeans;
//从默认检索器中读取监听器列表和监听器bean名称
synchronized (this.defaultRetriever) {
listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);
listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);
}
// 循环添加已经注册的监听器,包括ApplicationListenerDetector加载的监听器
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : listeners) {
//检查指定的监听器是否是需要关注的事件
if (supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
filteredListeners.add(listener);
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
// 通过bean名称来添加监听器,可能与上面的方式重叠,但这里会有一些新的元数据
if (!listenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
//获取bean工厂
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeans) {
try {
//判断指定的监听器bean是否是需要关注的事件
if (supportsEvent(beanFactory, listenerBeanName, eventType)) {
//获取监听器bean
ApplicationListener<?> listener =
beanFactory.getBean(listenerBeanName, ApplicationListener.class);
//最终判断
if (!allListeners.contains(listener) && supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)) {
if (retriever != null) {
if (beanFactory.isSingleton(listenerBeanName)) {
filteredListeners.add(listener);
}
else {
filteredListenerBeans.add(listenerBeanName);
}
}
allListeners.add(listener);
}
}
else {
// 移除不支持的监听器
Object listener = beanFactory.getSingleton(listenerBeanName);
if (retriever != null) {
filteredListeners.remove(listener);
}
allListeners.remove(listener);
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
}
}
}
//排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);
if (retriever != null) {
if (filteredListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {
retriever.applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(allListeners);
retriever.applicationListenerBeans = filteredListenerBeans;
}
else {
retriever.applicationListeners = filteredListeners;
retriever.applicationListenerBeans = filteredListenerBeans;
}
}
return allListeners;
}
看下最终判断的部分:supportsEvent(listener, eventType, sourceType)
protected boolean supportsEvent(
ApplicationListener<?> listener, ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
GenericApplicationListener smartListener = (listener instanceof GenericApplicationListener gal ? gal :
new GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(listener));
//通过判断给定的事件类型是否与要关注的事件类型一致,并且支持给定的源类型
return (smartListener.supportsEventType(eventType) && smartListener.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}
这里会将监听器包装成GenericApplicationListenerAdapter,在构造器中解析出监听器关注的事件类型信息。
public GenericApplicationListenerAdapter(ApplicationListener<?> delegate) {
Assert.notNull(delegate, "Delegate listener must not be null");
this.delegate = (ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>) delegate;
//解析出事件类型信息
this.declaredEventType = resolveDeclaredEventType(this.delegate);
}
public boolean supportsEventType(ResolvableType eventType) {
//如果是GenericApplicationListener 的实现,它扩展了SmartApplicationListener
if (this.delegate instanceof GenericApplicationListener gal) {
return gal.supportsEventType(eventType);
}
//如果是SmartApplicationListener的实现
else if (this.delegate instanceof SmartApplicationListener sal) {
Class<? extends ApplicationEvent> eventClass = (Class<? extends ApplicationEvent>) eventType.resolve();
return (eventClass != null && sal.supportsEventType(eventClass));
}
else {
//其他类型判断
return (this.declaredEventType == null || this.declaredEventType.isAssignableFrom(eventType));
}
}
@Override
public boolean supportsSourceType(@Nullable Class<?> sourceType) {
return (!(this.delegate instanceof SmartApplicationListener sal) || sal.supportsSourceType(sourceType));
}
2、addListener
由于addListener是在run方法执行之前就添加到了SpringApplication中,所以加载原理同第一种方式相同
3、context.listener.classes
该配置的监听器,由Spring Boot 内置的DelegatingApplicationListener处理,该监听器定义在Spring Boot Jar包的META-INF/spring.factories中。
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
//环境准备完毕
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent preparedEvent) {
//从context.listener.classes加载配置的事件监听器
List<ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>> delegates = getListeners(preparedEvent.getEnvironment());
if (delegates.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
//新创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,跟以前用的不是同一个
this.multicaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
for (ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> listener : delegates) {
this.multicaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
if (this.multicaster != null) {
//监听到其他事件的时候向所有注册在该广播器上的监听器广播事件
this.multicaster.multicastEvent(event);
}
}
this.multicaster.multicastEvent(event);后面的逻辑与前面的相同
4、@EventListener
在之前的实例中,我们监听了一个ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,但实际测试却没有监听到,因为@EventListener要在SpringApplication.run的refreshContext中才会被加载,而ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件发生在refreshContext之前。
@EventListener 是Spring 提供的注解,在EventListenerMethodProcessor中被加载,并包装成ApplicationListener实例。
Spring Boot 的refreshContext 最终会调用到Spring 的AbstractApplicationContext refresh() 。
EventListenerMethodProcessor是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,会在refresh 的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory) 中进行调用
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//使用注册委托类处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()会获取已经加载的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现,比如准备上下文中的PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor。
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors内部的方法很长
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
