springboot 2.2.5 错误处理机制(源码分析)
文章目录
- ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 错误处理自动配置类
- ErrorPageCustomizer 错误页面定制器
- BasicErrorController 默认处理/error请求控制器
- 响应页面 源码分析
- 举例
- 响应JSON 源码分析
首先,官方doc是这样介绍error的:
For machine clients, it produces a JSON response with details of the error, the HTTP status, and the exception message. For browser clients, there is a “whitelabel” error view that renders the same data in HTML format (to customize it, add a View that resolves to error) To replace the default behavior completely, you can implement ErrorController and register a bean definition of that type or add a bean of type ErrorAttributes to use the existing mechanism but replace the contents.
对于机器客户端(非浏览器)发生错误,会返回JSON数据格式的错误信息。
对于浏览器客户端发生错误,返回一个包含错误信息的"whitelabel"页面,如果想要定制,自己实现ErrorController即可。官方推荐:继承BasicErrorController。
The BasicErrorController can be used as a base class for a custom ErrorController. This is particularly useful if you want to add a handler for a new content type (the default is to handle text/html specifically and provide a fallback for everything else). To do so, extend BasicErrorController, add a public method with a @RequestMapping that has a produces attribute, and create a bean of your new type.
ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 错误处理自动配置类
先了解一下springboot中有关错误处理的类为:ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration。
位置:package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error;
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class })
// Load before the main WebMvcAutoConfiguration so that the error View is available
@AutoConfigureBefore(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ ServerProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class, WebMvcProperties.class })
public class ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration {
...
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Bean
public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath);
}
}
里面比较主要的类有:BasicErrorController 、ErrorPageCustomizer
ErrorPageCustomizer 错误页面定制器
源码如下:
//ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration.java
@Bean
public ErrorPageCustomizer errorPageCustomizer(DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
return new ErrorPageCustomizer(this.serverProperties, dispatcherServletPath);
}
// 静态内部类,默认的错误页面配置
private static class ErrorPageCustomizer implements ErrorPageRegistrar, Ordered {
private final ServerProperties properties;
private final DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath;
protected ErrorPageCustomizer(ServerProperties properties, DispatcherServletPath dispatcherServletPath) {
this.properties = properties;
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
}
// 注册错误页面的响应规则
@Override
public void registerErrorPages(ErrorPageRegistry errorPageRegistry) {
ErrorPage errorPage = new ErrorPage(
//[#2] 注意getPath()
this.dispatcherServletPath.getRelativePath(this.properties.getError().getPath()));
errorPageRegistry.addErrorPages(errorPage);
}
//...
}
继续往下点击看[#2]处源码,默认path为/error。
public class ErrorProperties {
/**
* Path of the error controller.
*/
@Value("${error.path:/error}")
private String path = "/error";
即系统出现错误以后会来到/error请求,进行处理;(类似web.xml注册的错误页面规则)
那么问题来了,通过ErrorPageCustomizer设置后,出现错误会来到/error请求,接下来给谁处理呢??—— BasicErrorController
BasicErrorController 默认处理/error请求控制器
一旦系统出现4xx或者5xx之类的错误 --> ErrorPageCustomizer就会生效(定制错误的响应规则) --> 就会来到/error请求 --> 就会被BasicErrorController处理;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
public BasicErrorController basicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes,
ObjectProvider<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) {
return new BasicErrorController(errorAttributes, this.serverProperties.getError(),
errorViewResolvers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
上面的源码里,有两个没见过的东西:ErrorViewResolver、BasicErrorController。
既然是返回BasicErrorController,肯定要看一下源码:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}")
// ${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}} 解释:
// 如果没有配置server.error.path,则使用error.path;如果error.path也没有配置,则使用/error
public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController {
// public static final String TEXT_HTML_VALUE = "text/html";
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) // 产生HTML数据
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); // modelAndView
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@RequestMapping // 产生JSON数据
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
if (status == HttpStatus.NO_CONTENT) {
return new ResponseEntity<>(status);
}
Map<String, Object> body = getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL));
return new ResponseEntity<>(body, status);
}
最开始的时候讲过:对于机器客户端(非浏览器)发生错误,会返回JSON数据格式的错误信息。对于浏览器客户端发生错误,返回一个包含错误信息的"whitelabel"页面。那么问题来了:
服务器是怎么区分浏览器还是别的客户端呢?如果是浏览器客户端——通过浏览器发送的请求头

如果是其他客户端(以postman为例),没有对应的请求头字段

上边的代码也正好对应上啦!
