【Spring】——Spring的创建与使用
目录
一、传统程序开发与控制反转
1、传统程序开发
传统程序开发的缺陷
解决传统开发中的缺陷
2、控制反转思维程序开发
3 对比总结规律
二、Spring创建与使用
1、创建Spring
Ⅰ、创建Maven项目
Ⅱ、添加Spring框架支持
Ⅲ、添加启动类
注意:maven 项目下载 jar 失败的解决方案
Ⅰ、配置好国内的Maven源
配置国内源
Ⅱ、重新下载jar包
Ⅲ、其他问题
2.存储 Bean 对象
Ⅰ、创建Bean
Ⅱ、将 Bean 注册到容器
3.获取并使用Bean 对象
Ⅰ、获取Spring对象
多学一招:ApplicationContext与BeanFactory(常见面试题)
Ⅱ、获取指定的 Bean 对象
Ⅲ、使用Bean对象
多学一招:getBean 方法的更多用法
Ⅰ、根据类型获取 Bean:
Ⅱ、根据名称 + 类型获取 Bean
两种方法的区别
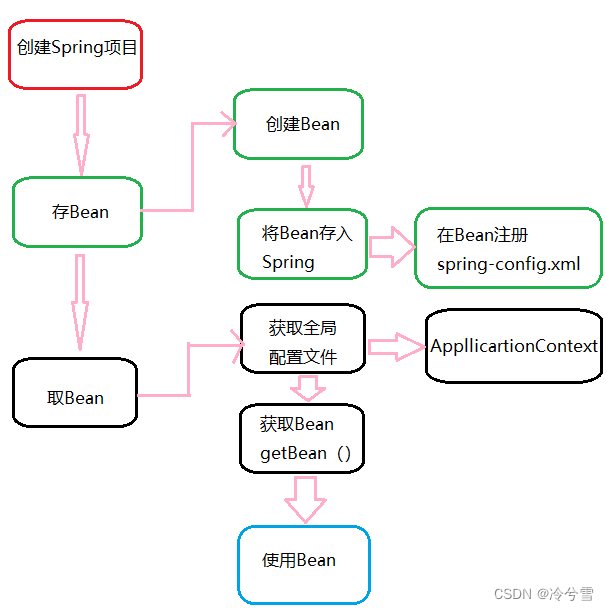
操作流程图
Spring_冷兮雪的博客-CSDN博客
上期我们讲解了Spring是什么及Spring的核心特点,其中重点讲解了控制反转(IoC)和依赖注入(DI),下面我们通过示例代码来去更深刻了解这其中的含义。
一、传统程序开发与控制反转
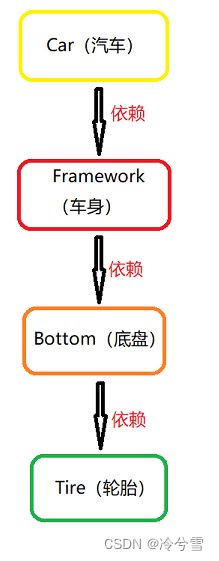
1、传统程序开发
public class NewCarExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car();
car.init();
}
/**
* 汽⻋对象
*/
static class Car {
public void init() {
// 依赖⻋身
Framework framework = new Framework();
framework.init();
}
}
/**
* ⻋身类
*/
static class Framework {
public void init() {
// 依赖底盘
Bottom bottom = new Bottom();
bottom.init();
}
}
/**
* 底盘类
*/
static class Bottom {
public void init() {
// 依赖轮胎
Tire tire = new Tire();
tire.init();
}
}
/**
* 轮胎类
*/
static class Tire {
public void init() {
// 尺⼨
int size = 30;
System.out.println("轮胎尺⼨:" + size);
}
}
}
传统程序开发的缺陷
public class NewCarUpdateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car car = new Car(20);
car.run();
}
/**
* 汽⻋对象
*/
static class Car {
