Java异常
目录
一、异常的概念
二、异常的层次结构
1.Error
2.Exception
三、异常的捕获与处理
1.异常处理概念
2.异常捕获演示
代码1:除0异常
代码2:捕获异常
代码3:将代码2中的e.printStackTrace()删去
3.异常捕获详解
四、抛出异常
1.抛出异常的概念
2.throws语句
3.throw语句
五、自定义异常类
六、通过异常捕获管理系统中的输入值类型错误
七、通过自定义异常规范管理系统中的输入长度
八、异常处理嵌套
一、异常的概念
在使用计算机语言进行项目开发的过程中,某些问题不是靠代码能够避免的,比如客户输入数据的格式、读取文件是否存在、网络是否始终保持通畅等。在Java语言中,将程序运行期间发生的不期而至的各种意外状况成为异常,如文件找不到、网络连接失败、非法参数等。
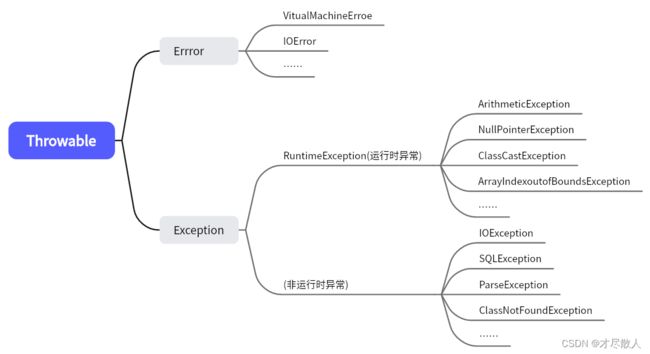
二、异常的层次结构
Java通过API中的Throwable类的众多子类描述各种不同的异常,所以Java异常是Throwable子类的实例化对象。 Throwable有两个重要的子类:Exception(异常)和Error(错误)。
1.Error
Error代表程序运行时Java系统内部的错误,与程序设计者操作无关。Error不可查也不必处理。
2.Exception
Exception通常是由某个资源不可用或者正确执行程序所需的条件不满足所造成的,是程序本身可以处理的异常。
Java将异常分为两类:运行时异常(RuntimeException,也称为未检查异常)和非运行时异常(也成为已检查异常)。运行时异常包含Java.Lang.RuntimeException类及所有子类,除此以外的属于Exception类及其子类的所有异常都属于非运行时异常。
三、异常的捕获与处理
1.异常处理概念
try{
//可能出现异常的代码
}catch(异常类型1 变量名1){
//异常处理方式1
}catch(异常类型2 变量名2){
//异常处理方式2
}finally{
//一定会执行的代码
} try-catch-finally的做法是将程序的业务功能代码放在try语句中,尝试是否能够顺利通过,将异常代码放在catch语句中,捕获并处理异常,try-catch协同工作,这是Java的异常处理方式。
2.异常捕获演示
代码1:除0异常
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
division(10, 0);
}
private static void division(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a / b);
}
}运行结果:
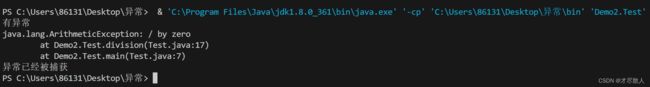
代码2:捕获异常
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
division(10, 0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("有异常");
e.printStackTrace();// 打印终端中的java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero ……
} finally {
System.out.println("异常已经被捕获");
}
}
private static void division(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a / b);
}
}运行结果:
代码3:将代码2中的e.printStackTrace()删去
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
division(10, 0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("有异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("异常已经被捕获");
}
}
private static void division(int a, int b) {
System.out.println(a / b);
}
}运行结果:
3.异常捕获详解
(1)try
- 将可能产生异常的代码放在try语句块中尝试执行,异常发生后,try结构内发生异常处理后的代码不会被执行。
- 在程序执行过程中,可能会产生并抛出一种或几种异常,这些异常都由它后面的catch负责捕获、处理。
- 一个try语句后面可以跟多个catch语句块,从语法的角度也可以一个catch都没有。
- 在try结构中生命变量,在此结构以外就不能再被调用。
(2) catch
- 每个catch语句块捕获、处理一种类型的异常。异常发生时,程序会中断正常的流程,离开try语句块去执行相应的catch语句块。
- 在catch中声明了异常对象(如ParseException e),异常对象封装了异常事件的相关信息,在catch语句块中可以使用这个对象获取这些信息,常用方法包括
- 编译器禁止定义永远不能到达的catch子句。存在多个catch语句时,必须先捕获子类异常,将异常按照从具体到最通用的顺序排列。
(3)finally
- finally语句块为可选。一旦有finally语句块,无论try语句块是否抛出异常,finally语句都要被执行。
- finally语句块为异常处理提供统一的善后处理,使流程转到其他部分之前,能够对程序的状态进行统一的管理。
- 通常在finally语句块中进行资源释放的工作,如关闭已打开的文件、关闭数据库连接等。
四、抛出异常
1.抛出异常的概念
如果当前方法不知道如何处理捕获的异常,用throws声明将此异常再次抛出,交给当前方法的上一层调用者;假设上一层方法仍然不知道如何处理,也可以继续向上抛出;直到某个方法可以处理此异常,或者最终交给JVM。异常对象沿着方法调用链进行反向传递,JVM对异常处理方法是打印异常的跟踪信息栈,并终止程序异常。
2.throws语句
throws在声明方法时,表示该方法可能要抛出异常,调用者必须做出处理,捕获或继续抛出异常。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NullPointerException{
