随机数发生器设计(二)
一、软件随机数发生器组成概述
密码产品应至少包含一个随机比特生成器。
软件随机数发生器应遵循GM/T 0105-2021《软件随机数发生器设计指南》要求,使用SM3或SM4算法作为生成随机比特算法。
本文以SM3算法为例描述软件随机数发生器的一个设计实例。需要注意的是,本实例仅为参考,实际熵源信息、熵估计方法和算法等都可根据需要变动。
软件随机数发生器采集当前运行环境的传感器信息作为熵源,包括当前时间、CPU信息、RAM信息、磁盘信息、网络信息。以上熵源信息经健康测试和熵评估后,作为熵数据输入到熵池。熵数据填满熵池后,可以经扩展函数处理后输入DRNG。扩展函数处理后的熵数据可以反馈到熵池。
DRNG根据熵输入数据和内部状态生成输出随机数,并维护自身种子信息和正确性。初始化函数获取扩展函数的输出和外部输入的nonce更新内部状态。当重播种计数器或时间间隔达到阈值时,产品会执行重播种函数更新内部状态。输出函数可以按照接口要求输出指定长度的随机数。DRNG实现已知答案自测试,在产品上电初始化或有自测试需求时执行。

二、熵源
软件随机数发生器采用系统信息作为熵源,包括当前时间、CPU信息、RAM信息、磁盘信息、网络信息。熵源信息如下表所示。
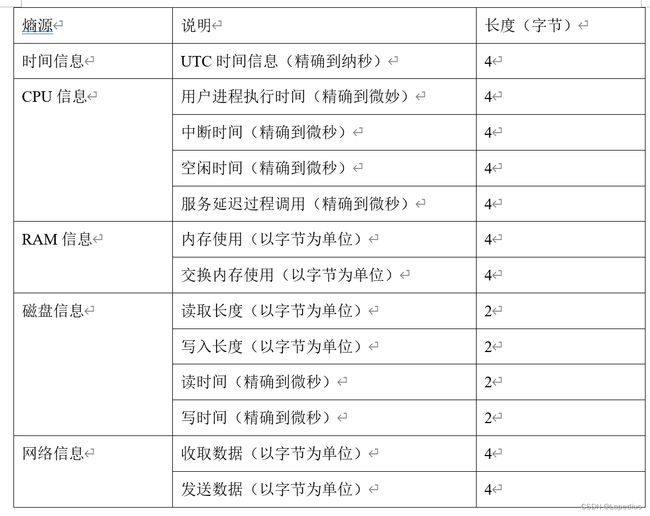
在熵池存在空闲空间时,产品获取熵源信息,经连续健康测试后写入熵池。每次采集的熵源信息RAW_ENTROPY =时间信息|| CPU信息||RAM信息||磁盘信息||网络信息,熵值约29.84比特。熵池为512字节大小。
当前时间信息随时间自然增长,精确到纳秒,外界很难预测产品获取当前时间的精确时间节点,从而无法预测产品得到的该熵源信息,因此在某一时间节点,时间信息相当于独占熵源;CPU信息、RAM信息、磁盘信息和网络信息都在系统运行过程中随系统业务环境动态变化。例如,外界几乎无法预测CPU中断的到来时间和执行时间。因此,CPU信息、RAM信息、磁盘信息和网络信息在某一时间节点相当于独占熵源。
本软件随机数发生器未采用硬件随机数发生器和系统随机数发生器。
采集熵源信息的代码如下。
#generate raw entropy from system source - time
#return 4 bytes
def RNG_Generate_Raw_Entropy_Source1():
return (int(time_ns()) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
#generate raw entropy from system source - cpu
# return 16 bytes
def RNG_Generate_Raw_Entropy_Source2():
usercputime = (int(psutil.cpu_times().user*1000000) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
idlecputime = (int(psutil.cpu_times().idle*1000000) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
interruptcputime = (int(psutil.cpu_times().interrupt*1000000) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
dpccputime = (int(psutil.cpu_times().dpc*1000000) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
return usercputime + idlecputime + interruptcputime + dpccputime
#generate raw entropy from system source - ram
# return 8 bytes
def RNG_Generate_Raw_Entropy_Source3():
usedvmmem = (int(psutil.virtual_memory().used) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
usedswapmem = (int(psutil.swap_memory().used) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
return usedvmmem + usedswapmem
#generate raw entropy from system source - disk
# return 8 bytes
def RNG_Generate_Raw_Entropy_Source4():
read_bytes = (int(psutil.disk_io_counters().read_bytes) & 0xFFFF).to_bytes(2, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
write_bytes = (int(psutil.disk_io_counters().write_bytes) & 0xFFFF).to_bytes(2, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
read_time = (int(psutil.disk_io_counters().read_time) & 0xFFFF).to_bytes(2, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
write_time = (int(psutil.disk_io_counters().write_time) & 0xFFFF).to_bytes(2, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