private Framework framework;
public Car(int size) {
framework = new Framework(size);
}
public void run() {
// 依赖⻋身
framework.init();
}
}
/**
* ⻋身类
*/
static class Framework {
private Bottom bottom;
public Framework(int size) {
bottom = new Bottom(size);
}
public void init() {
// 依赖底盘
bottom.init();
}
}
/**
* 底盘类
*/
static class Bottom {
private Tire tire;
public Bottom(int size) {
tire = new Tire(size);
}
public void init() {
// 依赖轮胎
tire.init();
}
}
/**
* 轮胎类
*/
static class Tire {
// 尺⼨
private int size;
public Tire(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public void init() {
System.out.println("轮胎尺⼨:" + size);
}
}
}
解决传统开发中的缺陷
PS:解耦指的是解决了代码的耦合性,耦合性也可以换⼀种叫法叫程序相关性。好的程序代码的耦合 性(代码之间的相关性)是很低的,也就是代码之间要实现解耦。
2、控制反转思维程序开发
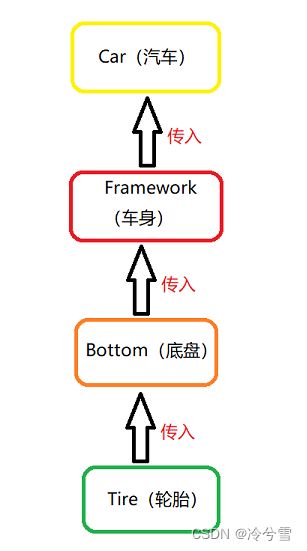
public class IocCarExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tire tire = new Tire(20);
Bottom bottom = new Bottom(tire);
Framework framework = new Framework(bottom);
Car car = new Car(framework);
car.run();
}
static class Car {
private Framework framework;
public Car(Framework framework) {
this.framework = framework;
}
public void run() {
framework.init();
}
}
static class Framework {
private Bottom bottom;
public Framework(Bottom bottom) {
this.bottom = bottom;
}
public void init(){
bottom.init();
}
}
static class Bottom {
private Tire tire;
