stream流多字段排序
1、前言
在开发过程中我们经常会遇到根据对象中不同字段的值进行排序,也就是我们常说的多字段排序。在Java8中我们可以使用stream流很便捷的进行排序。下面我将以年龄和班级两个字段的值来演示使用stream流进行多字段排序的操作。
1、数据准备
public class User {
//学生id
private Integer userId;
//学生姓名
private String userName;
//学生年龄
private Integer age;
//学生班级
private Integer classNo;
}
List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.add(new User(1, "shy01", 20, 1));
userList.add(new User(2, "shy02", 18, 3));
userList.add(new User(3, "shy03", 20, 4));
userList.add(new User(4, "shy04", 19, 2));
userList.add(new User(5, "shy05", 17, 5));
userList.add(new User(6, "shy06", 16, 4));
userList.add(new User(7, "shy07", 18, 9));
userList.add(new User(8, "shy08", 19, 8));
userList.add(new User(9, "shy09", 21, 7));
2、字段排序
1、单个字段排序
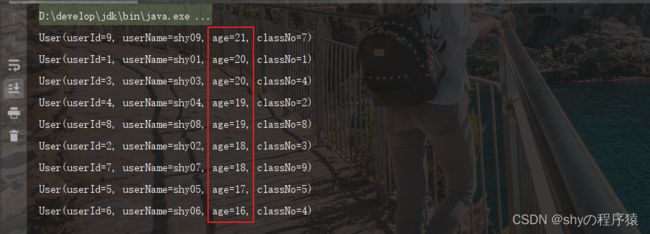
根据年龄升序排序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge)).collect(Collectors.toList());
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
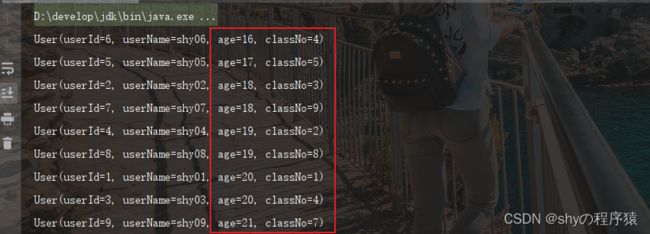
根据年龄降序排序
//方法1:先对年龄进行升序,结果进行反转
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
//方法2:直接对年龄进行降序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge, Comparator.reverseOrder())).collect(Collectors.toList());
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
2、多个字段排序
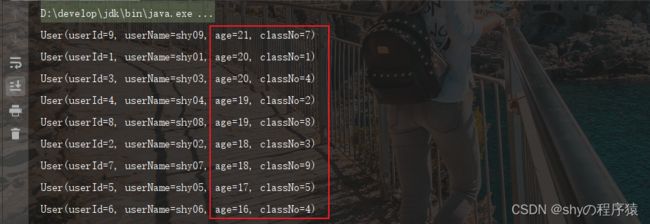
年龄升序,班级升序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge).thenComparing(User::getClassNo)).collect(Collectors.toList());
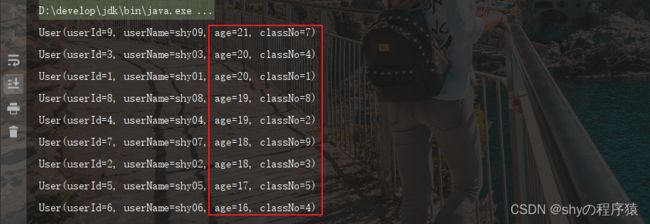
年龄降序,班级升序
//方法1:先对年龄进行升序,升序结果进行反转,再进行班级升序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge).reversed().thenComparing(User::getClassNo)).collect(Collectors.toList());
//方法2:直接对年龄进行降序,再对班级进行升序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge, Comparator.reverseOrder()).thenComparing(User::getClassNo)).collect(Collectors.toList());
年龄降序,班级降序
//方法1:先对年龄进行升序,升序结果进行反转,再对班级进行降序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge).reversed().thenComparing(User::getClassNo, Comparator.reverseOrder())).collect(Collectors.toList());
//方法2:直接对年龄进行降序,再对班级进行降序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge, Comparator.reverseOrder()).thenComparing(User::getClassNo, Comparator.reverseOrder())).collect(Collectors.toList());
//方式3:先对年龄进行升序,再对班级进行升序,最后对结果进行反转
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge).thenComparing(User::getClassNo).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
年龄升序,班级降序
//方法1:先对年龄进行升序,升序结果进行反转,再进行班级升序,结果进行反转(有点绕,年龄被排了三次升-降-升)
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge).reversed().thenComparing(User::getClassNo).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
//方法2:直接对年龄进行升序,再对班级进行降序
userList = userList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(User::getAge).thenComparing(User::getClassNo, Comparator.reverseOrder())).collect(Collectors.toList());
3、总结
如果只进行单个字段的升序降序排列,我们使用reversed() 或者 Comparator.reverseOrder() 都可以
如果要进行多个字段的升序降序排列,我们还是使用 Comparator.reverseOrder() 会更优雅、更好理解一些