2023-06-08:给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。 树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。 每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度
2023-06-08:给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回树的 最大宽度 。
树的 最大宽度 是所有层中最大的 宽度 。
每一层的 宽度 被定义为该层最左和最右的非空节点(即,两个端点)之间的长度。
将这个二叉树视作与满二叉树结构相同,两端点间会出现一些延伸到这一层的 null 节点,
这些 null 节点也计入长度。
题目数据保证答案将会在 32 位 带符号整数范围内。
输入:root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]。
输出:4。
答案2023-06-09:
大体步骤如下:
该算法使用一个容器来存储节点的信息,每个节点信息包含节点本身和其在满二叉树中的位置。
1.如果root为空,返回0,否则初始化一个变量ans来记录最大宽度。
2.使用一个队列queue来存储节点信息,将根节点的信息{root,1}加入队列。
3.循环处理队列,每次处理一层,对于每个节点:
-
a.pop出队列中的节点信息,将该节点作为当前节点cur。
-
b.如果当前节点是该层的第一个节点,则记录其Index为left。
-
c.如果当前节点是该层的最后一个节点,则记录其Index为right。
-
d.如果当前节点有左孩子,则将其左孩子信息{cur.Node.Left,cur.Index*2}加入队列。
-
e.如果当前节点有右孩子,则将其右孩子信息{cur.Node.Right,cur.Index*2+1}加入队列。
4.计算当前层的宽度,将其记录为max(right-left+1,ans)。
5.返回最大宽度ans。
时间复杂度:每个节点仅仅入队、出队各一次,因此时间复杂度为O(N),其中N为树中节点的数量。
空间复杂度:本算法使用了一个队列来存储节点信息,队列中的节点数量不会超过两层的节点数,因此空间复杂度为O(2^h),其中h为树的高度。如果是完全二叉树,h=logN,空间复杂度为O(N)。
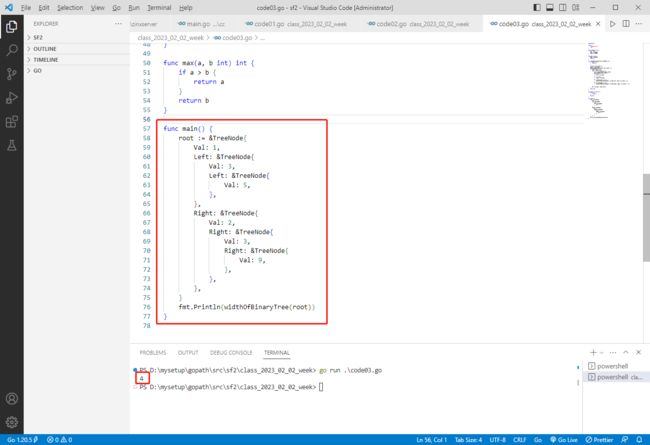
golang完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"container/list"
"fmt"
)
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
type Info struct {
Node *TreeNode
Index int
}
func widthOfBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
var ans, left, right int
queue := list.New()
queue.PushBack(&Info{Node: root, Index: 1})
for queue.Len() > 0 {
size := queue.Len()
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
cur := queue.Front().Value.(*Info)
queue.Remove(queue.Front())
if i == 0 {
left = cur.Index
}
if i == size-1 {
right = cur.Index
}
if cur.Node.Left != nil {
queue.PushBack(&Info{Node: cur.Node.Left, Index: cur.Index * 2})
}
if cur.Node.Right != nil {
queue.PushBack(&Info{Node: cur.Node.Right, Index: cur.Index*2 + 1})
}
}
ans = max(ans, right-left+1)
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
func main() {
root := &TreeNode{
Val: 1,
Left: &TreeNode{
Val: 3,
Left: &TreeNode{
Val: 5,
},
},
Right: &TreeNode{
Val: 2,
Right: &TreeNode{
Val: 3,
Right: &TreeNode{
Val: 9,
},
},
},
}
fmt.Println(widthOfBinaryTree(root))
}
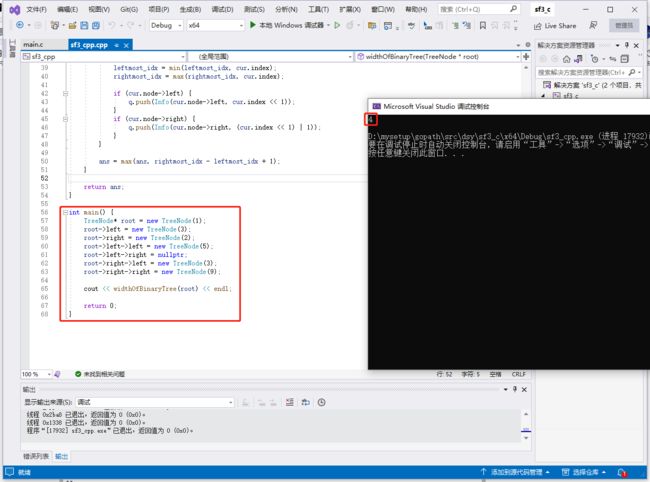
c++完整代码如下:
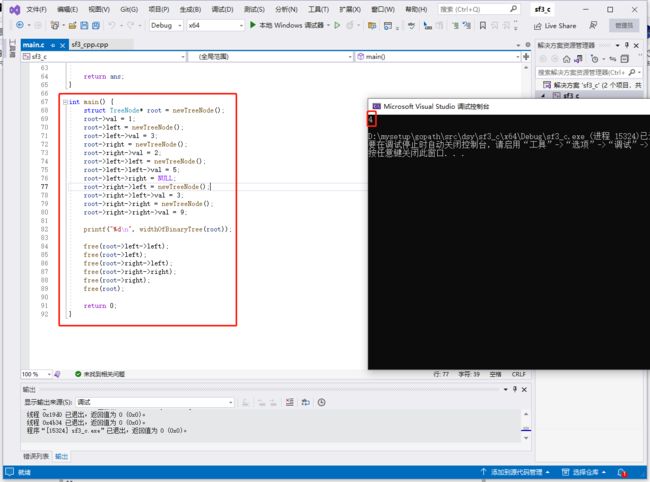
#include c语言完整代码如下:
#include