C#程序设计实验
C#实验
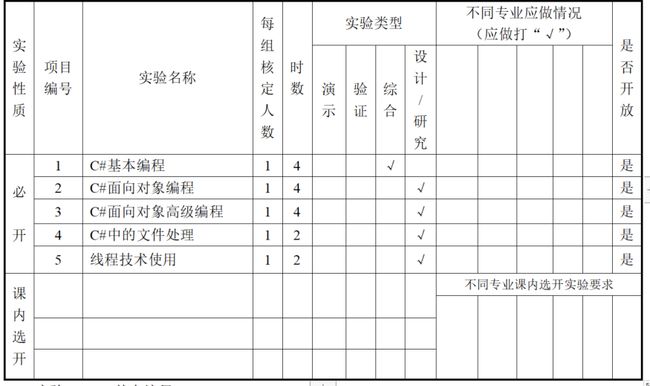
实验1 C# 基本编程
题目
VS下新建一个控制台项目:诸如:hello world程序,运行程序输出结果。并解释C#程序的结构:
诸如:一个基本的C#程序包含几部分 ,每一部分的功能是什么。。。
完整代码
using System;//导入System命名空间
namespace HelloWorldApplication//命名空间
{
/* 类名为 HelloWorld */
class HelloWorld
{
/* main函数 */
static void Main(string[] args)
{
/* 我的第一个 C# 程序 */
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");//在控制台输出Hello World!并换行
Console.ReadKey();//等待键盘输入,防止一闪而过
}
}
}
运行结果
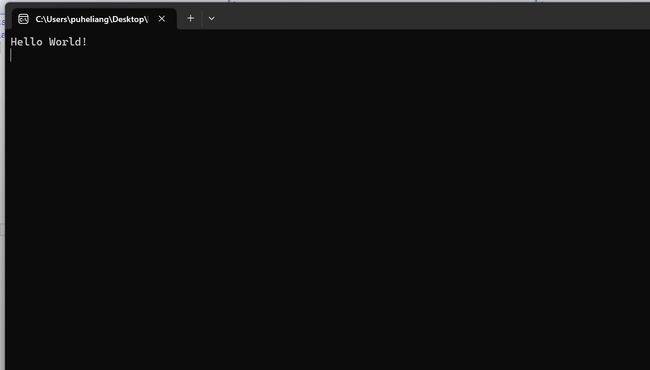 这段代码是一个经典的 “Hello World” 程序,用于展示 C# 语言的基本结构和输出功能。下面对代码进行解析:
这段代码是一个经典的 “Hello World” 程序,用于展示 C# 语言的基本结构和输出功能。下面对代码进行解析:
导入 System 命名空间
其中包含了 Console 类,用于处理控制台输入输出。
csharpCopy code
using System;
定义命名空间 HelloWorldApplication
命名空间用于组织和管理代码。
csharpCopy codenamespace HelloWorldApplication
{
}
定义一个类 HelloWorld
包含了程序的主要逻辑。
csharpCopy codeclass HelloWorld
{
}
在HelloWorld类中、定义了 static 的 Main 方法,是程序的入口点。
csharpCopy codestatic void Main(string[] args)
{
}
在 Main 方法中,使用 Console.WriteLine 方法打印文本 “Hello World!” 到控制台,并使用 Console.ReadKey 方法等待用户按下任意键。
csharpCopy codeConsole.WriteLine("Hello World!");
Console.ReadKey();
以上就是该代码的解析,它实现了一个简单的控制台应用程序,输出 “Hello World!” 到控制台,并等待用户按下任意键才退出。这是 C# 程序的基本结构,用于入门学习和展示语言特性。
实验2 C#面向对象编程
题目
建立一个控制台程序,设计一个cat 类,在该类中定义cat的颜色 年龄 等属性,并建立一个方法输出“叫声”。
在程序中建立类的对象读取 和 设置 cat 的属性值,并调用方法输出 猫的 “叫声”
完整代码
using System;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Cat
{
private string color;//猫的颜色
private int age; //年龄字段
public int Age//年龄属性,用户对外操作age
{
get
{
return age;
}
set
{
age = value;
}
}
public string Color//颜色属性,用户对外操作age
{
get
{
return color;
}
set
{
color = value;
}
}
public void hall()
{
Console.WriteLine("一只"+this.age+"岁"+this.color+"的猫正在叫:喵喵喵!");
}
}
class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.Age = 10;
cat.Color = "灰色";
cat.hall();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
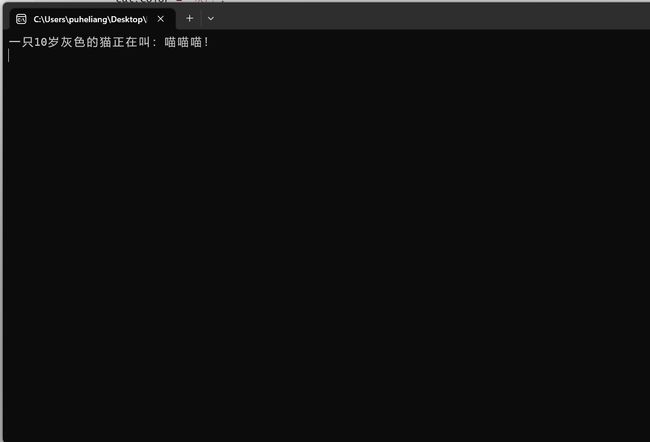
运行结果
这段代码定义了一个名为 Cat 的类,并在 Main 方法中创建了一个 Cat 的实例并使用其属性和方法。
定义 Cat 类
csharpCopy codeclass Cat
{
private string color;
private int age;
public int Age
{
get
{
return age;
}
set
{
age = value;
}
}
public string Color
{
get
{
return color;
}
set
{
color = value;
}
}
public void hall()
{
Console.WriteLine("一只"+this.age+"岁"+this.color+"的猫正在叫:喵喵喵!");
}
}
在这个类中,我们定义了私有字段 color 和 age,分别表示猫的颜色和年龄。然后,使用属性 Age 和 Color 封装了这两个字段,以提供对它们的访问和设置。Age 和 Color 属性具有 get 和 set 访问器,使得我们可以通过 cat.Age 和 cat.Color 来获取和设置猫的年龄和颜色。最后,定义了一个名为 hall 的方法,用于输出猫的叫声。
在 Main 方法中使用 Cat 类
csharpCopy codepublic static void Main(string[] args)
{
Cat cat = new Cat();
cat.Age = 10;
cat.Color = "灰色";
cat.hall();
Console.ReadKey();
}