响应页面 源码分析
还是上面那个程序
//BasicErrorController.java
// public static final String TEXT_HTML_VALUE = "text/html";
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) // 产生HTML数据
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); // 获得状态码
Map<String, Object> model = Collections // 获得model数据
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
//调用resolveErrorView()方法, 返回一个新的modelAndView,决定去哪个页面作为错误页面,包含页面地址、页面内容
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
resolveErrorView()源码:
// AbstractErrorController.java
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) { // 遍历异常视图解析器(ErrorViewResolver )
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
return null;
}
什么是ErrorViewResolver ——它是一个接口,默认实现类为DefaultErrorViewResolver
即,去哪个页面是由DefaultErrorViewResolver解析得到的。
public class DefaultErrorViewResolver implements ErrorViewResolver, Ordered {
private static final Map<Series, String> SERIES_VIEWS;
static {
Map<Series, String> views = new EnumMap<>(Series.class);
views.put(Series.CLIENT_ERROR, "4xx"); //客户端错误,用4xx表示
views.put(Series.SERVER_ERROR, "5xx"); //服务端错误,用5xx表示
SERIES_VIEWS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(views);
}
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpStatus status, Map<String, Object> model) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolve(String.valueOf(status.value()), model);
if (modelAndView == null && SERIES_VIEWS.containsKey(status.series())) {
// viewName根据状态码得到
modelAndView = resolve(SERIES_VIEWS.get(status.series()), model);
}
return modelAndView;
}
private ModelAndView resolve(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
//默认SpringBoot可以去找到一个页面: error/404
String errorViewName = "error/" + viewName;
// 如果模板引擎可以解析这个页面地址,就用模板引擎解析,并返回
TemplateAvailabilityProvider provider = this.templateAvailabilityProviders.getProvider(errorViewName,
this.applicationContext);
if (provider != null) {
//模板引擎可用的情况下返回到errorViewName指定的视图地址
return new ModelAndView(errorViewName, model);
}
// 否则模板引擎不可用,就在静态资源文件夹下找errorViewName对应的页面 error/404.html
return resolveResource(errorViewName, model);
}
private ModelAndView resolveResource(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model) {
for (String location : this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) {
try {
Resource resource = this.applicationContext.getResource(location);
resource = resource.createRelative(viewName + ".html");
if (resource.exists()) {
return new ModelAndView(new HtmlResourceView(resource), model);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
}
}
return null;
}
学到这里,知道我们该怎么定制自己的错误页面了!
1.有模板引擎的情况下——error/状态码:
-
将错误页面命名为错误状态码.html 放在templates/error文件夹下,发生此状态码的错误就会来到 对应的页面;
-
我们可以使用4xx和5xx作为错误页面的文件名来匹配这种类型的所有错误,精确优先(优先寻找精确的状态码.html);
-
页面能获取到的信息:timestamp时间戳、status状态码、error错误提示、exception异常对象、message异常消息、errorsJSR303数据校验的错误都在这里
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { HttpStatus status = getStatus(request); Map<String, Object> model = Collections .unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); response.setStatus(status.value()); // model里存的就是页面可以获取到的信息,根据getErrorAttributes() 点进去看有好多~ ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model); } -