public Bottom(Tire tire) {
this.tire = tire;
}
public void init() {
tire.init();
}
}
static class Tire {
private int size;
public Tire(int size) {
this.size = size;
}
public void init() {
System.out.println("轮胎:" + size);
}
}
}
3 对比总结规律
我们理解到了Spring的核心,下面我们来开始写第一个Spring代码。
二、Spring创建与使用
1、创建Spring
下面我们通过Maven 方式来创建⼀个 Spring 项目,具体可以分为三步:
- 创建⼀个普通 Maven 项目。
- 添加 Spring 框架支持(spring-context、spring-beans)。
- 创建一个普通类和main方法运行Spring框架。
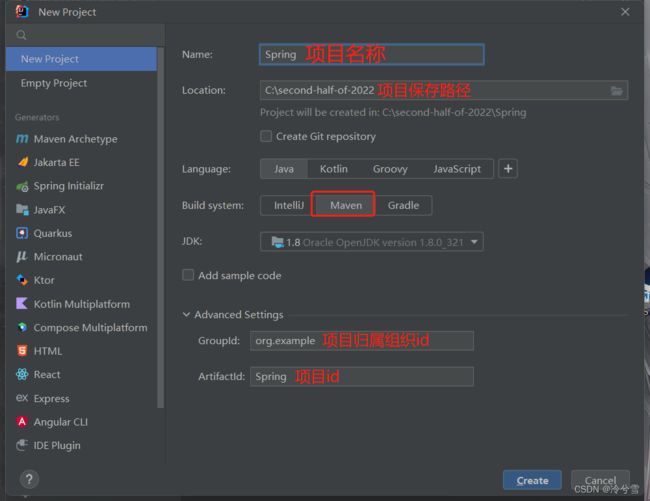
Ⅰ、创建Maven项目
Ⅱ、添加Spring框架支持
创建好了之后,在pom.xml添加 Spring 框架支持
org.springframework
spring-context
5.2.3.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-beans
5.2.3.RELEASE
添加之后
4.0.0
org.example
springdemo
1.0-SNAPSHOT
8
8
org.springframework
spring-context
5.2.3.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-beans
5.2.3.RELEASE
Ⅲ、添加启动类
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}注意:maven 项目下载 jar 失败的解决方案
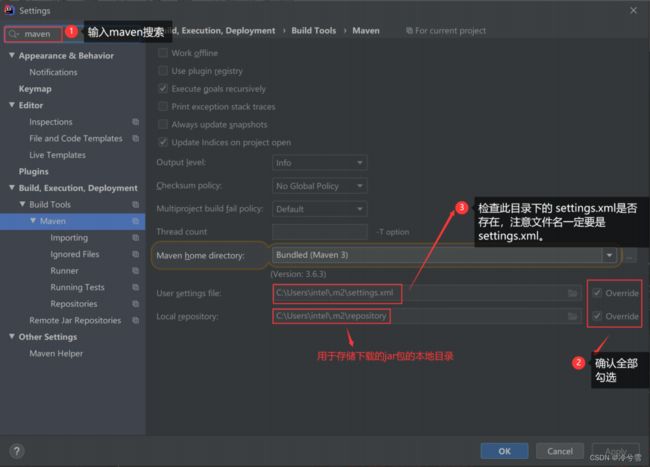
Ⅰ、配置好国内的Maven源
检查项⼀共有两个:
注意:两个路径中都不能出现中文!不能出现中文!不能出现中文!(重要的事说三遍)
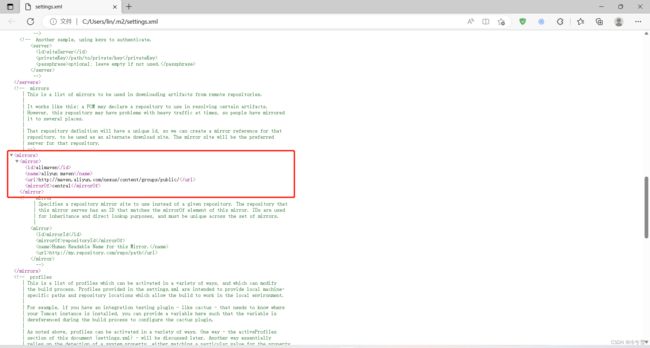
配置国内源
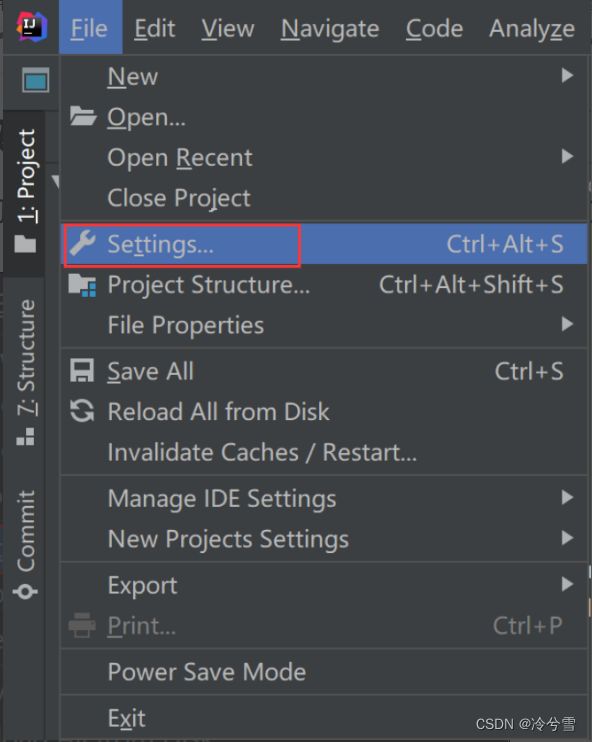
可以在Settings->搜索maven中 找到settings.xml 文件
C:\Users\intel\.m2\repository
alimaven
aliyun maven
http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/
central
Ⅱ、重新下载jar包
删除本地jar目录中的所有文件,切换到 Idea 中,重新下载 jar 包,如下图所示
待下载完成,如果还是下载失败那就是本地网速问题,重复步骤 1 和步骤 2 直到下载成功!