在 Main 方法中,我们创建了一个名为 cat 的 Cat 类型的实例。然后,使用属性访问器 cat.Age 和 cat.Color 分别设置猫的年龄为 10 和颜色为 “灰色”。接着,调用 cat.hall() 方法,输出猫的叫声。最后,使用 Console.ReadKey() 等待用户按下任意键退出程序。
实验3 C#面向对象高级编程
题目
建立一个控制台程序,(1)定义一个Person类,具有姓名(Name)、年龄(Age)、性别(Sex)等属性;
(2)从Person类派生一个Student类,具有三个课程成绩的数据成员,并具有SetScores方法(输入学生的3门成绩)、GetAverage方法(求平均成绩);
(3)Student类要求其构造函数具有三种重载形式:1、无参;2、具有姓名、年龄、性别三个参数的构造函数;3、具有姓名、年龄、性别、成绩六个参数的构造函数;
(4)在Program类的Main方法中,使用Student的三个重载形式创建对象,并调用其GetAverage方法显示平均成绩;
完整代码
using System;
namespace HelloWorld
{
class Person
{
protected string Name;
protected string Sex;
protected int Age;
}
// 派生类
class Student : Person
{
private int math;
private int english;
private int chinese;
public Student()
{
}
public string name
{
set
{
Name = value;
}
get
{
return Name;
}
}
public string sex
{
set
{
Sex = value;
}
get
{
return Sex;
}
}
public int age
{
set
{
Age = value;
}
get
{
return Age;
}
}
public Student(string Name,string Sex,int Age)
{
this.Name = Name;
this.Sex = Sex;
this.Age = Age;
}
public Student(string Name, string Sex, int Age,int math,int english,int chinese)
{
this.Name = Name;
this.Sex = Sex;
this.Age = Age;
this.math = math;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.english = english;
}
public void SetScores(int math,int chinese,int english)
{
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public void GetAverage()
{
Console.WriteLine(this.name+"的平均分为:"+((this.chinese)+(this.english)+(this.math))/3.0);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.name = "蒲贺良";
stu1.sex = "男";
stu1.age = 21;
stu1.SetScores(100,100,100);
stu1.GetAverage();
Student stu2 = new Student("小黑","男",22);
stu2.SetScores(99,98,97);
stu2.GetAverage();
Student stu3 = new Student("小白", "男", 22,96,96,96);
stu3.GetAverage();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
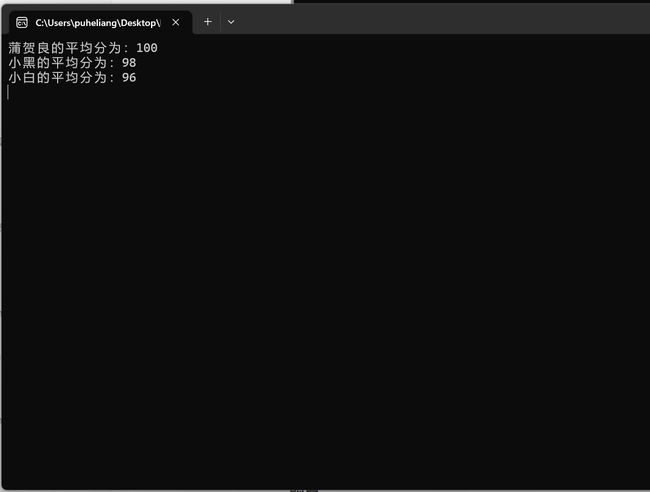
运行结果
这段代码定义了一个 Person 类和一个派生类 Student,并在 Main 方法中创建了几个 Student 的实例。
定义 Person 类和 Student 类
csharpCopy codeclass Person
{
protected string Name;
protected string Sex;
protected int Age;
}
Person 类定义了三个保护字段 Name、Sex 和 Age,用于表示人的姓名、性别和年龄。
csharpCopy codeclass Student : Person
{
private int math;
private int english;
private int chinese;
// 构造函数
public Student()
{
}
// 属性
public string name
{
set
{
Name = value;
}
get
{
return Name;
}
}
public string sex
{
set
{
Sex = value;
}
get
{
return Sex;
}
}
public int age
{
set
{
Age = value;
}
get
{
return Age;
}
}
// 构造函数重载
public Student(string Name, string Sex, int Age)
{
this.Name = Name;
this.Sex = Sex;
this.Age = Age;
}
public Student(string Name, string Sex, int Age, int math, int english, int chinese)
{
this.Name = Name;