页面能获取到的的信息看getErrorAttributes()源码,来自DefaultErrorAttributes(在ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration也出现了,很重要的一部分)。
-
timestamp时间戳、status状态码、error错误提示、exception异常对象、message异常消息、errorsJSR303数据校验的错误都存在model里了,因此在前端我们可以定制错误页面,提取出响应的信息。
<main role="main" class="col-md-9 ml-sm-auto col-lg-10 pt-3 px-4"> <h1>status:[[${status}]]h1> <h2>timestamp:[[${timestamp}]]h2> main>
官方手册的推荐也是和我们分析的一样:
//For example, to map 404 to a static HTML file, your folder structure would be as follows:
src/
+- main/
+- java/
| + <source code>
+- resources/
+- public/
+- error/
| +- 404.html
+- <other public assets>
//To map all 5xx errors by using a FreeMarker template, your folder structure would be as follows:
src/
+- main/
+- java/
| + <source code>
+- resources/
+- templates/
+- error/
| +- 5xx.ftlh
+- <other templates>
2.没有模板引擎(模板引擎找不到这个错误页面),静态资源文件夹下找;
3.以上都没有错误页面,就是默认来到SpringBoot默认的错误提示页面;
protected ModelAndView resolveErrorView(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpStatus status,
Map<String, Object> model) {
for (ErrorViewResolver resolver : this.errorViewResolvers) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolver.resolveErrorView(request, status, model);
if (modelAndView != null) {
return modelAndView;
}
}
// 1 如果找不到,就返回null
return null;
}
@RequestMapping(produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
Map<String, Object> model = Collections
.unmodifiableMap(getErrorAttributes(request, isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML)));
response.setStatus(status.value());
ModelAndView modelAndView = resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model);
// 2 如果返回的null,则返回error视图
return (modelAndView != null) ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model);
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "server.error.whitelabel", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
@Conditional(ErrorTemplateMissingCondition.class)
protected static class WhitelabelErrorViewConfiguration {
private final StaticView defaultErrorView = new StaticView(); // 默认的error视图
@Bean(name = "error")
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "error")
public View defaultErrorView() {
return this.defaultErrorView;
}
//...
}
// 默认视图的代码,是不是很眼熟的样子!
private static class StaticView implements View {
// ...
builder.append("Whitelabel Error Page
").append(
"This application has no explicit mapping for /error, so you are seeing this as a fallback.
")
.append("").append(timestamp).append("")
.append("There was an unexpected error (type=").append(htmlEscape(model.get("error")))
.append(", status=").append(htmlEscape(model.get("status"))).append(").");
if (message != null) {
builder.append("").append(htmlEscape(message)).append("");
}
if (trace != null) {
builder.append("").append(htmlEscape(trace)).append("");
}
builder.append("");
response.getWriter().append(builder.toString());
}
举例
举例分析:我们编写了一个自己的异常类 用户不存在
public class UserNotExistException extends RuntimeException {
public UserNotExistException() {
super("用户不存在");
}
}
模拟异常发生的场景