//使用throws抛出NullPointerException异常
}
}
3.throw语句
throw用于用户自定义的异常抛出
throw 异常对象;五、自定义异常类
public class MyException extends Exception {
public MyException() {
}
public MyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MyException {
UseException useException = new UseException();
try {
useException.division(10, 0);
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("异常已经被捕获");
}
}
}
public class UseException {
public void division(int a, int b) throws MyException {
if (b == 0) {
throw new MyException("/ by zero");
} else {
System.out.println(a / b);
}
}
}
六、通过异常捕获管理系统中的输入值类型错误
代码演示:
public class Student {
int id;
String name;
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Add {
public static void add(ArrayList students) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
System.out.println("请输入要添加的学生学号:");
int id = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入要添加的学生姓名:");
String name = in.next();
Student student = new Student(id, name);
students.add(student);
System.out.println("添加成功!");
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("输入类型错误");
}
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList students = new ArrayList();
Add.add(students);
}
} 七、通过自定义异常规范管理系统中的输入长度
代码演示:
public class MyException extends Exception {
public MyException() {
}
public MyException(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
public class LengthTest {
public void nameLength(String a) throws MyException {
if (a.length() > 10) {
throw new MyException("输入名字过长");// 当传入的字符串长度大于10,抛出自定义异常
}
}
}
public class Student {
int id;
String name;
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Add {
public static void add(ArrayList students) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
System.out.println("请输入要添加的学生学号:");
int id = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入要添加的学生姓名");
String name = in.next();
LengthTest lengthTest = new LengthTest();
lengthTest.nameLength(name);
Student student = new Student(id, name);
students.add(student);
System.out.println("添加成功!");
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws MyException {
ArrayList students = new ArrayList();
Add.add(students);
System.out.println(students.get(0).getName());
}
} 八、异常处理嵌套
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Add {
public static void add(ArrayList students) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
System.out.println("请输入要添加的学生学号:");
int id = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入要添加的学生姓名");
String name = in.next();
LengthTest lengthTest = new LengthTest();
lengthTest.nameLength(name);
Student student = new Student(id, name);
students.add(student);
System.out.println("添加成功!");
} catch (MyException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InputMismatchException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("输入值类型错误");
}
}
}