this.Sex = Sex;
this.Age = Age;
this.math = math;
this.chinese = chinese;
this.english = english;
}
// 方法
public void SetScores(int math, int chinese, int english)
{
this.math = math;
this.english = english;
this.chinese = chinese;
}
public void GetAverage()
{
Console.WriteLine(this.name + "的平均分为:" + ((this.chinese) + (this.english) + (this.math)) / 3.0);
}
}
Student 类是 Person 类的派生类,它添加了私有字段 math、english 和 chinese,用于表示学生的数学、英语和语文成绩。类中包含了构造函数重载,用于根据不同参数创建 Student 类的实例。另外,类中还定义了属性 name、sex 和 age,用于访问和设置 Person 类中的保护字段。此外,类中还定义了 SetScores 方法,用于设置学生的成绩,以及 GetAverage 方法,用于计算并输出学生的平均分。
在 Main 方法中使用 Student 类
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.name = "蒲贺良";
stu1.sex = "男";
stu1.age = 21;
stu1.SetScores(100,100,100);
stu1.GetAverage();
Student stu2 = new Student("小黑","男",22);
stu2.SetScores(99,98,97);
stu2.GetAverage();
Student stu3 = new Student("小白", "男", 22,96,96,96);
stu3.GetAverage();
Console.ReadKey();
}
在 Main 方法中使用 Student 类
实验四 C#中的文件处理
题目
建立一个控制台程序,利用所学读写文件类 封装一个读文件接口 一个 写文件接口,并完成对文件的读写。
完整代码
using System;
using System.IO;
namespace FileApplication
{
class File_Test
{
private string path;
public File_Test(string path)
{
this.path = path;
}
public void Read()
{
try
{
// 创建一个 StreamReader 的实例来读取文件
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(path, false);
string line;
// 从文件读取并显示行,直到文件的末尾
while ((line = sr.ReadLine()) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// 向用户显示出错消息
Console.WriteLine("The file could not be read:");
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
public void Write(string[] content)
{
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(path))
{
foreach (string s in content)
{
sw.WriteLine(s);
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string Path = @"C:\Users\puheliang\Desktop\Project\CS_Project\实验4\test.txt";
File_Test f = new File_Test(Path);
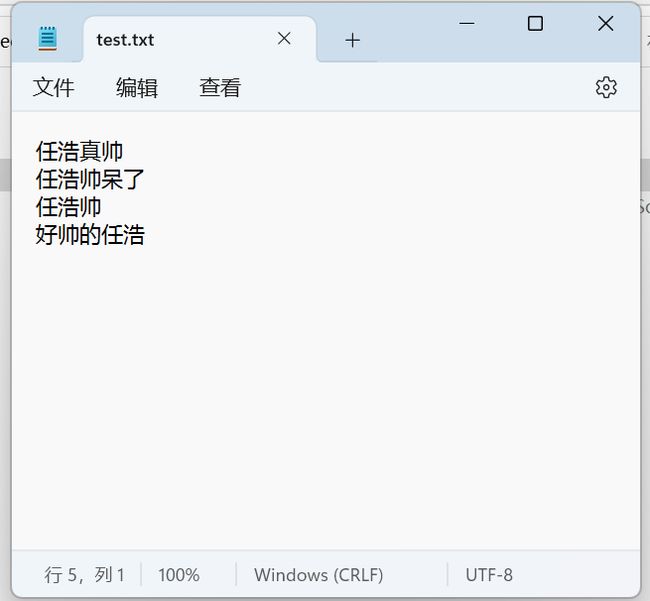
string[] test = { "任浩真帅", "任浩帅呆了", "任浩帅","好帅的任浩" };
f.Write(test);
f.Read();
}
}
}
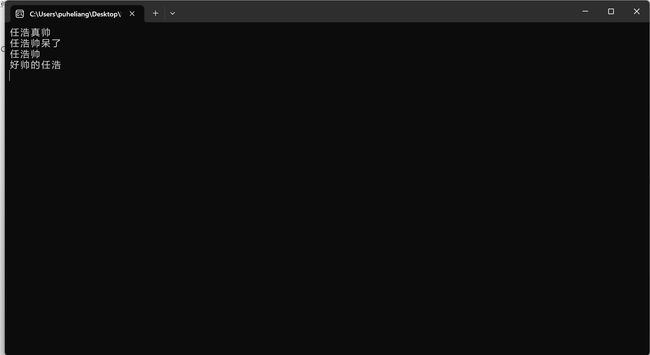
运行结果
这段代码演示了使用 StreamReader 和 StreamWriter 类来读取和写入文件。
定义 File_Test 类
csharpCopy codeclass File_Test
{
private string path;
public File_Test(string path)
{
this.path = path;
}
public void Read()
{
try
{
// 创建一个 StreamReader 的实例来读取文件
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(path, false);
string line;
// 从文件读取并显示行,直到文件的末尾
while ((line = sr.ReadLine()) != null)
{
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// 向用户显示出错消息
Console.WriteLine("The file could not be read:");
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
public void Write(string[] content)