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(@RequestParam("user") String user){
if(user.equals("aaa")){
throw new UserNotExistException();
}
return "Hello World";
}
如果没有配置自己的错误页,会来到springboot的默认error页面:

把自己写的html放到 src\main\resources\templates\error 下,命名为5xx.html之类的,就可以看到配置的页面了。
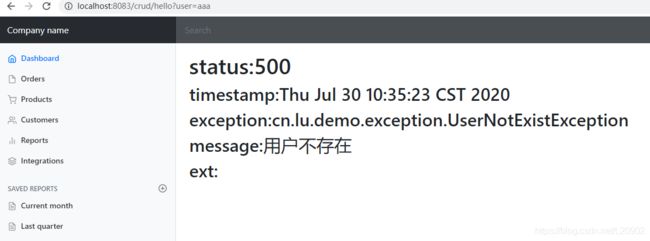
如果没打印出exception具体信息,添加配置server.error.include-exception=true
响应JSON 源码分析
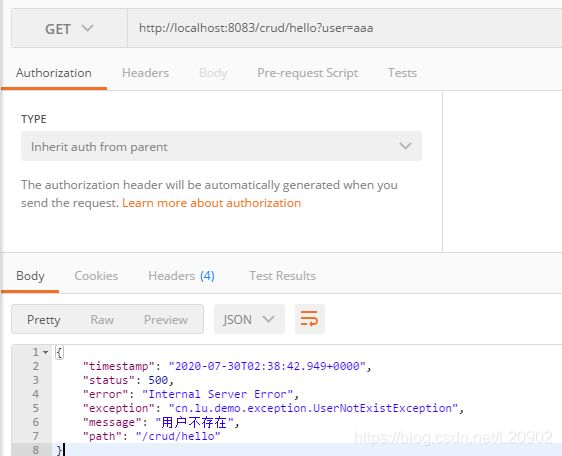
通过上面的分析,我们知道了怎么定制错误页面的修改信息,那么对于JSON显示的页面,同样支持自定义修改。上面举例的默认输出信息为:
官网原话:我们可以通过 @ControllerAdvice 配置自己的异常
You can also define a class annotated with @ControllerAdvice to customize the JSON document to return for a particular controller and/or exception type, as shown in the following example:
@ControllerAdvice(basePackageClasses = AcmeController.class)
public class AcmeControllerAdvice extends ResponseEntityExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(YourException.class)
@ResponseBody
ResponseEntity<?> handleControllerException(HttpServletRequest request, Throwable ex) {
HttpStatus status = getStatus(request);
return new ResponseEntity<>(new CustomErrorType(status.value(), ex.getMessage()), status);
}
private HttpStatus getStatus(HttpServletRequest request) {
Integer statusCode = (Integer) request.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
if (statusCode == null) {
return HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR;
}
return HttpStatus.valueOf(statusCode);
}
}
编写自己的异常类:
@ControllerAdvice
public class MyExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public Map<String,Object> handleException(Exception e){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code","user.notExist");
map.put("message",e.getMessage());
return map;
}
此时返回的JSON数据就是我们定制的了:
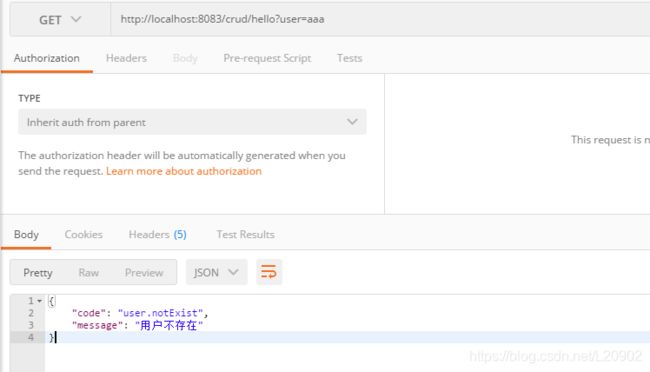
访问页面也是:

但这里有一个问题,这样配置后,浏览器返回的也是JSON数据。需要修改成自适应模式
@ExceptionHandler(UserNotExistException.class)
public String handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//传入我们自己的错误状态码 4xx 5xx
/**
* Integer statusCode = (Integer) request
.getAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code");
*/
request.setAttribute("javax.servlet.error.status_code",500);
map.put("code","user.notExist");
map.put("message","用户出错啦");
request.setAttribute("extByLuuu",map); // 把这里的map放到request里,后面还需要用到!
//转发到/error
return "forward:/error";
}
get

出现错误以后,会来到/error请求,会被BasicErrorController处理,响应出去可以获取的数据是由getErrorAttributes得到的(是AbstractErrorController(ErrorController)规定的方法);
1. 完全来编写一个ErrorController的实现类【或者是编写AbstractErrorController的子类】,放在容器中;
2. 页面上能用的数据,或者是json返回能用的数据都是通过errorAttributes.getErrorAttributes得到;
容器中DefaultErrorAttributes.getErrorAttributes();默认进行数据处理的;
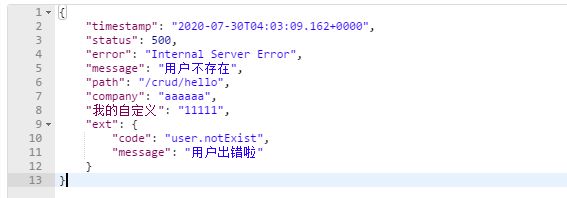
自定义ErrorAttributes
@Component
public class MyErrorAttributes extends DefaultErrorAttributes {
@Override
public Map getErrorAttributes(WebRequest webRequest, boolean includeStackTrace) {
Map map = super.getErrorAttributes(webRequest, includeStackTrace);
map.put("company","aaaaaa");
map.put("我的自定义","11111");
Map ext = (Map) webRequest.getAttribute("extByLuuu", 0); //int SCOPE_REQUEST = 0;
map.put("ext",ext);
return map;
}
}