//首先处理是BeanDefinitionRegistry的实例
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor) {
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// 然后其中分别处理实现了 PriorityOrdered、Ordered 和其余的处理器
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//处理实现了PriorityOrdered的处理器
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 处理实现了Ordered的处理器
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 最后是剩下的处理器
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// 调用迄今为止处理的所有处理器的postProcessBeanFactory回调
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// 其他情况调用在上下文实例中注册的工厂处理程序
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// 处理 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 实现的实例
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
//在实现PriorityOrdered、Ordered和其他的BeanFactoryPostProcessors之间分离
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// 跳过-已在上面的第一阶段中处理
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 首先,调用实现PriorityOrdered的BeanFactoryPostProcessors
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
//调用实现Ordered的BeanFactoryPostProcessors
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 最后调用其他的BeanFactoryPostProcessors
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
//EventListenerMethodProcessor会在此处被调用
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
//清除缓存的合并bean定义,因为后处理程序可能已经修改了原始元数据,例如替换值中的占位符。。。
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
//步骤记录器
StartupStep postProcessBeanFactory = beanFactory.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.context.bean-factory.post-process")
.tag("postProcessor", postProcessor::toString);
//循环调用postProcessBeanFactory
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
postProcessBeanFactory.end();
}
}
EventListenerMethodProcessor类中:
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
//获取EventListenerFactory实现类,其用于处理EventListener注解,
//将其封装成ApplicationListener
Map<String, EventListenerFactory> beans = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(EventListenerFactory.class, false, false);
List<EventListenerFactory> factories = new ArrayList<>(beans.values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(factories);
this.eventListenerFactories = factories;
}
EventListenerMethodProcessor 实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口,会在refresh中的finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)处调用,finishBeanFactoryInitialization 的作用是实例化所有剩余的非惰性单例。
DefaultListableBeanFactory类中:
//预实例化所有非懒加载的单例 bean,并触发所有适用 bean 的初始化后回调。
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// 访问 beanDefinitionNames,以允许初始化方法注册新的 bean 定义的列表的副本
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// 触发所有非延迟加载的单例 bean 的实例化
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
//如果是工厂 bean,检查是否需要实例化
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof SmartFactoryBean<?> smartFactoryBean && smartFactoryBean.isEagerInit()) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
//如果不是工厂bean,则实例化 bean
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// 触发所有适用bean的初始化后回调
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton) {
// 启动一个 smart-initialize 的 StartupStep 作为性能分析;
// 在执行完 smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated() 之后结束这个 StartupStep。
StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize")
.tag("beanName", beanName);
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
smartInitialize.end();
}
}
}
通过smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated()又执行到了EventListenerMethodProcessor的afterSingletonsInstantiated,后面又是一长串,我们直接看最后的重点吧。

首先根据@EventListener创建成ApplicationListener,然后通过addApplicationListener将监听器存入上下文中,后面的逻辑跟前面是相同的。
内置的监听器
Spring Boot 内置了不少监听器,每个监听器都有自己的作用
- ClearCachesApplicationListener
应用上下文加载完成后对缓存做清除工作 - ParentContextCloserApplicationListener
父应用程序上下文关闭时,会将关闭事件向下传播以关闭该应用程序上下文 - FileEncodingApplicationListener
用于监听应用程序环境准备完毕时,如果系统文件编码(spring.mandatory-file-encoding)与环境中配置的值(file.encoding)不匹配时(忽略大小写),会抛出异常,并停止应用程序 - AnsiOutputApplicationListener
根据spring.output.ansi.enabled参数配置AnsiOutput - DelegatingApplicationListener
用于委托管理context.listener.classes中配置的监听器 - LoggingApplicationListener
配置和初始化Spring Boot 的日志系统 - EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener
管理spring.factories文件中注册的EnvironmentPostProcessors
内置的事件
Spring Boot 包中部分事件:
BootstrapContextClosedEvent、ExitCodeEvent、AvailabilityChangeEvent、ParentContextAvailableEvent、ApplicationContextInitializedEvent、ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent、ApplicationFailedEvent、ApplicationPreparedEvent、ApplicationReadyEvent、ApplicationStartedEvent、ApplicationStartingEvent、WebServerInitializedEvent、ReactiveWebServerInitializedEvent、ServletWebServerInitializedEvent
Spring 包中部分事件:
ContextClosedEvent、ContextRefreshedEvent、ContextStartedEvent、ContextStoppedEvent、ServletRequestHandledEvent
总结
最后还是用一张图来总结整个流程
作者其他文章:
Prometheus 系列文章
- Prometheus 的介绍和安装
- 直观感受PromQL及其数据类型
- PromQL之选择器和运算符
- PromQL之函数
- Prometheus 告警机制介绍及命令解读
- Prometheus 告警模块配置深度解析
- Prometheus 配置身份认证
- Prometheus 动态拉取监控服务
- Prometheus 监控云Mysql和自建Mysql
Grafana 系列文章,版本:OOS v9.3.1
- Grafana 的介绍和安装
- Grafana监控大屏配置参数介绍(一)
- Grafana监控大屏配置参数介绍(二)
- Grafana监控大屏可视化图表
- Grafana 查询数据和转换数据
- Grafana 告警模块介绍
- Grafana 告警接入飞书通知
Spring Boot Admin 系列
- Spring Boot Admin 参考指南
- SpringBoot Admin服务离线、不显示健康信息的问题
- Spring Boot Admin2 @EnableAdminServer的加载
- Spring Boot Admin2 AdminServerAutoConfiguration详解
- Spring Boot Admin2 实例状态监控详解
- Spring Boot Admin2 自定义JVM监控通知
- Spring Boot Admin2 自定义异常监控
- Spring Boot Admin 监控指标接入Grafana可视化