{
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(path))
{
foreach (string s in content)
{
sw.WriteLine(s);
}
}
}
}
File_Test 类包含了两个方法:Read() 和 Write(string[] content)。Read() 方法使用 StreamReader 类来读取文件内容并逐行输出到控制台。Write(string[] content) 方法使用 StreamWriter 类来将字符串数组 content 的内容写入到文件中。
使用 File_Test 类
csharpCopy codestatic void Main(string[] args)
{
string Path = @"C:\Users\puheliang\Desktop\Project\CS_Project\实验4\test.txt";
File_Test f = new File_Test(Path);
string[] test = { "任浩真帅", "任浩帅呆了", "任浩帅", "好帅的任浩" };
f.Write(test);
f.Read();
}
在 Main 方法中,我们首先定义了一个文件路径 Path。然后,创建了一个 File_Test 的实例 f,并传入文件路径。接着,定义了一个字符串数组 test,包含了要写入文件的内容。调用 f.Write(test) 方法将内容写入文件,然后调用 f.Read() 方法读取文件并将内容输出到控制台。最后,使用 Console.ReadKey() 等待用户按下任意键退出程序。
实验五:线程技术使用
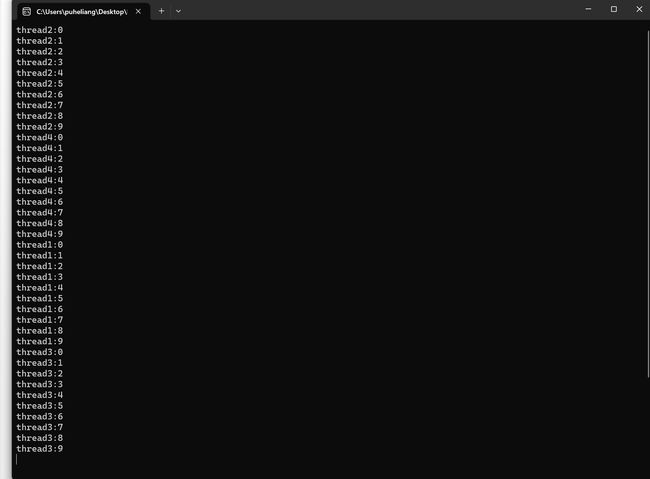
题目
建立一个控制台程序,建立四个线程,每个线程的功能为:输出0-9 共计10个数字,要求线程的输出为连续输出,借助信号量或者互斥锁进行实现。
完整代码
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace MultithreadingApplication
{
class ThreadCreationProgram
{
static Mutex mutex = new Mutex();
static Semaphore sem = new Semaphore(1, 1);
public static void CallToChildThread01()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread1:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
public static void CallToChildThread02()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread2:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
public static void CallToChildThread03()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread3:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
public static void CallToChildThread04()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread4:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ThreadStart childref01 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread01);
Thread childThread01 = new Thread(childref01);
childThread01.Name = "Thread1";
childThread01.Start();
ThreadStart childref02 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread02);
Thread childThread02 = new Thread(childref02);
childThread02.Name = "Thread2";
childThread02.Start();
ThreadStart childref03 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread03);
Thread childThread03 = new Thread(childref03);
childThread03.Name = "Thread3";
childThread03.Start();
ThreadStart childref04 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread04);
Thread childThread04 = new Thread(childref04);
childThread04.Name = "Thread4";
childThread04.Start();
;
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行结果
这段代码演示了使用多线程进行并发操作,并使用 Mutex 和 Semaphore 实现线程同步。
定义线程函数