Ⅲ、其他问题
- 上面的步骤没看仔细,可能遗漏了其中一步;
- Maven 路径中出现中文:出现中文会 导致下载的jar 包,在项目中不能正常使用;
- 当前网络运营商有问题:当前所在区域连接的网络运营商(中国电信、移动..)连接数据源有问题,尝试更好网络,使用手机热点或朋友的手机热点尝试,如果还是不行,就等三四个小时之后再试。
2.存储 Bean 对象
- 先创建⼀个 Bean。
- 将创建的 Bean 注册到 Spring 容器中。
Ⅰ、创建Bean
public class User {
public String sayHi(String name){
return "hello"+name;
}
}
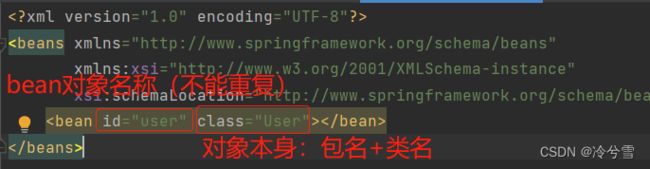
Ⅱ、将 Bean 注册到容器
创建之后
3.获取并使用Bean 对象
- 得到 Spring 上下文对象,因为对象都交给 Spring 管理了,所以获取对象要从 Spring 中获取,那么就得先得到 Spring 的上下文。
- 通过Spring 上下文,获取某⼀个指定的 Bean 对象。
- 使用Bean 对象。
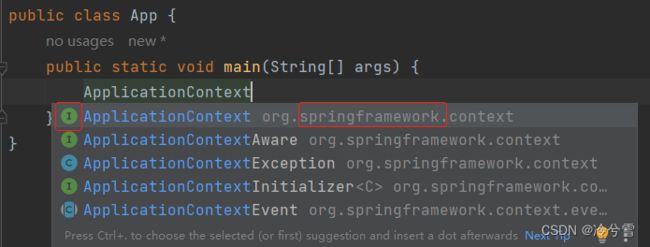
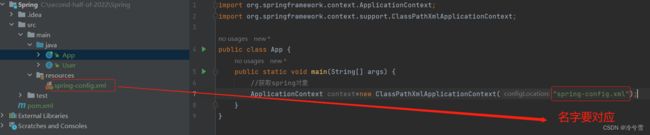
Ⅰ、获取Spring对象
ApplicationContext:来自于Spring框架的接口。通过这个接口去获取Spring对象。
多学一招:ApplicationContext与BeanFactory(常见面试题)
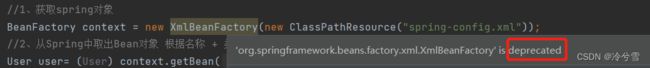
BeanFactory是以前的老方法了,现在已经被弃用,或者说现在比较少用了
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、获取spring对象
BeanFactory context = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("spring-config.xml"));
//2、从Spring中取出Bean对象 根据名称 + 类型获取 Bean
User user= (User) context.getBean("user",User.class);//输出hello张三
//3、使用Bean(可选)
System.out.println(user.sayHi("张三"));
}
}ApplicationContext VS BeanFactory
相同点:
- 都可以得到 Spring 上下文对象。
- 都是来自 Spring 的接口。
不同点
1、继承关系和功能: 虽然都是Spring 容器的接口,但 ApplicationContext 属于 BeanFactory 的子类 。其中BeanFactory提供了基础的访问容器的能力,ApplicationContext除了继承BeanFactory 的所有功能之外,它还拥有独特的特性,还添加了对国际化支持、资源访问支持、以及事件传播等方面的支持。2、性能:ApplicationContext 是⼀次性加载并初始化所有的 Bean 对象,而BeanFactory 是需要哪个才去加载哪个,因此更加轻量。
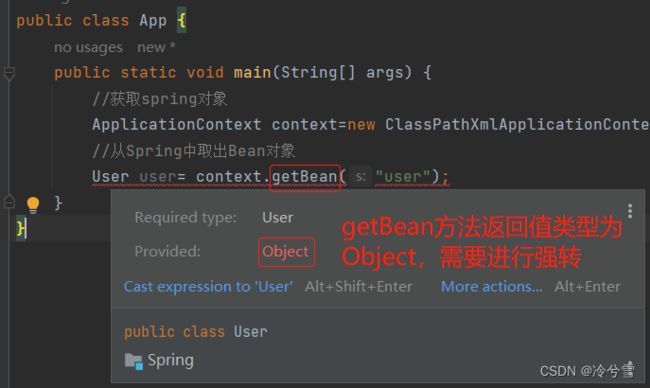
Ⅱ、获取指定的 Bean 对象
然后通过getBean方法取出Bean对象