return read_bytes + write_bytes + read_time + write_time
#generate raw entropy from system source - network
# return 8 bytes
def RNG_Generate_Raw_Entropy_Source5():
# print(psutil.net_io_counters())
bytes_sent = (int(psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
bytes_recv = (int(psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv) & 0xFFFFFFFF).to_bytes(4, byteorder = 'big', signed=False)
return bytes_sent + bytes_recv
三、熵池
随机数数发生器的熵池大小为512字节。在当前熵估计情况下,512字节大小的熵池具备的熵值可满足大于256比特的要求。
熵池采用SM3_df函数作为扩展函数,流程图如下。
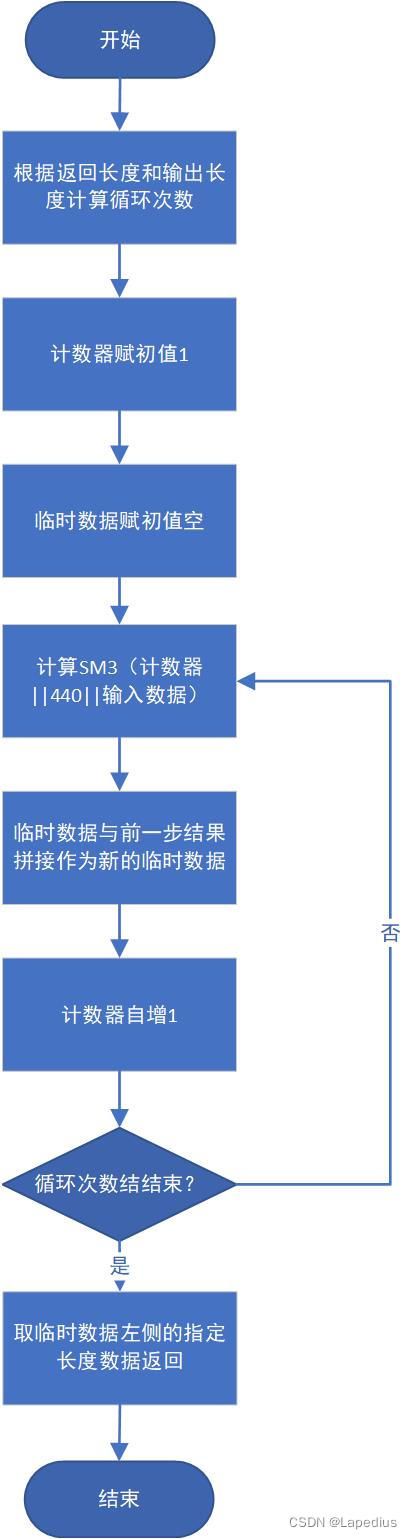
1) 根据输入的返回数据长度(实际为440比特)和输出数据长度256比特计算循环次数。计算循环次数时使用向上取整方式。
2) 对计数器赋初值1,对临时数据赋初值空。
3) 计算SM3(计数器值||返回数据长度||输入熵源数据)。
4) 临时数据更新为临时数据||SM3结果。
5) 计数器增1。
6) 判断循环是否结果,若结束则跳转至第7步,否则跳转至第3步。
7) 取临时数据左侧指定长度数据,返回
8) def sm3Hash(hashbytes:bytes):
9) temp = sm3_hash([i for i in hashbytes])
10) return bytes.fromhex(temp)
11)
12) def SM3_df(input_string, no_of_bits_to_return):
13) temp = bytes([])
14) len = math.ceil(no_of_bits_to_return/outlen)
15) counter = 0x01
16) for i in range(len):
17) temp = temp + sm3Hash(bytes([counter]) + no_of_bits_to_return.to_bytes(4, 'big') + input_string)
18) counter = counter + 1
19) return temp[0:int(no_of_bits_to_return/8)]
熵池更新是采用GM/T 0105 附录A所示方式。

1) 以熵池中第一个字(4字节)为当前字,开始执行遍历。
2) 临时数据temp更新为输入字与当前字异或结果。
3) 临时数据temp依次与某偏移字异或,异或结果更新至临时数据。偏移值分别设定为1、25、51、76、103。
4) 临时数据取低3位作为索引,获取预置表值。。
5) 临时数据右移3位与步骤4预置表值异或。
6) 更新当前值为步骤5结果。
7) 判断是否遍历熵池,若未完成,回到步骤2;否则结束熵池更新。
9) #init entropy pool
10) def RNG_Init_POOL():
11) global entropy_pool
12) entropy_pool = []
13) for i in range(128):
14) entropy_pool.append(bytes([0,0,0,0]))
15) #four bytes xor function
16) def RNG_Word_XOR(a:bytes, b:bytes):
17) return bytes([a[i] ^ b[i] for i in range(4)])
18) #word shift function
19) def RNG_Word_Shift_Right(a:bytes, len:int):
20) return bytes([a[i] >> len for i in range(4)])
21) table = [0x0, 0x3b6e20c8, 0x76dc4190, 0x4db26158, 0xedb88320, 0xd6d6a3e8, 0x9b64c2b0, 0xa00ae278]
22) #add 1 word entropy to entropy pool
23) def RNG_Add_Entropy(entropyWord:bytes):
24) global entropy_pool
25) global table
26) if len(entropy_pool) != 128:
27) RNG_Init_POOL()
28) for i in range(128):
29) temp = RNG_Word_XOR(entropyWord, entropy_pool[i])
30) temp = RNG_Word_XOR(temp, entropy_pool[(i+1)%128])
31) temp = RNG_Word_XOR(temp, entropy_pool[(i+25)%128])
32) temp = RNG_Word_XOR(temp, entropy_pool[(i+51)%128])
33) temp = RNG_Word_XOR(temp, entropy_pool[(i+76)%128])
34) temp = RNG_Word_XOR(temp, entropy_pool[(i+103)%128])
35) temp = RNG_Word_XOR(RNG_Word_Shift_Right(temp, 3), table[temp[3] & 7].to_bytes(4, 'big'))
36) entropy_pool[i] = temp
如果商用密码产品认证中遇到问题,欢迎加微信symmrz或13720098215沟通。