csharpCopy codepublic static void CallToChildThread01()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread1:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
public static void CallToChildThread02()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread2:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
public static void CallToChildThread03()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread3:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
public static void CallToChildThread04()
{
sem.WaitOne();
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("thread4:" + i);
Thread.Sleep(5);
}
}
sem.Release();
}
在这里定义了四个线程函数,分别是 CallToChildThread01、CallToChildThread02、CallToChildThread03 和 CallToChildThread04。每个函数都会使用 sem.WaitOne() 获取信号量,然后执行一个简单的循环输出,并使用 Thread.Sleep(5) 使线程休眠 5 毫秒,模拟一些处理时间。最后,通过 sem.Release() 释放信号量。
创建并启动线程
csharpCopy codeThreadStart childref01 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread01);
Thread childThread01 = new Thread(childref01);
childThread01.Name = "Thread1";
childThread01.Start();
ThreadStart childref02 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread02);
Thread childThread02 = new Thread(childref02);
childThread02.Name = "Thread2";
childThread02.Start();
ThreadStart childref03 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread03);
Thread childThread03 = new Thread(childref03);
childThread03.Name = "Thread3";
childThread03.Start();
ThreadStart childref04 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread04);
Thread childThread04 = new Thread(childref04);
childThread04.Name = "Thread4";
childThread04.Start();
在 Main 方法中,我们使用 ThreadStart 创建了四个线程的启动函数,并使用 Thread 类创建了四个线程实例 childThread01、childThread02、childThread03 和 childThread04。我们为每个线程指定了名称,然后通过调用 Start() 方法启动线程。
主线程等待
csharpCopy code
Console.ReadKey();
childThread01.Name = "Thread1";
childThread01.Start();
ThreadStart childref02 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread02);
Thread childThread02 = new Thread(childref02);
childThread02.Name = "Thread2";
childThread02.Start();
ThreadStart childref03 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread03);
Thread childThread03 = new Thread(childref03);
childThread03.Name = "Thread3";
childThread03.Start();
ThreadStart childref04 = new ThreadStart(CallToChildThread04);
Thread childThread04 = new Thread(childref04);
childThread04.Name = "Thread4";
childThread04.Start();
在 Main 方法中,我们使用 ThreadStart 创建了四个线程的启动函数,并使用 Thread 类创建了四个线程实例 childThread01、childThread02、childThread03 和 childThread04。我们为每个线程指定了名称,然后通过调用 Start() 方法启动线程。
主线程等待
csharpCopy code
Console.ReadKey();
最后,使用 Console.ReadKey() 让主线程等待用户按下任意键,以保持程序运行。