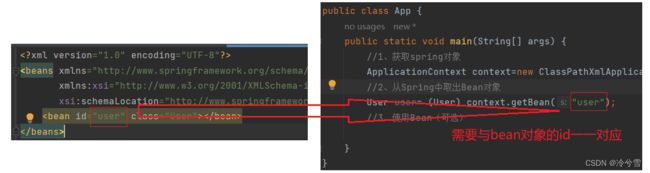
注意:Bean 的 Id 要⼀⼀对应:
Ⅲ、使用Bean对象
我们现在就可以使用Bean,然后调用其中的方法了
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、获取spring对象
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2、从Spring中取出Bean对象
User user= (User) context.getBean("user");
//3、使用Bean(可选)
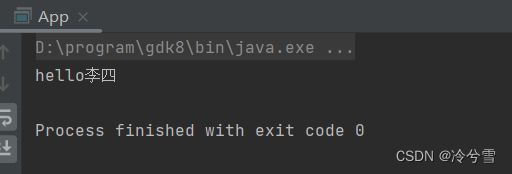
System.out.println(user.sayHi("李四"));
}
}多学一招:getBean 方法的更多用法
Ⅰ、根据类型获取 Bean:
User user= (User) context.getBean(User.class);import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、获取spring对象
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2、从Spring中取出Bean对象 Ⅰ、根据类型获取Bean
User user= (User) context.getBean(User.class);
//3、使用Bean(可选)
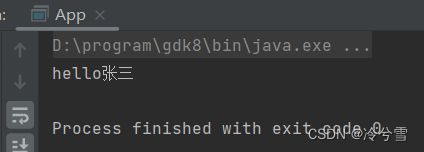
System.out.println(user.sayHi("张三"));
}
}Ⅱ、根据名称 + 类型获取 Bean
User user= (User) context.getBean("user",User.class);两种方法的区别
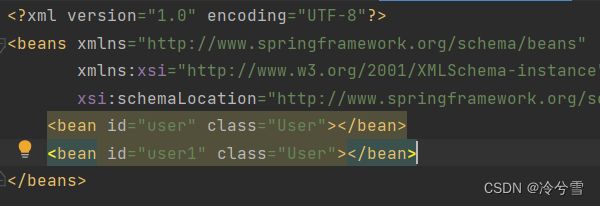
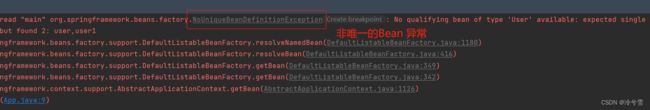
当有⼀个类型被重复注册到 spring-config.xml 中时,只能使用 根据名称+类型获取了,比如以下程序
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、获取spring对象
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2、从Spring中取出Bean对象 Ⅰ、根据类型获取Bean
User user= (User) context.getBean(User.class);//报错
//Ⅱ、根据名称 + 类型获取 Bean
//User user= (User) context.getBean("user",User.class);//输出hello张三
//3、使用Bean(可选)
System.out.println(user.sayHi("张三"));
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
//1、获取spring对象
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2、从Spring中取出Bean对象
User user= (User) context.getBean("user");
//3、使用Bean(可选)
System.out.println(user.sayHi("李四"));
}
}